Market Overview
The Malaysia lubricant market is valued at USD 1.56 billion, based on a five-year historical analysis. This valuation is driven by consistent growth in the automotive and manufacturing sectors, along with increasing demand for high-performance synthetic lubricants. According to the Malaysian Investment Development Authority (MIDA), Malaysia’s industrial output rose to RM 144.6 billion in the latest reported quarter, positively impacting lubricant consumption across machinery-intensive sectors. Rising vehicle registrations, which crossed 800,000 units as per the Road Transport Department, also contribute to the country’s lubricant demand, especially in the engine oil category.
Kuala Lumpur, Selangor, and Johor dominate the lubricant market due to high population density, robust industrial presence, and high vehicle ownership. Kuala Lumpur alone hosts more than 40% of Malaysia’s commercial vehicle workshops. Johor’s proximity to Singapore and its flourishing logistics and industrial zones make it a hotspot for both automotive and industrial lubricant demand. These regions also host major OEM service centers and lubricant blending facilities, further cementing their leadership.
Market Segmentation
By Product Type
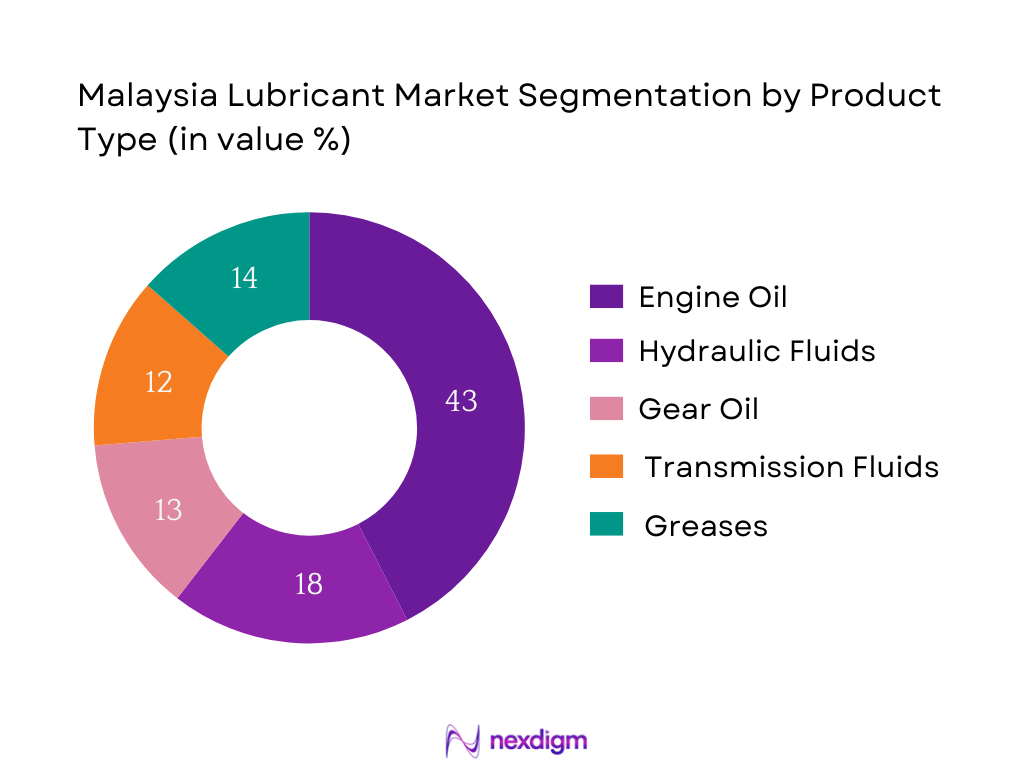
Malaysia’s lubricant market is segmented by product type into engine oil, hydraulic fluids, gear oil, transmission fluids, and greases. Recently, engine oil has a dominant market share under this segmentation. This is attributed to Malaysia’s vehicle density of over 1 vehicle per 1.3 people, leading to consistent demand for passenger and commercial vehicle lubrication. Furthermore, government regulations enforcing periodic servicing, coupled with the tropical climate leading to quicker oil degradation, have reinforced the frequency of engine oil change cycles. Brands like Petronas and Shell dominate this segment due to their strong distribution networks and OEM endorsements.
By Application
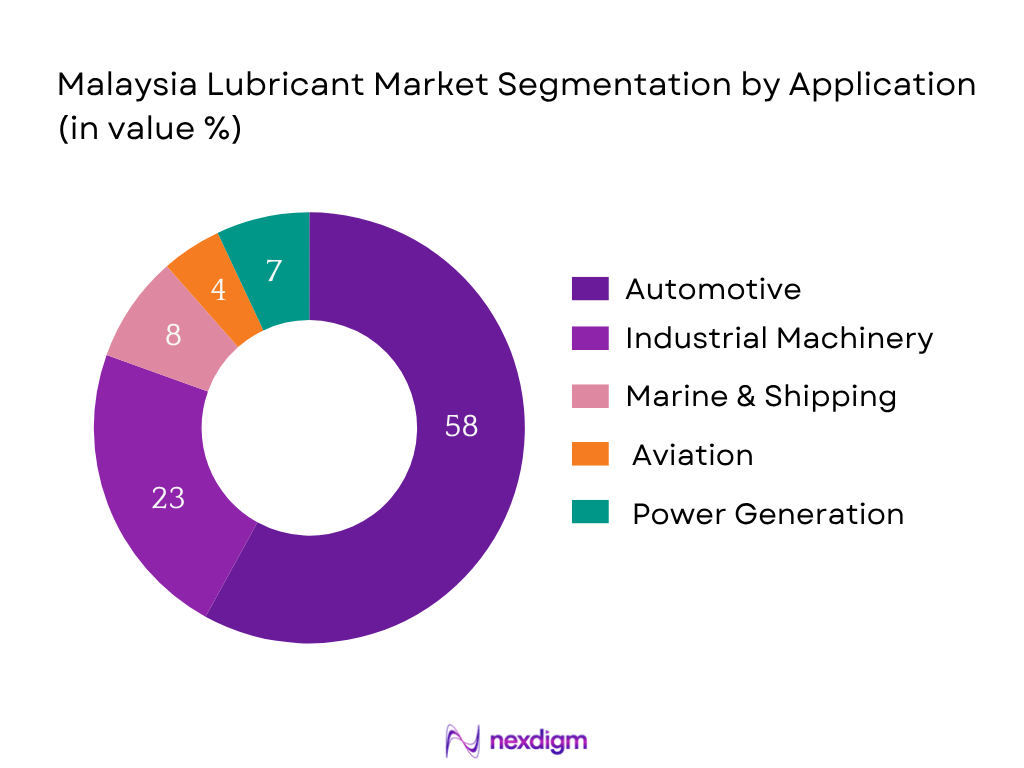
Malaysia lubricant market is segmented by application into automotive, industrial machinery, marine & shipping, aviation, and power generation. Automotive applications hold a dominant market share due to the high motorization rate and steady growth in used car transactions, which require more frequent oil changes. According to Malaysia Automotive Association, used car sales reached over 500,000 units, supporting aftermarket lubricant demand. The expansion of ride-hailing services, delivery fleets, and e-commerce logistics further propels this segment. OEM servicing mandates and the availability of high-margin synthetic lubricants also contribute to this segment’s profitability and volume growth.
Competitive Landscape
The Malaysia lubricant market is dominated by multinational and domestic players with blending facilities, localized partnerships, and OEM collaborations. Major players such as Shell, Petronas, and ExxonMobil have deep market penetration due to their extensive distributor networks and advanced synthetic product lines. Local production capacity and joint ventures with regional partners are key success factors. The presence of government-linked companies (GLCs) such as Petronas adds policy leverage to the competitive scenario.
| Company Name | Year of Establishment | Headquarters | OEM Partnerships | Local Blending Plant | Synthetic Portfolio | Distribution Touchpoints | Recent Development |
| Petronas Lubricants Intl. | 2008 | Kuala Lumpur | – | – | – | – | – |
| Shell Malaysia | 1891 | Kuala Lumpur | – | – | – | – | – |
| ExxonMobil Malaysia | 1947 | Kuala Lumpur | – | – | – | – | – |
| BP Castrol | 1919 | UK | – | – | – | – | – |
| TotalEnergies Malaysia | 1954 | France | – | – | – | – | – |
Malaysia Lubricant Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Industrialization and Infrastructure Investments
Malaysia’s industrial sector continues to be a cornerstone of lubricant consumption, supported by robust infrastructure expansion. According to the Department of Statistics Malaysia (DOSM), the total value of construction work done in the country stood at RM 34.9 billion in Q4 2023, up from RM 32.6 billion in the same quarter of 2022. Industrial production, which directly fuels lubricant usage in heavy machinery and hydraulics, recorded RM 144.6 billion in output in February 2024. Additionally, the manufacturing sector alone employed 2.38 million workers in early 2024, increasing machinery uptime and requiring more frequent lubricant change cycles. The government’s continued rollout of mega-projects under the 12th Malaysia Plan, including East Coast Rail Link (ECRL) and Pan Borneo Highway, has increased demand for industrial greases and hydraulic fluids across multiple states.
Automotive Sales Recovery and Used Car Boom
Malaysia’s lubricant demand is closely tied to its automotive recovery and the robust growth of the used car market. According to the Malaysian Automotive Association (MAA), the total industry volume (TIV) of vehicles sold in 2023 reached 799,731 units, marking a rebound from pandemic lows. Meanwhile, used car transactions remained high, with over 500,000 ownership transfer cases registered by the Road Transport Department (JPJ) between January and December 2023. Each transfer typically involves routine servicing, driving lubricant consumption. The automotive sector also employed over 700,000 people in 2023, many in service operations where lubricant usage is recurring. Workshop density, especially in Selangor and Johor, further accelerates consumption through preventive maintenance cycles.
Market Challenges
Price Volatility of Base Oils (Group I–V)
Lubricant manufacturers in Malaysia remain vulnerable to global base oil price volatility due to limited domestic refining capacity. According to the Department of Statistics Malaysia, 97.3% of Malaysia’s base oil requirements were imported in 2023, mainly from Singapore, South Korea, and India. Customs data show the CIF import value of base oils averaged USD 1,097 per metric ton in Q3 2023, fluctuating sharply due to geopolitical tensions and refinery downtimes. The Malaysian refining capacity for base oils is under 60,000 barrels per day, primarily allocated for domestic fuel demand, leaving lubricant producers reliant on volatile international markets. Such fluctuations significantly impact production planning and pricing models in the downstream lubricant sector.
Regulatory Pressure on Emission Norms
Malaysia is increasing regulatory scrutiny on emissions and lubricant quality standards. Under the Department of Environment’s (DOE) clean air initiatives, emission standards aligned with Euro 5 and above are now mandated for all new diesel vehicles and selected industrial operations. According to DOE, over 2,700 factories were audited in 2023 for emissions and lubricant discharge practices, with 218 non-compliance notices issued. Such regulations are pushing lubricant manufacturers to reformulate products with low-sulfur, low-ash compositions, increasing R&D and compliance costs. In the auto sector, DOE’s push for low-viscosity and fuel-efficient lubricants has mandated many OEMs to shift their service center protocols, impacting legacy lubricant SKUs.
Market Opportunities
EV-Specific Lubricants (Thermal Fluids, E-transmission Oils)
Electric vehicle adoption in Malaysia is growing rapidly, creating demand for specialized lubricants such as thermal fluids, dielectric coolants, and e-transmission oils. According to the Ministry of Transport Malaysia, 13,274 electric cars were registered as of Q1 2024, a fivefold increase compared to two years ago. These vehicles require advanced cooling and lubrication systems to manage battery temperature and drivetrain performance. The Ministry of Investment, Trade and Industry (MITI) approved 34 new EV infrastructure projects in 2023, laying the foundation for high-volume EV fleets. As most traditional engine oils are obsolete in EVs, the shift necessitates entirely new fluid formulations, opening white space for local and global lubricant players with R&D in EV fluids.
Synthetic Lubricants and Bio-based Alternatives
Malaysia’s tropical climate and growing demand for longer drain intervals have spurred interest in synthetic and bio-based lubricants. According to MPOB, Malaysia produced 1.67 million metric tons of palm-based oleochemicals in 2023, creating a viable feedstock for sustainable base oils. Concurrently, the Energy Commission of Malaysia recorded a rise in industrial sectors demanding high-performance synthetic oils to support 24/7 operational cycles. Synthetic lubricants provide enhanced thermal stability in high-temperature environments, making them ideal for both automotive and industrial applications. In 2024, Petronas initiated a pilot with palm-based lubricants in heavy-duty applications across Sabah, while Shell’s synthetic lineup expanded to more than 30 SKUs distributed nationwide.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Malaysia lubricant market is expected to show moderate yet steady growth, driven by evolving vehicle technologies, OEM lubricant programs, and the emergence of electric vehicles (EVs). The shift toward low-viscosity, fuel-efficient, and synthetic lubricants will become more prominent, aided by rising environmental awareness and stricter emission standards. Expansion in logistics, e-commerce, and industrial automation will also contribute to lubricant demand.
Furthermore, as EV penetration increases—expected to grow tenfold by the end of the forecast period—there will be a surge in demand for thermal fluids, e-transmission oils, and cooling lubricants. Additionally, new construction projects under the 12th Malaysia Plan and increased private manufacturing investments will create incremental industrial lubricant requirements.
Major Players
- Petronas Lubricants International
- Shell Malaysia
- ExxonMobil Malaysia
- BP Castrol
- TotalEnergies Malaysia
- Fuchs Lubricants
- Idemitsu Malaysia
- Eneos Malaysia
- Sinopec Malaysia
- Caltex (Chevron)
- Repsol Malaysia
- Liqui Moly
- UMW Lubricants
- Amsoil Distributors Malaysia
- Cyclon Lubricants
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEMs and Authorized Service Centers
- Industrial Equipment Manufacturers
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Department of Environment Malaysia, MITI)
- Logistics and Transport Fleet Operators
- Power Generation and Utility Operators
- E-commerce and Last-Mile Delivery Aggregators
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Marine and Offshore Engineering Companies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves constructing an ecosystem map encompassing all major stakeholders within the Malaysia Lubricant Market. This step is underpinned by extensive desk research, utilizing a combination of secondary and proprietary databases to gather comprehensive industry-level information. The primary objective is to identify and define the critical variables that influence market dynamics.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, we compile and analyze historical data pertaining to the Malaysia Lubricant Market. This includes assessing market penetration, the ratio of marketplaces to service providers, and the resultant revenue generation. Furthermore, an evaluation of lubricant type-specific usage across sectors ensures accuracy in volume and value estimates.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses are developed and validated through computer-assisted telephone interviews (CATIs) with industry experts, including lubricant distributors, service station managers, and OEM workshop heads. These consultations provide financial, operational, and procurement insights essential for refining the dataset.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase involves direct engagement with lubricant manufacturers and bulk consumers. This interaction supports the validation of sales volumes, consumer preferences, and technology trends, ensuring a robust and credible bottom-up market size analysis.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology
(Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Expert Interview Insights, Primary Research, Limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Evolution and Market Genesis
- Value Chain and Supply Chain Mapping
- Lubricant Blending Value Chain in Malaysia
- Import Dependency and Local Refining Capacity Analysis
- Major Regulatory Authorities and Licensing Process
- Growth Drivers
Industrialization and Infrastructure Investments
Automotive Sales Recovery and Used Car Boom
Expansion of Manufacturing & Palm Oil Processing Units - Market Challenges
Price Volatility of Base Oils (Group I–V)
Regulatory Pressure on Emission Norms
High Import Dependency on Additives - Market Opportunities
EV-Specific Lubricants (Thermal Fluids, E-transmission Oils)
Synthetic Lubricants and Bio-based Alternatives
Regional Supply Chain Hubs Development - Market Trends
Shift Toward Low-viscosity and Fuel-efficient Oils
Private Label and OEM Branding Growth
Blending-as-a-Service (BaaS) Partnerships - Regulatory Landscape
DOE & MITI Norms for Industrial Lubricants
Import Tariffs, Excise Duties & SIRIM Certification
Lubricant Licensing and Quality Benchmarking - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem Mapping
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume (in million liters), 2019-2024
- By Average Price (USD/liter), 2019-2024
- By Product Type (In Value %)
Engine Oil
– Passenger Car Motor Oil (PCMO)
– Heavy-Duty Motor Oil (HDMO)
– Motorcycle Engine Oil
Hydraulic Fluids
– Mineral-based Hydraulic Oil
– Synthetic Hydraulic Oil
Gear Oil
– Manual Transmission Gear Oil
– Industrial Gear Oil
Transmission Fluids
– Automatic Transmission Fluid (ATF)
– Continuously Variable Transmission Fluid (CVT)
Greases
– Lithium Grease
– Calcium Grease
– Complex Greases
Compressor Oil
– Rotary Compressor Oil
– Reciprocating Compressor Oil
Others
– Turbine Oil
– Metalworking Fluids
– Heat Transfer Fluids - By Application (In Value %)
Automotive
– Passenger Vehicles
– Commercial Vehicles
– Two-Wheelers
Industrial Machinery
– CNC Machines
– Hydraulic Systems
Marine & Shipping
– Cargo Ships
– Ferries
Aviation
– Aircraft Engines
– Ground Support Equipment
Power Generation
– Wind Turbines
– Thermal Power Plants
Others
– Construction Equipment
– Mining Machinery - By End User (In Value %)
OEM Workshops
Independent Workshops
Transportation & Logistics Companies
Government & Institutional Buyers - By Distribution Channel (In Value %)
Direct Sales
Authorized Dealers/Distributors
Online Channels (B2B Platforms)
Retail Outlets & Auto Shops
E-commerce & Aggregator Apps - By Region (In Value %)
Central Region
Northern Region
Southern Region
East Coast Region
East Malaysia
- Market Share of Major Players (By Value/Volume), Automotive vs. Industrial Segments
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Lubricant Product Portfolio Depth, Base Oil Sourcing Strategy, Distribution Reach, Number of dealers/distributors, Local Blending Facility Presence, R&D and Innovation Capabilities, OEM Partnerships and Certifications, Revenue Contribution from Automotive vs. Industrial Segments)
- SWOT Analysis of Top Players
- SKU-Level Pricing Strategy (5W30, 15W40, Gear Oil Grades)
- Detailed Profile of Major Players
PETRONAS Lubricants International
Shell Malaysia
BP Castrol
ExxonMobil Malaysia
TotalEnergies Marketing Malaysia
Fuchs Lubricants
Idemitsu Malaysia
Sinopec Lubricants
Eneos Malaysia
Caltex (Chevron)
Repsol Malaysia
Liqui Moly
Amsoil Distributors Malaysia
UMW Lubricants
Cyclon Lubricants
- Key Consumption Clusters
- Purchase Patterns and Buying Cycle
- Budget Allocation and Procurement Process
- Pain Points and Expectations
- Decision Influencers (Technicians, Dealers, Fleet Managers)
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume (in million liters), 2025-2030
- By Average Price (USD/liter), 2025-2030


