Market Overview
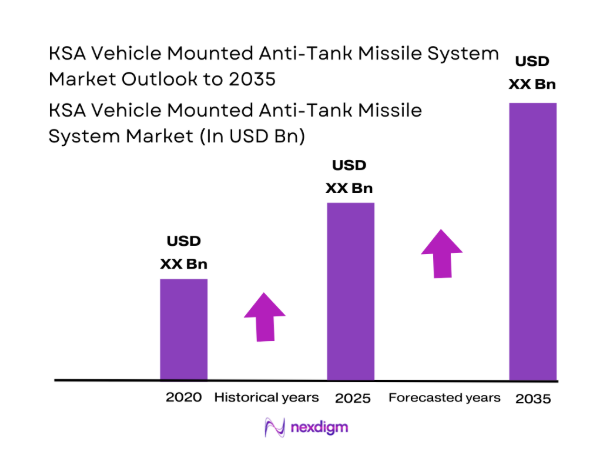
The KSA Vehicle Mounted Anti-Tank Missile System market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady procurement activity across armored platforms and border security units. During the last two observed periods, deployment volumes increased across ~ units in 2024 and ~ units in 2025, driven by operational readiness priorities. Active systems exceeded ~ platforms as legacy vehicles received launcher integrations. Technology refresh cycles shortened, while average system utilization rates crossed ~ percent due to higher training intensity and deployment frequency.
Demand is concentrated in central and southern operational zones where armored brigades and rapid response units maintain higher readiness postures. Key cities host maintenance depots, testing ranges, and command centers supporting system lifecycle management. Industrial clusters benefit from localized assembly initiatives and technology partnerships. Policy alignment with national defense programs strengthens ecosystem maturity. Infrastructure density and logistics accessibility further reinforce these regions as primary deployment and sustainment hubs.
Market Segmentation
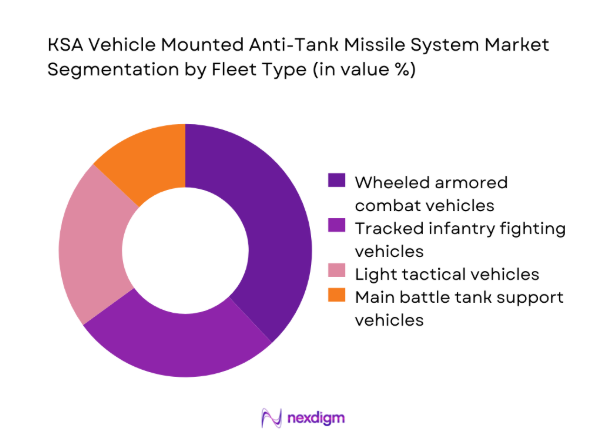
By Fleet Type
Wheeled armored combat vehicles dominate adoption due to their operational flexibility, rapid mobility, and suitability for diverse terrain conditions across national borders. These platforms allow efficient missile integration without significant chassis modifications, supporting faster deployment cycles. Tracked infantry fighting vehicles follow closely, particularly within mechanized brigades emphasizing combined arms operations. Light tactical vehicles remain relevant for patrol and rapid response missions. Main battle tank support vehicles contribute selectively, mainly in defensive overwatch roles rather than frontline missile engagements.
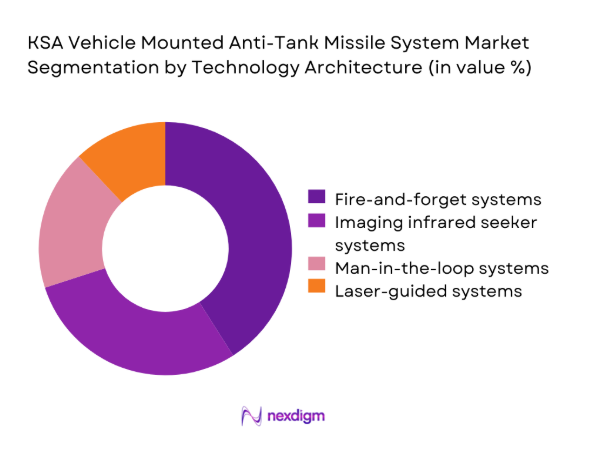
By Technology Architecture
Fire-and-forget systems represent the leading technology architecture due to reduced operator exposure and higher engagement efficiency. Imaging infrared seekers enable improved target discrimination in complex environments, supporting operational effectiveness. Man-in-the-loop systems retain relevance for precision engagements and training scenarios. Laser-guided architectures are gradually declining but remain installed on legacy platforms. Technology selection reflects a balance between cost, survivability, and integration complexity within existing vehicle fleet.
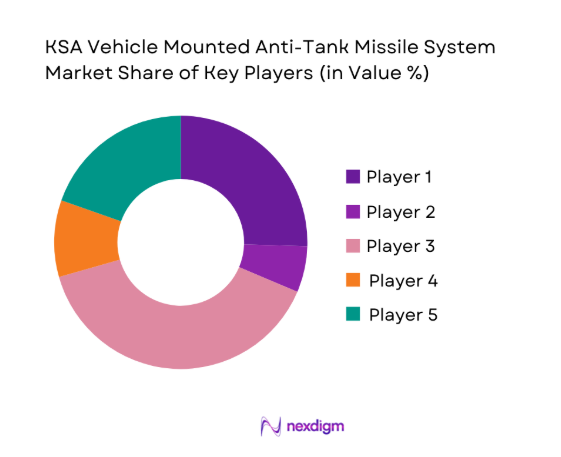
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is moderately consolidated, characterized by a mix of global defense manufacturers and regional integrators supporting localization objectives. Long-term contracts, platform compatibility, and technology transfer capabilities strongly influence positioning.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Lockheed Martin | 1912 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Raytheon Technologies | 1922 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MBDA | 2001 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saab AB | 1937 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Vehicle Mounted Anti-Tank Missile System Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising border security requirements
Heightened border security requirements increased armored patrol frequency across multiple regions, driving consistent demand for vehicle mounted anti-tank missile systems. Cross-border threats observed during 2024 reinforced operational doctrines emphasizing mobile firepower and rapid response capabilities. Surveillance integration with missile platforms improved situational awareness and engagement readiness across deployed units. Security planners prioritized deterrence through visible armored presence equipped with advanced missile launchers. Training exercises expanded deployment scenarios, increasing system utilization rates and maintenance cycles. Border terrain diversity necessitated adaptable vehicle platforms supporting missile systems across desert and mountainous environments. Command structures emphasized decentralized fire support, benefiting vehicle mounted missile deployments. Interoperability with allied forces influenced system configuration preferences and procurement specifications. Tactical doctrine updates integrated missile equipped vehicles into layered defense strategies. Operational feedback loops accelerated capability refinement and incremental system upgrades.
Modernization of armored vehicle fleets
Armored vehicle fleet modernization programs accelerated replacement and upgrade cycles, creating integration opportunities for contemporary anti-tank missile systems. Legacy vehicles underwent midlife upgrades during 2024 to extend operational relevance and combat effectiveness. Modular turret designs simplified missile launcher installation across diverse vehicle classes. Digitized fire control systems improved targeting accuracy and reduced engagement times significantly. Fleet commonality initiatives supported standardized missile interfaces and maintenance practices. Modernization budgets favored platforms capable of multi-role battlefield functions. Enhanced crew protection requirements influenced system selection and mounting configurations. Training simulators aligned with modernized fleets improved operator proficiency. Lifecycle planning integrated missile systems as core combat enablers. Modernization efforts reinforced sustained procurement momentum across evaluation periods.
Challenges
High system acquisition and integration costs
High system acquisition and integration costs constrained procurement pacing despite operational demand across armored units. Budget allocation processes required extended justification cycles for missile platform investments. Integration complexity increased engineering timelines for legacy vehicle compatibility assessments. Custom mounting solutions elevated non-recurring engineering requirements. Sustainment planning incorporated higher spare part inventories and specialized tooling. Training costs expanded due to advanced guidance and seeker technologies. Testing and validation phases lengthened acceptance schedules. Cost sensitivity influenced prioritization between new acquisitions and retrofitting programs. Procurement authorities balanced quantity against technological sophistication. Financial scrutiny remained a persistent barrier throughout observed periods.
Dependence on foreign technology suppliers
Dependence on foreign technology suppliers introduced supply chain risks and extended lead times during procurement cycles. Export control compliance added administrative layers affecting delivery predictability. Limited domestic alternatives constrained bargaining leverage during negotiations. Technology transfer restrictions impacted local assembly ambitions. Spare parts availability depended on international logistics stability. Software updates required external approvals and coordination. Interoperability adjustments faced proprietary interface limitations. Training support relied on foreign technical teams. Political considerations occasionally influenced supplier engagement continuity. Strategic planners increasingly highlighted supplier diversification needs.
Opportunities
Localization under Vision 2030 defense initiatives
Localization initiatives under Vision 2030 created opportunities for domestic assembly and subsystem manufacturing partnerships. Government incentives encouraged foreign manufacturers to establish local production lines. Workforce development programs supported skills transfer in missile integration and testing. Local maintenance hubs reduced system downtime and logistics dependency. Indigenous component sourcing improved long-term cost control. Co-development frameworks enhanced technology absorption capabilities. Localization targets influenced tender evaluation criteria. Incremental localization milestones aligned with phased procurement schedules. Industrial participation strengthened ecosystem resilience. Policy consistency reinforced investor confidence in defense manufacturing.
Upgrades and retrofitting of legacy platforms
Upgrading and retrofitting legacy platforms offered cost-efficient capability enhancement across existing armored fleets. Structural assessments confirmed compatibility for missile launcher installations on older vehicles. Retrofit programs reduced acquisition timelines compared to new platform purchases. Incremental upgrades extended service life while improving lethality. Digital interface kits simplified integration with modern fire control systems. Retrofit demand increased during 2025 due to budget optimization priorities. Training continuity benefited from familiar vehicle platforms. Maintenance crews adapted quickly to upgraded configurations. Operational units favored retrofits for rapid deployment. Retrofit pipelines supported sustained market activity.
Future Outlook
The outlook for the KSA Vehicle Mounted Anti-Tank Missile System market remains positive through 2035, supported by sustained defense modernization priorities. Localization and platform upgrades will shape procurement strategies. Technology evolution will emphasize survivability and network integration. Policy alignment and industrial participation will continue influencing long-term demand patterns.
Major Players
- Lockheed Martin
- Raytheon Technologies
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- MBDA
- Saab AB
- Thales Group
- BAE Systems
- Denel Dynamics
- Roketsan
- Aselsan
- Norinco
- Rosoboronexport
- L3Harris Technologies
- Elbit Systems
- Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
Key Target Audience
- Saudi Arabian Ministry of Defense
- General Authority for Military Industries
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- Royal Saudi Land Forces procurement units
- Saudi National Guard acquisition departments
- Defense-focused investment and venture capital firms
- National security policy and regulatory bodies
- Local armored vehicle integrators and OEM partners
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
This step focused on identifying key variables influencing vehicle mounted anti-tank missile demand, including platform types, deployment doctrines, and localization mandates. Operational requirements, force structure priorities, and procurement frameworks were mapped across relevant defense units to define scope boundaries and analytical assumptions.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
This step involved constructing the market structure through segmentation by fleet type and technology architecture. Deployment intensity, upgrade cycles, and integration pathways were assessed to establish demand contours and interaction between vehicle platforms and missile system configurations.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
This step validated hypotheses through structured consultations with defense engineers, procurement specialists, and system integrators. Expert feedback refined assumptions related to technology adoption, platform compatibility, localization feasibility, and operational deployment constraints.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
This step synthesized qualitative and quantitative insights into a coherent analytical framework. Operational findings were aligned with policy direction and industrial dynamics to ensure consistency, robustness, and relevance of the final market outlook.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and vehicle-mounted ATGM scope alignment, KSA armored fleet taxonomy and platform mapping, bottom-up program-based market sizing, contract value and lifecycle revenue attribution, primary interviews with MoD procurement and OEM program managers, triangulation across SIPRI data defense budgets and tender disclosures, assumptions on localization and technology transfer)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution within Saudi land forces modernization
- Operational usage and deployment doctrine
- Defense industrial ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and localization framework
- Regulatory and procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising border security requirements
Modernization of armored vehicle fleets
Increasing asymmetric warfare threats
Government focus on indigenous defense capabilities
Integration of advanced guidance and seeker technologies
Strategic defense partnerships and offset programs - Challenges
High system acquisition and integration costs
Dependence on foreign technology suppliers
Complexity of platform integration and testing
Long procurement and approval cycles
Maintenance and lifecycle support constraints
Technology transfer limitations - Opportunities
Localization under Vision 2030 defense initiatives
Upgrades and retrofitting of legacy platforms
Demand for network-enabled weapon systems
Joint development programs with global OEMs
Expansion of regional defense export capabilities
Advanced training and simulation solutions - Trends
Shift toward fire-and-forget missile systems
Increased adoption of imaging infrared seekers
Integration with digital battlefield management systems
Modular launcher and turret designs
Emphasis on survivability and mobility
Lifecycle service and support contracts - Government Regulations
SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Main battle tank support vehicles
Wheeled armored combat vehicles
Tracked infantry fighting vehicles
Light tactical and patrol vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Border security and territorial defense
Conventional battlefield operations
Urban and asymmetric warfare
Rapid response and expeditionary missions - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Fire-and-forget missile systems
Man-in-the-loop guided missile systems
Imaging infrared seeker-based systems
Laser-guided missile systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Saudi Arabian Army
Saudi National Guard
Royal Saudi Land Forces special units
Joint and allied operational commands - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone weapon platforms
C4ISR-integrated platforms
Network-enabled battlefield systems - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Eastern Region
Western Region
Southern Region
Northern Region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (system range, guidance technology, vehicle compatibility, integration complexity, localization capability, lifecycle cost, delivery timelines, after-sales support)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Lockheed Martin
Raytheon Technologies
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
MBDA
Saab AB
Thales Group
BAE Systems
Denel Dynamics
Roketsan
Aselsan
Norinco
Rosoboronexport
L3Harris Technologies
Elbit Systems
Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


