Market Overview
The Philippines automotive relays market is valued at USD ~ million, derived from a five-year historical analysis of vehicle assembly volumes, imported relay units, and aftermarket replacement cycles. The market is driven by the country’s growing vehicle parc exceeding ~ registered vehicles, alongside increasing relay density per vehicle due to higher adoption of power windows, electronic mirrors, infotainment systems, and electronic safety features. Rising imports of Japanese and ASEAN-assembled vehicles, combined with limited domestic relay manufacturing, sustain steady demand across OEM and aftermarket channels.
Metro Manila dominates the automotive relays market due to its concentration of vehicle ownership, authorized service centers, fleet operators, and automotive parts distributors. Calabarzon follows closely, driven by its role as the country’s primary automotive assembly and supplier corridor, hosting major OEM plants and Tier- component integrators. Cebu and Davao contribute through growing vehicle density and aftermarket activity, particularly for commercial vehicles and two-wheelers. These regions dominate due to higher workshop density, faster replacement cycles, and stronger logistics access rather than production scale.
Market Segmentation
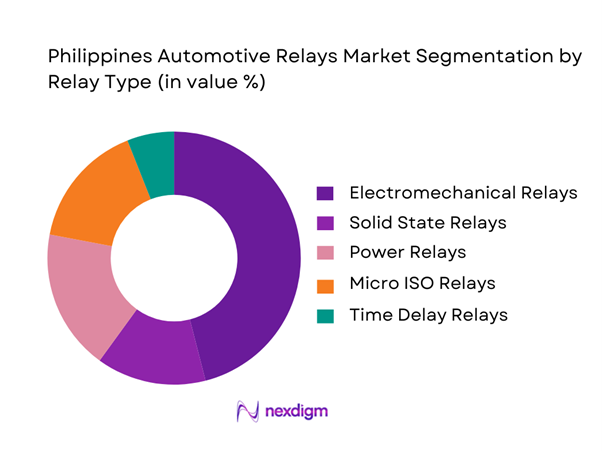
By Relay Type
The Philippines automotive relays market is segmented by relay type into electromechanical relays, solid state relays, power relays, micro ISO relays, and time delay relays. Electromechanical relays dominate the market due to their widespread application across conventional vehicle systems such as lighting, horn circuits, fuel pumps, HVAC blowers, and starter motors. These relays offer a strong balance between cost, durability, and ease of replacement, making them the preferred choice for both OEM fitment and aftermarket servicing. Given the country’s high ICE vehicle penetration and cost-sensitive aftermarket, electromechanical relays remain the default solution across passenger cars and light commercial vehicles. Their compatibility with existing wiring architectures and availability across multiple amperage ratings further reinforces their dominance.
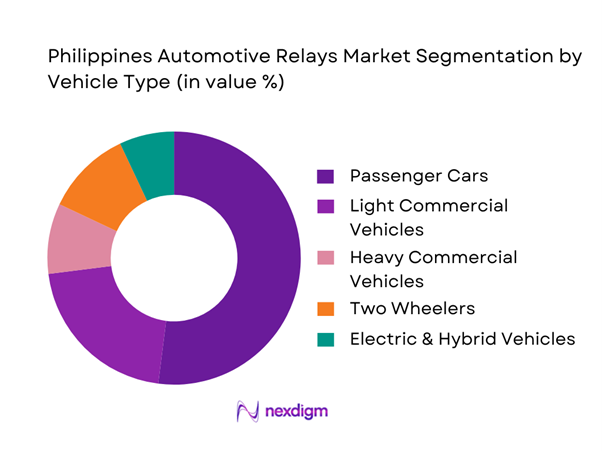
By Vehicle Type
The market is segmented into passenger cars, light commercial vehicles, heavy commercial vehicles, two-wheelers, and electric & hybrid vehicles. Passenger cars hold the dominant market share due to their large installed base and higher electrical feature penetration. Each passenger vehicle typically integrates multiple relays across body electronics, comfort systems, infotainment, and safety functions. The dominance is further reinforced by higher ownership density in urban centers and more frequent relay replacement during routine servicing. Imported Japanese and ASEAN-assembled passenger cars rely heavily on standardized relay architectures, ensuring consistent aftermarket demand. Additionally, aging passenger vehicles require relay replacements due to thermal degradation and contact wear, sustaining long-term volume dominance.
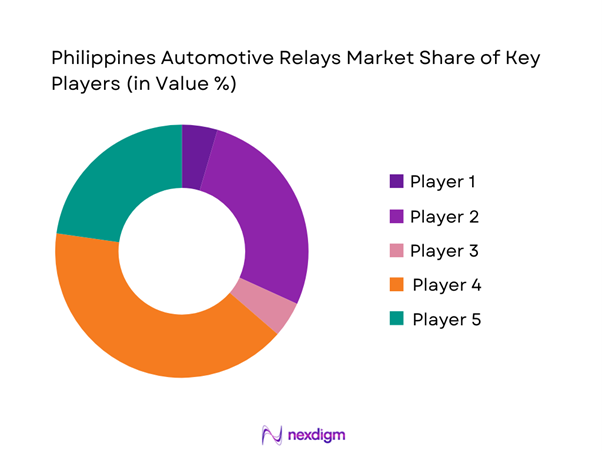
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines automotive relays market is moderately consolidated, with dominance shared between global Tier-1 automotive electrical suppliers and strong aftermarket brands distributed through authorized channels. Japanese relay manufacturers retain a structural advantage due to vehicle origin alignment, while European and US suppliers dominate premium and fleet-grade segments. Market competition is primarily driven by reliability reputation, OEM approvals, and distributor reach rather than aggressive pricing.
| Company | Established | Headquarters | Relay Portfolio Breadth | OEM Approvals | Aftermarket Presence | Voltage Coverage | Distribution Strength | Key Differentiation |
| Omron | 1933 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Panasonic Automotive | 1918 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Denso | 1949 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Bosch | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| TE Connectivity | 2007 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Automotive Relays Market Analysis
Growth Driver
Vehicle Parc Expansion
The Philippines’ automotive relay demand expands structurally with the country’s on-road vehicle base because every additional registered unit adds multiple relay “nodes” across starter and ignition, fuel pump, cooling fan, lighting, wiper and washer, horn, power windows, and HVAC circuits, then repeats as vehicles age and undergo electrical repairs. At the macro layer, the Philippines’ GDP in current US dollars increased to ~ from ~, while total population rose to ~ from ~, a scale effect that supports vehicle ownership, logistics activity, and workshop density that ultimately consumes relays through both OE-linked and aftermarket channels. On the market-activity layer, national vehicle production and sales movement across ASEAN reporting sets shows the Philippines continuing to move meaningful unit volumes through assembler and importer pipelines, sustaining relay pull-through via harness-level content and service demand. Practically, relay consumption clusters around high-congestion, high-mileage operating environments where heat, vibration, water ingress, and repeated switching cycles shorten relay life; these conditions are most visible in the country’s principal demand centers where fleet utilization, delivery density, and stop-and-go duty cycles increase electrical switching events per day.
Electrification Content per Vehicle
Relay intensity per vehicle rises as the fleet shifts from simple electrical to feature-dense electrical, even before full battery-electric adoption, because modern vehicles add more actuators, more comfort features, and more electronic loads that still require robust switching and protection. In the Philippines, electrification is already visible in the national EV sales trajectory, where government-reported EV sales increased to ~ units from ~ units, expanding the in-market base of vehicles that often carry higher-current switching requirements for thermal management, auxiliary power distribution, and safety-related power routing. Meanwhile, the macro environment supports electronics-heavy import flows, with current-dollar GDP at ~ and population at ~ correlating with sustained consumer and commercial demand for feature-rich models and fleet replenishment in logistics and ride-hailing ecosystems. Even for ICE vehicles, electrification within the car grows because OEMs add electronically controlled subsystems to comply with efficiency and safety expectations, which drives up harness complexity and increases relay count or shifts to higher-reliability, sealed, and micro-ISO formats. This trend is reinforced by the Philippines’ trade-linked consumption model, where the service ecosystem increasingly deals with relay-related failures because more circuits are switched more frequently and workshop troubleshooting often resolves to relay replacement as a fast, modular fix.
Challenges
Price Sensitivity
Automotive relay purchasing in the Philippines is highly price-sensitive because a large portion of the addressable market is served through the independent aftermarket, where buyers often optimize for immediate repair cost rather than total lifetime reliability, especially for older vehicles, motorcycles, and utility fleets with tight operating budgets. Macro fundamentals shape this behavior, as even while GDP rose to ~, the market remains income-diverse across regions, and purchasing decisions vary sharply between dealership-serviced segments and the broader parts ecosystem. Price sensitivity affects the relay market in three concrete ways: substitution toward generic or unbranded relays with weaker contact metallurgy, higher acceptance of repair-first approaches that delay replacement, and increased demand for multi-fit, high-rotation SKUs that minimize inventory burden for small retailers. It also impacts specification decisions, where fleet managers may standardize on fewer relay types to control spares, while individual consumers buy the cheapest part that restores functionality. This sensitivity becomes more visible when the cost of imports and logistics rises, as import-dependent categories like relays face volatility from freight and port throughput conditions. Official port statistics underline the magnitude of national cargo movement that underpins these flows, with shipcalls reported at ~, indicating the scale and complexity of the logistics system through which parts move, where delays and cost pressures can transmit into retail pricing and consumer behavior.
Counterfeit Parts Influx
Counterfeit and substandard automotive electrical parts are a persistent constraint in the Philippines because relays are small, easy to replicate visually, and hard to validate without testing, yet failures can still look like wiring issues or battery and alternator problems, making root-cause accountability difficult. This encourages gray-market circulation, especially in price-sensitive channels, and can suppress demand for higher-quality relays when buyers lose trust in the category’s reliability. Macro scale makes enforcement challenging, with a population of ~ and a trade-linked economy supported by GDP of ~, as the country processes high volumes of imported goods, creating many entry points and distribution layers where counterfeit products can slip into supply chains. The risk is amplified by the breadth of ports and inter-island logistics routes, where parts can be broken down into small consignments and redistributed. While enforcement actions are episodic, the structural issue is that counterfeit parts create false savings that later convert into repeat failures, electrical fires, or roadside breakdowns, outcomes that raise fleet downtime and reduce consumer willingness to pay for legitimate brands. For distributors and fleet buyers, this means the cost of quality assurance rises, with documentation, supplier audits, batch traceability, and controlled channels becoming competitive advantages rather than overhead..
Opportunities
EV Relay Demand
EV growth creates an upgrade path for the Philippines relay market because electrified platforms typically increase the need for higher-reliability switching and power distribution components, either through relays designed for higher duty cycles and harsher thermal environments, or through specialized high-voltage switching architectures where applicable. The key is that opportunity can be demonstrated using current, verified adoption signals rather than future projections, with government-reported EV sales rising to ~ units from ~ units, meaning more electrified vehicles are already entering service networks that will require electrical parts maintenance, diagnostics, and eventual replacement cycles. This sits on top of a large macro base, with GDP at ~ and population at ~ providing the consumption and mobility scale that supports ongoing vehicle turnover and electrification adoption in commercial and private fleets. The immediate relay opportunity is also indirect, as EVs and hybrids intensify demand for high-quality low-voltage relays used in thermal management, cabin HVAC control, lighting, and auxiliary systems, because these loads remain critical regardless of propulsion type. As EV penetration grows in delivery fleets and corporate pools, maintenance programs become more standardized, which tends to favor branded, validated relays and documented sourcing, raising the quality bar and improving margins for legitimate distributors.
High-Reliability Relays for Fleet Vehicles
Fleet operations in the Philippines, including logistics vans, last-mile delivery, buses, UV services, and utility vehicles, create a premium opportunity for high-reliability relays because uptime has a direct economic value, where a single immobilized vehicle can disrupt route density and service-level commitments. Current trade and logistics statistics highlight the operational scale that fleets support, with shipcalls reported at ~, underscoring how much movement and distribution activity is occurring through the national transport system, activity that depends heavily on commercial vehicles and service fleets across ports, warehouses, and urban delivery routes. Macro scale further supports this, with GDP at ~ and population ~ implying large daily mobility and goods demand, which increases fleet utilization intensity and therefore electrical switching cycles. High utilization accelerates relay wear in circuits that cycle constantly, creating a business case for sealed, vibration-resistant, temperature-stable relays that reduce repeat failures. The opportunity is also channel-driven, as fleets buy through structured procurement, making them receptive to documented quality and preventive replacement schedules rather than reactive spot buys.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Philippines automotive relays market is expected to witness sustained growth driven by increasing vehicle electrification, rising average vehicle age, and higher electrical complexity per vehicle. Expansion of hybrid and electric vehicle models will accelerate demand for high-voltage and sealed relays. Additionally, fleet modernization, logistics sector expansion, and increased adoption of electronic safety systems will further support long-term demand. While import dependency remains high, opportunities exist for localized assembly and private-label aftermarket expansion.
Major Players
- Omron
- Panasonic Automotive
- Denso
- Bosch
- TE Connectivity
- Mitsuba
- Hella
- Fujitsu Components
- Song Chuan
- Hongfa
- LS Automotive
- Eaton
- Finder Relays
- Schrack Technik
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEMs and vehicle assemblers
- Tier-1 and Tier-2 automotive electrical suppliers
- Automotive aftermarket distributors and wholesalers
- Fleet operators and logistics companies
- Authorized service centers and large workshop chains
- Electric vehicle manufacturers and system integrators
- Investment and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research begins with mapping the complete automotive electrical ecosystem in the Philippines, including OEMs, relay suppliers, distributors, and aftermarket channels. Extensive desk research using trade databases and automotive production data is conducted to identify variables influencing relay demand.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical data on vehicle registrations, import volumes, and relay replacement cycles is compiled and analyzed. Market sizing is constructed using a bottom-up approach, correlating relay usage per vehicle with total vehicle parc and servicing frequency.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market assumptions are validated through structured interviews with distributors, workshop operators, and automotive electrical component suppliers. These interactions provide operational insights on pricing, failure rates, and demand variability.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All quantitative and qualitative inputs are synthesized to produce a validated market model. Cross-checks are performed against regional ASEAN benchmarks to ensure accuracy and reliability of final estimates.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Automotive Relay Taxonomy Mapping, Abbreviations, Bottom-Up OEM–Aftermarket Sizing Logic, Import–Assembly Consumption Model, Channel-wise Demand Attribution, Primary Interviews with OEM Tier-1s/Distributors/Assemblers, Validation Through Customs & Vehicle Parc Data, Limitations and Forward-Looking Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Timeline of Relay Technology Adoption in Philippine Vehicles
- Automotive Production, Import, and Vehicle Parc Linkage
- Automotive Electrical & Electronics Value Chain Mapping
- Growth Drivers
Vehicle Parc Expansion
Electrification Content per Vehicle
Relay Replacement Cycles
Import Dependency
Wiring Complexity - Challenges
Price Sensitivity
Counterfeit Parts Influx
Import Lead Times
Low Localization of Electrical Components - Opportunities
EV Relay Demand
High-Reliability Relays for Fleet Vehicles
Local Assembly Potential
Diagnostic-Linked Relay Replacement - Trends
Miniaturization
High-Temperature Resistance
Sealed Relays
PCB-Integrated Relays - Regulatory & Compliance Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Industry Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Price, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Cars
Light Commercial Vehicles
Heavy Commercial Vehicles
Two Wheelers
Electric & Hybrid Vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Powertrain & Engine Management
Body Electronics
Lighting Systems
HVAC & Thermal Systems
Safety & Control Systems - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Electromechanical Relays
Solid State Relays
Micro ISO Relays
Power Relays
Time Delay Relays - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Wired Relays
PCB-Mounted Relays
Socket-Mounted Relays - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
OEM & Tier-1 Assembly
Authorized Aftermarket Distribution
Independent Workshops & Retailers
Fleet Operators
E-commerce Automotive Parts Platforms - By Region (in Value %)
NCR
Luzon (Ex-NCR)
Visayas
Mindanao
- Market Share of Major Players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Product Portfolio Breadth, Relay Load Ratings Coverage, Vehicle Application Coverage, OEM Approval Status, Local Distribution Strength, Price Positioning, Aftermarket SKU Depth, Supply Lead Time)
- Competitive Positioning Matrix
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing Benchmarking Analysis
- Detailed Company Profiles
TE Connectivity
Omron
Panasonic Automotive
Bosch
Denso
Mitsuba
Hella
Song Chuan
Fujitsu Components
Hongfa
LS Automotive
Nidec
Schrack Technik
Finder Relays
- OEM Demand Characteristics
- Aftermarket Consumption Patterns
- Fleet & Commercial Vehicle Usage
- Purchasing & Decision-Making Criteria
- Pain Points & Unmet Needs
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Price, 2025–2030


