Market Overview
The KSA Vehicle Crash Test Systems Market is valued at USD ~ million. It sits within the Kingdom’s broader testing infrastructure that supports vehicle safety validation, conformity assessment, and product assurance. Saudi Arabia’s overall Testing, Inspection, and Certification market revenue is reported at USD ~ million, underscoring the scale of regulated testing demand that funds labs, instrumentation, and safety-validation programs. In parallel, Saudi Arabia’s electric-vehicle TIC revenue is reported at USD ~ million, reflecting the rapid build-out of specialized EV safety and compliance testing that increasingly overlaps with crashworthiness and occupant protection validation.
Within the Kingdom, Riyadh and Jeddah dominate crash-safety and compliance-linked procurement because they concentrate national regulators, importer/OEM decision-makers, and large certification/testing operations. Eastern Province industrial corridors also drive demand due to heavy-duty fleets and supplier ecosystems that require repeatable validation and certification workflows. Outside the Kingdom, Germany, the U.S., Japan, and China influence KSA demand patterns through platform standards, safety engineering practices, and validation protocols that KSA importers and OEM-aligned assemblers adopt for approvals and competitive positioning—especially as EV testing, inspection, and certification scales toward more advanced safety and security validation.
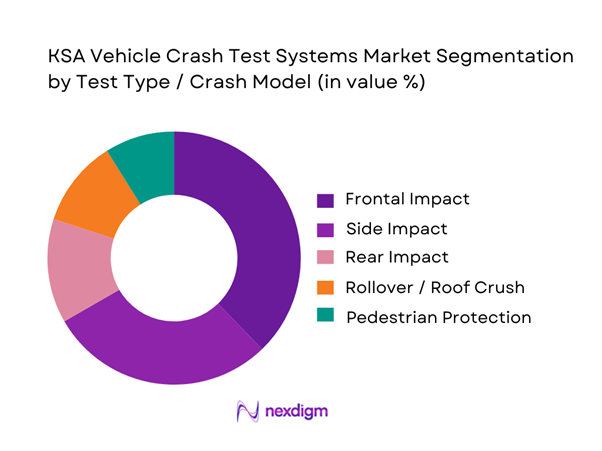
Market Segmentation
By Test Type / Crash Mode
Frontal impact testing dominates because it is the most widely used baseline for occupant protection validation across vehicle classes and is the “first-pass” requirement for many safety engineering cycles—especially for high-volume imported passenger vehicles and SUVs where OEMs prioritize restraint tuning, airbag timing, and structural load paths. In KSA, the business case is reinforced by the prevalence of multi-variant trims where small configuration changes require repeated confirmation, and the operational practicality of frontal rigs: standardized barrier configurations, mature instrumentation packages, and well-established dummy/sensor setups make frontal testing the fastest path from design intent to compliance evidence. Frontal testing also drives recurring demand for high-wear consumables such as barriers, load cells, and accelerometers, calibration services, and data acquisition upgrades—creating a dependable revenue engine for both labs and system integrators.
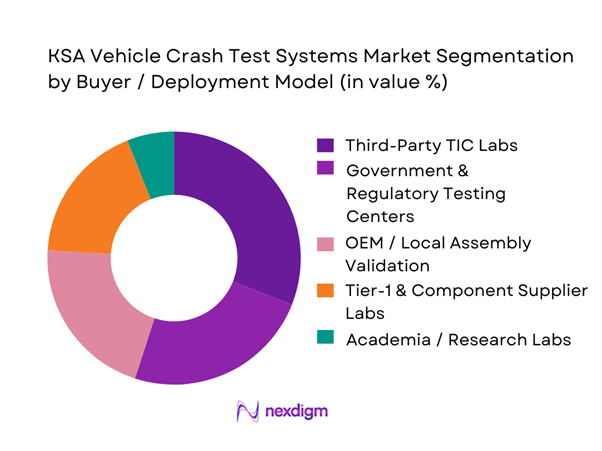
By Buyer / Deployment Model
Third-party TIC labs dominate because they aggregate demand from multiple importers, distributors, and component suppliers who cannot justify dedicated full-scale crash infrastructure on their own. These labs also monetize across adjacent services—homologation support, test planning, instrumentation rental, calibration, and engineering interpretation—making them the most economically efficient “hub” model in KSA. The model fits the Kingdom’s market structure where a large portion of vehicles are imported and require structured compliance evidence and repeatable validation workflows. TIC labs can also ramp faster: they standardize procedures, maintain multi-client scheduling, and negotiate preferred pricing for critical equipment such as dummies, sensors, and data acquisition systems. As EV-related testing scales in KSA, TIC labs extend into battery safety, EMC, and component validation programs—creating bundled commercial offers that naturally pull crash-related system upgrades and new facility investments.
Competitive Landscape
The KSA Vehicle Crash Test Systems Market is served by a mix of global TIC majors, automotive engineering and testing specialists, and crash-test equipment and instrumentation manufacturers. The ecosystem tends to consolidate around firms that can bundle facility engineering, test execution, compliance documentation, and data analytics, which is especially relevant as Saudi Arabia expands regulated testing intensity and EV-linked compliance activity.
| Company | Est. Year | Headquarters | KSA Commercial Footprint | Core Crash Testing Offer | Standards / Regulatory Coverage Orientation | Facility Engineering / Turnkey | Instrumentation & DAQ Depth | Digital Simulation Integration | Typical Buyer Profile |
| Applus+ IDIADA | 1996 | Spain | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| DEKRA | 1925 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| TÜV SÜD | 1866 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Intertek | 1885 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SGS | 1878 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Vehicle Crash Test Systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Regulatory Enforcement Intensity
Saudi Arabia’s crash-test system demand is structurally pulled by enforcement-led safety governance and a widening compliance perimeter. Road transport statistics show serious traffic accidents exceeded ~ thousand and the national road mortality rate reached ~ deaths per ~ population, which keeps road-safety outcomes on the agenda for regulators, insurers, and fleet owners and sustains demand for repeatable validation evidence and defensible test documentation. At the macro level, Saudi Arabia’s economy is large enough to fund regulated testing capacity, with GDP reported at USD ~ million and population estimated at ~, creating a sizeable vehicle parc and usage base that regulators must govern through standards, conformity checks, and enforcement workflows. These pressures translate into equipment refresh cycles and more frequent protocol alignment exercises, because enforcement is only credible when labs can demonstrate traceability, repeatability, and audit-ready data pipelines.
Import Inspection Scale
Crash-test systems and lab capability investments in KSA are strongly tied to the reality that the Kingdom is a major vehicle-import market, making conformity assessment and safety validation a recurring operational need. Officially cited figures indicate ~ cars were imported and ~ cars were imported in the immediately preceding period, evidence of high import throughput that drives inspection load, documentation checks, and the downstream need for credible safety assurance signals. At the same time, the macro backdrop supports sustained demand, with GDP per capita listed at USD ~ and total GDP at USD ~ trillion, enabling continued vehicle purchasing and fleet renewal that keeps import pipelines active. In practical terms, higher import scale increases the number of platforms circulating in-market, raising the value of third-party testing and validation capacity so distributors and compliance stakeholders can de-risk recalls, disputes, and safety investigations with defensible data.
Challenges
High CAPEX and Utilization Risk
Full-scale crash halls, propulsion tracks, and high-speed measurement stacks are capital intensive, and the business risk is under-utilization if test volumes are lumpy or concentrated among a few buyers. This risk is material even in a large economy, with GDP reported at USD ~ million, but crash infrastructure still requires sustained scheduling density to justify maintenance, calibration cycles, and specialist staffing. Road transport statistics indicate serious traffic accidents exceeded ~ thousand, which creates urgency for safety validation, yet that urgency does not automatically translate into stable test bookings at the facility level. In addition, procurement and commissioning cycles can be long, so utilization ramp-up may lag capital deployment, increasing idle capacity risk. For operators, the challenge becomes building multi-client pipelines and bundling adjacent services so utilization remains healthy even when full-vehicle crash runs fluctuate.
Specialist Talent Scarcity
Crash testing requires a narrow talent mix—instrumentation engineers, test conductors, dummy technicians, metrology and calibration specialists, and safety officers—who must operate to strict procedures with low tolerance for error. The scale of the national operating environment is large, with population estimated at ~, but the specialization level required for crash labs makes talent a constraint even in big markets. Road transport statistics showing ~ deaths per ~ population also raise the reputational and policy stakes, which pushes labs to maintain high procedural discipline and audit-ready operations, increasing reliance on experienced personnel rather than general technicians. Meanwhile, a macro environment with stable inflation, with average annual CPI inflation reported at ~, helps long-term hiring plans but does not solve the pipeline problem. Specialist capability takes time to develop, certify, and retain, slowing lab expansion and delaying commissioning and acceptance testing for new systems.
Opportunities
GCC Regional Testing Hub Potential
KSA has a credible pathway to become a GCC testing hub because it combines large domestic vehicle demand signals with the economic capacity to fund high-grade testing, inspection, and certification infrastructure. Saudi Arabia’s TIC market revenue is reported at USD ~ million, showing a substantial national testing economy that can support specialized automotive safety validation capabilities as an extension. The Kingdom also records high vehicle activity and safety urgency, with serious traffic accidents cited at ~ thousand and a mortality rate of ~ per ~ population, keeping safety policy and testing capability in focus. On the macro side, GDP is reported at USD ~ trillion, indicating the fiscal and commercial scale needed to operate hub facilities that serve multiple GCC buyers and justify continuous upgrades. The near-term opportunity is to expand multi-client capacity, standardized reporting, and cross-border acceptance of results, turning KSA-based labs into the region’s default option for time-sensitive validation and compliance evidence.
Localization of Calibration and Repair
Localization of calibration and repair can materially improve uptime, reduce scheduling volatility, and increase trust in test outputs, because traceability and instrument health become easier to control onshore. The operational case is supported by the complexity reflected in national transport outcomes, where serious traffic accidents exceeded ~ thousand, elevating the consequence of poor-quality evidence and increasing the value of robust, auditable measurement systems. Macroeconomic conditions support sustained localization, with average annual CPI inflation reported at ~ and GDP at USD ~ trillion, indicating the scale to develop local service ecosystems rather than relying exclusively on overseas support. Additionally, the Kingdom’s growing EV-related TIC activity, with EV TIC revenue reported at USD ~ million, signals a rising need for specialized test instrumentation and compliance support that benefits from local maintenance and calibration capability. The opportunity is to build accredited calibration services, local parts refurbishment, and faster failure-response programs without waiting for international turnaround cycles.
Future Outlook
Over the next five-year window, the KSA Vehicle Crash Test Systems Market is expected to expand steadily as Saudi Arabia deepens regulated testing activity, scales EV-related compliance programs, and modernizes validation capabilities across safety and security domains. The strongest momentum is likely in lab modernization, EV-adjacent safety validation, and multi-client third-party testing capacity that can absorb importer and supplier demand efficiently. This direction is consistent with the Kingdom’s broader testing, inspection, and certification growth trajectory and the fast-growing EV TIC segment that increasingly overlaps with safety validation workflows.
Major Players
- Applus+ IDIADA
- DEKRA
- TÜV SÜD
- TÜV Rheinland
- SGS
- Bureau Veritas
- Intertek
- Element Materials Technology
- Eurofins Scientific
- MISTRAS Group
- Humanetics
- Kistler
- HBK / HBM
- AB Dynamics / MESSRING
Key Target Audience
- Vehicle importers and distributor groups
- OEMs and local vehicle assembly programs
- Tier-1 safety systems suppliers
- Third-party automotive testing labs and TIC operators
- Insurance and claims analytics organizations
- Fleet operators and fleet safety procurement teams
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We build a KSA crash-safety ecosystem map covering regulators, testing centers, TIC firms, importers, OEM assemblers, and Tier-1 suppliers. Desk research is conducted across standards and regulatory material, company capability disclosures, and credible market datasets to define variables such as test mix, lab utilization drivers, and equipment procurement cycles.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historic and current signals that proxy crash-test system demand, including regulated testing intensity, EV TIC growth, and TIC service revenue pools. We then construct a bottom-up view of addressable demand using facility requirements, replacement cycles, and service-to-capex linkages.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses are validated through structured interviews with lab operators, OEM safety teams, instrumentation suppliers, and certification stakeholders. These inputs refine assumptions on test mix, utilization, pricing architecture, and near-term procurement triggers.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We synthesize findings into a consolidated model and narrative covering segmentation shares, competitive positioning, capability benchmarks, and future roadmap. Outputs are cross-validated against published datasets for testing, inspection, and certification and EV TIC activity in Saudi Arabia to ensure consistency and defensibility.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Scope Boundary, Abbreviations, Currency & Inflation Handling, Data Triangulation Framework, Bottom-Up Market Build (Installed Base × Utilization × ASP), Top-Down Validation (Regulatory/Testing Demand Signals), Primary Interview Plan (OEMs/Tier-1/Test Labs/Regulators/Insurers), Sampling Logic, Data Quality & Confidence Scoring, Limitations and Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Market Development Timeline
- Business Cycle and Demand Cyclicality
- Ecosystem Map
- Growth Drivers
Regulatory Enforcement Intensity
Import Inspection Scale
New Platform Launch Cadence
EV Safety Validation Needs
Infrastructure Investment - Challenges
High CAPEX and Utilization Risk
Specialist Talent Scarcity
Calibration and Traceability Burden
Protocol Upgrade Requirements
Spare Parts Lead-Time Risk - Opportunities
GCC Regional Testing Hub Potential
Localization of Calibration and Repair
EV Battery Safety Testing Expansion
Roadside Safety Hardware Validation
Simulation-to-Test Correlation Services - Trends
Increasing Protocol Complexity
Data-Rich Instrumentation Adoption
Expanded Dummy Diversity
Advanced High-Speed Imaging
Digital Twin Correlation - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019–2024
- By Services Value, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Full-Scale Vehicle Crash Test Systems
Sled Test Systems
Component & Sub-System Impact Test Rigs
Roadside Safety Hardware Test Systems
Pedestrian Protection Test Systems - By Application (in Value %)
Frontal Full-Width
Frontal Offset
Side MDB
Side Pole Impact
Rear Impact
Rollover / Roof Strength
Far-Side / Oblique Scenarios - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Anthropomorphic Test Devices and Dummy Accessories
Barriers, Impactors and Deformable Elements
Propulsion, Guidance and Speed Control
Data Acquisition and Signal Conditioning
High-Speed Video and Photogrammetry - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Government and Regulatory Bodies
Vehicle OEMs
Tier-1 and Component Suppliers
Independent Test Laboratories
Universities and R&D Centers - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Southern Region
Northern Region
- Market Share Snapshot
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Installed Base in KSA/GCC, Local Service and Calibration Capability, Protocol Coverage Breadth, System Performance Envelope, DAQ Capability, ATD Portfolio Depth, High-Speed Video Capability, Delivery and Uptime Model)
- Competitive Intensity Map
- Partnership Ecosystem
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Models
- Company Profiles
Humanetics
MESSRING
AB Dynamics
Cellbond
Kistler
Diversified Technical Systems
HBK
Photron
DEKRA
TÜV Rheinland
Applus+ IDIADA
UTAC
SGS
Bureau Veritas
KSA Crash Lab
- Demand and Utilization Model
- Budget Ownership and Procurement Path
- Decision Criteria and Pain Points
- Tender Specifications and Compliance Checklists
- Outsourcing versus In-House Strategy
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Price, 2025–2030
- By Services Value, 2025–2030


