Market Overview
The KSA UAV Flight Training and Simulation market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady expansion driven by defense modernization initiatives. Training infrastructure investments increased during recent periods, supported by higher UAV fleet induction and operational readiness programs. Simulator deployment expanded across military training bases, improving pilot proficiency and mission preparedness. Adoption of virtual and synthetic training environments accelerated due to safety requirements and operational efficiency goals. Demand growth remained consistent as unmanned systems gained wider deployment across surveillance and tactical missions.
The market is primarily concentrated across central and western regions where defense infrastructure, airbases, and training academies are established. These areas benefit from stronger logistics connectivity, advanced simulation facilities, and higher concentration of skilled operators. Government-backed defense ecosystems and localization initiatives further strengthen regional dominance. The presence of command centers, testing facilities, and regulatory authorities supports faster technology integration. Policy alignment and long-term defense modernization programs continue to reinforce regional leadership in training adoption.
Market Segmentation
By Application
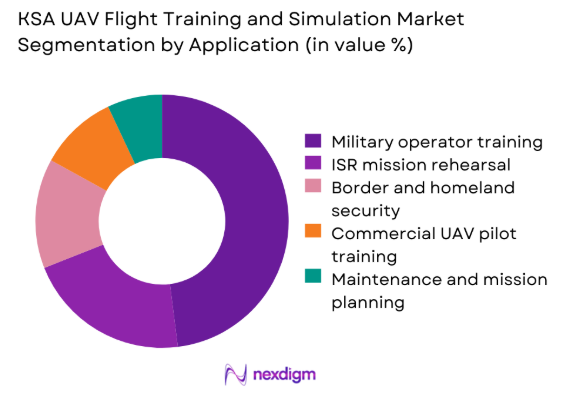
The application landscape is dominated by military and defense training requirements, driven by expanding UAV deployments across surveillance, reconnaissance, and tactical missions. Training programs increasingly prioritize simulator-based instruction to enhance mission preparedness while minimizing operational risks. Border security and internal surveillance applications further contribute to sustained demand for simulation platforms. Commercial UAV pilot training is emerging gradually, supported by regulatory clarity and growing civilian drone operations. Maintenance and mission planning simulations are gaining traction as operators seek lifecycle optimization and operational efficiency. Overall, application diversity strengthens long-term market stability and encourages continuous technology upgrades.
By Technology Architecture
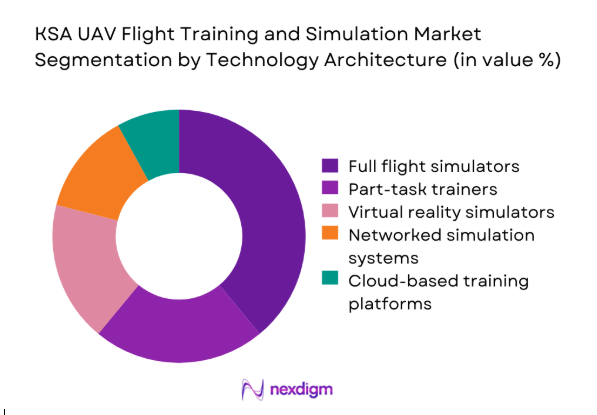
Technology segmentation reflects increasing preference for immersive and networked training solutions. Full flight simulators remain the dominant category due to their realism and certification alignment. Part-task trainers support modular learning and cost-effective skill development. Virtual reality systems are witnessing accelerated adoption as they enable scalable and flexible training environments. Networked simulation platforms facilitate coordinated mission rehearsal across multiple units. Cloud-enabled architectures are gradually emerging, driven by data integration needs and centralized training management requirements.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by a mix of international defense technology providers and regional system integrators. Market participants focus on long-term defense contracts, customization capabilities, and compliance with local training standards. Strategic partnerships with government entities and defense agencies strengthen market positioning. Technology differentiation is driven by simulator realism, integration capability, and lifecycle support offerings.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| CAE Inc. | 1947 | Canada | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| L3Harris Technologies | 2019 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales Group | 1893 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo S.p.A. | 1948 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA UAV Flight Training and Simulation Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising UAV procurement by Saudi defense forces
Rising defense procurement programs continue accelerating demand for structured UAV pilot training across military and security organizations nationwide. Fleet expansion during 2024 and 2025 increased simulator utilization requirements for safe mission readiness across multiple operational units. Defense acquisition strategies emphasize synthetic environments to reduce live flight risks and operational expenses while improving mission rehearsal effectiveness. Training throughput requirements expanded as UAV fleet diversity increased across surveillance and tactical missions supporting operational readiness goals. Government-backed modernization initiatives encouraged structured simulation adoption within air force training commands nationwide to standardize pilot competency benchmarks. Procurement alignment with long term capability planning strengthened simulator demand across operational bases supporting force readiness objectives nationally. Operational tempo increases required scalable training solutions capable of supporting concurrent trainee cohorts across multiple mission profiles simultaneously. Simulator-based training improved availability of aircraft assets for frontline mission deployment while reducing maintenance scheduling conflicts significantly overall. Training command budgets increasingly allocated resources toward immersive simulation infrastructure enhancements supporting long-term operational readiness objectives nationwide planning. Overall procurement momentum continues reinforcing sustained demand for advanced UAV training ecosystems across defense organizations nationally today consistently.
Increasing emphasis on indigenous operator training
National workforce development strategies increasingly emphasize localized UAV operator training to enhance operational independence and skills sustainability. Domestic training initiatives expanded during 2024 and 2025 to reduce reliance on foreign instruction frameworks. Localized curricula enable alignment with regional mission requirements and operational doctrines effectively. Indigenous training programs support faster deployment readiness through culturally and operationally aligned instruction models. Simulation-based learning accelerates skill acquisition while maintaining compliance with national aviation regulations. Training localization reduces logistical complexity associated with overseas certification pathways. Government incentives encouraged domestic training infrastructure investments supporting long-term workforce development goals. Increased availability of local instructors strengthened training continuity and knowledge retention across defense units. Simulation centers enabled standardized assessment methodologies across multiple training cohorts consistently. Emphasis on national capability building continues reinforcing demand for localized UAV training ecosystems.
Challenges
High capital cost of advanced simulators
High acquisition costs of advanced simulators present significant barriers to rapid deployment across training facilities. Budget allocation constraints limit the pace of simulator upgrades despite growing operational requirements. Advanced hardware integration demands substantial upfront investment in computing and visualization systems. Maintenance and calibration expenses further elevate total ownership costs for training operators. Smaller training units face difficulties justifying capital expenditure without long-term utilization certainty. Budget prioritization often favors platform acquisition over training infrastructure development. Financial planning complexities delay modernization cycles within training commands. High initial investment reduces flexibility for technology experimentation or phased implementation strategies. Cost pressures increase reliance on shared or centralized simulation facilities nationwide. These financial constraints collectively moderate the speed of market expansion.
Limited local manufacturing of training systems
Limited domestic manufacturing capability restricts rapid customization of UAV training solutions for local requirements. Dependence on imported simulation hardware increases lead times for system deployment. Localization challenges affect integration with indigenous command and control platforms. Technology transfer limitations constrain domestic value creation and skill development. Supply chain dependencies introduce vulnerability to external regulatory or geopolitical disruptions. Local assembly capabilities remain insufficient for large-scale deployment programs. Integration complexity increases when adapting foreign systems to national standards. Technical support reliance on external providers affects operational continuity and responsiveness. Localization gaps hinder scalability of training infrastructure expansion efforts. These factors collectively slow the pace of self-sustained market growth.
Opportunities
Localization of UAV training infrastructure
Localization initiatives create opportunities for establishing dedicated UAV training centers within national defense ecosystems. Domestic infrastructure development enhances operational sovereignty and reduces reliance on foreign training facilities. Investment in local simulation capabilities supports long-term workforce sustainability objectives. Training centers aligned with national standards improve consistency across operational units. Localization enables faster customization of curricula for mission-specific requirements. Domestic facilities reduce training downtime associated with overseas deployments. Collaboration with local technology providers fosters knowledge transfer and capability development. Localized ecosystems encourage innovation tailored to regional operational challenges. Government support accelerates establishment of compliant training infrastructure nationwide. These developments position localization as a critical long-term growth catalyst.
Growth of simulation-as-a-service models
Simulation-as-a-service models offer flexible access to advanced training capabilities without heavy capital investment. Subscription-based platforms enable scalable training aligned with fluctuating operational demand. Cloud-enabled simulation reduces infrastructure maintenance responsibilities for operators. Service-based delivery supports rapid technology upgrades and feature enhancements. Centralized management improves training standardization across distributed user groups. Usage-based models enhance cost predictability for defense training budgets. Remote access capabilities expand training reach across geographically dispersed units. Data-driven insights improve training effectiveness and performance monitoring. Service models enable faster adoption of emerging simulation technologies. These advantages drive increasing acceptance of service-oriented training solutions.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to maintain steady growth supported by continued defense modernization and UAV fleet expansion initiatives. Increased emphasis on localized training and digital simulation will shape future investment patterns. Integration of advanced analytics and immersive technologies will further enhance training effectiveness. Policy alignment and long-term defense planning will remain critical to sustained market development.
Major Players
- CAE Inc.
- L3Harris Technologies
- Thales Group
- Leonardo S.p.A.
- Elbit Systems
- Boeing Defense
- Lockheed Martin
- BAE Systems
- Raytheon Technologies
- Saab AB
- Rheinmetall Defence
- Indra Sistemas
- General Atomics
- Turkish Aerospace Industries
- Kratos Defense
Key Target Audience
- Ministry of Defense of Saudi Arabia
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- General Authority of Civil Aviation
- Border Guard and Internal Security Forces
- Defense procurement agencies
- UAV fleet operators
- Training and simulation service providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market scope was defined through analysis of UAV deployment trends, training requirements, and simulator classifications relevant to national defense usage. Key performance indicators were identified based on operational, technological, and regulatory factors.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Data was structured using segmentation frameworks aligned with application, technology, and end-user demand. Market dynamics were assessed using qualitative and quantitative indicators relevant to training infrastructure development.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Industry insights were validated through expert interactions, operational benchmarks, and defense training workflow analysis. Assumptions were refined based on consistency checks and practical feasibility.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated through triangulation of qualitative insights and quantitative indicators. Final outputs were structured to ensure consistency, clarity, and strategic relevance.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and UAV training scope mapping, Platform and simulator taxonomy development, Bottom-up market sizing using KSA defense and civil UAV programs, Revenue attribution across training hardware software and services)
- Definition and scope
- Market evolution
- Operational and training use cases
- Ecosystem structure
- Training delivery and simulator supply chain
- Regulatory and defense accreditation environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising UAV procurement by Saudi defense forces
Increasing emphasis on indigenous operator training
Growth of ISR and border surveillance missions
Saudi Vision 2030 defense localization initiatives
Expansion of civil and commercial UAV operations - Challenges
High capital cost of advanced simulators
Limited local manufacturing of training systems
Integration complexity with classified UAV platforms
Dependence on foreign OEMs and technology transfer
Regulatory restrictions on simulation data - Opportunities
Localization of UAV training infrastructure
Growth of simulation-as-a-service models
Integration of AI-based training analytics
Expansion of joint military training programs
Development of civil drone pilot certification programs - Trends
Adoption of immersive VR and AR training
Shift toward networked and cloud-based simulation
Increasing use of digital twins for UAV training
Integration of mission rehearsal with C2 systems
Focus on lifecycle training and sustainment solutions - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Fixed-wing UAVs
Rotary-wing UAVs
Hybrid VTOL UAVs
MALE and HALE UAVs
Tactical and mini UAVs - By Application (in Value %)
Military operator training
ISR mission rehearsal
Border and homeland security training
Commercial UAV pilot training
Maintenance and mission planning simulation - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Full flight simulators
Part-task trainers
Desktop simulation systems
Virtual reality based simulators
Live virtual constructive training systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Defense and armed forces
Internal security and border control
Oil and gas surveillance operators
Infrastructure and utility operators
Academic and training institutes - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone simulators
Networked training systems
Cloud-enabled simulation platforms
Integrated command-and-control training systems - By Region (in Value %)
Central Saudi Arabia
Western Saudi Arabia
Eastern Province
Northern Saudi Arabia
Southern Saudi Arabia
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Product portfolio depth, Simulator realism level, Localization capability, Military certification compliance, Pricing model, After-sales support, Technology integration capability, Regional presence)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
L3Harris Technologies
Thales Group
Boeing Defense
Lockheed Martin
Elbit Systems
Leonardo S.p.A.
BAE Systems
Raytheon Technologies
Saab AB
Kratos Defense & Security Solutions
General Atomics Aeronautical Systems
Turkish Aerospace Industries
Rheinmetall Defence
Indra Sistemas
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035