Market Overview
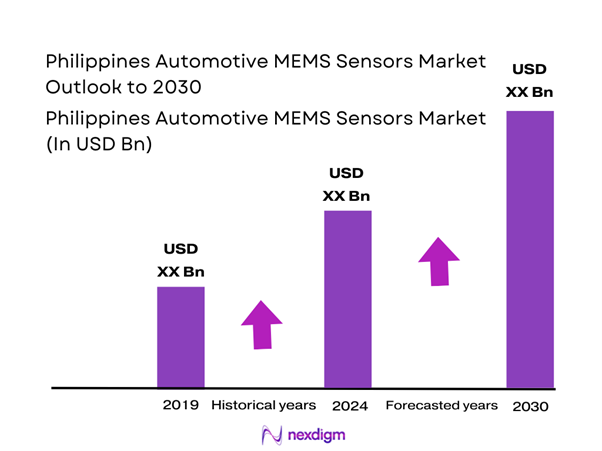
The Philippines Automotive MEMS Sensors market is valued at USD ~ million, derived from a bottom-up consolidation of vehicle production volumes, ECU penetration rates, and sensor content per vehicle across safety, powertrain, body electronics, and infotainment systems. The market expanded from USD ~ million, supported by rising vehicle electronics integration, mandatory safety features such as airbags and ABS, and increasing ECU count per vehicle platform. Growth is further sustained by the country’s expanding automotive fleet, rising electronics imports, and increasing adoption of sensor-rich electric and hybrid vehicle architectures.
The market is primarily influenced by Metro Manila and the CALABARZON region, due to their concentration of vehicle assembly plants, automotive electronics distributors, logistics hubs, and aftermarket service networks. Internationally, Japan, South Korea, and China dominate sensor supply due to established MEMS fabrication ecosystems, Tier-1 automotive electronics suppliers, and strong trade linkages with Philippine OEMs. These regions lead because of their ability to supply automotive-grade, AEC-Q qualified MEMS sensors at scale, aligned with Japanese and ASEAN vehicle platform standards widely adopted in the Philippines.
Market Segmentation
By Sensor Type
The Philippines Automotive MEMS Sensors market is segmented by sensor type into accelerometers, pressure sensors, gyroscopes, temperature sensors, and magnetometers. Accelerometers dominate this segment due to their mandatory role in airbag deployment systems, electronic stability control, rollover detection, and vibration sensing across passenger and commercial vehicles. Their dominance is reinforced by regulatory safety compliance requirements and their integration across multiple ECUs rather than single-use applications. Accelerometers are also embedded in EV battery management and traction control systems, further expanding their deployment. The aftermarket demand for replacement crash and stability sensors additionally supports this segment’s leadership, as accelerometers are among the most frequently replaced MEMS components following vehicle incidents or ECU faults.

By Application
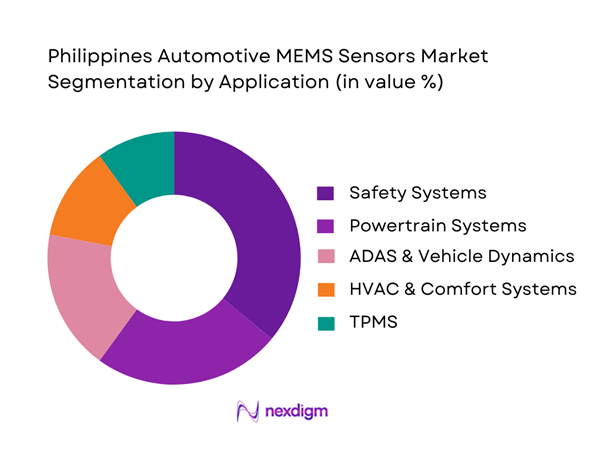
The market is segmented into safety systems, powertrain systems, ADAS & vehicle dynamics, HVAC & comfort systems, and tire pressure monitoring systems. Safety systems account for the dominant share due to mandatory airbag installations, increasing adoption of stability control systems, and heightened focus on occupant protection. MEMS sensors used in safety systems often require redundancy and multi-axis configurations, increasing sensor count per vehicle. Additionally, insurance-linked safety requirements and fleet compliance standards drive consistent replacement demand. Safety applications also benefit from stricter homologation processes, ensuring MEMS sensors remain non-discretionary components across vehicle segments, including entry-level passenger cars and commercial fleets.
Competitive Landscape
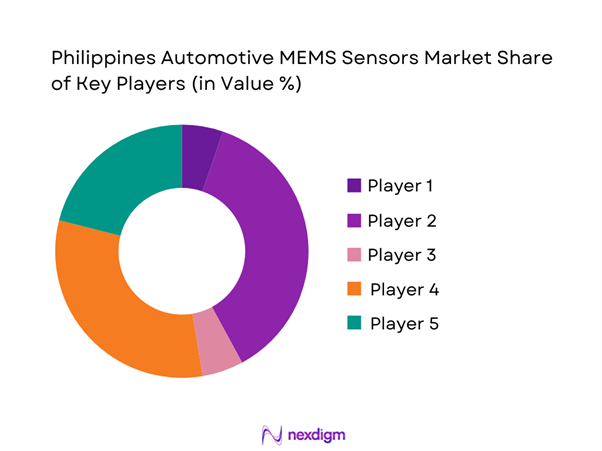
The Philippines Automotive MEMS Sensors market is highly consolidated, dominated by global semiconductor manufacturers supplying through Tier-1 automotive electronics integrators and regional distributors. The absence of local MEMS fabrication results in strong reliance on international suppliers with established automotive qualification credentials. Competitive strength is defined by sensor portfolio breadth, AEC-Q certification depth, long-term OEM supply agreements, and supply reliability rather than local manufacturing presence. Global players benefit from long validation cycles that create high switching costs, reinforcing market concentration.
| Company | Established | Headquarters | Sensor Portfolio Breadth | Automotive Certification | OEM Program Presence | Local Distribution | Packaging Capability | Reliability Record |
| Bosch Sensortec | 1995 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| STMicroelectronics | 1987 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| TDK InvenSense | 2003 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| NXP Semiconductors | 2006 | Netherlands | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Infineon Technologies | 1999 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Automotive MEMS Sensors Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Vehicle Electronics Content per Unit
The Philippines’ on-road vehicle base is large enough to sustain rising “electronics-per-vehicle” demand even without local MEMS wafer fabs, because most MEMS content is embedded in imported ECUs, modules, and sensors that flow through the country’s trade and electronics ecosystem. The macro base is expanding: nominal GDP increased from USD ~ to USD ~, supporting higher new-vehicle affordability, higher utilization intensity, and more electronics-enabled feature demand in safety, body, and powertrain systems. In parallel, the Philippines remains an electronics-linked economy—electronics exports declined while automotive electronics exports increased, indicating active throughput and ecosystem capability that also supports automotive-grade sensor/module test, calibration, and sub-assembly workflows. Even with import dependency, the country’s trade structure keeps MEMS-relevant IC categories moving: total imports were USD ~ billion and exports were USD ~ billion, showing the scale of inbound components and outbound electronics shipments that typically include sensor-containing modules. With a national scale approaching ~ registered motor vehicles, even incremental electronics additions per vehicle materially raise demand for MEMS accelerometers, gyros, pressure sensors, and microphones used across stability control, airbag trigger systems, TPMS, HVAC, and infotainment voice front-ends.
Safety Regulation Alignment
Philippines road-safety pressure is increasingly measurable and policy-visible, which structurally pulls MEMS-heavy safety systems such as airbags, ESC/ABS, rollover sensing, and crash detection. National vital statistics used by policymakers cite ~ deaths due to land transportation accidents versus ~ deaths earlier, numbers that elevate enforcement intensity and strengthen the business case for sensing, diagnostics, and event data capture in both private vehicles and fleets. This aligns with urban enforcement evidence: Metro Manila recorded ~ road-crash cases with ~ fatal collisions and ~ pedestrian-involved fatal incidents among those fatal collisions, reinforcing the value of in-vehicle sensing tied to braking, stability, and driver-alert stacks that depend on accelerometers and gyros. On the macro side, the country’s nominal GDP at USD ~ supports higher public and private spend capacity for safety-linked upgrades, including fleet compliance retrofits, newer vehicle purchases, and insurance-linked risk controls. The EV and e-mobility policy stack also indirectly strengthens safety electronics adoption: government roadmaps reference ~ registered motor vehicles and EV registration baselines used for planning, which typically require better data systems and inspection regimes, both of which intensify demand for compliant modules and validated sensor performance during type approval and periodic inspections.
Challenges
Cost Sensitivity in Assembly Plants
Cost sensitivity in Philippine vehicle assembly and downstream service channels constrains how quickly higher-MEMS feature sets penetrate beyond premium trims, because the buyer ecosystem of fleet operators, mass-market consumers, and parts distributors often prioritizes reliability and compliance over optional sensing add-ons. Macroeconomic conditions shape this dynamic: nominal GDP of USD ~ indicates expanding capacity, but the same macro environment must also absorb large trade flows, with USD ~ billion in imports and USD ~ billion in exports, which exposes electronics inputs to FX and logistics shocks that assembly plants and distributors manage through tighter BOM discipline and cautious feature adoption. The electronics export trend also signals competitive pressure: overall electronics exports moved from USD ~ billion to USD ~ billion, which can intensify cost-down mandates across electronics manufacturing services and suppliers, including automotive-grade lines. Even though automotive electronics exports grew to USD ~ million from USD ~ million, scaling often happens with strict yield, scrap, and rework targets that limit willingness to adopt higher-cost sensing architectures unless strongly justified by regulation or OEM specifications. Safety outcomes create must-have demand, but not always premium-sensor demand: with ~ land-transport accident deaths, buyers focus first on baseline safety compliance rather than advanced sensing tiers. Finally, EV adoption baselines with EV registrations at ~ show early-stage electrification where cost-optimized platforms dominate initial scaling, which can delay deployment of higher-end MEMS arrays until volume economics improve.
Limited Local Fabrication
A key structural constraint is the absence of local automotive MEMS wafer fabrication, which keeps the Philippines positioned primarily in downstream electronics value-add such as assembly, test, calibration, and sub-assembly rather than upstream silicon. The national EV roadmap itself frames near-term actions around creating uniform databases and policy coordination across agencies, signaling industrial-system building rather than a mature upstream fabrication base. This limitation increases dependence on imported MEMS die and sensor ICs, which then show up as part of broader import flows, with USD ~ billion in monthly imports versus USD ~ billion in exports, making supply availability and lead time more sensitive to global semiconductor cycles and shipping disruptions. Still, the electronics ecosystem is sizable: electronics exports were USD ~ billion from USD ~ billion earlier, and within that, automotive electronics exports increased from USD ~ million to USD ~ million, demonstrating competence in electronics operations that can support sensor-module integration even if wafers are sourced externally. The macro backdrop supports investment appetite but does not remove the barrier: nominal GDP reached USD ~, which supports industrial upgrading, yet fabrication localization requires long-horizon, scale-dependent commitments that typically exceed what an early-stage domestic automotive-electronics pull can anchor on its own.
Opportunities
Local Assembly Localization
The most realistic near-term opportunity is not MEMS wafer fabrication but deeper localization of module assembly, calibration, end-of-line testing, and service-channel integration for automotive MEMS sensor-containing systems such as IMUs for stability and airbag triggering, pressure modules for HVAC and powertrain, and MEMS microphones for infotainment. The country already demonstrates electronics throughput at scale: electronics exports were USD ~ billion from USD ~ billion, and the automotive electronics export line increased, indicating expanding automotive-electronics handling capability that can be redirected toward more localized sensor-module assembly and testing work packages. Macro capacity supports capex and workforce expansion: nominal GDP of USD ~ supports industrial investment cycles, and the trade system moving USD ~ billion of imports in a single month shows that component inflows are already large enough to anchor localization via import-parts, assemble-and-test locally models that shorten effective lead times for OEMs and fleets. Policy system-building is also underway, improving traceability and compliance infrastructure, which are prerequisites for automotive-grade localized electronics production and warranty analytics. Safety urgency strengthens the business case: with ~ deaths due to land transportation accidents, localized sensor-module test, calibration, and failure analysis capabilities become valuable to insurers, fleets, and regulators seeking verifiable system performance under Philippine operating conditions. Net effect: localization opportunities exist now in downstream steps that increase domestic value-add without requiring upstream MEMS fabrication, while directly improving supply assurance and compliance.
EV Platform Scaling
EV platform scaling in the Philippines expands MEMS demand via higher per-vehicle sensor density and a broader set of sensorized subsystems including battery thermal management, traction and stability control, cabin sensing, and telematics. Government planning baselines already indicate EV presence across segments, with ~ registered EVs across multiple vehicle categories, creating an installed base that drives ongoing service demand for sensor calibration, replacement, and diagnostics even before mass adoption. The scale of the overall fleet, with ~ registered motor vehicles, means even modest EV penetration increases absolute MEMS unit demand rapidly because EVs are sensor-richer than comparable internal combustion platforms. Macro fundamentals support continued scaling: nominal GDP at USD ~ underpins consumer and fleet investment capacity, while the country’s large monthly trade flows with USD ~ billion in imports and USD ~ billion in exports indicate that logistics channels bringing in EVs, modules, and sensor ICs are already active at meaningful scale. The electronics ecosystem can capture more EV value-add: despite overall electronics exports shifting from USD ~ billion to USD ~ billion, automotive electronics exports rose from USD ~ million to USD ~ million, suggesting increasing capability to handle automotive-grade electronics that EV platforms require.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Philippines Automotive MEMS Sensors market is expected to grow at a CAGR of ~, driven by increasing ECU proliferation, EV platform scaling, and deeper integration of safety and ADAS features across mass-market vehicles. Sensor fusion modules, higher redundancy in safety applications, and rising aftermarket replacement demand will remain key growth themes. Continued electrification, even at moderate adoption levels, will materially increase MEMS content per vehicle.
Major Players
- Bosch Sensortec
- STMicroelectronics
- Analog Devices
- NXP Semiconductors
- Infineon Technologies
- TDK InvenSense
- Murata Manufacturing
- Texas Instruments
- ROHM Semiconductor
- Melexis
- Sensata Technologies
- Omron
- Panasonic Industry
- Honeywell
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEMs
- Tier-1 Automotive Electronics Integrators
- EV Platform Developers
- Fleet Operators and Fleet Technology Providers
- Automotive Parts Importers and Distributors
- Insurance-Linked Automotive Risk Assessment Firms
- Investment and Venture Capital Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
This phase involved mapping the Philippine automotive electronics ecosystem, identifying MEMS sensor demand drivers across vehicle categories, applications, and ECU architectures using secondary databases and industry literature.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical vehicle parc data, electronics penetration ratios, and sensor deployment rates were analyzed to construct market value using a bottom-up approach.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market assumptions were validated through structured interviews with automotive electronics distributors, service centers, and component specialists operating within the Philippines.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Data triangulation was performed using vehicle production, import, and electronics consumption indicators to ensure consistency and accuracy in market estimates.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Philippines Automotive Electronics Ecosystem Mapping, MEMS Sensor Taxonomy, Market Sizing Approach, Bottom-Up Vehicle Production Mapping, Import–Export Data Correlation, Primary OEM–Tier Interview Framework, Validation Through Component-Level Teardown Analysis, Limitations and Future Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Overview Genesis
- Evolution of MEMS Adoption in Philippine Automotive Assembly
- Automotive Business Cycle Alignment
- Automotive Electronics Supply Chain and MEMS Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Vehicle Electronics Content per Unit
Safety Regulation Alignment
ECU Proliferation Rate
EV Sensor Density
Import Dependency Ratio - Challenges
Cost Sensitivity in Assembly Plants
Limited Local Fabrication
Qualification Cycles
Supply Chain Lead Time - Opportunities
Local Assembly Localization
EV Platform Scaling
ADAS Retrofit Demand - Trends
Sensor Fusion Adoption
Multi-Axis MEMS Integration
ASIC Co-Packaging - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- Installed Base by Sensor Units, 2019–2024
- Average Sensor ASP, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Cars
Commercial Vehicles
Two Wheelers
Electric Vehicles
Fleet Vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Airbag and Safety Systems
Powertrain and Engine Management
ADAS and Vehicle Dynamics
Tire Pressure Monitoring
HVAC and Comfort Systems - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Bulk MEMS
Surface MEMS
Wafer-Level Packaging
System-in-Package
Sensor Fusion Modules - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Discrete Sensor Integration
ECU-Embedded Sensors
Domain Controller Integrated Sensors
Zonal Architecture Sensors
Networked Sensor Arrays - By Region (in Value %)
Metro Manila
CALABARZON
Central Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao
- Market Share by Value and Volume
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Sensor Portfolio Breadth, Automotive Qualification Depth, Local Distribution Presence, OEM Program Wins, ASP Range, Packaging Capability, Supply Reliability, Automotive ECU Compatibility)
- SWOT of Key Players
- Pricing Benchmarking by Sensor Type
- Company Profiles
Bosch Sensortec
STMicroelectronics
Analog Devices
NXP Semiconductors
Infineon Technologies
TDK InvenSense
Murata Manufacturing
Texas Instruments
ROHM Semiconductor
Melexis
Sensata Technologies
Omron
Panasonic Industry
Honeywell
- MEMS Penetration per Vehicle
- Cost-to-Performance Trade-offs
- Procurement Cycles
- Validation & Testing Requirements
- Failure Sensitivity Analysis
- By Value, 2025–2030
- Installed Base by Sensor Units, 2025–2030
- Average Sensor ASP, 2025–2030