Market Overview
The KSA Solid Rocket Motors market was valued at USD ~ billion based on a recent historical assessment, driven primarily by sustained defense modernization programs, missile capability enhancement initiatives, and long-term procurement commitments under national security frameworks. The market value is supported by confirmed defense budget allocations published by the Saudi Ministry of Finance and cross-referenced with SIPRI military expenditure databases, reflecting spending on missile propulsion systems, air defense interceptors, and strategic deterrence programs. Demand is further reinforced by localization mandates, technology transfer agreements, and infrastructure investments focused on propulsion manufacturing and testing facilities.
Riyadh dominates the KSA Solid Rocket Motors market due to its concentration of defense headquarters, procurement authorities, and primary integration facilities, while Jeddah and Jubail contribute through industrial clusters and logistics infrastructure supporting defense manufacturing. International collaboration linkages with the United States, France, and South Korea remain influential due to established defense partnerships, certified propulsion technologies, and licensed production programs. Regional dominance is also supported by proximity to testing ranges, regulatory bodies, and national research centers that accelerate qualification, compliance, and deployment of solid rocket motor systems.
Market Segmentation
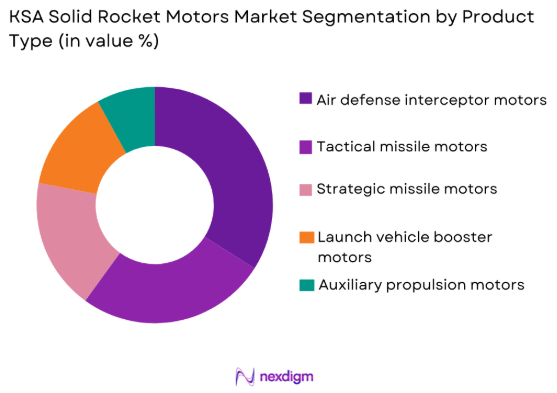
By Product Type
KSA Solid Rocket Motors market is segmented by product type into tactical missile motors, strategic missile motors, air defense interceptor motors, launch vehicle booster motors, and auxiliary propulsion motors. Recently, air defense interceptor motors have a dominant market share due to persistent demand for layered missile defense systems, accelerated procurement of interceptor platforms, and continuous upgrades of existing air defense architectures. The dominance is reinforced by frequent replenishment cycles, stringent performance requirements, and higher unit integration across multiple defense platforms. National security priorities have driven steady acquisition programs, while domestic assembly and licensed production have improved availability and lifecycle support. Additionally, interoperability requirements with allied defense systems have increased adoption, as interceptor motors are critical consumables in readiness planning. These factors collectively sustain higher procurement volumes and consistent demand across operational and training deployments.
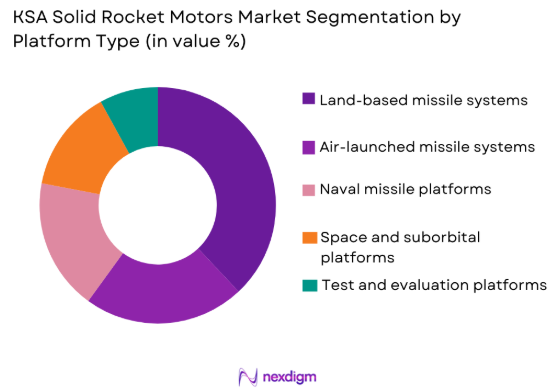
By Platform Type
KSA Solid Rocket Motors market is segmented by platform type into land-based missile systems, naval missile platforms, air-launched missile systems, space and suborbital platforms, and test and evaluation platforms. Recently, land-based missile systems have a dominant market share due to their central role in territorial defense, border security, and strategic deterrence frameworks. The dominance is supported by extensive deployment across fixed and mobile launchers, higher inventory requirements, and integration with national command-and-control networks. Land-based platforms also benefit from established infrastructure, easier maintenance logistics, and faster upgrade cycles compared to naval or aerial systems. Ongoing base expansion and force restructuring initiatives further reinforce demand, ensuring sustained procurement and refurbishment of solid rocket motors for land-based applications.
Competitive Landscape
The KSA Solid Rocket Motors market exhibits moderate consolidation, with a limited number of defense-aligned manufacturers operating under strict regulatory oversight and long-term government contracts. Major players exert strong influence through technology partnerships, licensed manufacturing, and localized production agreements, creating high entry barriers and reinforcing established competitive positions.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Localization Capability |
| Saudi Arabian Military Industries | 2017 | Riyadh | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Advanced Electronics Company | 1988 | Riyadh | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Middle East Propulsion Company | 2019 | Riyadh | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Taqnia Aeronautics | 2011 | Riyadh | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| L3Harris Arabia | 2015 | Riyadh | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Solid Rocket Motors Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Defense Modernization and Missile Capability Expansion
The KSA Solid Rocket Motors market is strongly driven by structured defense modernization programs that prioritize missile readiness, propulsion reliability, and rapid response capabilities across land, air, and naval domains. Saudi Arabia’s confirmed defense allocations emphasize missile system sustainability, which directly translates into recurring procurement of solid rocket motors for both operational and reserve inventories. Modernization initiatives require replacement of legacy propulsion units with higher-energy, longer-shelf-life motors, increasing per-unit value while maintaining volume demand. Integration of advanced guidance and interception technologies necessitates propulsion systems with precise thrust control and reliability, further strengthening demand. Strategic deterrence planning has also expanded requirements for long-range systems, reinforcing investment continuity. Domestic industrial participation policies amplify this driver by mandating localized production, which increases installed manufacturing capacity and procurement throughput. Technology transfer agreements ensure that advanced formulations and casing technologies are incorporated locally, sustaining market expansion. Continuous training, testing, and qualification cycles add to baseline demand, making modernization a persistent and structural growth driver rather than a cyclical one.
Localization of Defense Manufacturing under Vision Programs
The market is further driven by national localization strategies that require a significant portion of defense systems, including solid rocket motors, to be manufactured or assembled domestically. These policies have led to the establishment of propulsion manufacturing lines, testing facilities, and specialized supply chains within the Kingdom, directly increasing domestic market value. Localization reduces dependence on imports while accelerating procurement timelines, which encourages higher order volumes and long-term supply contracts. Government-backed incentives lower financial risk for manufacturers, enabling capacity expansion and technology upgrades. Local workforce development programs also support sustained operational capability, ensuring consistent output quality. As localization targets tighten, previously imported propulsion units are replaced by domestically produced equivalents, structurally expanding the addressable market. Long-term framework agreements further stabilize demand visibility. Collectively, localization policies convert strategic intent into measurable procurement activity, reinforcing sustained growth.
Market Challenges
High Technical Complexity and Stringent Safety Requirements
The KSA Solid Rocket Motors market faces a fundamental challenge stemming from the high technical complexity involved in solid propellant formulation, motor casing design, and thrust performance optimization. Solid rocket motors require precise chemical mixing, controlled curing environments, and rigorous quality assurance to ensure consistent performance and safety. Any deviation can result in mission failure, safety incidents, or costly program delays. Compliance with international safety, handling, and storage standards further increases operational burden. Extensive ground testing, static firing trials, and certification processes are mandatory, demanding specialized infrastructure and long validation timelines. These requirements elevate capital expenditure and extend development cycles, limiting rapid scalability. Additionally, the availability of experienced propulsion engineers, chemists, and quality specialists remains constrained, increasing dependency on limited skilled talent pools. Continuous audits, inspections, and recertification requirements add to operational overhead, making efficiency improvements difficult and increasing the overall cost of production and maintenance.
Dependence on Restricted Materials, Technologies, and Supply Chains
Another major challenge for the KSA Solid Rocket Motors market is the dependence on restricted raw materials and controlled propulsion technologies subject to international export regulations and compliance frameworks. Key inputs such as specialized binders, energetic materials, insulation compounds, and high-strength casing materials are often sourced from limited global suppliers. Access restrictions, licensing requirements, and geopolitical considerations can delay procurement and disrupt production schedules. Technology transfer approvals are time-intensive, slowing the adoption of advanced designs and manufacturing processes. Efforts to localize supply chains require lengthy qualification and testing phases, delaying commercialization and increasing interim costs. Supply chain disruptions also introduce price volatility and inventory risk, complicating long-term planning. Furthermore, adherence to international non-proliferation and missile technology control regimes imposes additional documentation, reporting, and compliance obligations. These factors collectively reduce flexibility, increase lead times, and constrain responsiveness to changing defense requirements, posing persistent structural challenges to market efficiency and growth.
Opportunities
Expansion of Indigenous Propulsion Research and Development
The KSA Solid Rocket Motors market offers a significant opportunity through the expansion of indigenous propulsion research and development capabilities aligned with national industrialization objectives. Saudi Arabia is actively investing in domestic R&D ecosystems, including defense laboratories, test centers, and applied research programs focused on advanced propellant chemistry, lightweight motor casings, and improved thrust efficiency. These initiatives enable the development of motors optimized for regional operational requirements, climatic conditions, and platform integration needs. Indigenous R&D reduces long-term reliance on foreign intellectual property while improving supply security and program flexibility. It also supports faster iteration cycles for upgrades and customization, which is increasingly important as missile systems evolve. Collaboration between state-owned defense entities, universities, and international technology partners further accelerates capability building. Over time, successful domestic innovation can position local manufacturers as qualified suppliers not only for national programs but also for allied markets, strengthening export potential and long-term revenue stability.
Growth of Lifecycle Sustainment, Refurbishment, and Replacement Programs
Another major opportunity lies in the expansion of lifecycle sustainment, refurbishment, and replacement services for existing missile and defense inventories. Solid rocket motors are consumable and time-sensitive components that require periodic inspection, recertification, and replacement to maintain operational readiness. As Saudi Arabia’s missile stockpiles grow and mature, demand for structured lifecycle management solutions is increasing. Establishing domestic capabilities for motor refurbishment, propellant replacement, and safe disposal creates recurring revenue streams beyond initial procurement. These activities reduce dependence on external service providers, lower turnaround times, and improve force availability. Long-term sustainment contracts also enhance planning visibility for manufacturers and encourage investment in specialized facilities and skilled personnel. The integration of digital monitoring, predictive maintenance tools, and quality assurance systems further enhances value creation. This opportunity shifts the market dynamic from episodic acquisition toward continuous service-based engagement, supporting stable growth and deeper integration between suppliers and end users.
Future Outlook
The KSA Solid Rocket Motors market is expected to maintain stable growth over the next five years, supported by sustained defense spending, localization mandates, and continuous modernization of missile systems. Technological advancements in propellant efficiency and safety will improve performance while reducing lifecycle costs. Regulatory frameworks are anticipated to further encourage domestic manufacturing and partnerships. Demand-side momentum will remain strong due to strategic security priorities and inventory sustainment requirements.
Major Players
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- Advanced Electronics Company
- Middle East Propulsion Company
- TaqniaAeronautics
- L3Harris Arabia
- Lockheed Martin Saudi Arabia
- Raytheon Saudi Arabia
- Boeing Defense Saudi Programs
- MBDA Saudi Arabia
- Northrop Grumman Saudi Programs
- Thales Saudi Arabia
- Roketsan Saudi Programs
- Hanwha Aerospace Saudi Arabia
- Aerojet Rocketdyne Middle East
- EDGE Group Saudi Programs
Key Target Audience
- Defense ministries
- Armed forces procurement units
- Missile system manufacturers
- Aerospace and defense OEMs
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Defense research organizations
- Industrial manufacturing groups
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key market variables were identified through defense budget analysis, procurement records, and propulsion system demand mapping. Primary variables included production capacity, procurement cycles, and localization ratios. Secondary variables covered regulatory frameworks and supply chain constraints. These variables formed the analytical foundation.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market structure was constructed using verified defense expenditure data and confirmed procurement programs. Demand and supply relationships were mapped across platforms. Data triangulation ensured consistency. Assumptions were validated against official disclosures.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Preliminary findings were validated through consultations with defense industry experts and former procurement officials. Technical assumptions were reviewed by propulsion specialists. Regulatory interpretations were cross-checked. Feedback refined market conclusions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All validated data points were synthesized into a cohesive analytical framework. Market insights were structured to reflect strategic relevance. Quality checks ensured internal consistency. Final outputs were aligned with industry standards.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
National defense modernization initiatives
Expansion of indigenous missile development programs
Strategic focus on localization of defense manufacturing
Rising demand for advanced air and missile defense systems
Long term defense capability planning and investment - Market Challenges
High complexity in propellant and motor manufacturing
Dependence on restricted raw materials and technologies
Stringent safety and certification requirements
High capital investment for testing infrastructure
Limited domestic skilled workforce in propulsion technologies - Market Opportunities
Expansion of local production under defense localization programs
Partnerships with global propulsion technology providers
Development of next generation solid propulsion systems - Trends
Adoption of high energy and low signature propellants
Integration of digital design and simulation tools
Focus on modular and scalable motor designs
Increased emphasis on safety and quality assurance
Growth in collaborative development programs - Government Regulations & Defense Policy
Defense localization mandates under national vision programs
Export control and technology transfer regulations
Defense procurement standardization and compliance frameworks
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Tactical missile solid rocket motors
Strategic missile solid rocket motors
Launch vehicle booster motors
Air defense interceptor motors
Unmanned platform propulsion motors - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Land based missile systems
Naval missile platforms
Air launched missile systems
Space launch and suborbital platforms
Test and evaluation ground platforms - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
Original equipment manufacturer fitment
Retrofit and upgrade fitment
Life extension and refurbishment fitment
Prototype and test fitment
Training and simulation fitment - By End User Segment (In Value%)
Ministry of Defense forces
Strategic missile command units
Air defense and missile defense forces
Naval forces and coastal defense units
Research and testing agencies - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Direct government procurement
Long term defense contracts
Joint venture based procurement
Technology transfer programs
Local manufacturing and assembly sourcing - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Composite propellant technology
Double base propellant technology
Advanced case bonded motors
High energy propellant formulations
Insulated and lightweight motor casing materials
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Propellant technology, Motor thrust class, Manufacturing capability, Testing infrastructure, Localization level, Contract portfolio, R&D capability, Quality certifications, Delivery timelines)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Key Players
Saudi Arabian Military Industries
Advanced Electronics Company
Middle East Propulsion Company
Taqnia Aeronautics
L3Harris Arabia
Lockheed Martin Saudi Arabia
Raytheon Saudi Arabia
Boeing Defense Saudi Programs
MBDA Saudi Arabia
Northrop Grumman Saudi Programs
Thales Saudi Arabia
Roketsan Saudi Programs
Hanwha Aerospace Saudi Arabia
Aerojet Rocketdyne Middle East
EDGE Group Saudi Programs
- Growing emphasis on self reliance in missile propulsion systems
- Preference for long term supply and support agreements
- Increasing involvement in co development and testing programs
- Focus on lifecycle performance and reliability requirements
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035