Market Overview
The Philippines automotive doors market is valued at approximately USD ~ billion in 2025, with projections indicating significant growth in 2025. Key drivers for this market include the increasing automotive production within the ASEAN region, particularly the Philippines’ growing automotive assembly sector. The country’s car manufacturing industry is set to expand with increased foreign investments and automotive sector incentives by the Philippine government. The demand for automotive doors is also bolstered by rising consumer preferences for enhanced vehicle safety and luxury, which emphasizes the integration of advanced door mechanisms like electric and automatic systems.
Metro Manila, Cavite, and Laguna are the leading hubs for automotive production and assembly in the Philippines, with the highest concentration of both OEMs and tier suppliers. These areas are attractive for their strategic proximity to key ports, well-established industrial zones, and governmental incentives promoting the automotive sector. As the largest automotive assembly markets, they continue to dominate due to the increasing demand for both passenger vehicles and light commercial vehicles. Furthermore, their accessibility to international trade routes and robust workforce contribute to their dominance in the automotive door systems market.
Market Segmentation
By Product Type
The Philippine automotive doors market is segmented by product type into front doors, rear doors, sliding doors, liftgate, and tailgate doors. In 2025, front doors hold the largest market share, primarily driven by their functional necessity and widespread demand in both passenger vehicles and light commercial vehicles. Front doors not only offer easy access but are also crucial in enhancing vehicle safety and functionality, which has made them a focal point in OEM and aftermarket offerings. The rise in safety standards, including side-impact airbags and electronic door locks, further drives the preference for front doors.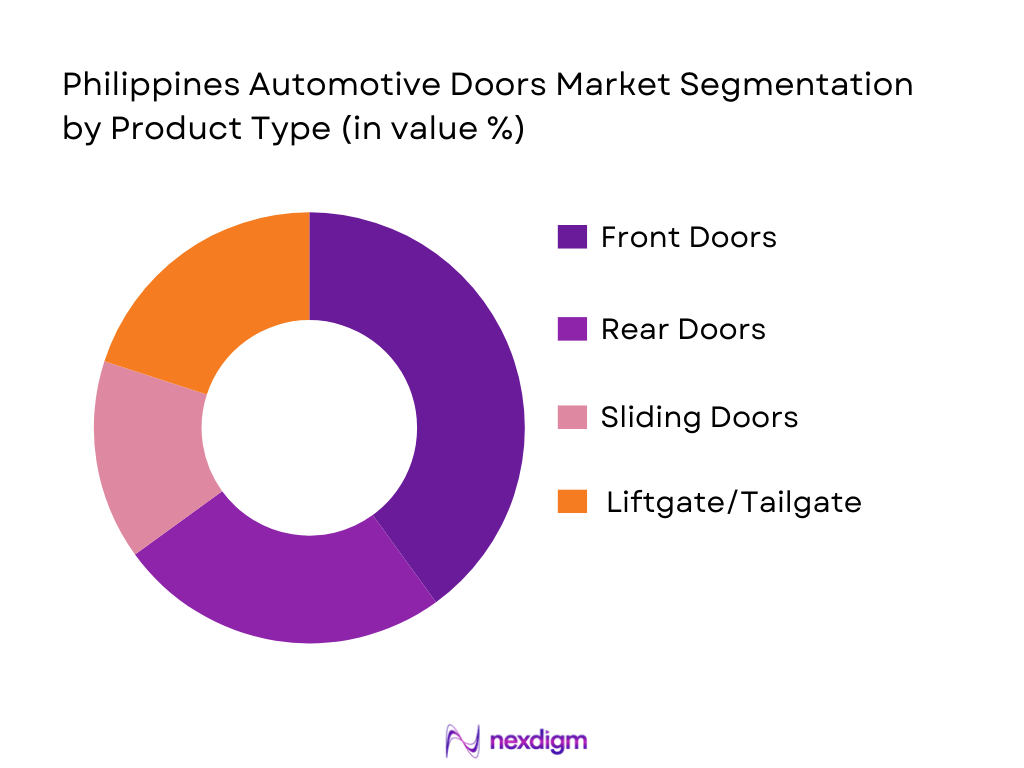
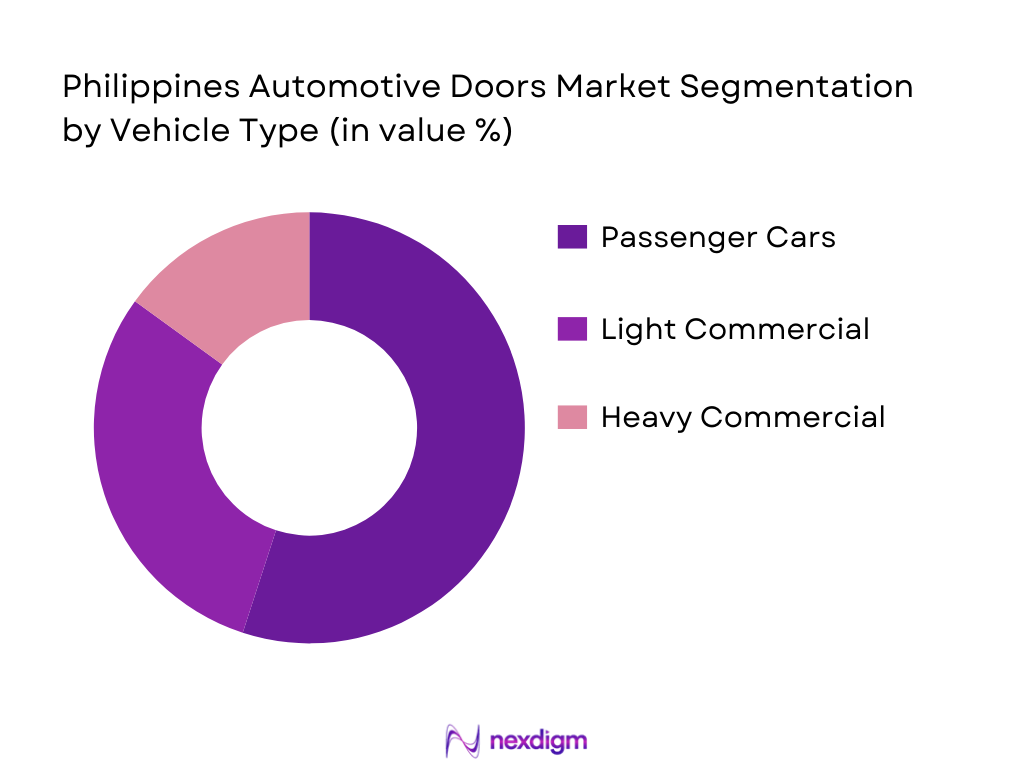
By Vehicle Type
The market is divided into passenger cars, light commercial vehicles (LCVs), and heavy commercial vehicles (HCVs). Among these, passenger cars dominate the market, holding a significant share in the Philippines. The strong preference for passenger vehicles is attributed to the growing middle class, urbanization, and increasing disposable income, which have expanded the customer base. Additionally, rising consumer awareness of safety features and aesthetic upgrades in vehicle design has led to an increased adoption of premium doors with better materials and additional functionality.
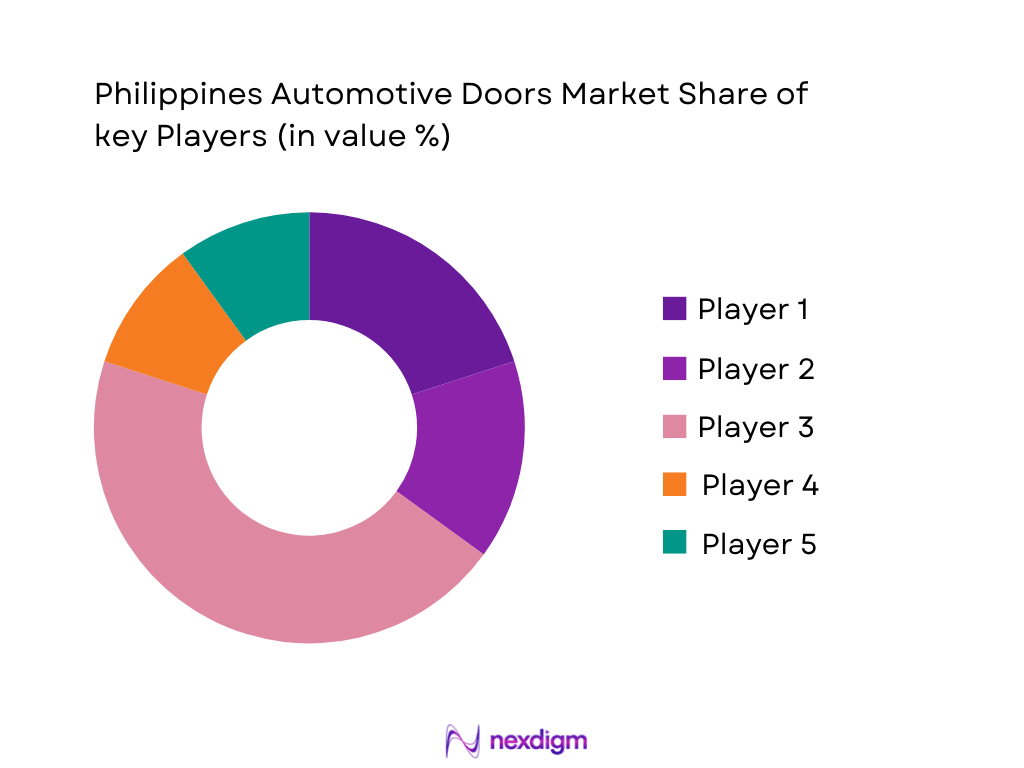
Competitive Landscape
The automotive doors market in the Philippines is competitive, with a few major players holding significant sway. Companies like Toyota Motor Philippines, Honda Cars Philippines, and Mitsubishi Motors Philippines lead in the OEM market due to their extensive production facilities and strong brand presence. These companies are focusing on enhancing the quality and design of their door systems, driving their competitive edge. Furthermore, tier suppliers like Yanfeng Automotive and Samvardhana Motherson play crucial roles in providing advanced door components and modules, further intensifying market competition.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Market Focus | Product Portfolio | Production Capacity | Technology Innovations |
| Toyota Motor Philippines | 1988 | Manila, Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Honda Cars Philippines | 1990 | Quezon City, Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Mitsubishi Motors Philippines | 1988 | Manila, Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Yanfeng Automotive | 2001 | Shanghai, China | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Samvardhana Motherson Group | 1986 | Noida, India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Automotive Doors Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Urbanization
Urbanization in the Philippines is a significant macro driver of demand in the automotive doors market, as rapid urban population growth fuels increased vehicle ownership, particularly in cities with high economic activity. The country’s urban population stood at approximately ~ million people, reflecting sustained migration to urban centers where transport options demand personal vehicles, directly influencing automotive part sales including doors. This urban expansion has also underpinned infrastructure development and rising middle‑class spending capacity, which in turn supports broader automotive adoption and demand for enhanced vehicle components. Urban hubs such as Metro Manila serve as focal points generating concentrated demand for passenger vehicles and replacement automotive doors. Access to electricity is high in urban regions at ~% of the population, supporting automotive dealerships and service centers.
Industrialization
Industrial activity in the Philippines continues to bolster the automotive production ecosystem that supports automotive doors manufacturing and supply chain development. Manufacturing output was valued at approximately USD ~ billion in 2025, increasing from USD ~ billion in 2025, indicating ongoing production strength in goods sectors linked to vehicle parts and assemblies. At the same time, manufacturing value added accounted for roughly ~ percent of GDP in 2025, showing a robust industrial base integral for automotive components production. The industrial sector’s expansion contributes to strengthening supply chains, assembly operations, and localized production of auto body parts, which are essential to producing doors and associated hardware. The industry’s employment base also remains substantial, reinforcing production capacity for automotive components.
Restraints
High Initial Costs
High initial costs present a major restraint for scaling domestic automotive doors production in the Philippines. Establishing manufacturing facilities, acquiring advanced tooling, and integrating automation require substantial capital expenditure, which is a barrier for local firms and new entrants. Large OEM players typically allocate significant budget for capital investments before achieving production economies of scale. Additionally, vehicle assembly and parts production depend heavily on imported inputs, which expose suppliers to foreign exchange fluctuations and increased landed costs. The Philippine economy posted a GDP of USD ~ billion in 2025, indicating that while demand exists, investment in industrial assets competes with other capital demands, such as infrastructure and services. These high upfront costs in manufacturing impede rapid expansion of automotive doors production capacity within the country.
Technical Challenges
Technical challenges associated with producing advanced automotive doors also constrain market growth in the Philippines. Automotive doors incorporate precision engineering elements, such as electronic locking systems, reinforcement structures, and integration with safety standards, which require high‑skill technical capabilities. The industry’s technical workforce supply must keep pace with evolving automotive technology requirements, but gaps in specialized manufacturing skills persist, affecting local production efficiency. Furthermore, the Philippine manufacturing sector share of GDP, at ~ percent, lags behind regional peers, indicating structural constraints in high‑end manufacturing activities. Such limitations affect component quality, production throughput, and the ability to meet stringent OEM technical specifications. As the automotive industry increasingly adopts smart and lightweight door technologies, addressing these technical barriers remains critical.
Opportunities
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in automotive design and manufacturing create substantial opportunities for growth in the Philippines automotive doors market. As modern vehicles increasingly incorporate smart features—including electronic locking, sensor integration, and lightweight materials—local manufacturers and part suppliers can leverage these innovations to produce high‑value door systems. The Philippine automotive industry registered improved sales performance in 2025, reflecting a decade high vehicle market performance with expanding model ranges from major OEMs, stimulating demand for advanced components. Adoption of new materials and digital manufacturing methods, such as computer‑aided design and modular assembly, can accelerate domestic suppliers’ competitiveness. Integrating technologies such as automated welding, robotics, and quality control enhances product durability and aligns local production capabilities with global standards, presenting long‑term market growth potential.
International Collaborations
International collaborations represent powerful opportunities for the Philippine automotive doors market by enabling knowledge transfer, foreign investment, and access to global supply chains. The Philippine automotive industry comprises locally assembled and imported vehicles from countries like Thailand and Indonesia, indicating strong regional linkages supporting parts sourcing and technology exchange. Collaborations between Philippine manufacturers and multinational automotive suppliers can facilitate training, joint ventures, and co‑development of components such as door modules, enhancing local capability and competitiveness. Industrial freeport zones and export processing zones in provinces like Bataan have attracted investment across manufacturing sectors, creating environments conducive to partnerships. By participating in global automotive networks, the Philippines can capitalize on its strategic geographic position in ASEAN and integrate into broader automotive component ecosystems.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the automotive doors market in the Philippines is expected to experience sustained growth driven by the government’s push for greater manufacturing localization, increasing demand for vehicle safety features, and the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). As consumer preferences shift towards advanced vehicle technologies, there will be a growing demand for smarter, more functional automotive doors, integrating sensors, electronic locks, and automation. This trend, along with continued infrastructure development, is likely to foster growth in both the OEM and aftermarket segments.
Major Players in the Market
- Toyota Motor Philippines
- Honda Cars Philippines
- Mitsubishi Motors Philippines
- Ford Philippines
- Isuzu Philippines Corporation
- Hyundai Asia Resources, Inc.
- Suzuki Philippines
- Nissan Philippines
- Yanfeng Automotive
- Samvardhana Motherson Group
- Futaba Industrial Co., Ltd.
- Magna International
- Lear Corporation
- Delphi Technologies
- Faurecia
Key Target Audience
- Automotive Manufacturers (OEMs)
- Automotive Tier 1 & Tier 2 Suppliers
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Department of Trade and Industry)
- Automotive Retailers and Dealership Networks
- Automotive Aftermarket Players (e.g., parts distributors)
- Automotive Component Manufacturers
- Logistics and Distribution Service Providers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The first phase involves conducting desk research, where we compile all major players and stakeholders within the automotive doors market in the Philippines. This is done by gathering industry-level data through secondary databases and market reports.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
This phase includes compiling historical data on market trends, production volumes, and the vehicle segment breakdown. We will evaluate OEM and aftermarket distribution channels and the resulting impact on market growth, considering the number of manufacturing plants, local versus global production volumes, and material adoption.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We will validate market hypotheses by interviewing key experts in the automotive door systems space, including OEM manufacturers, tier suppliers, and key industry professionals. These interviews will help confirm the market’s dynamics, trends, and future projections.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase involves compiling all data, including expert insights, secondary research, and historical market data. We will create a comprehensive report, analyzing the collected data and deriving accurate insights on the market dynamics, product segmentations, and competitor landscape.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions & Automotive Door System Taxonomy, Assumptions (Vehicle Production Drivers, Door Module Content), Abbreviations & Automotive Terminology, Primary & Secondary Intelligence Sources, Market Sizing & Forecast Modeling (Units, Door Content Value), Consolidated Research Approach, Limitations & Data Confidence)
- Definition and Scope of Automotive Doors
- Industry Genesis & Philippine Automotive Evolution
- Major Regulatory Timelines
- Business Cycle Analysis
- Supply Chain & Value Chain Mapping
- Growth Drivers
Rising Vehicle Ownership & Production Growth in Philippines
EV/Hybrid Incentives & Parts Tariff Policies
Demand for Lightweight & Safety‑Enhanced Doors (Material Adoption Metrics) - Market Challenges
Supply Chain Volatility (Imported Components & Lead Times)
Counterfeit Aftermarket Parts & Quality Enforcement (Quality Standards)
Tariff Structures & Compliance Costs (Tariffs & Trade Parameters) - Opportunities
Aftermarket Retrofitting & Smart Door Systems
ASEAN Export Potential for Door Components (Export Readiness)
Partnerships with Local Assemblers & Tier Suppliers (Partnership Pipeline) - Long‑Term Trends
Lightweighting & Sustainability
Integrated Safety & Sensor Door Subsystems
Digital Distribution & Aftermarket Penetration - Regulatory Landscape
Automotive Safety & Certification Norms (PS/ICC Mark & Philippine Standards)
ASEAN Harmonization Regulations
EV Parts Incentive & Compliance Framework (Incentives & Standards)
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem Mapping
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Technology & Innovation Index
- By Value, 2019-2025
- By Volume, 2019-2025
- By Average Price of Platforms/Services, 2019-2025
- By Vehicle Type (In Value %)
Passenger Vehicles (Sedans/Hatchbacks/Sub‑Compacts)
Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs/Pickups)
Heavy Commercial Vehicles (HCVs/Buses & Trucks)
EV & Hybrid Vehicles
Specialty & Niche Vehicles (Jeepneys/Utility) - By Door Type (In Value %)
Front‑Hinged Doors
Rear‑Hinged Doors
Sliding Door Systems (Vans/MPVs)
Liftgate / Tailgate Assemblies
Smart/Integrated Doors (Sensor/Control Modules) - By Material Composition (In Value %)
Steel Door Panels
Aluminum & Lightweight Alloys
Composite & Plastic Reinforced Structures
High‑Strength & Advanced Materials
Soft‑Trim & Acoustic Door Systems - By Distribution Channel (In Value %)
OEM
Aftermarket (Replacement & Retrofitting Parts)
Direct Importers & Specialty Distributors
E‑Commerce & Digital Aftermarket Platforms
Tier‑1 & Sub‑Tier Supplier Networks
- Market Share – OEM vs Aftermarket (Units & Value) (Share by Channel)
- Cross‑Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Door System Portfolio Breadth, Installed Capacity & Production Footprint, OEM Contract Wins & Aftermarket Reach, Quality & Safety Certifications, Price & Value, Positioning, R&D & Innovation Initiatives)
- Distribution & Dealer Network Strength (Channel Penetration)
- SWOT of Leading Competitors
- Pricing Benchmark (SKU & Door Content)
- Detailed Company Profiles
Toyota Motor Philippines
Mitsubishi Motors Philippines
Honda Cars Philippines
Isuzu Philippines Corporation
Hyundai Asia Resources, Inc.
Ford Philippines
Nissan Philippines, Inc.
Suzuki Philippines, Inc.
AC Industrials / AC Motors (Dealer & Component Strategies)
Francisco Motors Corporation (Local Body & Component OEM)
Sarao Motors (Local Fabrication & Utility Vehicles)
Almazora Motors Corporation (Commercial Body OEM)
Aisin Seiki / First Tier Door Subsystems
Yanfeng Automotive (Interior & Door Systems)
Samvardhana Motherson Group (Module Supplier)
- OEM Demand & Door Program Allocation (OEM Program Metrics)
- Aftermarket Customer Segments & Lifetime Demand
- Fleet Operators & Commercial Buyer Preferences
- EV Buyer Patterns & Door Feature Expectations (EV Adoption Metrics)
- Pain Points & Procurement Decision Triggers
- Future Market Size by Value, 2026-2030
- Future Market Size by Volume, 2026-2030
- Average Frame Cost Outlook, 2026-2030


