Market Overview
The Philippines Automotive Power Tools Market is valued at USD ~ million, derived from historical import values, distributor revenues, and workshop equipment expenditure patterns. Demand is driven by a national vehicle parc exceeding ~ units, increasing average vehicle age beyond ~ years, and the rapid expansion of independent repair workshops across urban centers. Rising labor costs, shortage of skilled mechanics, and the need for higher throughput in service bays have accelerated adoption of power tools, particularly impact wrenches, cordless drills, and grinders, replacing manual hand tools in routine automotive servicing.
Market demand is concentrated in Metro Manila, CALABARZON, Central Luzon, Cebu, and Davao, due to high vehicle density, logistics hub concentration, and dense clusters of automotive workshops. Metro Manila dominates due to the largest registered vehicle base, dealership concentration, and fleet servicing demand. CALABARZON benefits from proximity to ports and industrial zones, enabling efficient tool distribution. Cebu and Davao serve as regional automotive service hubs for Visayas and Mindanao, supported by growing urban populations, commercial vehicle activity, and inter-island logistics operations.
Market Segmentation
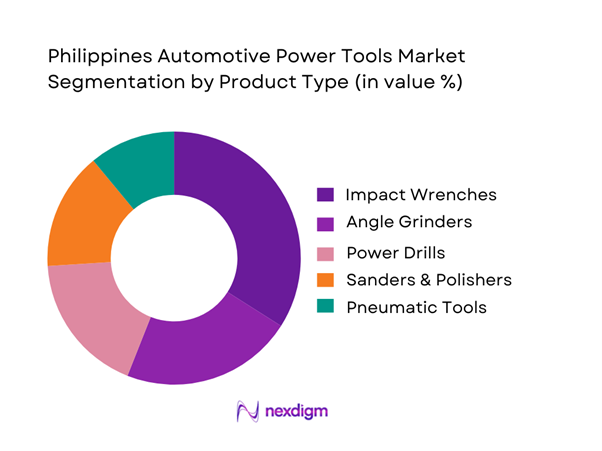
By Product Type
The Philippines Automotive Power Tools Market is segmented by product type into impact wrenches, angle grinders, power drills, sanders & polishers, and pneumatic tools. Impact wrenches dominate the product type segment, holding the largest market share due to their critical role in tire replacement, suspension servicing, and underbody repairs. Their dominance is driven by increasing vehicle ownership, growth of tire service centers, and rising preference for high-torque cordless models that reduce mechanic fatigue and service time. Impact wrenches are indispensable in both dealership workshops and independent garages, where speed and consistency directly affect daily revenue. The increasing availability of mid-priced Asian brands has further expanded adoption among small and informal workshops.
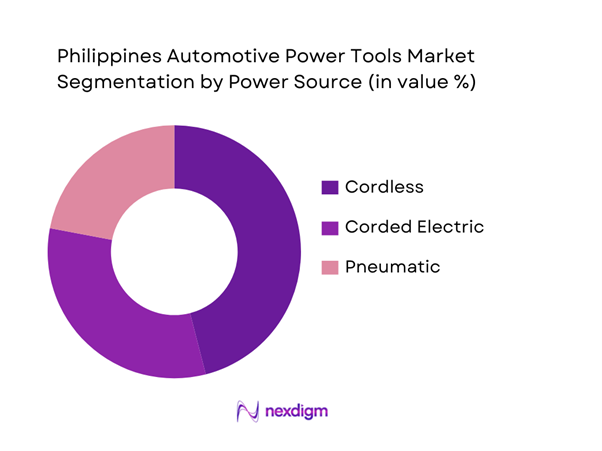
By Power Source
The market is segmented into corded electric, cordless battery-powered, and pneumatic tools. Cordless power tools dominate the power source segment, driven by advancements in lithium-ion battery technology, improved torque output, and reduced dependence on compressors and extension wiring. Workshops increasingly prefer cordless tools due to flexibility in crowded service bays and lower infrastructure costs. Cordless platforms also allow brand lock-in through battery ecosystems, encouraging repeat purchases. While pneumatic tools remain relevant in high-volume workshops, their dependence on compressed air systems limits adoption among smaller garages, accelerating the shift toward cordless solutions across the market.
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines Automotive Power Tools Market is moderately consolidated, dominated by established global brands and increasingly competitive Asian manufacturers. Global players leverage strong distributor networks, warranty coverage, and product reliability, while Asian brands compete aggressively on pricing and expanding retail presence. Market competition is driven by torque performance, battery compatibility, pricing tiers, and after-sales support, making distributor relationships a key differentiator.
| Company | Established | Headquarters | Product Breadth | Power Platform | Distribution Strength | Warranty Coverage | Price Positioning | Key End Users |
| Bosch Power Tools | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Makita | 1915 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Stanley Black & Decker | 1843 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| DeWalt | 1924 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| INGCO | 2006 | China | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Automotive Power Tools Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Vehicle Parc Expansion
The Philippines’ expanding road fleet keeps raising day-to-day demand for automotive power tools used in repair, maintenance, tire service, and body work—especially impact wrenches, angle grinders, polishers, and cordless ratchets. Macro fundamentals continue to support this utilization base: the country’s population rose to ~ persons and nominal GDP reached USD ~, indicating a larger, more active mobility-and-services economy where vehicles are worked on more frequently. New vehicle sales also stayed elevated, adding fresh vehicles into the service cycle that require periodic undercarriage work, brake jobs, suspension checks, and warranty-linked scheduled maintenance—jobs where shops increasingly prefer powered fastening and cutting tools for repeatability. This parc expansion effect is especially visible in high-density corridors where vehicle utilization and workshop throughput are structurally higher, including Metro Manila and its adjacent growth provinces, key port and logistics corridors, and major regional metros. As inflation averaged ~, workshops remain under pressure to control cycle time and rework, pushing adoption of power tools that reduce bay time per job, such as faster wheel-off operations, quicker surface preparation, and more consistent torque application with calibrated tools
Workshop Modernization Rate
Workshop modernization is a practical driver of power tool penetration as more shops shift from basic hand-tool and informal processes to structured bays, standard operating procedures, and faster turnaround commitments. The macro environment supports modernization investments, as GDP per capita reached USD ~ and a larger operating economy sustains higher volumes of service transactions, parts movement, and fleet activity that reward productivity tools. At the same time, the repair ecosystem is dominated by small enterprises, meaning modernization often happens in step changes rather than full greenfield builds, and power tools are typically among the first upgrades because the return is immediate through reduced labor hours, better consistency, and fewer comebacks on fastening-intensive jobs.
Challenges
High Import Reliance
Automotive power tools sold in the Philippines are heavily exposed to import logistics, foreign exchange movements, and global supply allocation because most leading tool brands and battery platforms are manufactured outside the country and brought in via distributors and retail channels. This structural dependence becomes more operationally sensitive in a large, import-driven economy where GDP is USD ~ and inflation is ~, conditions that make inventory planning and working-capital discipline more important for tool importers and shop buyers. When freight disruptions or supply constraints occur, tool availability can become uneven across regions, pushing informal channels and parallel imports that weaken warranty compliance and aftersales support. Import reliance also increases total lead times for professional-grade products and for safety-critical consumables that shops need continuously. For workshop operators, this often shows up as platform lock-in risk, where shortages or delayed replenishment of batteries and chargers can disrupt operations more than a missing corded tool would. Macro scale magnifies the issue, as a population of ~ supports a very large aftermarket, so even short-lived supply gaps can ripple into downtime and workaround behaviors.
Counterfeit Tool Penetration
Counterfeit power tools are a material challenge because they undermine safety, reliability, and legitimate channel economics, especially in a market where informal procurement is common. Enforcement data shows the scale of counterfeit activity in the country, with seized counterfeit goods valued at PHP ~ across the year and prior record levels also running into tens of billions of pesos, evidencing how large illicit supply can be. While those totals span many product categories, tool-specific cases have included the seizure of PHP ~ worth of counterfeit power tools, highlighting that power tools are directly implicated. From a workshop operations standpoint, counterfeit penetration creates safety and failure risk, as fake electrical and cordless tools can have substandard insulation, cells, or internal protection, increasing the probability of overheating or mechanical failure under load. It also creates hidden productivity loss, as inconsistent torque and faster wear lead to rework such as stripped bolts, poor surface preparation, and uneven finishing. Channel distortion follows when legitimate distributors and authorized dealers struggle to compete with informal or online sellers, weakening service networks and making genuine spare parts less available locally.
Opportunities
Cordless Tool Platform Adoption
Cordless tool platform adoption is a high-leverage opportunity because it directly addresses unstable shop layouts and the need for faster turnaround. The macro base supports expanding tool utilization, as GDP stands at USD ~ and population at ~, sustaining large volumes of daily vehicle movement and maintenance demand. Cordless platforms are especially attractive for automotive use cases requiring mobility and repeatability, including wheel service, undercarriage work, field repairs, roadside assistance, and quick-service bays, because technicians can standardize on one battery ecosystem across multiple tools. Inflation averaging ~ reinforces the economic rationale for cordless adoption through current operating realities, as workshops need to complete more jobs per day using the same floor space and staffing. Cordless impacts and ratchets reduce fatigue and cycle time, cordless grinders and polishers enable flexible bay assignment, and standardized battery and charger setups reduce tool sharing conflicts and downtime. The opportunity also lies in right-sizing platforms to the local service mix so that genuine cordless ecosystems displace counterfeit and grey tools by offering reliability, safety, and uptime for workshops competing on faster delivery and fewer comebacks.
Fleet Servicing and Contract Maintenance
Fleet servicing and contract maintenance is a strong opportunity because it shifts workshops from ad-hoc retail repairs to predictable, recurring workloads where power tools become mandatory for throughput consistency, documentation, and standardized processes. Macro signals support the scaling of fleet operations, as an economy of USD ~ and a population of ~ underpin expanding logistics, urban delivery, and service mobility demand that relies on vehicles with higher utilization rates and tighter uptime requirements. In fleet contexts, maintenance is time-boxed, requiring quick completion of tire rotations, brake servicing, suspension work, and minor body repairs. This requirement favors professional-grade impact tools, torque-controlled fastening workflows, powered polishing and finishing tools for minor damage correction, and durable cordless work lights for extended operating hours. Even without pricing or market-size statistics, the operational logic is clear: fleet customers value turnaround time, repeatable quality, and reduced breakdown risk, translating into tooling requirements such as redundancy, disciplined battery inventory, and consistent consumables supply.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Philippines Automotive Power Tools Market is expected to witness steady and structurally supported growth, driven by sustained expansion of the national vehicle fleet, rising complexity of automotive servicing, and increasing professionalization of independent garages. The shift toward cordless platforms will accelerate, supported by declining battery costs and higher torque capabilities. Demand from fleet maintenance operators, logistics companies, and ride-hailing vehicle servicing will further strengthen market fundamentals. E-commerce and digital tool retailing are also expected to improve market access beyond major urban centers.
Major Players
- Bosch Power Tools
- Makita
- Stanley Black & Decker
- DeWalt
- Milwaukee Tool
- HiKOKI
- INGCO
- TOTAL Tools
- Ronix Tools
- Toptul
- SATA Tools
- Einhell
- Hyundai Power Products
- Crown Power Tools
Key Target Audience
- Automotive power tool manufacturers
- Authorized automotive dealerships and service centers
- Independent and multi-brand automotive workshops
- Fleet operators and logistics service providers
- Automotive spare parts distributors and wholesalers
- E-commerce and organized tool retail chains
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
This phase involved mapping the automotive service ecosystem, including workshops, distributors, importers, and fleet operators. Extensive secondary research was conducted using trade databases, industry publications, and government statistics to identify demand drivers and pricing benchmarks.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical import data, distributor revenues, and workshop equipment expenditure patterns were analyzed to construct bottom-up market estimates. Vehicle parc data and service density metrics were used to validate demand assumptions.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market assumptions were validated through structured interviews with distributors, workshop owners, and regional sales managers using computer-assisted telephone interviews to refine pricing, volume, and product mix insights.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Final data triangulation was conducted using manufacturer disclosures and distributor inputs to ensure consistency across product categories and regions, resulting in a validated and comprehensive market model.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Scope Validation, Industry Assumptions, Abbreviations, Automotive Power Tools Classification Framework, Market Sizing Logic, Bottom-Up Demand Modeling, Top-Down Supply Validation, Primary Interviews Across Dealers and Workshops, Distributor-Level Data Normalization, Limitations and Analytical Boundaries)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution Pathway
- Timeline of Automotive Power Tools Penetration in the Philippines
- Automotive Aftermarket and Workshop Business Cycle
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Vehicle Parc Expansion
Workshop Modernization Rate
Mechanic Productivity Requirements - Challenges
High Import Reliance
Counterfeit Tool Penetration
Price Sensitivity of Informal Workshops - Opportunities
Cordless Tool Platform Adoption
Fleet Servicing and Contract Maintenance
Tool-as-a-Service and Financing Models - Trends
Shift Toward Cordless Platforms
Battery Standardization Across Brands
Demand for Ergonomic and High-Torque Tools - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Vehicles
Commercial Vehicles
Two-Wheelers
Three-Wheelers and Light Utility Vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Mechanical Repair
Tire and Wheel Service
Body Repair and Detailing
Electrical and Diagnostics Support - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Corded Electric Tools
Cordless Battery-Operated Tools
Pneumatic Power Tools - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Authorized Dealership Workshops
Independent Multi-Brand Garages
Informal and Roadside Workshops
Fleet Maintenance Centers
Tire and Quick-Service Chains - By Region (in Value %)
National Capital Region
CALABARZON
Central Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao
- Market Share of Major Players by Value and Volume
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Brand Presence and Distribution Depth, Product Portfolio Breadth, Torque and Performance Benchmarking, Pricing Tier and ASP Positioning, After-Sales and Warranty Coverage, Channel Margins and Dealer Incentives, Battery Platform Compatibility, Grey Market Exposure Risk)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis Across Key SKUs
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Bosch Power Tools
Makita
Stanley Black & Decker
DeWalt
Milwaukee Tool
Hitachi / HiKOKI
INGCO
TOTAL Tools
Ronix Tools
Toptul
SATA Tools
Einhell
Hyundai Power Products
Crown Power Tools
Dongcheng Tools
- Demand Intensity and Tool Utilization Rates
- Workshop Purchasing Power and Budget Allocation
- Compliance and Safety Expectations
- Pain Points and Replacement Decision Triggers
- Brand Loyalty and Switching Behavior
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Selling Price, 2025–2030


