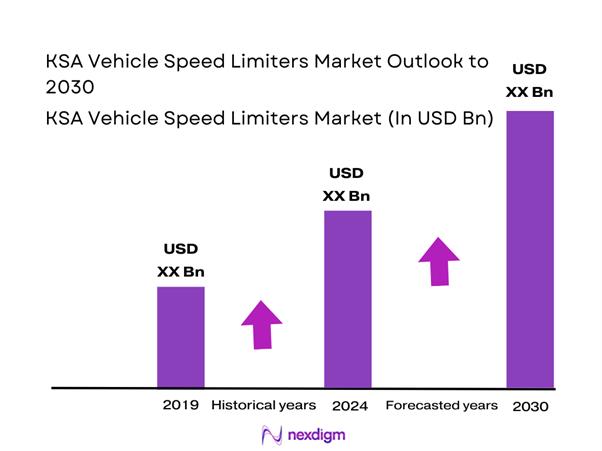
Market Overview
The road speed limiter ecosystem is expanding globally due to safety mandates and policy-driven enforcement: the road speed limiter market is cited at USD ~ billion in the latest-year baseline, with growth tied to regulatory tightening and fleet safety programs. In KSA, adoption is structurally pulled by GCC/GSO conformity references for speed limiting devices and inspection/certification expectations that shape how fleets procure limiter solutions (standalone devices, ECU functions, or telematics-enforced policies).
KSA demand is concentrated in cities and corridors where fleet density + enforcement intensity + high-utilization duty cycles intersect. Riyadh dominates through national logistics control towers and government-linked fleets; the Western region (Jeddah–Makkah–Madinah axis) is structurally important due to high bus/coach movement peaks and long intercity runs; and the Eastern region (Dammam/Khobar industrial belt) leads in industrial freight and petrochemical-linked transport patterns, where HSE policies typically formalize speed governance in SOPs. These clusters also accelerate telematics adoption, making limiter solutions more often purchased as bundled compliance stacks rather than a single hardware SKU.
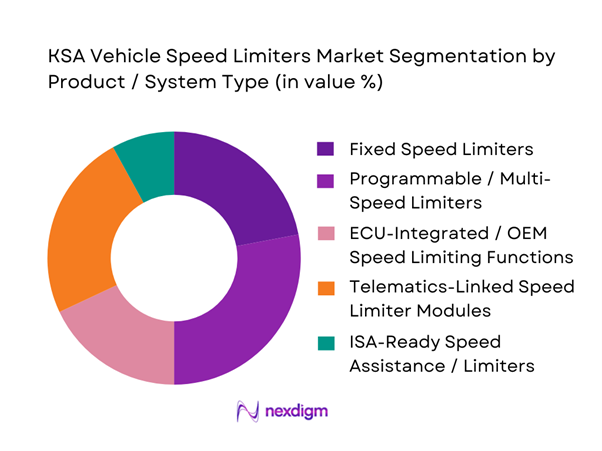
Market Segmentation
By Product / System Type
The KSA Vehicle Speed Limiters market can be segmented by product/system type into fixed speed limiters, programmable/multi-speed limiters, ECU-integrated/OEM speed limiting functions, telematics-linked limiter modules, and ISA-ready architectures. ISA-style direction is visible globally through mandatory intelligent assistance requirements in certain jurisdictions, and it matters in KSA because fleets with longer vehicle replacement cycles increasingly prioritize “future-proof” electronics stacks even when immediate enforcement is achieved via retrofit + telematics policy.
KSA fleets value limiter systems that can demonstrate auditability (policy logs), support multi-vehicle brand compatibility, and reduce tamper and bypass risk through event trails. Fixed limiters remain relevant for simple compliance cases, but large operators typically standardize around solutions that connect to a fleet platform (or at least produce inspection-ready evidence). This is reinforced by the growth of commercial telematics spend in KSA, which pulls limiter procurement into broader IVMS and compliance bundles rather than a standalone workshop purchase.
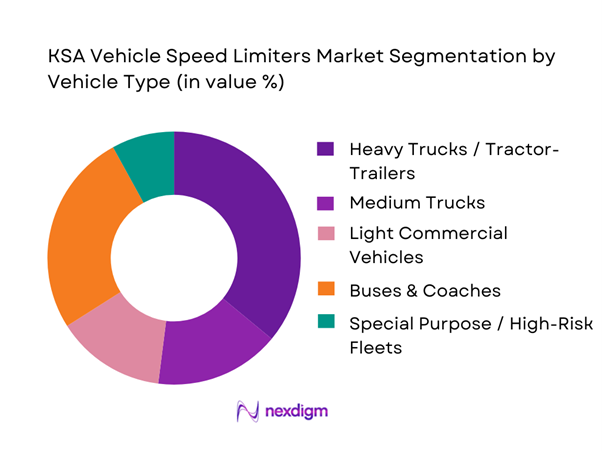
By Vehicle Type
The market is segmented into heavy trucks/tractor-trailers, medium trucks, light commercial vehicles, buses & coaches, and special purpose/high-risk fleets (e.g., hazmat/fuel/oversize). Speed limiting has its strongest compliance gravity in commercial and passenger transport operations where duty cycles are long and incident costs are high. The GCC regulatory posture also explicitly calls out speed limiting for certain heavy-duty use cases.
Why heavy trucks + buses dominate (market logic): Long-haul exposure, higher kinetic risk, and stricter operational governance make limiter adoption “non-discretionary” in many fleets. In the Western region, coach/bus operators face intense peaks; in freight corridors, heavy vehicles’ speed governance is typically embedded into HSE KPI frameworks. Light commercial vehicles are rising through last-mile scale-up, but limiter procurement is more mixed because many LCV operators rely on telematics alerts and policy rather than a hard limiter unless required by contracts or insurance conditions. The Saudi commercial vehicle market expansion outlook also increases the addressable base for limiter-equipped fleets.
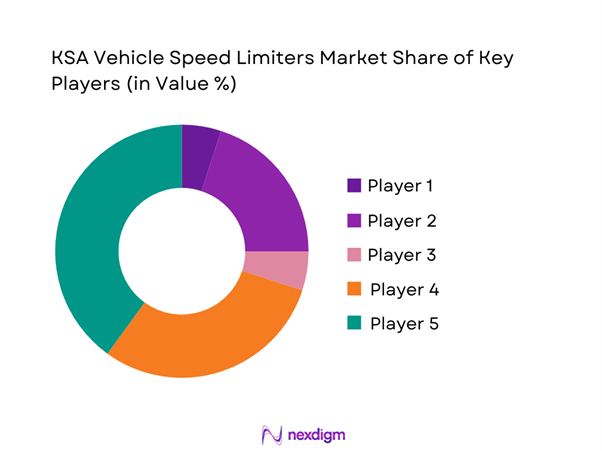
Competitive Landscape
The KSA Vehicle Speed Limiters competitive environment is best understood as a three-layer stack: Tier-1 automotive electronics/OEM ecosystem (ECU-native limiting, safety electronics), road speed limiter hardware specialists (retrofit limiters, calibration-led offerings), and fleet telematics & compliance platforms (policy orchestration + audit trails). Global competitive sets for road speed limiters frequently include players such as Autoliv, Continental, Denso, Bosch, Valeo, Vodafone Automotive, and ZF, highlighting that “speed limiting” is often sold as part of broader safety/vehicle electronics architectures, not only as a standalone device.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | KSA Route-to-Market | Core Offering Type | Integration Depth | Tamper Controls | Compliance/Audit Outputs | Typical Buyer |
| Continental (VDO) | 1871 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Robert Bosch | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ZF Friedrichshafen | 1915 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Vodafone Automotive | 2006* | UK/Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Denso | 1949 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Vehicle Speed Limiters Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Heavy Vehicle Safety and Compliance Mandates
Saudi Arabia’s speed-limiter demand is structurally anchored to the scale of “high-exposure” road activity and the country’s measurable safety burden on highways and arterial routes used by trucks and buses. National road-safety outcomes remain material: serious traffic accidents were ~ and road fatalities were ~, while road-traffic injuries were ~ in the latest official road-transport release—figures that keep speed compliance a board-level priority for fleet owners and regulators managing systemic risk. Freight intensity reinforces the compliance pull: official cross-border road freight through land ports shows ~ tons of imports and ~ tons of exports, implying sustained heavy-truck movements where limiter calibration, sealing, and verification become operational necessities rather than “nice-to-have” add-ons. The macro base is also large enough to sustain enforcement investment: Saudi Arabia’s economy is reported at USD ~ trillion (GDP, current US$) with GDP per capita of USD ~, which underpins ongoing road-transport demand, municipal/industrial logistics activity, and the administrative capacity to enforce technical requirements around speed control for commercial vehicles.
Fleet Risk Governance and Insurance Controls
Speed limiter adoption in KSA is increasingly shaped by how fleets quantify, price, and govern road risk—because the underlying loss environment is visible in national safety counts and the economy’s absolute scale. With ~ fatalities and ~ injuries recorded in the latest official road-transport statistics, fleet operators face a measurable exposure base that directly affects underwriting scrutiny, internal HSE governance, and insurer-imposed controls (e.g., telematics-backed policies, driver scoring, and evidence-based compliance). At the macro level, the Kingdom’s capacity to professionalize risk management is reinforced by the size of the economy (USD ~ trillion GDP) and public-sector fiscal architecture that continues to fund oversight and enforcement systems. The Ministry of Finance’s FY budget statement highlights the government’s fiscal-management posture, including maintaining reserves at the Saudi Central Bank around SAR ~ billion, a signal of resilience capacity that supports continuity of safety programs, digital enforcement, and regulatory operations even under external shocks. In parallel, logistics intensity (road-freight flows of ~ tons imports and ~ tons exports through land ports) means insurers and fleet managers increasingly prefer controls that can be proven—tamper-evident limiters, calibration logs, and audit-ready data trails—over “policy-only” approaches. This pushes the market toward integrated limiter + monitoring packages that translate risk governance into enforceable, vehicle-level controls.
Challenges
Multi-Brand ECU Integration Complexity
Speed limiter deployment in KSA is technically challenged by fleet heterogeneity—mixed OEMs, diverse ECU architectures, and variation in diagnostic access—especially in logistics-heavy operators running long-haul tractors, rigid trucks, buses, and specialized units. The integration burden exists at scale because the underlying vehicle-activity base is large: road transport indicators show cross-border road freight totaling ~ tons (imports ~, exports ~) through land ports, implying significant numbers of commercial vehicles cycling through duty-intensive operations where limiter fitment, calibration, and diagnostic validation must work across different powertrain/ECU stacks. The safety context heightens the cost of integration mistakes: ~ serious accidents and ~ fatalities underscore that limiter effectiveness is judged not only by installation completion but by reliable operation under real driving conditions. Macro capacity helps but doesn’t eliminate complexity—Saudi GDP at USD ~ trillion supports advanced workshops and tooling, yet integration still requires per-OEM harnessing strategies, parameter mapping, and verification routines that can differ materially between vehicle families. Digital readiness (e.g., ~ mobile subscriptions) supports connected diagnostics and remote support, but ECU-level constraints—secure gateways, OEM-specific calibration logic, and compatibility with telematics/IVMS devices—remain a core friction point. As a result, fleets and installers face longer engineering lead times, higher documentation needs, and more stringent post-installation verification processes to prove that limiter behavior aligns with compliance rules across every truck/bus type in the fleet.
Retrofit Downtime and Operational Disruption
Retrofit programs create a hard trade-off between compliance and utilization—every hour in a bay is an hour not hauling freight, moving passengers, or meeting SLA windows. In Saudi Arabia, this utilization pressure is amplified by the measurable scale of transport flows and the high-stakes safety environment. Land-port road freight totals ~ tons of imports and ~ tons of exports, which implies continuous scheduling commitments across border corridors and domestic distribution networks; pulling vehicles off-road for limiter installation, ECU interfacing, and post-fit road tests can ripple into missed delivery slots and backlogs. The national accident burden remains non-trivial—~ serious accidents, ~ fatalities, and ~ injuries—so fleets cannot simply defer compliance without reputational and risk consequences. From a macro capacity angle, the Kingdom’s economic scale (USD ~ trillion GDP) supports strong logistics demand; at the same time, it increases the opportunity cost of downtime because transport work is abundant. Fiscal signals in the budget statement (including maintaining reserves around SAR ~ billion) indicate continued government capacity to invest in enforcement and infrastructure—meaning compliance windows may tighten rather than loosen. Digital readiness helps fleets schedule and coordinate workshops (reported ~ internet penetration and ~ mobile device usage), yet the physical constraint remains: workshop throughput, technician availability, and test-lane capacity can bottleneck when large fleets retrofit simultaneously—especially around peak logistics periods and major events. The net effect is a market preference for faster-fit solutions, standardized kits, mobile installation teams, and “one-visit” compliance packages that reduce bay time while still producing auditable verification evidence.
Opportunities
Unified IVMS and Speed Limiter Compliance Suites
A major growth opportunity is the bundling of speed limiters into unified IVMS compliance suites—because KSA now has the digital scale to make “always-on compliance” practical and auditable. Reported ~ internet penetration and ~ mobile-based browsing enable real-time driver coaching, remote configuration, and centralized exception handling across fleets operating nationwide. Device density supports M2M growth: mobile subscription counts of ~ help sustain large connected-vehicle fleets where limiter events, overspeed attempts, and tamper signals can be streamed into compliance dashboards. This is not “tech for tech’s sake”—the safety baseline is still heavy, with ~ serious accidents and ~ fatalities, so fleets and regulators can justify integrated control suites as a practical way to reduce exposure while strengthening audit trails. Trade-linked trucking adds another reason suites win: road freight through land ports totals ~ tons (imports ~, exports ~), and such cross-border legs often require demonstrable compliance (internal governance, insurer demands, and client SLAs). Macro capacity also supports suite adoption: USD ~ trillion GDP and USD ~ GDP per capita signal strong enterprise spending capability for managed services, software platforms, and compliance analytics. The opportunity, therefore, is to shift demand from standalone limiter installs to subscription-like, data-backed compliance systems that reduce downtime, strengthen enforcement defensibility, and standardize oversight across mixed OEM fleets.
High-Risk Fleet Specialization
Another opportunity is specialization—solution providers focusing on high-risk fleet categories (intercity buses, hazardous loads, high-mileage cross-border trucks, and event/pilgrimage-linked transport) where compliance budgets and governance scrutiny are structurally higher. Saudi Arabia’s mass-mobility operations provide a measurable case: official statistics report ~ pilgrims for the latest Hajj statistics publication, with ~ pilgrims entering via land border crossings in the detailed release, illustrating the logistical load that includes regulated bus movements, convoy planning, and safety controls under national visibility. Trade and freight intensity reinforce the “high-risk specialization” logic: land-port road freight includes ~ tons imports and ~ tons exports, where fatigue and schedule pressure can elevate overspeed risk, making tamper-evident limiters and continuous monitoring more valuable. The road-safety baseline stays significant, which increases the reputational and legal downside for high-risk operators and encourages adoption of premium compliance packages. Macro indicators support continued activity: USD ~ trillion GDP provides sustained demand for logistics, industrial movement, and travel services, while fiscal posture (e.g., reserves planning around SAR ~ billion) supports ongoing oversight capacity. In this context, the market’s growth is not only “more installs,” but more specialized offerings—Arabic-first coaching, harsh-environment reliability, rapid verification workflows, and audit-grade reporting tailored to fleets with the highest consequence of non-compliance.
Future Outlook
Over the next planning horizon, KSA speed limiter demand is expected to strengthen as fleets industrialize safety governance, regulators emphasize auditability, and telematics penetration pulls limiter purchasing into bundled compliance programs rather than one-time retrofits. Global market baselines show sustained growth driven by regulation and safety mandates, and KSA’s logistics expansion (roads, ports, industrial zones) increases the number of high-utilization vehicles where limiter economics are compelling through reduced incident exposure and standardized driver governance.
Major Players
- Continental
- Robert Bosch GmbH
- ZF Friedrichshafen AG
- Valeo SA
- Denso Corporation
- Autoliv
- Vodafone Automotive
- SABO Electronic Technology
- Remote Control Technologies
- Stoneridge
- Aptiv
- Geotab
- Samsara
- Trimble Transportation
Key Target Audience
- Logistics & Freight Fleet Operators
- Public Transport & Intercity Coach Operators
- Oil & Gas / Petrochemical Transport Operators
- Construction & Mining Fleet Owners / EPC Contractors
- Commercial Vehicle OEMs & Authorized Dealer Networks
- Fleet Telematics / IVMS Solution Buyers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We map the KSA speed compliance ecosystem—regulators, certification pathways, OEM channels, retrofit installer networks, and fleet operators—to define variables such as enforceable speed policies, tamper risk, downtime tolerance, and audit pack requirements. This is supported by desk research across standards references and sector adoption signals.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historical demand indicators using commercial vehicle parc growth signals, telematics adoption proxies, and deployment modes (OEM vs retrofit vs bundled). We analyze how procurement shifts when limiter is sold as a device versus as a telematics policy engine.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validate market hypotheses via CATIs with fleet HSE heads, workshop networks, and telematics program managers to confirm installation costs, downtime windows, tamper patterns, and calibration SLAs—then reconcile findings with compliance expectations.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We synthesize primary feedback with standards/regulatory references and competitive benchmarking to finalize segmentation logic, buyer decision criteria, and opportunity mapping (bundling, audit packs, installer footprint strategy).
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Adoption Milestones
- Speed Compliance Ecosystem in KSA
- KSA Fleet Operating Context
- Value Chain and Stakeholder Map
- Growth Drivers
Heavy Vehicle Safety and Compliance Mandates
Fleet Risk Governance and Insurance Controls
Long-Haul Corridor Exposure
Telematics Penetration and Policy Automation
Vision-Aligned Infrastructure Expansion - Challenges
Multi-Brand ECU Integration Complexity
Retrofit Downtime and Operational Disruption
Tampering and Bypass Risks
Calibration and Verification Bottlenecks
Procurement Price Pressure versus Reliability - Opportunities
Unified IVMS and Speed Limiter Compliance Suites
High-Risk Fleet Specialization
ISA-Ready Transition Pathways
Service Network Expansion
Data-Driven Driver Coaching and Policy Enforcement - Trends
Shift from Standalone Limiters to Connected Policy Engines
Enhanced Tamper Evidence and Secure Firmware
Geo-Conditional Speed Policies
Integration with Digital Inspection Workflows
OEM Software-Defined Speed Governance - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Heavy Trucks / Tractor-Trailers
Medium Trucks
Light Commercial Vehicles
Buses & Coaches
Special Purpose / High-Risk Fleets - By Application (in Value %)
Logistics & Freight Operations
Public & Semi-Public Transport
Construction & Mining Operations
Oil & Gas / Petrochemical Transport
Municipal & Utility Services - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Fixed Speed Limiters
Programmable / Multi-Speed Limiters
ECU-Integrated / OEM Speed Limiting Functions
Telematics-Linked Speed Limiter Modules
ISA-Ready Speed Assistance / Limiters - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone / Non-Connected Limiters
CAN / OBD Integrated Systems
Telematics-Connected / Cloud-Managed Systems
IVMS-Bundled Limiter Architectures - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Logistics and Warehousing
Passenger Transportation
Construction and Infrastructure
Energy and Utilities
Public Sector Services - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Northern Region
Southern Region
- Market Structure and Competition Landscape
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Regulatory Readiness Pack, Installation Footprint in KSA, Vehicle Compatibility Breadth, Tamper Resistance and Forensics, Calibration and Re-Certification SLA, Telematics Integration Depth, Downtime Minimization Model, Warranty and Failure Economics)
- Pricing and Commercial Models
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Competitive Moats and Differentiation Factors
- Detailed Company Profiles
Continental
Robert Bosch GmbH
ZF Friedrichshafen AG
Valeo SA
Denso Corporation
Autoliv
Vodafone Automotive
SABO Electronic Technology
Remote Control Technologies
Stoneridge
Aptiv
Geotab
Samsara
Trimble Transportation
Omnitracs
- Fleet Purchase Triggers and Budget Ownership
- Decision-Making Unit
- Installation & Maintenance Preferences
- Pain Points
- Vendor Selection Criteria
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Selling Price, 2025–2030


