Market Overview
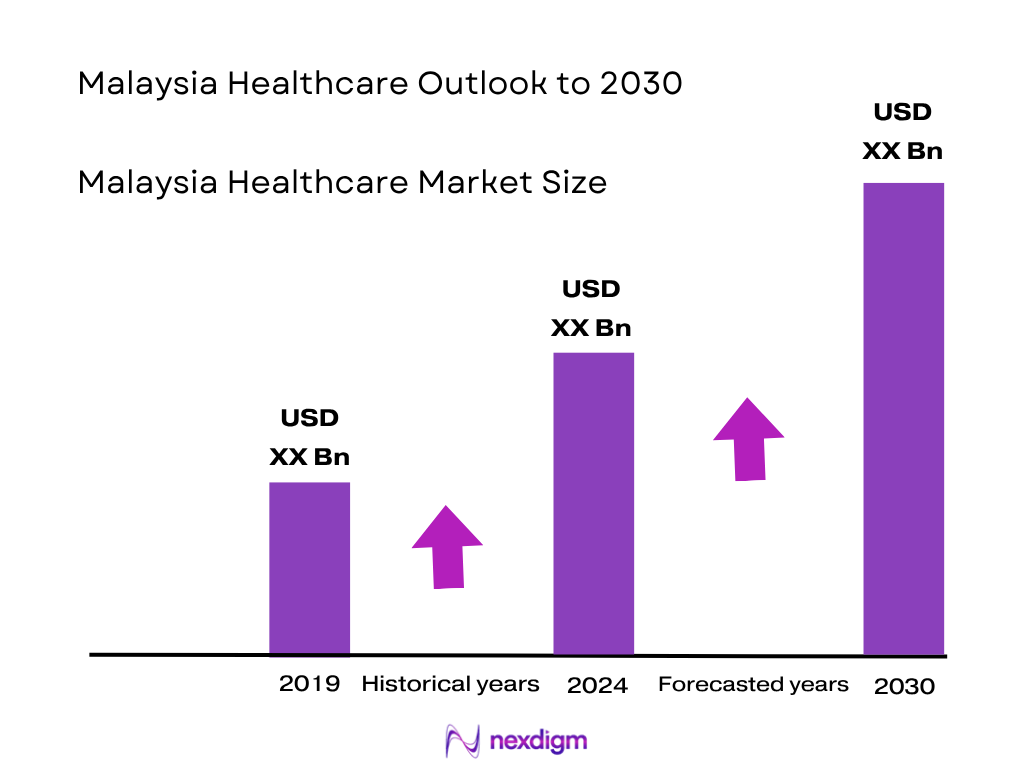
The Malaysia healthcare market is valued at USD 27.87 billion based on 2024 estimates. This growth is primarily propelled by continuous government investments in public health infrastructure, significant increases in private health spending, and rising demand fueled by aging demographics and expanding medical tourism
Malaysia’s healthcare landscape is dominated by the Greater Klang Valley (including Kuala Lumpur) and Penang, thanks to their high concentration of JCI-accredited tertiary hospitals, advanced medical infrastructure, and well-developed private healthcare networks. These urban centers also benefit from substantial medical tourism inflows owing to seamless facilities, international accessibility, and specialized service offerings.
Market Segmentation
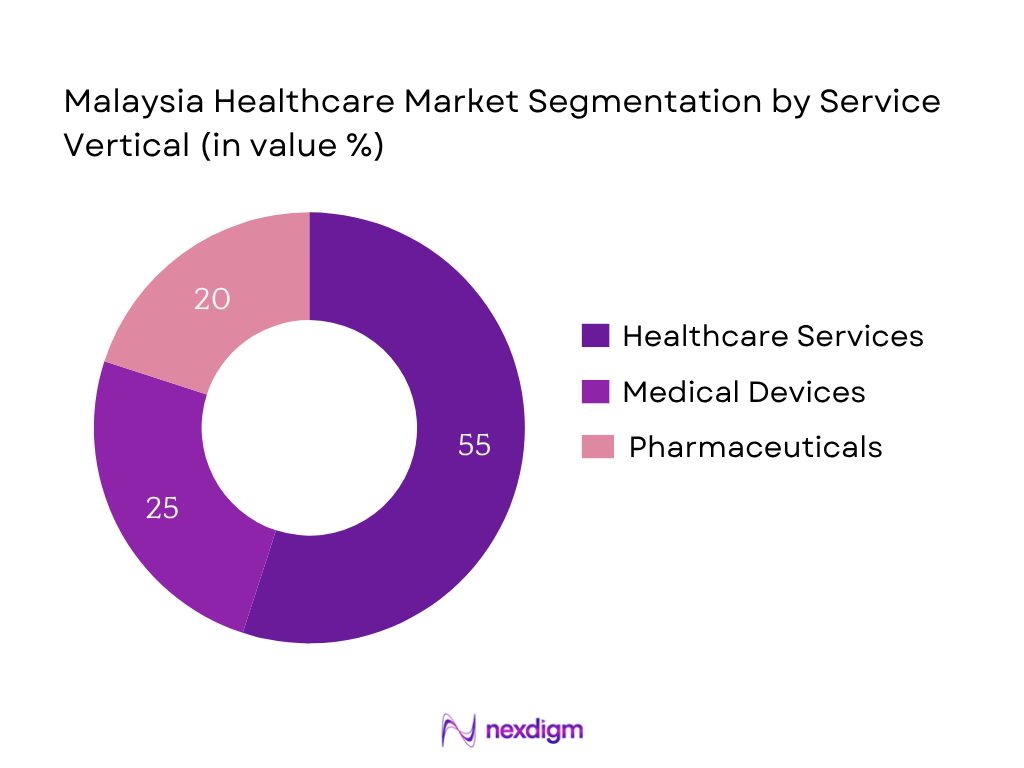
By Service Vertical
Within this vertical, Healthcare Services dominates the market. This segment leads because of Malaysia’s robust public and private hospital networks, extensive outpatient services, and the surge in consumer spending on clinical care, outpatient visits, and hospital admissions. These are backed by national healthcare reforms and funding which expanded public facility capacity and adoption of private care.
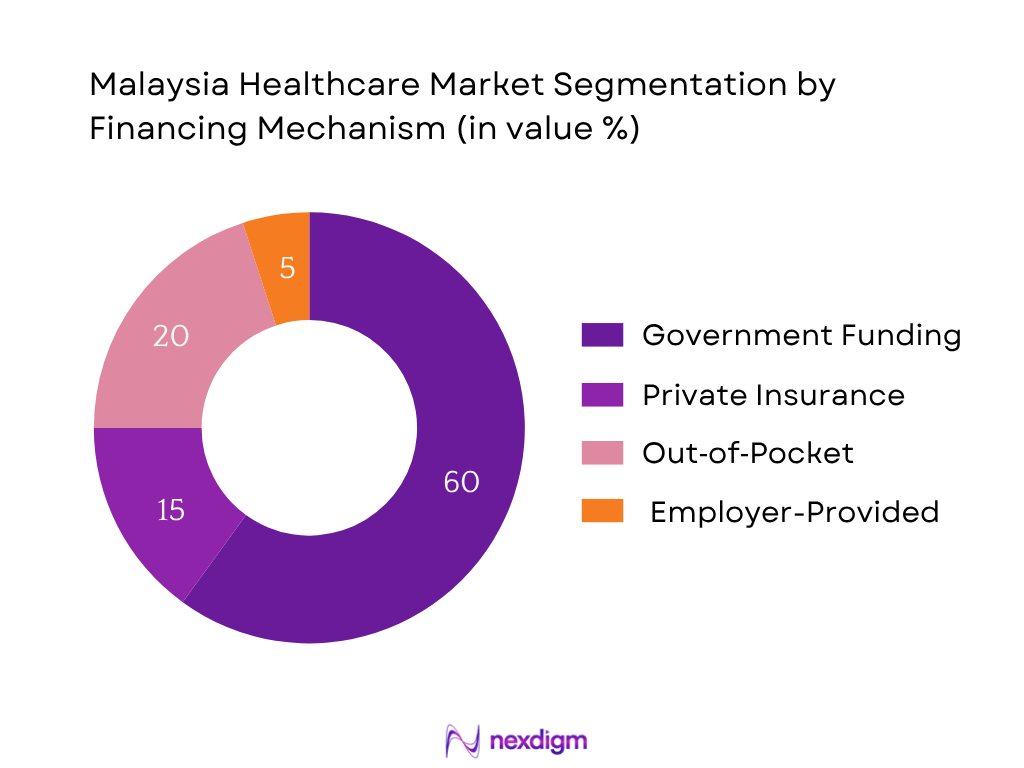
By Financing Mechanism
Here, Government Funding continues to dominate, accounting for the largest share by financing majority of public healthcare services and subsidized care. This dominance is supported by substantial budget allocations and policy prioritization of universal access and rural service expansion.
Competitive Landscape
The Malaysia healthcare market is shaped by a handful of key private and quasi-public players that command strong influence due to brand equity, infrastructure, and service diversity. Public healthcare also remains a foundational backbone. Consolidation is seen as private groups expand footprint and invest in medical tourism.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Key Parameter 1 | Key Parameter 2 | Key Parameter 3 | Key Parameter 4 | Key Parameter 5 | Key Parameter 6 |
| IHH Healthcare Berhad | 2010 | Kuala Lumpur | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| KPJ Healthcare Berhad | 1984 | Negeri Sembilan | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Sunway Medical Centre | 2006 | Selangor | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Columbia Asia | 1996 | Kuala Lumpur | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Pharmaniaga Berhad | 1994 | Selangor | – | – | – | – | – | – |
Malaysia Healthcare Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Aging Population and Rising NCDs
Malaysia’s population aged 65 and above constitutes 7.74 % of the total population, up from 7.45 % in 2023 and 7.19 % in 2022. This demographic shift increases demand for chronic disease management, long‑term care, and geriatric services, placing sustained pressure on healthcare infrastructure. Complementarily, the old‑age dependency ratio rose to 10.98 % of the working-age population in 2024, compared to 10.61 % in 2023 and 10.27 % in 2022. These trends heighten resource utilization in outpatient and inpatient services for non‑communicable diseases, as the aging population typically requires frequent medical attention and specialized care pathways.
Public‑Private Integration Initiatives
Malaysia allocates 5 % of its government social sector development budget to public healthcare, representing an increase of over RM 2 billion compared to prior allocations. This additional funding is directed toward refurbishing hospitals, constructing new facilities, expanding polyclinics, and scaling telehealth systems. Such integration efforts reduce the burden on public facilities by redirecting non-critical and chronic care to private sector partners and digital channels, deepening collaboration. The reinvestment strengthens service delivery and enhances capacity across urban and rural areas through coordinated public–private partnership models.
Market Challenges
Regional Healthcare Disparity
Despite increased funding, disparities persist: advanced diagnostic and imaging facilities predominantly reside in urban private hospitals, while rural and remote areas lack access to specialized care. Urban centers receive the lion’s share of infrastructure upgrades and talent, emphasizing a concentration of services. The absence of specialists in rural clinics undermines equitable access, particularly as the rural aging population grows. Hence, regional inequity remains a prominent challenge that undermines national coverage aspirations.
Capacity Constraints in Public Facilities
Though specific bed counts are unavailable, Malaysia’s public system is burdened by rising demand, especially from the expanding elderly population (now 7.74 % of total) and increasing load from urban outpatient visits. Infrastructure investments via the social sector budget added RM 2 billion, yet many public hospitals remain congested. This gap is aggravated by slow expansions in human capital; the persistent shortage of specialists limits throughput, contributing to overcrowding and extended wait times, highlighting capacity constraints within public healthcare facilities.
Market Opportunities
Growth of Digital Health and Virtual Clinics
Telehealth expansion is actively supported via budget reallocation of over RM 2 billion, funding “tele‑primary care” systems to bridge rural service gaps indicate a mature population with chronic care needs. Digital platforms can enhance management for NCDs, extend specialist reach, and streamline follow-up. As broadband penetration increases and public policy favours e-health, virtual clinics offer scalable, location-agnostic service delivery—especially valuable in under-served geographies.
Investments in Tier‑2 and Rural Infrastructure
More than RM 2 billion has been allocated to healthcare upgrades, including polyclinic expansion in underserved regions. Improved infrastructure can narrow urban-rural disparity by enabling diagnostics and outpatient care beyond major cities. The aging population’s growth—7.74 % of total citizens—underscores demand for distributed services. Investment in Tier‑2 towns amplifies access to primary and specialist care, enhancing preventive and chronic disease management for broader populations.
Future Outlook
Over the next six years, the Malaysia healthcare market is poised for robust expansion, driven by increasing public and private spending, continued momentum in medical tourism, and sustained interest in digital health innovation. Government reforms, aging population needs, and corporate and international patient demand will collectively accelerate growth.
Major Players
- IHH Healthcare Berhad
- KPJ Healthcare Berhad
- Sunway Medical Centre
- Columbia Asia
- Ramsay Sime Darby Health Care
- Pantai Holdings Berhad
- Prince Court Medical Centre
- Mahkota Medical Centre
- Island Hospital
- Thomson Hospital Kota Damansara
- Beacon Hospital
- ALTY Orthopaedic Hospital
- National Heart Institute (IJN)
- TMC Fertility Centre
- Pharmaniaga Berhad
Key Target Audience
- Health-focused Investment and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Ministry of Health Malaysia
- Malaysia Healthcare Travel Council
- Securities Commission Malaysia (for capital market implications)
- Regional State Health Departments (e.g., Selangor, Penang)
- Major Hospital Operator Boards
- Public sector Hospital Administrators
- Medical Tourism Promotion Agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We began by mapping all stakeholders across public hospitals, private chains, insurers, and medical tourism facilitators using industry databases and national statistics to identify key market drivers.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical and current data on market size, service volumes, financing flows, and segmentation were compiled from published reports and government budgets to structure the market model.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings and hypotheses were validated through structured interviews with executives from major hospital groups, insurers, and government agencies to solidify data reliability and contextual insight.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated data were aligned with bottom-up revenue estimates and triangulated with company disclosures to produce a comprehensive and accurate market narrative.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Healthcare Ecosystem (Public, Private, Hybrid)
- National Health Financing System
- Supply Chain and Stakeholder Value Chain
- Growth Drivers
Aging Population and Rising NCDs
Public-Private Integration Initiatives
Expansion of Private Insurance and Takaful
Medical Tourism Development in Penang, Johor
Government Spending on MOH Infrastructure - Market Challenges
Regional Healthcare Disparity
Capacity Constraints in Public Facilities
Rising Out-of-Pocket Healthcare Costs
Shortage of Medical Specialists and Nurses - Market Opportunities
Growth of Digital Health and Virtual Clinics
Investments in Tier-2 and Rural Infrastructure
Entry of Global Healthcare Chains
Demand for Geriatric and Preventive Care - Key Trends
Consolidation of Hospital Groups
Bundled Health and Wellness Packages
AI and Remote Monitoring Integration
Expansion of Mobile Health Platforms - Regulatory Landscape
Licensing, Facility Accreditation (MSQH, JCI)
Pricing Controls on Medical Devices and Drugs
Medical Tourism Regulations
Takaful and Insurance Policy Guidelines - SWOT Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- By Total Healthcare Expenditure (Public & Private), 2019-2024
- By Inpatient and Outpatient Volume, 2019-2024
- By Medical Tourism Revenue and Patient Volume, 2019-2024
- By Insurance Penetration (General Insurance, Takaful, Government Subsidy), 2019-2024
- By Facility Type (In Value %)
Public Hospitals
Private Hospitals
Ambulatory Surgical Centres
Polyclinics & General Practitioner Clinics
Elderly and Long-term Care Facilities - By Service Type (In Value %)
Primary Care Services
Tertiary & Specialty Care
Emergency & Critical Care
Rehabilitative Services
Telemedicine and Virtual Care - By Payer Type (In Value %)
Ministry of Health (MOH)
Private Insurance Providers
Takaful Operators
Corporate Employers & Wellness Plans
Direct Out-of-Pocket - By Medical Specialty (In Value %)
Cardiology
Oncology
Orthopaedics
Endocrinology (Diabetes, Thyroid)
Maternal and Child Health - By Region (In Value %)
Klang Valley
Johor
Penang
Sabah & Sarawak
Other Peninsular Regions
- Market Share of Major Players by Revenue and Patient Footfall
Market Share by Medical Specialty and Region - Cross Comparison Parameters (Total Number of Beds and Facilities, Service Mix (Primary vs Tertiary Focus), Accreditation Status (MSQH, JCI), Inbound Medical Tourism Footfall, Insurance Tie-ups and Corporate Wellness Programs, Digital Health Capabilities, Revenue Stream Breakdown, Expansion Pipeline and Upcoming Projects)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing and Revenue Analysis by Service Type
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
IHH Healthcare Berhad
KPJ Healthcare Berhad
Sunway Medical Centre
Columbia Asia Hospitals
Ramsay Sime Darby Health Care
Pantai Holdings
Prince Court Medical Centre
Mahkota Medical Centre
Island Hospital
Thomson Hospital Kota Damansara
Beacon Hospital
ALTY Orthopaedic Hospital
National Heart Institute (IJN)
TMC Fertility Centre
Pharmaniaga Berhad (Public Pharma Distribution)
- Utilization Patterns Across Income Groups
- Budget Allocations for Employer Health Benefits
- Penetration of Insurance Among Age Bands
- Preferences for Public vs Private Providers
- Telehealth Adoption among Urban & Rural Users
- By Total Healthcare Expenditure, 2025-2030
- By Regional Market Share, 2025-2030
- By Patient Visits and Hospital Utilization, 2025-2030
- By Digital Healthcare Share, 2025-2030


