Market Overview
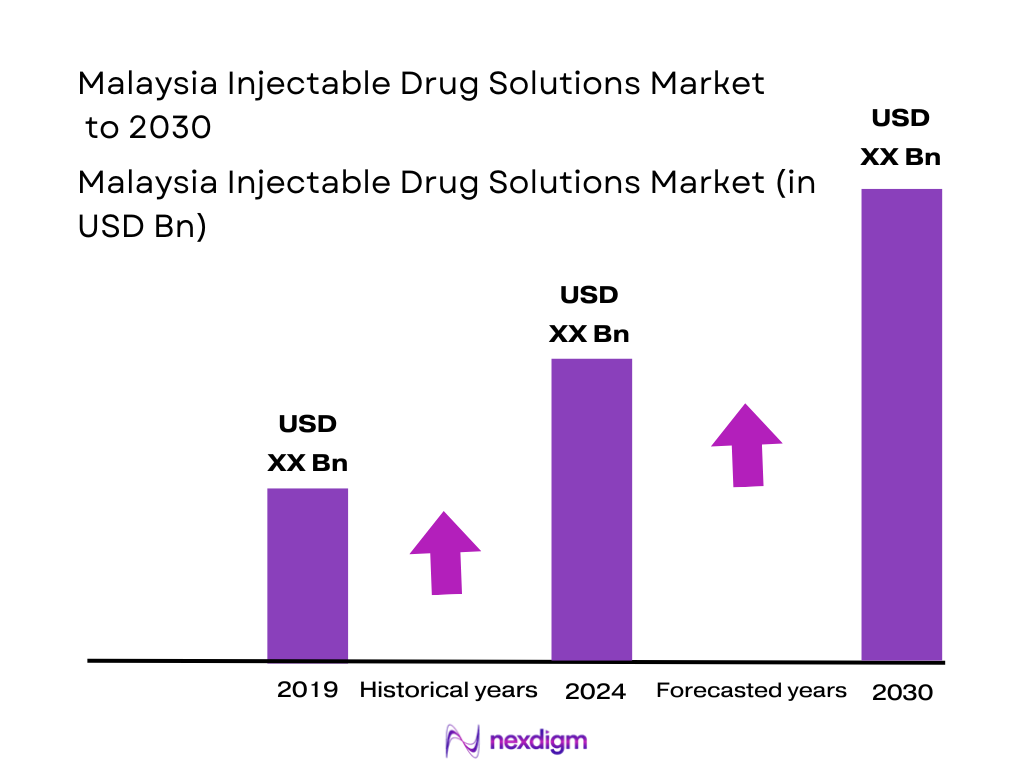
The Malaysia pharmaceuticals-in-dosage market is valued at about USD ~ billion, with injectables accounting for a sizeable, hospital-driven share. This scale is supported by an active upstream ecosystem where the active pharmaceutical ingredients segment alone generates around USD 472 million, reflecting strong manufacturing depth and formulation capabilities for parenteral drugs. Within downstream delivery, prefilled syringe solutions contribute roughly USD 444 million, underscoring the growing shift toward safer, unit-dose injectable formats in chronic and acute therapies. Together, these data points indicate a robust injectable backbone underpinning Malaysia’s broader pharma value chain.
Market Segmentation
By Therapeutic Area
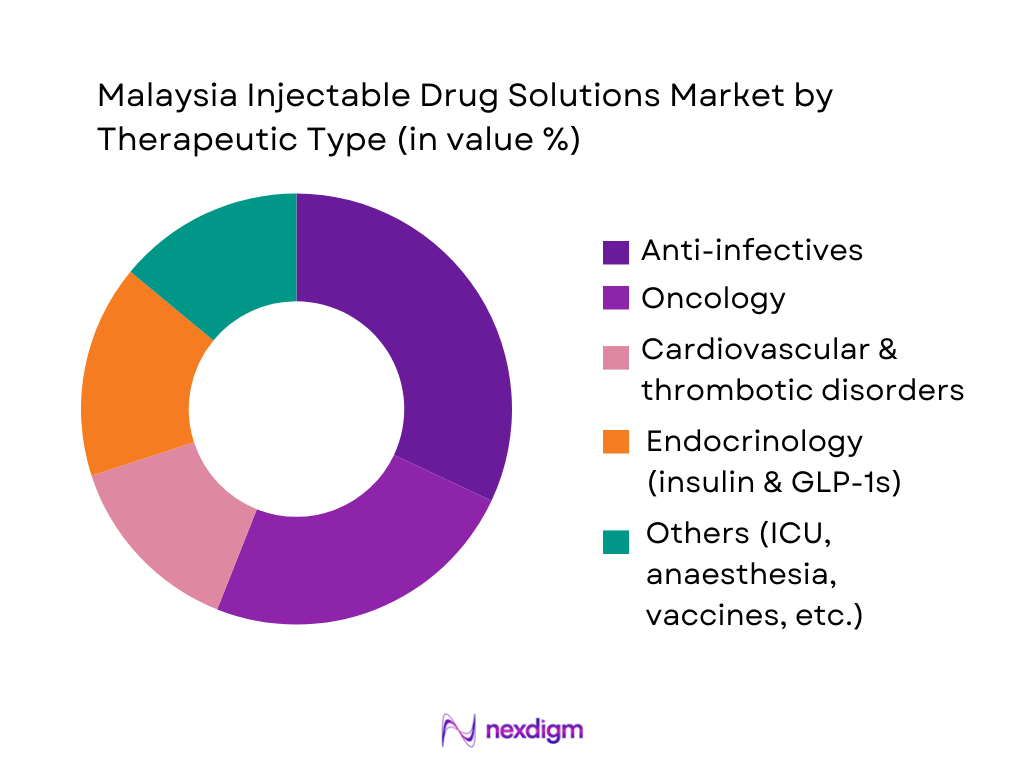
The Malaysia Injectable Drug Solutions Market is segmented by therapeutic area into anti-infectives, oncology, cardiovascular and thrombotic disorders, endocrinology (insulin and GLP-1s), and others (critical care, anaesthetics, vaccines, pain, etc.). Recently, anti-infective injectables hold a dominant share due to their central role in hospital formularies, intensive care units, and peri-operative prophylaxis. Malaysia’s high burden of non-communicable diseases, recurring sepsis, and post-surgical infections in tertiary facilities keeps broad-spectrum antibiotics, antifungals, and antiviral injectables in constant demand. At the same time, rising cancer incidence and the expansion of biologics and targeted therapies are rapidly expanding oncology and endocrinology injectables, but anti-infectives remain the backbone of inpatient injectable consumption.
By Formulation Type
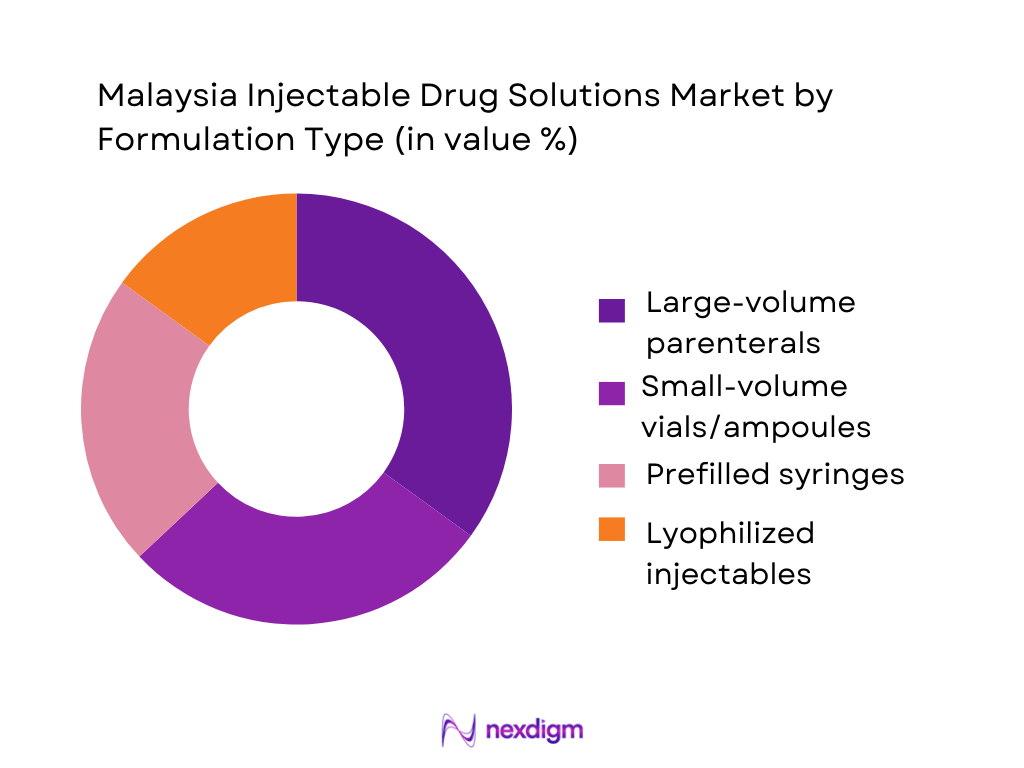
The Malaysia Injectable Drug Solutions Market is segmented by formulation into large-volume parenterals (LVPs), small-volume vials and ampoules, prefilled syringes, and lyophilized injectables. Large-volume parenterals currently lead, supported by extensive use of IV fluids, electrolytes, parenteral nutrition, and antibiotic infusions in public and private hospitals. IV therapy suppliers such as Fresenius Kabi emphasise broad portfolios for anaesthesia, oncology, and critical-care IV drugs, underscoring the importance of LVPs in local clinical practice. Meanwhile, prefilled syringes show the fastest growth trajectory—especially in vaccines, insulin, and biologics—supported by their Malaysian market already exceeding USD 440 million, but their share still trails entrenched LVP and vial-based regimens in high-volume ward usage.
Competitive Landscape
The Malaysia Injectable Drug Solutions Market is characterised by a mix of large domestic generics manufacturers and multinational innovators. Pharmaniaga and Duopharma anchor the local supply of essential injectables for public hospitals and tenders, while Biocon Biologics operates one of the world’s largest integrated insulin facilities in Johor, supplying insulin and biosimilars to global and regional markets. Multinational companies such as Pfizer, Roche, Novartis, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, and Fresenius Kabi complement the landscape with oncology, immunology, biologics, and critical-care injectable portfolios. Overall, the market is moderately consolidated at molecule level, with tender-driven competition on commoditised injectables and brand-driven differentiation in biologics and specialty therapies
| Company | Establishment Year* | Headquarters (for Malaysia Ops) | Ownership Type | Core Injectable Strengths | Local Manufacturing / Fill-Finish Presence | Role in Malaysian Market | Recent Strategic Highlight* |
| Pharmaniaga Berhad | 1994 | Shah Alam, Selangor | ~
|
~
|
~
|
~
|
~
|
| Duopharma Biotech Berhad | ~2000 | Klang Valley, Malaysia | ~ | ~
|
~
|
~
|
~
|
| Biocon Biologics (Biocon Sdn Bhd) | 2010s (Malaysia ops) | Johor, Malaysia | ~ | ~
|
~
|
~
|
~
|
| Pfizer (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd | 1978 | Kuala Lumpur | ~ | ~
|
~
|
~
|
~
|
| Roche (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd | 20th-century presence | Subang Jaya / Petaling Jaya, Selangor | ~ | ~
|
~
|
~
|
~
|
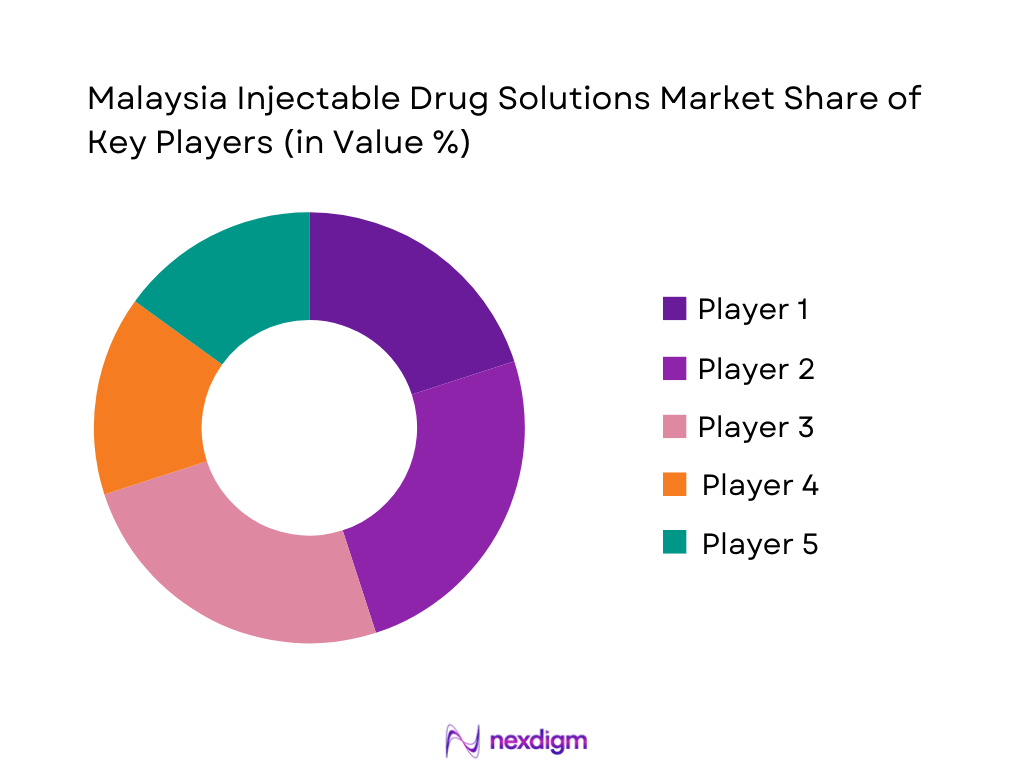
Malaysia Injectable Drug Solutions Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising biologics penetration & biosimilar uptake
Malaysia’s injectable drug solutions market is underpinned by a heavy chronic-disease burden that structurally favours biologics and biosimilars. The National Health and Morbidity Survey reports diabetes in 15.6% of adults, placing Malaysia among the highest in the region and sustaining long-term demand for insulin and other parenteral therapies. The World Health Organization’s population estimates show Malaysia at around 35.1 million people, with continuous ageing adding complexity to treatment needs datadot GLOBOCAN data indicate over 48,000–50,000 new cancer cases in the country, with breast and colorectal cancers prominent, each typically treated with injectable systemic regimens.gco.iarc.who.int A 2025 analysis of NPRA approvals shows 18 international non-proprietary name (INN) biosimilars across 38 brands registered in Malaysia by August 2023, with 76.3% (29 brands) approved in the 2016–2023 window, signalling rapid uptake of biosimilar injectables JAPS.
Expansion of sterile manufacturing & fill–finish units
The expansion of sterile injectable capacity is anchored in Malaysia’s broader manufacturing and investment profile. The Malaysian Investment Development Authority reports that the manufacturing sector attracted RM84.3 billion of approved investments, representing 31.9% of total approved investments in one recent year, with continued commitments in chemicals and pharmaceuticals. MITI Biocon’s large-scale insulin facility in Johor alone represents an investment of over USD 350 million, serving as a global hub for recombinant insulin cartridges and vials exported to more than 40 countries. Biocon UN Comtrade-based data indicate that Malaysia imported US$2.4 billion of pharmaceutical products in 2024, while exporting US$471.43 million in pharmaceutical products, reflecting a growing role in both inward processing and outbound finished-dose supply.
Market Challenges
High dependence on imported APIs
Malaysia’s injectable ecosystem remains structurally exposed to imported APIs and finished injectables. UN Comtrade-derived statistics show that pharmaceutical products imports reached US$2.4 billion in 2024, compared with US$471.43 million in exports, indicating a sizeable net import position. Trading Economics+1 OEC data for packaged medicaments show MYR 5.16 billion of imports versus MYR 1.05 billion of exports in a recent year, reinforcing the reliance on external manufacturing hubs for many sterile molecules.OEC+1 Trade-portal analysis notes that Germany, the USA, Switzerland, France, Australia, China, Ireland, Singapore and the UK together account for more than two-thirds of Malaysia’s pharmaceutical imports, while India alone supplies about US$136.45 million of pharmaceutical products in 2024.
Cold-chain logistical vulnerabilities
Malaysia’s injectables supply chain depends on temperature-sensitive logistics across ports, airports and hospital pharmacies. The World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index ranks Malaysia 26th out of 139 economies in 2023 on overall logistics performance, reflecting strong but not flawless infrastructure for time- and temperature-sensitive cargo. Logistics Performance Index. UN Comtrade shows US$2.4 billion in pharmaceutical imports in 2024, much of which comprises finished injectables and high-value cold-chain products that must transit through Malaysia’s ports and airports. Trading Economics Data from the Ministry of Health’s KKMNOW platform show that several large state hospitals periodically run at more than 80–90% bed occupancy, leaving limited buffer for stock-outs or logistics delays, especially for oncology, intensive care and anti-infective injectables that cannot be easily substituted.
Opportunities
Growth of prefilled syringes and RTU formats
Demographic and care-delivery shifts in Malaysia are ideal for scaling prefilled syringes and ready-to-use (RTU) injectable formats. Department of Statistics Malaysia estimates show 2.6 million people aged 65 and above, representing 7.7% of the population in 2024, with the number of seniors projected to exceed 3.9 million over the medium term. Malay Mail Older patients with diabetes, cardiovascular disease and cancer often require long-term self-administration or ambulatory injectables that are easier and safer in prefilled devices. NHMS 2023 data showing diabetes in 15.6% of adults and a high burden of hypertension and dyslipidaemia reinforces demand for chronic parenteral therapies that can be delivered at home or in day-care settings.
Expansion of biosimilar oncology injectables
Malaysia’s oncology burden and evolving biosimilar framework create strong upside for oncology injectables. GLOBOCAN 2022 data confirm that Asia accounts for about 49% of global new cancer cases, with Malaysia contributing a rising share of breast, colorectal and lung cancers that are predominantly treated with injectable regimens. American Cancer Society+1 The 2025 biosimilar-lag study documents 18 INN biosimilars approved in Malaysia by August 2023, with 44.4% (8 INNs) in the antineoplastic and immunomodulating class and multiple brands registered for trastuzumab, bevacizumab, rituximab and pegfilgrastim. JAPS NPRA’s alignment with EMA and WHO guidelines, plus participation in PIC/S GMP frameworks, allows oncology biosimilars manufactured in Europe, India and East Asia to be registered and supplied into Malaysian hospitals, often with two to four brands per molecule to support procurement competition.
Future Outlook
Over the next several years, the Malaysia Injectable Drug Solutions Market is expected to expand steadily, tracking the broader pharmaceutical sector’s high single-digit growth and the rising complexity of clinical care. IQVIA projects Malaysia among the fastest-growing Asian pharma markets in value terms, underpinned by demographic ageing, urbanisation, and broader insurance coverage. The burden of diabetes alone spans more than 4.75 million adults, and national surveys show substantial overlap with hypertension and dyslipidaemia, sustaining long-term demand for parenteral therapies, biologics, and insulin.
Major Players
- Pharmaniaga Berhad
- Duopharma Biotech Berhad
- Biocon Biologics (Biocon Sdn Bhd)
- Hovid Berhad
- Pfizer (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd
- Roche (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd
- Novartis Corporation (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd
- Sanofi-Aventis (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd
- AstraZeneca Sdn Bhd
- Fresenius Kabi Malaysia Sdn Bhd
- Bayer Co (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd
- Merck Sharp & Dohme (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd
- Takeda Malaysia Sdn Bhd
- Novo Nordisk Pharma (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd
- GSK Pharmaceutical (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd
Key Target Audience
- Injectable and sterile-drug manufacturers
- Biologics and biosimilar companies
- Contract manufacturing organisations (CMOs) and fill-finish facilities
- Hospital groups and private healthcare chains
- Pharmaceutical distributors and logistics providers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Drug-delivery and device companies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The first step involves mapping the ecosystem of the Malaysia Injectable Drug Solutions Market, including domestic manufacturers, multinational innovators, distributors, hospital buyers, regulators, and med-tech partners. Extensive secondary research from NPRA, MOH, PhAMA, IQVIA publications, and global market reports is used to identify variables such as therapy-area mix, dosage-form split, public–private volume distribution, biologics penetration, and tender dynamics. These variables frame both demand- and supply-side modelling.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical and current data points on Malaysia’s pharmaceutical sales, API production, and injectable-related sub-segments (e.g., prefilled syringes) are compiled and normalised into a unified dataset. This includes evaluating per-capita medicine spend, hospital vs retail shares, biologics uptake, and disease-burden indicators (diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular risk). Revenue flows across therapeutic and formulation categories are apportioned using analogues from global injectable-delivery benchmarks, then cross-checked against Malaysian tender and product-portfolio structures to construct the base market size and segmentation.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Quantitative hypotheses about injectable share, therapy-area dominance, and formulation mix are stress-tested through structured discussions and computer-assisted interviews with stakeholders such as hospital pharmacists, procurement managers, medical oncologists, endocrinologists, and senior executives at domestic and multinational pharma companies. These interviews focus on formulary composition, usage intensity, price bands, and emerging shifts (e.g., movement toward prefilled syringes and biosimilars). Feedback is used to refine model coefficients, adjust segment shares, and validate the practical realism of growth assumptions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
In the final stage, bottom-up segment estimates are reconciled with top-down macro indicators (total pharma spend, disease-burden trends, and international injectable-delivery benchmarks).
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Primary–Secondary Synthesis Framework, Regulatory Validation Through Malaysia NPRA Filings, Sterile Manufacturing Benchmarking, Hospital Procurement Interview Framework, Limitations and Forward-Looking Considerations)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Evolution Pathway
- Timeline of Major Market Events
- Pharmaceutical Business Cycle (Injectables-Specific)
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Rising biologics penetration & biosimilar uptake
Expansion of sterile manufacturing & fill-finish units
Increasing hospital admissions in tertiary care
Strong demand for anti-infective & oncology injectables - Market Challenges
High dependence on imported APIs
Cold-chain logistical vulnerabilities
Regulatory delays for sterile injectables
Rising production costs & aseptic compliance demands - Opportunities
Growth of prefilled syringes and RTU formats
Expansion of biosimilar oncology injectables
Contract manufacturing for global firms
Rising demand for specialty hospital injectables - Emerging Trends
Shift toward preservative-free injectables
Adoption of automation in aseptic filling
Growth in non-PVC IV bag usage
Digital procurement & hospital inventory systems - Government Regulation
NPRA registration pathways for injectables
GMP guidelines for sterile & aseptic facilities
Import licensing, biologics submission requirements
Cold-chain pharmaceutical compliance enforcement - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019-2024
- By Therapeutic Class (in Value %)
Anti-infectives Injectables
Oncology Injectables
Cardiovascular Injectables
Analgesics & Anesthetics
Immunology & Biologic Injectables
Endocrinology Injectables (Insulin, Hormones) - By Formulation Type (in Value %)
Sterile Solutions (IV/IM/SC)
Lyophilized Powder for Reconstitution
Ready-to-Use (RTU) Prefilled Syringes
Ready-to-Dilute (RTD) Bags
Large-Volume Parenterals (LVP) - By Packaging Format (in Value %)
Glass Vials
Plastic Ampoules
Prefilled Syringes
IV Bags (PP/Non-PVC)
Cartridges - By End User (in Value %)
Public Hospitals (MOH)
Private Hospitals
Ambulatory / Day-care Centers
Retail Pharmacies
Clinics & Physician Practices - By Distribution Channel (in Value %)
Direct Hospital Procurement
Tender-Based Government Procurement
Pharmaceutical Distributors
Wholesalers (Cold-Chain Enabled)
Online B2B Platforms - By Origin of Molecule (in Value %)
Branded Injectables
Generic Injectables
Biosimilars
Imported Specialty Injectables
Locally Manufactured Injectables - By Region (in Value %)
Central Malaysia
Northern Malaysia
Southern Malaysia
East Malaysia (Sabah & Sarawak)
- Market Share Analysis (Value/Volume)
- Market Share by Therapeutic Class
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Sterile Manufacturing Capacity (mL, vials/day), Portfolio Depth in Critical Injectables, Biologics & Biosimilar Capabilities, NPRA Approval Speed & Regulatory Strength, Cold-chain Distribution Strength, Tender Participation & Win Ratio, R&D Capability for Formulation Innovation, Hospital Penetration & Key Account Coverage)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Pharmaniaga
Duopharma Biotech
Biocon
Roche
Pfizer
Novartis
AstraZeneca
Fresenius Kabi
Baxter
Sanofi
Johnson & Johnson (Janssen)
Takeda
AbbVie
Kalbe Farma
Inno Bio Ventures
- Demand Drivers among Public Hospitals
- Private Hospital Procurement Behaviour
- Regulatory & Compliance Requirements
- Pain Point Analysis Across End-Users
- Decision-Making Process
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Average Selling Price, 2025-2030