Market Overview
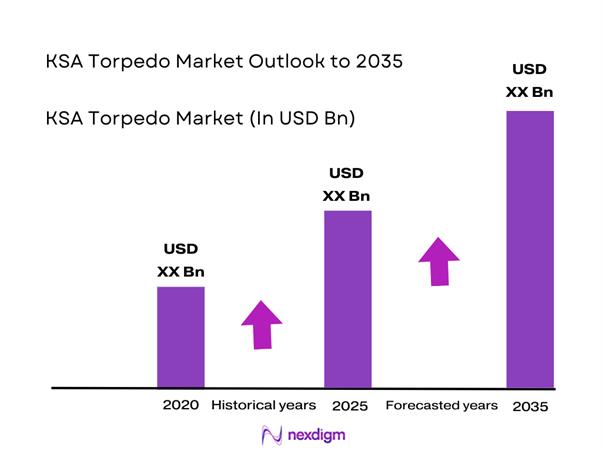
The KSA Torpedo market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady procurement activity and fleet modernization momentum. Demand levels in 2024 and 2025 were supported by naval capability upgrades, platform modernization programs, and sustained defense allocation toward underwater warfare readiness. The market shows stable procurement cycles driven by long-term naval planning, with procurement volumes aligned to fleet replacement schedules and operational readiness requirements across multiple maritime commands.
The market is primarily concentrated across coastal naval bases and strategic maritime zones with established defense infrastructure. Western and Eastern operational regions dominate demand due to fleet density, naval command presence, and logistics accessibility. Strong government backing, localized defense manufacturing initiatives, and structured procurement frameworks further support ecosystem maturity. Policy alignment with national defense objectives and modernization mandates continues to reinforce sustained demand concentration across key naval hubs.
Market Segmentation
By Fleet Type
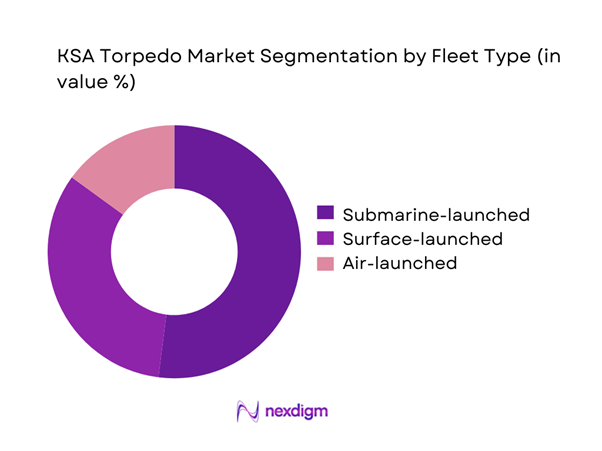
The fleet type segmentation is dominated by submarine-launched systems, reflecting the strategic emphasis on undersea deterrence and maritime defense readiness. Surface-launched platforms follow, supported by fleet modernization and patrol vessel upgrades. Air-launched torpedoes maintain a limited but specialized role within naval aviation units. In 2024 and 2025, procurement focus remained aligned with platform compatibility, mission endurance, and operational flexibility. Submarine fleet expansion programs have driven consistent demand, while surface combatants contribute through upgrade cycles rather than new acquisitions. Fleet composition strategies increasingly prioritize interoperability, lifecycle efficiency, and adaptability to evolving maritime threat environments.
By Technology Architecture
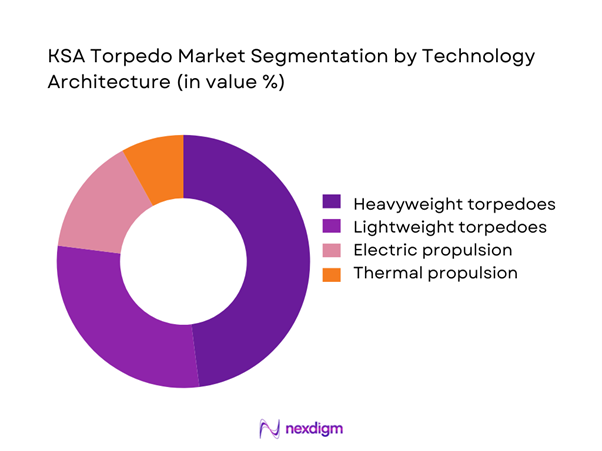
Technology architecture segmentation is led by heavyweight torpedo systems due to extended range, payload capacity, and operational reliability. Lightweight torpedoes continue to serve anti-submarine roles, particularly in littoral and patrol missions. Electric propulsion systems are gaining preference for stealth and efficiency, while thermal propulsion remains relevant for legacy platforms. In 2024 and 2025, procurement decisions increasingly favored modular architectures enabling easier upgrades. Technology selection is strongly influenced by acoustic performance, guidance precision, and integration compatibility with existing combat systems across naval platforms.
Competitive Landscape
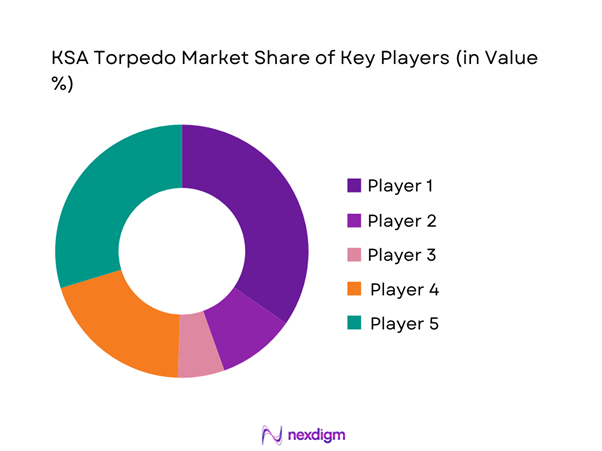
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of international defense manufacturers and regional partners engaged in supply, integration, and lifecycle support. Market participants compete on technology maturity, system reliability, integration capability, and long-term service support. Procurement decisions are influenced by compliance readiness, platform compatibility, and localization commitments.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Leonardo S.p.A. | 1948 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saab AB | 1937 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Atlas Elektronik | 1902 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Naval Group | 1624 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Raytheon Technologies | 1922 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Torpedo Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising naval modernization programs
Rising naval modernization programs continue to reshape procurement priorities across the KSA maritime defense ecosystem during recent operational planning cycles. In 2024, fleet recapitalization activities emphasized underwater warfare readiness and platform survivability improvements across multiple naval commands nationwide. Modernization roadmaps increasingly prioritize torpedo capability alignment with new submarine and surface combatant acquisitions within planned defense force structures. During 2025 planning cycles, defense authorities linked torpedo upgrades to broader naval combat system integration across frontline fleet assets. Modernization spending prioritizes lethality enhancement, acoustic performance, and compatibility with evolving maritime doctrines across national naval capability objectives. These programs are supported by long-term naval planning documents guiding acquisition sequencing and deployment readiness across fleet modernization phases. Increased emphasis on undersea dominance reinforces sustained demand for advanced torpedo integration solutions within future naval force structures. Operational readiness benchmarks increasingly link torpedo capability metrics to mission success evaluations across maritime security operations contexts. Fleet commanders emphasize modernization consistency to ensure interoperability between platforms deployed across regions during joint maritime operations planning. Overall, modernization momentum continues shaping procurement pipelines and sustaining long-term torpedo program relevance within national defense capability frameworks.
Expansion of submarine fleet capabilities
Expansion of submarine fleet capabilities remains a central focus of naval force development strategies across KSA waters. Submarine acquisitions during 2024 emphasized enhanced endurance, stealth, and weapons integration requirements for underwater dominance. Fleet expansion plans align torpedo procurement with evolving operational doctrines and extended patrol mandates. In 2025, submarine force development emphasized multi-role mission readiness supported by advanced underwater weapon systems. Increased submarine deployment necessitates reliable torpedo availability for training, deterrence, and operational deployment scenarios. Procurement authorities prioritize compatibility between torpedo systems and new submarine combat management systems. Expansion initiatives also emphasize sustainment planning, ensuring long-term availability of mission-critical munitions. Submarine fleet growth directly influences inventory planning, maintenance cycles, and replenishment schedules. Integration testing and certification processes further reinforce sustained procurement requirements across operational timelines. Collectively, submarine expansion efforts remain a primary demand driver within the national torpedo acquisition framework.
Challenges
High procurement and lifecycle costs
High procurement and lifecycle costs continue to challenge procurement planning across naval modernization initiatives. Torpedo systems require substantial investment across manufacturing, testing, integration, and long-term maintenance phases. In 2024, budget planning emphasized cost optimization without compromising operational capability requirements. Lifecycle costs extend beyond acquisition, encompassing storage, testing, upgrades, and periodic refurbishment activities. These financial pressures influence procurement pacing and platform prioritization decisions. Budgetary constraints often require phased acquisitions aligned with multi-year defense planning cycles. Cost considerations also impact supplier selection and technology adoption strategies. Sustaining readiness levels demands consistent funding allocations across operational lifecycles. High cost structures necessitate careful balancing between modernization ambitions and fiscal discipline. Financial oversight mechanisms increasingly shape procurement governance frameworks. Overall, cost intensity remains a persistent constraint affecting long-term torpedo program scalability.
Technology transfer restrictions
Technology transfer restrictions continue to limit domestic integration capabilities within torpedo acquisition programs. Regulatory controls influence access to critical guidance, propulsion, and seeker technologies. In 2024, procurement strategies faced delays due to export control compliance requirements. Restricted technology access complicates localization efforts and slows indigenous capability development. Defense authorities must navigate complex approval processes for advanced subsystem integration. These restrictions affect timelines for system upgrades and platform interoperability improvements. Limited transferability also impacts maintenance autonomy and long-term sustainment planning. Dependence on foreign approvals introduces uncertainty into procurement scheduling and system upgrades. Strategic partnerships partially mitigate constraints but require extended negotiation cycles. Technology transfer limitations remain a structural challenge for capability expansion objectives.
Opportunities
Localization and licensed production initiatives
Localization and licensed production initiatives present strong growth opportunities within the KSA torpedo ecosystem. National defense strategies increasingly emphasize domestic manufacturing participation and knowledge transfer frameworks. In 2024, localization policies encouraged joint ventures and technology collaboration agreements. Licensed production enhances supply chain resilience and reduces long-term dependency risks. Local assembly capabilities improve turnaround times for maintenance and refurbishment activities. Workforce development initiatives support skill enhancement in advanced defense manufacturing disciplines. Localization also strengthens compliance with national industrial participation mandates. Increased domestic involvement improves lifecycle management efficiency and cost control. Strategic alignment with industrial development goals supports sustained program continuity. These initiatives create long-term value across defense manufacturing ecosystems.
Next-generation lightweight torpedo adoption
Next-generation lightweight torpedo adoption offers significant opportunity for capability enhancement across naval operations. These systems support anti-submarine missions with improved maneuverability and detection accuracy. In 2025, development efforts emphasized modular designs and enhanced acoustic processing capabilities. Lightweight systems offer deployment flexibility across surface vessels and aerial platforms. Reduced size enables improved storage efficiency and faster deployment cycles. Operational doctrines increasingly favor versatile munitions adaptable to diverse mission profiles. Integration with modern sonar systems enhances overall combat effectiveness. Adoption trends reflect shifting emphasis toward agile and networked naval warfare concepts. Lightweight torpedoes also support training efficiency through scalable deployment. These advantages position next-generation systems as key growth enablers.
Future Outlook
The KSA torpedo market is expected to maintain steady development driven by naval modernization and strategic maritime priorities. Continued fleet upgrades, localization initiatives, and technology adoption will shape procurement patterns. Emphasis on underwater warfare readiness and operational autonomy will sustain long-term demand. Policy alignment and defense investment stability are expected to reinforce market continuity through the forecast period.
Major Players
- Leonardo S.p.A.
- Saab AB
- Atlas Elektronik
- Naval Group
- Raytheon Technologies
- L3Harris Technologies
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- BAE Systems
- Hanwha Defense
- Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
- Bharat Dynamics Limited
- ASELSAN
- Roketsan
Key Target Audience
- Ministry of Defense procurement departments
- Royal Saudi Naval Forces
- Naval modernization program offices
- Defense manufacturing and integration firms
- Maritime security agencies
- Government procurement authorities
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries and affiliated agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key operational, technical, and procurement variables were identified through defense capability mapping and platform assessment. Emphasis was placed on operational requirements, deployment patterns, and system interoperability.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market structure was developed using platform-level assessment, procurement cycles, and capability alignment. Demand patterns were analyzed across fleet categories and operational use cases.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through expert consultations with defense professionals and domain specialists. Insights focused on procurement behavior, technology adoption, and operational constraints.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated through triangulation of qualitative insights and quantitative indicators. The final output reflects validated trends, market dynamics, and strategic implications.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and platform-based torpedo classification, defense procurement and naval inventory mapping, bottom-up and top-down market sizing, contract value and lifecycle cost attribution, primary interviews with naval procurement and defense OEMs, data triangulation using defense budgets and fleet modernization plans, assumption validation based on classified-to-open source correlation)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and operational deployment framework
- Ecosystem and value chain structure
- Supply chain and localization dynamics
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising naval modernization programs
Expansion of submarine fleet capabilities
Increased focus on maritime border security
Strategic investments under Vision 2030
Growing emphasis on indigenous defense production
Regional naval power competition - Challenges
High procurement and lifecycle costs
Technology transfer restrictions
Dependence on foreign OEMs
Complex maintenance and upgrade cycles
Long defense procurement timelines
Integration challenges with legacy platforms - Opportunities
Localization and licensed production initiatives
Next-generation lightweight torpedo adoption
Integration with advanced sonar systems
Upgrades of existing submarine fleets
Partnerships with global defense OEMs
Growth in naval training and simulation systems - Trends
Shift toward electric propulsion systems
Increased use of fiber-optic guidance
Focus on low-noise and stealth capabilities
Digital fire-control system integration
Modular torpedo architecture development
Emphasis on lifecycle support contracts - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Submarine-launched torpedoes
Surface ship-launched torpedoes
Air-launched torpedoes - By Application (in Value %)
Anti-submarine warfare
Anti-surface warfare
Training and testing
Countermeasure and decoy deployment - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Heavyweight torpedoes
Lightweight torpedoes
Electric propulsion torpedoes
Thermal propulsion torpedoes
Wire-guided systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Naval forces
Defense research and testing agencies
Maritime security forces - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Wire-guided
Fiber-optic guided
Autonomous guidance systems - By Region (in Value %)
Western Region
Eastern Region
Central Region
Southern Region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (product portfolio strength, technology maturity, localization capability, contract value, delivery timelines, lifecycle support, pricing strategy, regional presence)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Leonardo S.p.A.
Saab AB
Atlas Elektronik
Naval Group
Raytheon Technologies
L3Harris Technologies
Lockheed Martin
Northrop Grumman
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
BAE Systems
Hanwha Defense
Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
Bharat Dynamics Limited
ASELSAN
Roketsan
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


