Market Overview
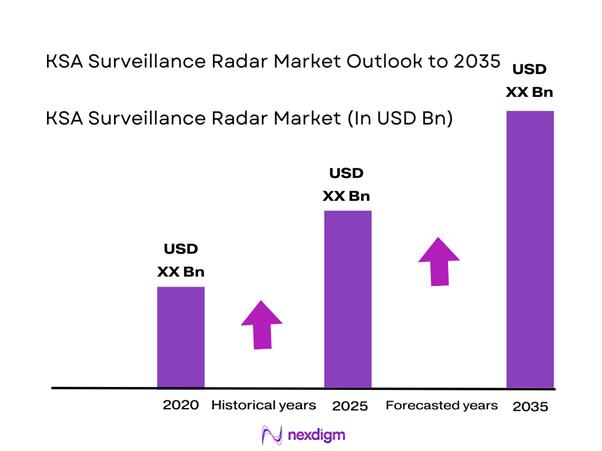
The KSA Surveillance Radar market current size stands at around USD ~ million and reflects steady procurement momentum driven by defense modernization priorities and border security programs. In 2024 and 2025, system deployments increased across air, land, and coastal surveillance applications, supported by national security investments. Radar installations expanded across military bases, border zones, and critical infrastructure sites. Demand has remained resilient due to geopolitical considerations, technology upgrades, and increasing adoption of advanced detection capabilities across multiple operational environments.
The market is primarily concentrated in Riyadh, Eastern Province, and Western coastal regions where defense infrastructure density remains high. Demand is shaped by air defense modernization, maritime monitoring requirements, and protection of critical assets. Strong government backing, defense localization policies, and integrated command systems continue strengthening the ecosystem. The presence of military bases, industrial corridors, and strategic maritime routes further supports sustained radar deployment across regions.
Market Segmentation
By Application
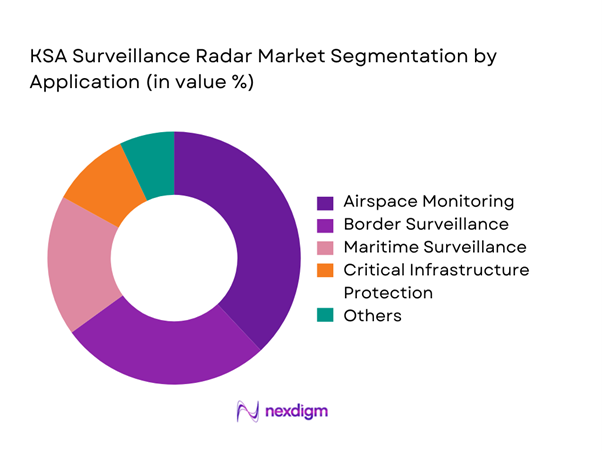
Airspace monitoring dominates the market due to continuous investments in national air defense systems and early warning infrastructure. Border surveillance represents another major segment, driven by the need to monitor extensive land boundaries and manage cross-border security risks. Maritime surveillance adoption is rising due to increased focus on coastal protection and port security. Critical infrastructure protection continues to expand with radar usage across energy facilities and industrial zones. Defense modernization programs reinforce long-term demand across all application categories.
By Technology Architecture
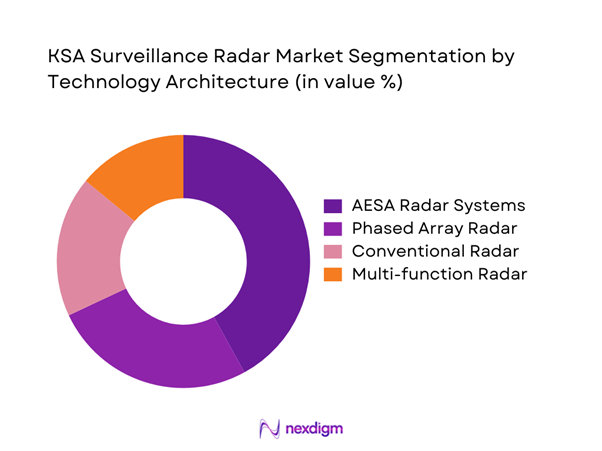
AESA-based radar systems dominate due to superior detection accuracy, multi-target tracking, and electronic warfare resistance. Phased array radars maintain strong adoption for air defense and long-range surveillance. Conventional radar systems continue operating in legacy installations, particularly for perimeter security. Multi-function radar systems are gaining attention for integrated operations across surveillance and targeting functions. Technology upgrades are driven by the need for interoperability, real-time data processing, and enhanced situational awareness.
Competitive Landscape
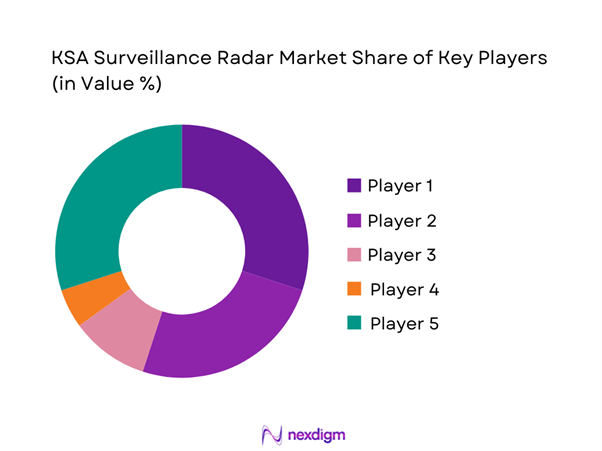
The competitive landscape is characterized by the presence of global defense technology providers and regional system integrators. Market participants compete on technological depth, system reliability, integration capabilities, and long-term service support. Localization initiatives and offset requirements significantly influence contract awards. Strategic partnerships with domestic entities play a critical role in securing long-term programs and government contracts.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Lockheed Martin | 1912 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Raytheon Technologies | 1922 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales Group | 1893 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saab AB | 1937 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo S.p.A. | 1948 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Surveillance Radar Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising border security and airspace monitoring needs
Border security requirements intensified during 2024 due to increasing cross-border monitoring obligations and aerial threat detection priorities. National defense agencies expanded radar coverage to improve early warning response and airspace situational awareness. Increased drone activity encouraged deployment of advanced detection and tracking technologies across sensitive regions. Continuous infrastructure expansion further strengthened radar deployment needs across strategic zones. Integrated command systems improved radar utilization efficiency across air and ground operations. Surveillance modernization programs supported procurement momentum across defense agencies. Enhanced interoperability between radar networks increased operational effectiveness significantly. Border protection mandates sustained investment in long-range surveillance capabilities. Rising regional security concerns further reinforced monitoring requirements across key locations. Long-term defense strategies continue emphasizing radar-based situational awareness systems.
Increased defense spending under Vision 2030
Defense modernization programs under Vision 2030 accelerated radar procurement initiatives across military branches. Budget allocations favored technology upgrades supporting national security objectives and force readiness. Radar acquisition aligned with broader military digitization and modernization frameworks. Multi-year procurement planning enabled sustained system deployment cycles. Investment focus remained on advanced surveillance and detection capabilities. Indigenous defense manufacturing initiatives further supported radar system integration. Government-backed projects encouraged long-term technology partnerships. Increased funding stability enhanced supplier confidence and program continuity. Strategic alignment with national defense goals strengthened acquisition pipelines. Defense spending growth remained a key market catalyst.
Challenges
High capital and maintenance costs
Surveillance radar systems involve high acquisition costs due to complex hardware and integration requirements. Maintenance expenses increase due to calibration, upgrades, and lifecycle management needs. Budget constraints sometimes delay system replacement or expansion initiatives. Long deployment cycles increase total ownership costs for end users. Skilled manpower requirements further elevate operational expenses. Maintenance contracts add long-term financial commitments for operators. Spare parts availability affects operational continuity and cost efficiency. Technology obsolescence risks increase replacement expenditures. Financial planning complexity impacts procurement timelines. Cost pressures remain a persistent adoption challenge.
Dependence on foreign technology suppliers
Heavy reliance on imported radar technologies creates supply chain vulnerabilities for national programs. Technology transfer limitations restrict domestic capability development in some areas. Procurement delays occur due to export controls and regulatory approvals. Limited local manufacturing capacity affects system customization flexibility. Dependence on external maintenance support increases operational risk. Geopolitical factors influence technology availability and upgrades. Localization targets face challenges due to proprietary system architectures. Integration complexity increases when using foreign platforms. Domestic skill gaps hinder rapid localization efforts. Strategic autonomy remains constrained by supplier dependencies.
Opportunities
Localization and defense manufacturing initiatives
Government-backed localization programs create opportunities for domestic radar manufacturing and assembly. Technology transfer initiatives support development of indigenous radar components. Local production reduces long-term dependency on imports. Industrial partnerships encourage skill development and employment creation. Domestic testing facilities improve system validation capabilities. Localization policies enhance supply chain resilience. Defense offsets stimulate private sector participation. Local manufacturing supports faster system deployment timelines. Cost efficiencies improve through reduced import reliance. Localization strengthens long-term defense sustainability.
Integration of AI and advanced signal processing
Artificial intelligence enhances target recognition and threat classification accuracy. Advanced signal processing improves detection in complex environments. AI-driven analytics support faster decision-making and response times. Automation reduces operator workload and improves operational efficiency. Machine learning enhances adaptive radar performance over time. Integration with command systems strengthens situational awareness. Data fusion capabilities enable multi-source intelligence integration. AI adoption improves surveillance coverage reliability. Advanced processing supports counter-drone and stealth detection. Technological evolution drives next-generation radar development.
Future Outlook
The KSA surveillance radar market is expected to maintain steady growth through 2035, supported by defense modernization and border security priorities. Increasing emphasis on localized manufacturing and technology integration will shape procurement strategies. Adoption of AI-enabled and networked radar systems will continue expanding. Strategic defense initiatives and infrastructure investments are expected to sustain long-term market development.
Major Players
- Lockheed Martin
- Raytheon Technologies
- Thales Group
- Saab AB
- Leonardo S.p.A.
- Northrop Grumman
- Airbus Defence and Space
- HENSOLDT AG
- Indra Sistemas
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- ELTA Systems
- ASELSAN
- BAE Systems
- L3Harris Technologies
- Rheinmetall Defence
Key Target Audience
- Saudi Ministry of Defense
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- General Authority for Military Industries
- Saudi Border Guard
- Royal Saudi Air Defense Forces
- Defense system integrators
- Aerospace and defense manufacturers
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market boundaries, system classifications, application scope, and deployment environments were identified based on defense sector structures and procurement frameworks.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market structure was developed using technology segmentation, application mapping, and operational deployment trends across Saudi defense sectors.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through expert discussions, defense sector insights, and cross-verification of procurement and deployment patterns.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated through data triangulation, qualitative validation, and consistency checks to ensure analytical accuracy.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and operational scope for surveillance radar systems in KSA, Platform and application-based segmentation framework for defense and security radars, Bottom-up market sizing using radar deployment and procurement data, Revenue estimation through contract value and system lifecycle costing, Primary validation through defense officials and radar system integrators)
- Definition and scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and operational deployment landscape
- Ecosystem and stakeholder structure
- Supply chain and localization dynamics
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising border security and airspace monitoring needs
Increased defense spending under Vision 2030
Growing adoption of AESA and multi-function radars
Modernization of air defense and surveillance infrastructure
Rising geopolitical and regional security concerns - Challenges
High capital and maintenance costs
Dependence on foreign technology suppliers
Complex integration with legacy defense systems
Long procurement and approval cycles
Skilled workforce and technical training gaps - Opportunities
Localization and defense manufacturing initiatives
Integration of AI and advanced signal processing
Expansion of coastal and maritime surveillance
Upgrades of legacy radar installations
Public-private partnerships in defense electronics - Trends
Shift toward network-centric surveillance systems
Increased demand for mobile and deployable radars
Adoption of AI-based threat detection
Emphasis on multi-band and multi-mission radars
Growing role of domestic defense manufacturing - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Ground-based surveillance radar
Airborne surveillance radar
Naval surveillance radar
Border and coastal surveillance radar
Mobile and tactical radar systems - By Application (in Value %)
Airspace monitoring and air defense
Border and perimeter security
Maritime surveillance
Critical infrastructure protection
Early warning and threat detection - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA)
Passive Electronically Scanned Array (PESA)
Conventional radar systems
Multi-function integrated radar
3D and phased array radar - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Defense forces
Homeland security
Border security agencies
Coast guard and naval forces
Critical infrastructure operators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone radar systems
Network-centric radar systems
Integrated C4ISR-enabled radar
AI-enabled sensor fusion systems - By Region (in Value %)
Central Saudi Arabia
Western Saudi Arabia
Eastern Province
Southern Border Region
Northern Border Region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Technology capability, Radar range and accuracy, Platform integration, Localization presence, Contract value, After-sales support, Compliance with Saudi defense standards, Pricing strategy)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Lockheed Martin
Raytheon Technologies
Thales Group
Saab AB
Leonardo S.p.A.
HENSOLDT AG
Indra Sistemas
Northrop Grumman
Airbus Defence and Space
Israel Aerospace Industries
ELTA Systems
ASELSAN
BAE Systems
L3Harris Technologies
Rheinmetall Defence
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and defense financing practices
- Implementation challenges and operational risks
- Post-deployment support and lifecycle service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


