Market Overview
The Philippines Automotive Software Updates (OTA) Market is being pulled forward by (a) a fast-expanding new-vehicle parc that is increasingly software-defined, and (b) the country’s improving mobile broadband environment that makes SOTA/FOTA campaign delivery viable at scale. New-vehicle sales reported by CAMPI–TMA rose from ~ units to ~ units, widening the addressable base for infotainment, telematics, and ECU update orchestration. Globally, automotive OTA update revenue moved from USD ~ billion to USD ~ million, reflecting how OEMs monetize and protect vehicles through remote patching, feature enablement, and cybersecurity fixes.
Market activity in the Philippines concentrates in Metro Manila (NCR) first, followed by Cebu and Davao corridors, because these areas concentrate OEM dealer networks, fleet operators, higher-income buyers, and denser 4G/5G coverage needed for dependable downloads and install windows. On the supply side, Japan and South Korea dominate OTA-enabled vehicle volumes in the country through mainstream OEM line-ups; U.S. and Europe dominate many enabling layers (cloud, cybersecurity tooling, middleware), while China is rising via connected EV introductions and aggressive feature roadmaps. Network readiness also supports this clustering—Globe reported ~ million 5G subscribers rising to over ~ million, while site rollouts increased urban coverage, reinforcing NCR-led adoption for OTA-heavy use cases.
Market Segmentation
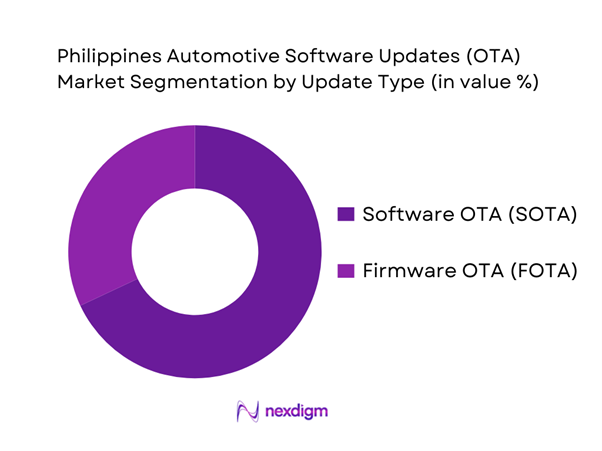
By Update Type
The Philippines Automotive Software Updates (OTA) Market is segmented by update type into Software Over-the-Air (SOTA) and Firmware Over-the-Air (FOTA). Recently, SOTA typically dominates deployments because it maps directly to high-frequency consumer-facing improvements—infotainment UX upgrades, app ecosystem fixes, navigation/media enhancements, and feature enablement—and can be delivered with lower perceived functional risk than deep firmware changes. SOTA also aligns with the country’s dealer reality: reducing workshop visits matters in dense NCR traffic, and OEMs increasingly position connected services (apps, remote functions, infotainment refreshes) as part of ownership experience. OEM references to OTA processes commonly anchor on user-approved downloads and installs via the head unit and connected services stack, reinforcing why SOTA is the “default” OTA motion for many mainstream models.
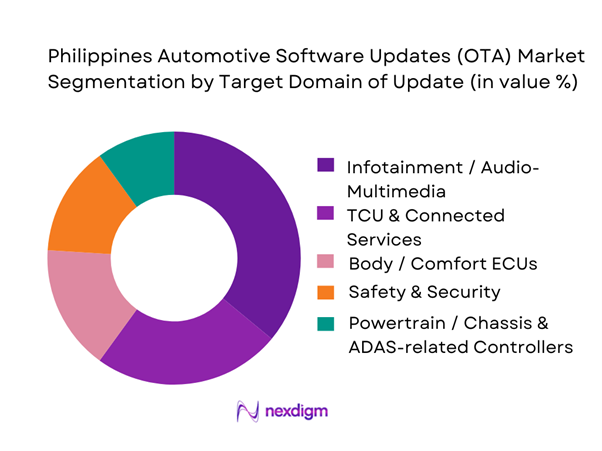
By Target Domain of Update
The Philippines Automotive Software Updates (OTA) Market is segmented by target domain into Infotainment/Audio-Multimedia, Telematics Control Unit (TCU) & Connected Services, Body/Comfort ECUs, Safety & Security, and Powertrain/Chassis & ADAS-related controllers. Recently, infotainment/audio-multimedia typically leads OTA event volume because OEMs can ship improvements with clearer customer value and lower homologation friction than safety-critical control domains. Toyota’s guidance, for example, emphasizes OTA updates for audio-multimedia platforms, and Hyundai’s connected-services materials highlight OTA experiences tied to navigation/infotainment stacks and user notification/approval flows. As a result, the “dominant” OTA pathway in the Philippines tends to start at infotainment and connected-services layers, then expands into broader ECU domains as OEM confidence, cybersecurity governance, and regulatory alignment mature.
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines Automotive Software Updates (OTA) Market is shaped by a layered ecosystem: OEMs decide OTA scope and cadence; Tier-1 suppliers provide embedded stacks and update agents; cloud and cybersecurity vendors deliver campaign tooling, device identity, encryption, and monitoring; and local telcos/dealers influence connectivity quality and customer enablement. Competition is therefore less about a single “OTA vendor” and more about end-to-end reliability across: package creation → campaign scheduling → differential delivery → secure install → rollback/fail-safe → post-update telemetry and compliance.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | OTA Stack Role | Typical OTA Scope | Security/Compliance Posture | Cloud/Hosting Model | Key Differentiator for PH-Relevance | Integration Footprint |
| Bosch Mobility / Bosch Engineering | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Continental (incl. CAEdge direction) | 1871 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| HARMAN (Samsung) | 1980 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elektrobit | 1986 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Toyota Connected / OEM OTA frameworks | 2016 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |

Philippines Automotive Software Updates (OTA) Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Connected-car roadmap expansion
The OTA market expands as the Philippines adds more “OTA-addressable” vehicles each year and as OEMs bring more connected trims into dealer pipelines. CAMPI–TMA reported ~ units sold and then ~ units, increasing the pool of vehicles that can receive infotainment/telematics software releases over cellular or Wi-Fi. This is reinforced by the country’s macro capacity to spend on mobility and digital services: GDP of USD ~ billion and GDP per capita of USD ~, while the population base reaches ~—a large installed base for OEM apps, telematics subscriptions, and update campaigns that reduce workshop dependence. As importers broaden connected line-ups (remote diagnostics, app-based ownership, cloud-linked head units), OTA becomes the practical mechanism to keep software baselines aligned across fast-growing model parks.
Smartphone-first user experience expectations
OTA adoption in the Philippines is tightly linked to smartphone-led ownership journeys—users expect app-driven notifications, consent prompts, and seamless head-unit refresh cycles similar to phone OS updates. This expectation is more commercially viable because the macro base supports large-scale digital consumption: GDP per capita of USD ~ and population of ~, enabling OEMs to treat connected services as a mainstream feature rather than a niche premium add-on. Network-side readiness underpins smartphone-first UX: ~ million mobile subscribers and an increase in 5G subscriptions from ~ million to more than ~ million, supporting larger in-vehicle software packages and faster download windows in dense corridors where smartphone tethering and in-car data plans are common. As these conditions strengthen, OEMs push more frequent UX iterations—navigation logic, voice/assistant integrations, app compatibility—using OTA rather than dealer visits.
Challenges
Network coverage variability
OTA reliability is constrained by uneven coverage and inconsistent throughput outside priority urban corridors, which affects download success rates, install timing, and rollback safety—especially for larger infotainment or multi-ECU packages. Even as headline readiness improves, the Philippines still shows a practical “coverage gradient” that shapes where OEMs confidently push large campaigns. Disclosures show a large national subscriber base of ~ million, and reporting notes 5G subscription growth from ~ million to more than ~ million, but these adoption numbers do not remove last-mile variability in provincial routes, mountainous areas, and inter-island travel. For OEMs, this means campaign design must be engineered for intermittent connectivity (resume support, delta updates, staged rollouts, Wi-Fi offload prompts). The macro backdrop reinforces why the challenge matters: with USD ~ billion GDP and ~ population, the market scale demands consistent service experience across many geographies—yet the network reality can create uneven post-sale outcomes, forcing dealer-assisted OTA or “service-bay completion” steps for customers outside dense coverage zones.
Gray-market device and vehicle impact
Gray-market vehicles and non-standard device ecosystems complicate OTA eligibility, identity provisioning, and aftersales governance. In the Philippines, enforcement signals around smuggling show that undocumented vehicle inflows are actively pursued; the Bureau of Customs reported tracking down ~ smuggled luxury sports cars as part of enforcement actions, illustrating how non-compliant imports exist and can bypass formal service ecosystems. For OTA programs, the impact goes beyond luxury cases: gray-market units may run unsupported head units, region-mismatched telematics stacks, or missing compliance documentation, making it risky to push remote updates at scale without bricking risk or legal exposure. The macro base—USD ~ billion GDP and ~ population—creates strong demand for vehicles across price tiers, which can enlarge the incentive for informal channels. OEMs and importers therefore face a local challenge: they must build VIN validation, entitlement control, and dealer gating processes so OTA campaigns reach only authorized baselines, while still supporting customer experience in a market where informal flows exist.
Opportunities
Feature monetization and software feature unlocks
An immediate opportunity is using OTA for software feature unlocks (infotainment bundles, navigation enhancements, remote convenience functions, connected safety add-ons) because it converts the growing vehicle parc into an addressable digital channel without requiring hardware retrofits. This opportunity is supported by current macro capacity and current connectivity scale rather than future projections: GDP per capita of USD ~ and GDP of USD ~ billion, supporting consumer willingness to pay for convenience and service experiences in urban centers, while the population reaches ~—a large base for tiered digital offerings. Vehicle flow continues to expand the eligible base—CAMPI–TMA sales rose from ~ to ~, meaning more vehicles sold with capable head units and TCUs that can receive entitlements over-the-air. Connectivity makes feature delivery practical: ~ million mobile subscribers and expanding 5G usage from ~ million to more than ~ million, enabling richer in-car digital experiences that can be updated or unlocked remotely.
Managed OTA services for importers and fleets
A Philippines-specific growth opportunity is “managed OTA” for importers and fleets—outsourcing campaign operations, compliance logging, incident response, and dealer enablement to specialized service operators. This is attractive in a market where importer structures and diverse model baselines raise operational complexity, while fleet operators prioritize uptime and predictable maintenance planning. Current indicators support the readiness for managed models: CAMPI–TMA sales increased from ~ to ~, expanding the number of vehicles whose software must be maintained; ~ million mobile subscribers signal broad connectivity reach in key operating corridors, enabling remote execution rather than workshop-only workflows. Privacy governance also makes managed capability valuable: ~ breach notifications in an official reporting period and a public breach statement show how incident handling and reporting discipline matter in connected ecosystems. With GDP of USD ~ billion and ~ population, the scale is large enough for importers and fleets to justify standardized operating playbooks—secure delivery, audit logs, consent capture, and dealer escalation—without relying on ad-hoc processes.
Future Outlook
Over the next planning cycle, the Philippines Automotive Software Updates (OTA) Market is expected to deepen from infotainment-centric OTA into broader multi-ECU, feature-on-demand, and cybersecurity patching programs as OEMs expand software-defined architectures. Growth is reinforced by rising vehicle volumes, denser 5G footprints, and stronger attention to data governance under the country’s privacy and security expectations for personal data handling. OTA maturity will increasingly be measured by campaign success rate, delta-update efficiency, rollback discipline, and incident response readiness, not only by “OTA availability.”
Major Players
- Bosch Mobility / Bosch Engineering
- Continental
- HARMAN
- Elektrobit
- Qualcomm
- NXP Semiconductors
- Microsoft
- Amazon Web Services
- HERE Technologies
- Airbiquity
- KPIT Technologies
- Toyota
- Hyundai
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEM Country Organizations & National Sales Companies
- Authorized Dealer Groups and Dealer Management Operators
- Fleet Owners and Fleet Management Operators
- Ride-hailing and Mobility Platform Operators
- Commercial Vehicle & Public Transport Operators
- Telecommunications Operators and Connectivity Providers
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We build an OTA ecosystem map for the Philippines covering OEMs, Tier-1s, cloud/security vendors, telcos, and dealer networks. Desk research consolidates OTA feature availability, connected-services penetration signals, and regulatory constraints around data handling and cybersecurity expectations.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historical automotive volume indicators (new vehicle sales, mix shifts) and overlay connectivity readiness (4G/5G expansion signals) to size the “OTA-addressable parc.” We structure OTA revenue drivers by campaign type: infotainment updates, telematics updates, ECU updates, and feature enablement.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validate assumptions via CATIs with OEM aftersales heads, dealer service directors, Tier-1 program leads, and telco enterprise teams. Validation focuses on update frequency, failure/rollback rates, customer consent flows, and workshop deflection impact.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We triangulate findings using OEM documentation, supplier technical disclosures, and Philippines policy frameworks for personal data processing. Final outputs emphasize operational KPIs (update success, delta efficiency, downtime) and adoption constraints (coverage, privacy, support readiness).
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Scope Boundaries, OTA Taxonomy FOTA SOTA Firmware Configuration, Assumptions and Exclusions, Abbreviations, Data Triangulation Framework, Bottom-Up Build vehicle parc OTA-capable base attach, Top-Down Build software and services spend OEM programs, Primary Research Approach OEMs importers dealers fleets telcos Tier-1s, Validation via Expert Panels, Scenario Building connectivity and regulation, Limitations and Confidence Scoring)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis software-defined vehicle shift connected services evolution
- OTA Adoption Timeline in the Philippines model-line readiness importer-led rollouts
- Philippines Automotive Digital Ecosystem Map OEMs importers dealers telcos cloud cybersecurity regulators
- Value Chain and Data Flow Architecture vehicle TCU eSIM MNO cloud campaign manager vehicle
- Growth Drivers
Connected-car roadmap expansion
Smartphone-first user experience expectations
Fleet uptime and maintenance optimization economics
Warranty cost reduction through remote updates
Cybersecurity patch urgency - Challenges
Network coverage variability
Gray-market device and vehicle impact
Fragmented model mix and software baselines
Integration debt across ECUs and platforms
Customer consent and data privacy friction - Opportunities
Feature monetization and software feature unlocks
Managed OTA services for importers and fleets
Fleet-first OTA deployment strategies
Retrofit telematics OTA enablement
Compliance-as-a-service and audit tooling - Trends
Software-defined vehicle architectures
Domain and zonal controller migration
Differential and delta update packaging
Edge caching and bandwidth optimization
Cryptographic signing and secure boot enforcement - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- Installed Base OTA-capable vehicles and update volume, 2019–2024
- Service Revenue 2019–2024
- Cost-to-Serve and Margin Structure, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Cars
SUVs and Utility Vehicles
Light Commercial Vehicles
Buses and Fleet Vans
Two-Wheeler and Three-Wheeler Connected Platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Powertrain and Emissions-Related Software
Body and Comfort ECUs
ADAS and Active Safety Software
Infotainment and Digital Cockpit
Telematics Remote Diagnostics and Vehicle Health - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
TCU-Based OTA Embedded Modem
Gateway or Domain Controller-Led OTA
Infotainment-Led OTA
Dealer-Assisted Hybrid OTA
OBD or Aftermarket Telematics Mediated OTA - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
4G LTE
5G
Wi-Fi Offload
Multi-IMSI eSIM Profiles
Store-and-Forward Edge Caching - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
OEM and Regional HQ Controlled Programs
Philippines Importers and Distributors
Dealer Networks
Fleet Operators
Public and Enterprise Mobility Operators
- Competitive Intensity Map OEM-led versus platform-led models
- Cross Comparison Parameters (OTA capability depth by ECU domain, campaign management sophistication, security controls and key management, compliance and audit readiness, connectivity strategy eSIM Wi-Fi caching, integration footprint vehicle OS cloud dealer systems, operational KPIs success rollback time-to-patch, Philippines deployment practicality local support dealer enablement telco partnerships)
- Competitive Benchmarking Matrix feature parity latency tooling observability incident response
- Partnership and Route-to-Market Mapping OEM importer Tier-1 telco cloud alliances
- Company Profiles
Toyota Motor Philippines
Ford Philippines
Mitsubishi Motors Philippines
Nissan Philippines
Hyundai Motor Philippines
Kia Philippines
Isuzu Philippines
Mercedes-Benz Philippines
BMW Philippines AC Motors
Bosch Mobility
Continental Automotive
HARMAN Samsung
Qualcomm
Sibros
Airbiquity
- OEM and distributor OTA readiness assessment
- Dealer network operational impact and training readiness
- Fleet and enterprise SLA and compliance requirements
- Customer consent onboarding and digital journey mapping
- Vendor selection and procurement criteria
- By Value, 2025–2030
- Installed Base OTA-capable vehicles and update volume, 2025–2030
- Service Revenue 2025–2030
- Cost-to-Serve and Margin Structure, 2025–2030


