Market Overview
The KSA Supersonic and Hypersonic Weapons market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting accelerating investments in advanced strike and deterrence capabilities. Development momentum has intensified due to evolving regional threat dynamics and increasing prioritization of high-speed precision systems. Deployment programs expanded across air, land, and sea platforms, supported by indigenous integration initiatives. Procurement activity increased across testing, guidance, and propulsion subsystems. Research activity expanded across defense laboratories and strategic manufacturing facilities. Capability enhancement programs emphasized speed, maneuverability, and survivability enhancements. Technology validation cycles accelerated due to geopolitical and defense readiness considerations.
The market is primarily concentrated across central and western regions of Saudi Arabia where defense command infrastructure and research installations are located. These regions benefit from advanced military bases, testing corridors, and aerospace manufacturing clusters. Government-backed defense ecosystems support supplier participation and technology assimilation. Strong logistics connectivity and defense industrial zones enable smoother system integration. Strategic naval and air force hubs further drive localized demand. Policy alignment with long-term national defense programs continues shaping regional concentration patterns.

Market Segmentation
By Platform Type
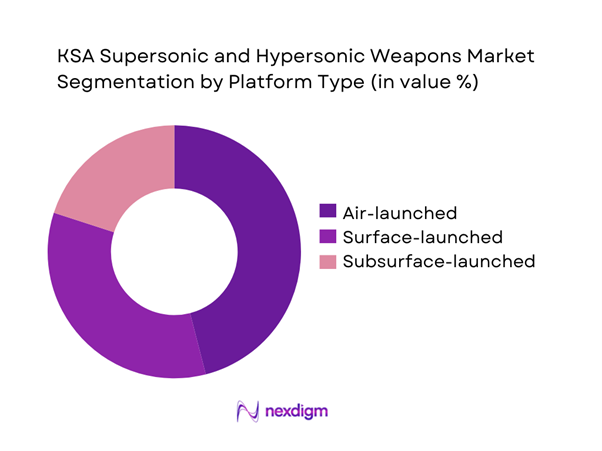
The platform-based segmentation highlights air-launched systems as the dominant category due to their flexibility, extended range, and integration with advanced fighter aircraft. Surface-launched systems continue gaining relevance for strategic deterrence and coastal defense applications. Subsurface platforms are emerging gradually, driven by naval modernization efforts. The dominance of air platforms is reinforced by continuous aircraft fleet upgrades and interoperability requirements. Platform selection is also influenced by mission adaptability, survivability, and response time optimization. Ongoing testing programs further strengthen the preference for aerial deployment capabilities.
By Technology Architecture
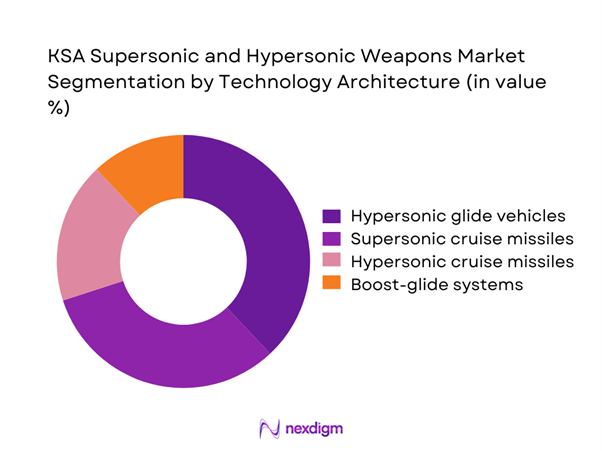
Technology-based segmentation indicates hypersonic glide vehicles as the fastest advancing category due to superior maneuverability and penetration capabilities. Supersonic cruise missiles maintain relevance because of operational maturity and deployment readiness. Hypersonic cruise systems are gradually gaining attention as propulsion technologies evolve. Boost-glide systems remain under active development with limited operational deployment. Technological preference is shaped by mission profile requirements, survivability needs, and integration feasibility. Continued investments in propulsion and thermal protection systems further influence technology selection trends.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of global defense manufacturers and regional partners supporting indigenous development initiatives. Market participants compete on technology maturity, integration capability, and long-term support offerings. Strategic collaborations and defense offset agreements play a significant role in market positioning.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Lockheed Martin | 1912 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Raytheon Technologies | 1922 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Northrop Grumman | 1939 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Boeing Defense | 1916 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MBDA | 2001 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Supersonic and Hypersonic Weapons Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising regional security threats
Rising regional security threats continue driving accelerated investment in advanced strike systems across Saudi defense programs. Increased regional instability has amplified demand for rapid response and high-precision weapon platforms. Defense planners prioritize systems capable of penetrating advanced air defense environments effectively. Continuous military modernization initiatives further support acquisition of next-generation missile technologies. Strategic deterrence requirements remain central to long-term defense planning frameworks. Enhanced interoperability with allied systems increases emphasis on advanced missile capabilities. Operational readiness mandates faster deployment and improved strike accuracy across defense forces. Evolving threat landscapes require adaptive and technologically superior weapon systems. Increased defense exercises validate performance and encourage procurement continuity. Overall, security dynamics remain a primary catalyst for sustained market expansion.
Defense modernization under Vision 2030
Defense modernization under Vision 2030 significantly accelerates adoption of advanced missile technologies across military branches. National defense localization goals promote investment in domestic production and technology transfer. Procurement policies emphasize long-term capability development rather than short-term acquisitions. Integrated defense planning aligns missile programs with broader modernization objectives. Expansion of research facilities supports testing and indigenous design efforts. Increased funding allocations strengthen development pipelines across multiple weapon categories. Collaborative development initiatives enhance technological absorption and system customization. Vision-driven procurement supports continuous upgrade cycles and lifecycle management. Emphasis on self-reliance drives supplier diversification strategies. Modernization objectives collectively sustain long-term market momentum.
Challenges
High development and acquisition costs
High development and acquisition costs pose significant barriers to widespread deployment of advanced weapon systems. Complex engineering requirements increase production timelines and financial commitments. Specialized materials and propulsion technologies elevate manufacturing complexity. Testing and validation processes demand extensive infrastructure investments. Budgetary constraints influence prioritization across defense procurement programs. Long development cycles delay operational readiness of advanced systems. Cost escalation risks affect project approval and continuation decisions. Maintenance and lifecycle expenses further increase overall ownership burden. Procurement planning must balance performance goals with fiscal sustainability. These cost-related challenges continue constraining rapid market expansion.
Technology transfer restrictions
Technology transfer restrictions limit access to critical components and advanced design capabilities. Export control regulations restrict availability of key propulsion and guidance technologies. Dependence on foreign suppliers creates vulnerabilities in supply continuity. Licensing constraints delay development timelines and system integration efforts. Indigenous capability development requires extended learning curves and investments. Restricted access impacts customization and system optimization efforts. Compliance requirements add complexity to collaborative development projects. Technology control regimes influence strategic procurement decisions significantly. Delays in approvals affect program execution schedules. Overall, transfer limitations remain a structural challenge for market growth.
Opportunities
Domestic manufacturing and localization
Domestic manufacturing and localization present significant opportunities for long-term capability development. Government initiatives encourage local production of subsystems and components. Indigenous manufacturing reduces dependency on external suppliers over time. Localization programs stimulate skill development and technology absorption. Establishment of defense industrial clusters enhances supply chain resilience. Local production improves lifecycle support and maintenance efficiency. Increased domestic participation supports economic diversification objectives. Policy incentives attract private sector involvement in defense manufacturing. Localized testing facilities accelerate development cycles. These factors collectively strengthen domestic industry competitiveness.
Joint ventures with global defense OEMs
Joint ventures with global defense OEMs offer pathways for technology acquisition and capability enhancement. Strategic partnerships facilitate access to advanced design and engineering expertise. Collaborative development accelerates learning and reduces technological gaps. Joint ventures support compliance with localization and offset requirements. Shared production models enhance cost efficiency and risk sharing. Partnerships improve access to global supply chains and standards. Cooperative research initiatives drive innovation in propulsion and guidance systems. Joint programs enable faster commercialization of advanced platforms. Long-term alliances strengthen strategic defense relationships. Such collaborations represent critical growth avenues for the market.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to witness steady technological advancement driven by modernization priorities and evolving threat environments. Continued focus on indigenous capabilities will reshape procurement strategies. Integration of advanced guidance and propulsion systems will remain central to development efforts. Collaborative programs and defense partnerships will influence innovation pathways. Overall, long-term demand will remain resilient as strategic defense priorities continue expanding.
Major Players
- Lockheed Martin
- Raytheon Technologies
- Northrop Grumman
- Boeing Defense
- MBDA
- BAE Systems
- Thales Group
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- L3Harris Technologies
- Aerojet Rocketdyne
- Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
- Hanwha Defense
- Rostec
- China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
Key Target Audience
- Ministry ofDefenseof Saudi Arabia
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- General Authority for Military Industries
- Royal Saudi Air Force
- Naval Forces Command
- Defense procurement agencies
- Investments and venture capital firms
- National security and regulatory authorities
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market scope was defined through assessment of weapon categories, deployment platforms, and operational use cases. Core variables included technology types, deployment models, and procurement structures. Data points were aligned with defense acquisition frameworks and capability planning benchmarks.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Qualitative and quantitative indicators were mapped to identify demand patterns and development intensity. Segment relationships were analyzed based on deployment trends and defense modernization initiatives. Data consistency was maintained across platform and technology layers.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through expert consultations involving defense analysts and industry specialists. Assumptions were tested against operational feasibility and policy alignment. Feedback loops ensured refinement of market dynamics and structural accuracy.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated insights were consolidated into coherent analytical frameworks. Cross-verification ensured logical consistency and relevance. Final outputs were structured to reflect strategic, operational, and technological perspectives.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and weapons classification framework, Platform and mission-based segmentation logic, Bottom-up defense budget and program-based market sizing, Revenue attribution by system lifecycle and contract value, Primary interviews with defense officials and OEMs, Validation through SIPRI and regional defense procurement databases, Assumptions and limitations related to classified programs)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational deployment and deterrence role
- Ecosystem structure
- Defense supply chain and procurement channels
- Regulatory and defense policy environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising regional security threats
Defense modernization under Vision 2030
Increasing defense budget allocation
Strategic deterrence requirements
Technology transfer and localization initiatives - Challenges
High development and acquisition costs
Technology transfer restrictions
Limited indigenous propulsion capabilities
Complex testing and validation requirements
Export control and compliance barriers - Opportunities
Domestic manufacturing and localization
Joint ventures with global defense OEMs
Development of hypersonic test infrastructure
Integration with missile defense systems
R&D investment in propulsion and guidance - Trends
Shift toward hypersonic glide vehicles
Emphasis on precision and maneuverability
Integration with C4ISR systems
Increased simulation-based testing
Focus on indigenous defense capabilities - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Air-launched platforms
Surface-launched platforms
Subsurface-launched platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Strategic deterrence
Precision strike missions
Air defense penetration
Tactical battlefield deployment - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Supersonic cruise missiles
Hypersonic glide vehicles
Hypersonic cruise missiles
Boost-glide systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Defense forces
Strategic missile command
Research and testing agencies - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone weapon systems
Network-centric integrated systems
AI-enabled targeting systems - By Region (in Value %)
Central Saudi Arabia
Western Region
Eastern Region
Southern Region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Technology capability, Range and speed profile, Guidance and navigation systems, Indigenous content level, Contract value, Delivery timeline, After-sales support, Strategic partnerships)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Lockheed Martin
Raytheon Technologies
Northrop Grumman
Boeing Defense
MBDA
BAE Systems
Thales Group
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
L3Harris Technologies
Aerojet Rocketdyne
Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
Rostec
Hanwha Defense
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


