Market Overview
The KSA UAS Warfare market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained procurement momentum and accelerated operational deployment across defense branches. Platform induction volumes increased during 2024 and 2025 as surveillance and combat readiness priorities intensified. Fleet modernization programs supported consistent procurement of ISR and strike-capable platforms. Indigenous production initiatives also expanded system availability while reducing reliance on imports. Technology absorption increased through licensed manufacturing and system integration. Operational utilization rose due to border security, reconnaissance, and tactical mission requirements.
The market is primarily concentrated across Riyadh, Eastern Province, and Southern operational zones due to defense infrastructure density and deployment requirements. These regions benefit from proximity to command centers, airbases, and maintenance facilities. The ecosystem is supported by established defense industrial zones and policy-driven localization mandates. Government-backed manufacturing clusters and testing ranges strengthen deployment readiness. Strong interagency coordination and evolving defense doctrines further reinforce adoption levels across operational commands.
Market Segmentation
By Fleet Type
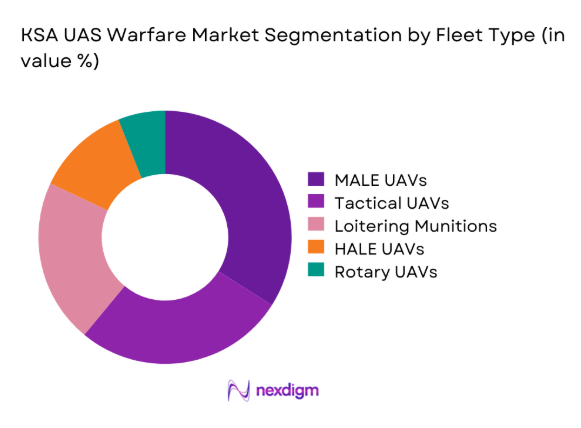
The market is dominated by MALE and tactical UAV platforms due to their multi-mission adaptability and endurance advantages. These platforms are widely deployed for surveillance, reconnaissance, and precision operations across border regions. Loitering munitions are gaining rapid traction owing to evolving combat doctrines emphasizing precision engagement. Rotary UAVs remain limited but are increasingly evaluated for urban and naval missions. Fleet diversification is driven by mission specialization and integration with command systems.
By Application
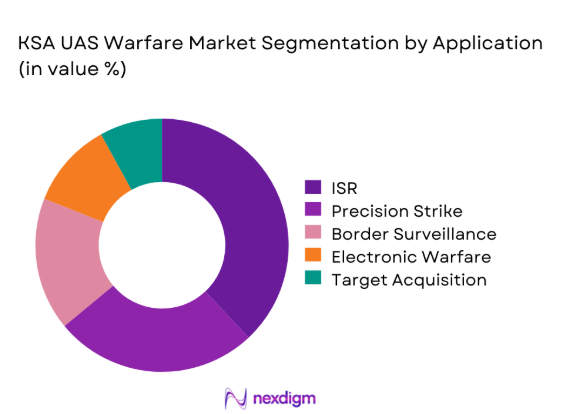
ISR applications account for the largest deployment share due to continuous border monitoring requirements. Precision strike capabilities have expanded following integration of guided munitions. Electronic warfare and SIGINT roles are growing with digital battlefield transformation. Maritime surveillance usage is increasing along coastal security zones. Target acquisition remains a core function supporting air and ground coordination.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by a mix of domestic defense integrators and international UAV manufacturers. Market participation is shaped by localization policies, offset requirements, and long-term defense partnerships. Companies compete on platform reliability, autonomy levels, and lifecycle support capabilities. Indigenous players are expanding through joint ventures and technology transfer agreements. The market remains moderately consolidated with strong government influence on procurement decisions.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Saudi Arabian Military Industries | 2017 | Saudi Arabia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Advanced Electronics Company | 1988 | Saudi Arabia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| TAQNIA Defense | 2011 | Saudi Arabia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| General Atomics | 1993 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Baykar Technologies | 1984 | Turkey | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA UAS Warfare Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Modernization of Saudi defense capabilities under Vision 2030
Saudi defense modernization programs prioritize unmanned aerial warfare capabilities to enhance surveillance precision and operational reach nationwide across diverse mission profiles. Increased defense allocations during 2024 supported accelerated procurement of advanced UAV systems across multiple operational units. Integration of digital command networks improved real-time data utilization for tactical and strategic missions. Modernization initiatives emphasize interoperability between air, land, and maritime defense platforms. Advanced sensor payload adoption improved situational awareness in complex threat environments. Training investments expanded operator readiness for autonomous system management. Indigenous production facilities enabled faster system customization and deployment cycles. Platform standardization improved maintenance efficiency and operational availability rates. Defense reforms supported technology absorption through joint development programs. These initiatives collectively strengthened unmanned warfare readiness across national defense infrastructure.
Rising asymmetric warfare and border surveillance needs
Growing asymmetric threats increased demand for persistent aerial monitoring and rapid response capabilities across border regions. UAV platforms enabled continuous surveillance without exposing personnel to hostile environments. Increased infiltration risks drove deployment of long-endurance systems for perimeter monitoring. Terrain complexity necessitated flexible aerial platforms capable of rapid redeployment. Integration with ground intelligence units enhanced situational awareness and response accuracy. UAV usage improved detection of irregular movement patterns along sensitive zones. Operational feedback in 2024 demonstrated improved mission success rates using unmanned assets. Border security operations increasingly rely on automated reconnaissance workflows. Real-time data transmission strengthened decision-making speed during incidents. These dynamics continue to drive sustained investment in unmanned surveillance assets.
Challenges
High dependency on foreign technology and IP
Reliance on foreign technology limits strategic autonomy across critical UAV subsystems and mission software layers. Import dependencies create vulnerabilities in supply continuity and upgrade cycles. Licensing restrictions constrain local modification and system customization capabilities. Intellectual property limitations restrict deeper integration of indigenous innovations. Technology access delays affect rapid deployment during evolving operational scenarios. Maintenance complexity increases due to reliance on external technical support channels. Supply chain disruptions can impact fleet readiness and availability rates. Localization goals face hurdles due to restricted technology transfer agreements. Skilled workforce development remains constrained by limited exposure to core technologies. These challenges collectively slow full operational independence in UAV warfare capabilities.
Export control and technology transfer restrictions
International export regulations impose constraints on advanced sensor and propulsion system acquisitions. Approval timelines often delay deployment schedules for critical UAV platforms. Technology transfer limitations restrict local manufacturing depth and system upgrades. Compliance requirements increase administrative complexity for procurement programs. Restrictions affect integration of advanced communication and encryption modules. Dependency on foreign approvals impacts long-term operational planning flexibility. Licensing uncertainties discourage rapid scaling of indigenous production capabilities. Collaborative development programs face regulatory scrutiny across jurisdictions. These factors collectively limit speed of technological advancement. Strategic autonomy objectives are challenged by persistent regulatory barriers.
Opportunities
Expansion of indigenous UAV manufacturing
Local manufacturing expansion enables greater control over system design and production timelines. Government incentives encourage domestic assembly and component localization initiatives. Increased industrial participation strengthens supply chain resilience and employment generation. Indigenous manufacturing supports faster customization for mission-specific requirements. Collaboration with global partners enhances technology absorption capabilities. Facility expansion improves scalability for future defense needs. Local production reduces dependency on external suppliers. Enhanced quality control improves platform reliability and lifecycle management. Policy support accelerates industrial ecosystem maturation. These developments create long-term sustainability for national UAV programs.
Development of armed UAV and loitering munition programs
Growing focus on precision engagement drives development of armed UAV platforms. Loitering munitions offer cost-effective solutions for tactical strike missions. Operational flexibility improves with extended endurance and autonomous targeting features. Defense planners prioritize scalable strike capabilities for asymmetric engagements. Indigenous weapon integration enhances operational sovereignty. Testing programs validate effectiveness across diverse combat scenarios. Deployment flexibility increases responsiveness during dynamic mission requirements. Platform modularity supports multi-role battlefield applications. These systems align with evolving defense doctrines. Continued investment strengthens overall combat readiness and deterrence posture.
Future Outlook
The KSA UAS Warfare market is expected to witness sustained expansion driven by modernization initiatives and evolving security dynamics. Continued localization efforts will enhance domestic production capabilities. Integration of autonomous technologies will reshape operational doctrines. Strategic partnerships are likely to deepen technology transfer and manufacturing depth. Long-term defense planning will further strengthen unmanned system adoption across multiple mission profiles.
Major Players
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- Advanced Electronics Company
- TAQNIA Defense
- General Atomics
- Baykar Technologies
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- Elbit Systems
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Leonardo
- Thales Group
- Boeing Defense
- RTX
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
- Airbus Defence and Space
Key Target Audience
- Saudi Ministry of Defense
- General Authority for Military Industries
- Royal Saudi Air Force
- Border Guard Command
- Defense procurement agencies
- Systems integrators and OEMs
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies such as GAMI
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market scope, platform classification, operational usage, and procurement structures were defined based on defense deployment patterns and program mandates.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Segmentation logic was developed using platform type, application scope, and operational deployment data from defense agencies.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Insights were validated through consultations with defense professionals, system integrators, and operational specialists.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All findings were consolidated through triangulation, ensuring consistency across qualitative and quantitative assessments.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and operational scope for military UAS warfare in KSA, Platform and mission-based segmentation framework for unmanned combat systems, Bottom-up market sizing using procurement contracts and fleet induction data, Revenue attribution across ISR strike and loitering munitions programs, Primary interviews with defense officials system integrators and UAV operators)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational usage and mission profiles
- Defense ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and localization framework
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Modernization of Saudi defense capabilities under Vision 2030
Rising asymmetric warfare and border surveillance needs
Localization and domestic manufacturing initiatives
Increased investment in ISR and precision strike systems
Growing adoption of autonomous and AI-enabled platforms
Strategic partnerships with global UAV OEMs - Challenges
High dependency on foreign technology and IP
Export control and technology transfer restrictions
Cybersecurity and data sovereignty risks
Operational integration with legacy defense systems
High acquisition and lifecycle maintenance costs
Skilled workforce and training limitations - Opportunities
Expansion of indigenous UAV manufacturing
Development of armed UAV and loitering munition programs
Integration of AI-driven swarm and autonomy features
Public-private partnerships under localization mandates
Regional export potential to GCC and MENA markets - Trends
Shift toward autonomous and semi-autonomous systems
Rising demand for loitering munitions
Integration of AI-based targeting and analytics
Increased SATCOM-enabled long endurance missions
Emphasis on modular and mission-flexible UAV platforms - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
MALE UAVs
HALE UAVs
Tactical UAVs
Loitering Munitions
Armed Rotary UAVs - By Application (in Value %)
Intelligence Surveillance and Reconnaissance
Strike and Precision Attack
Border and Maritime Security
Electronic Warfare and SIGINT
Target Acquisition and Battle Damage Assessment - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Fixed Wing Systems
Rotary Wing Systems
Hybrid VTOL Systems
Autonomous Swarm Platforms - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Saudi Armed Forces
Royal Saudi Air Defense
Royal Saudi Naval Forces
Ministry of Interior and Border Security - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Line of Sight Communication
Beyond Line of Sight SATCOM
Hybrid Communication Architecture - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Southern Border Region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (platform capability, combat range, payload capacity, autonomy level, localization depth, pricing structure, lifecycle support, combat readiness)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Advanced Electronics Company (AEC)
TAQNIA Defense
Intra Defense Technologies
General Atomics Aeronautical Systems
Northrop Grumman
Lockheed Martin
RTX (Raytheon Technologies)
Boeing Defense
Israel Aerospace Industries
Elbit Systems
Baykar Technologies
Leonardo S.p.A.
Thales Group
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase support and lifecycle management expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035