Market Overview
The Philippines automotive welding equipment market is valued at USD ~ million. The market is best tracked through import proxies because most welding power sources, cutters, and automation-ready welding packages used by vehicle OEMs, Tier-1s, and collision-repair networks are imported rather than locally manufactured at scale. For example, the Philippines’ imports of electric machines and apparatus for arc welding (HS 851531) reached USD ~ million in 2024 visible in trade tables, compared with USD ~ million imported from China alone in 2023—highlighting both the import-driven nature of demand and the strong role of low-to-mid price arc-welding platforms in workshop replenishment and capacity additions.
Dominance in the market concentrates around the Philippines’ main industrial and vehicle-servicing clusters where automotive assembly, body-building, parts fabrication, and dense repair ecosystems create repeat demand for MIG/MAG, TIG, spot welding, and plasma cutting. Metro Manila anchors distribution, fleet maintenance, and large multi-branch collision-repair chains; CALABARZON (Laguna–Cavite–Batangas–Rizal–Quezon) concentrates industrial parks and supplier factories that require higher-duty cycle welding and QA discipline; and Central Luzon adds logistics/industrial spillover that supports fabrication and workshop modernization. On the supply side, China and Japan dominate equipment inflows due to breadth of product range, availability of consumables and parts ecosystems, and distributor footprints that can support service, training, and warranty turnaround.

Market Segmentation
By Welding Technology / Equipment Category
Arc welding systems dominate because they match the Philippines’ largest volume of automotive work: collision repair, body fabrication for commercial vehicles, brackets and jigs, and general aftermarket maintenance. MIG/MAG platforms are favored for speed, forgiving operation, and compatibility with common mild-steel body and chassis jobs, while inverter-based units reduce power draw—important for workshops operating with constrained electrical infrastructure. Arc also benefits from the widest distributor ecosystem, simpler technician training pathways, and faster serviceability versus more capital-intensive laser or robotic cells. Even where OEM-adjacent suppliers adopt spot welding and jigs, arc remains the universal capacity layer that scales across sites and skill bands—from informal garages to multi-branch body shops.
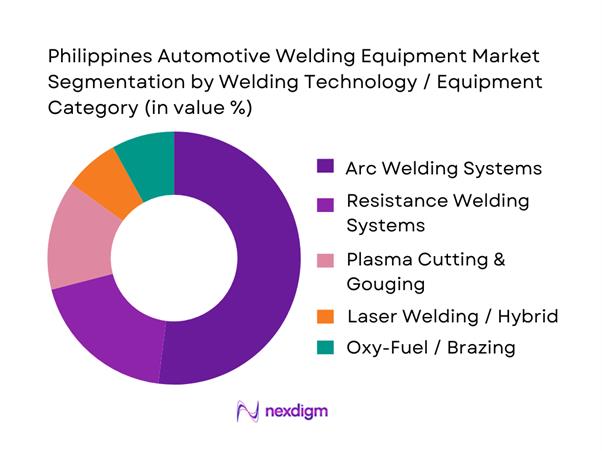
By Automotive End-Use
Collision repair and body shops dominate because the Philippines has a highly fragmented yet dense repair ecosystem, where steady accident repair, repainting, and refurbishment drive recurring demand for welders, cutters, torches, wire feeders, and shop-grade safety accessories. This segment buys frequently—either replacing entry units, upgrading to higher duty-cycle inverters, or adding dedicated machines for aluminum-capable TIG and thin-sheet MIG with better control. The business model also supports equipment bundling, making the body-shop segment commercially attractive and easier to serve at scale. In contrast, OEM or assembler procurement cycles are fewer, more specification-heavy, and often tied to automation projects, while supplier workshops may centralize purchases under industrial capex governance, reducing transaction frequency.
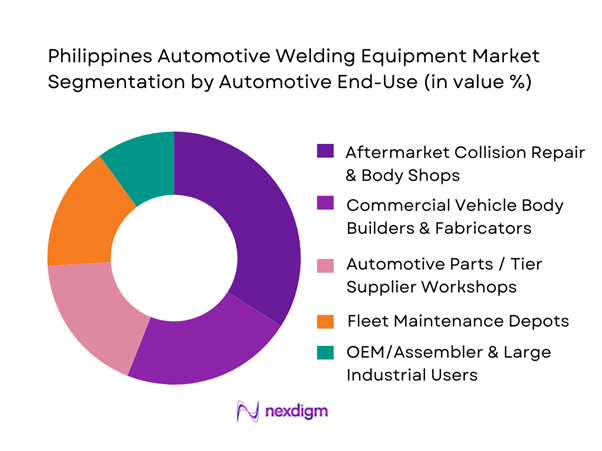
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines automotive welding equipment market is distribution-led: global OEM brands and industrial technology leaders compete through local dealers, industrial supply houses, and service partners who differentiate on uptime, training, consumables availability, and application support. Competition typically stratifies into premium industrial systems, mid-tier value systems, and price-competitive imports optimized for fast replacement cycles in small workshops.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | Philippines Go-to-Market | Core Automotive-Relevant Portfolio | Automation Readiness (Robotic/MFDC/Interfaces) | Service & Training Model | Consumables Ecosystem | Typical Buyer Fit |
| Lincoln Electric | 1895 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ESAB | 1904 | Sweden (global) | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Miller Electric (ITW) | 1929 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Fronius | 1945 | Austria | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Panasonic Welding Systems | 1918 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Automotive Welding Equipment Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Vehicle Parc Servicing Load
The Philippines’ automotive welding-equipment demand is anchored in routine repair and maintenance load created by a large on-road vehicle base and a growing macro utilization economy. The regional consolidation for motor vehicle classification shows ~ registered road motor vehicles in the referenced snapshot, reinforcing sustained workshop throughput for chassis repair, exhaust fabrication, bracket and fixture welding, and underbody corrosion remediation. On the macro side, the Philippines’ GDP is ~ and the population is ~, indicating large-scale mobility needs and continuous service demand that keeps repair bays active and equipment duty cycles high. Together, the combination of a large registered vehicle stock and a large, still-expanding user base sustains high-frequency welding jobs in independent garages, fleet workshops, and dealer body shops—supporting consistent replenishment of consumables and periodic replacement of power sources and feeders.
Body Repair Demand
Collision and body repair directly drives welding equipment usage through panel replacement, structural pull-and-weld operations, and subframe and crossmember repairs that require consistent weld quality and repeatability. The Philippines’ scale effects are evident in national fundamentals: GDP of ~ and GNI per capita of ~ support ongoing vehicle utilization, higher repair ticket sizes in formal shops, and more frequent restoration of accident-damaged vehicles rather than immediate replacement. A parallel proxy for active repair ecosystems is the presence of formalized, accredited service networks that indicate a structured aftermarket footprint where welding is a recurring capability requirement. In practice, higher traffic density and continuous vehicle use convert into repeat demand for welders, cutters, and related accessories—especially for body repair clusters around large urban corridors where shop density and turnaround-time expectations are higher.
Challenges
Import Dependence
Import dependence remains a structural constraint because a significant portion of welding power sources, torches, consumables, and electronics-heavy spares are sourced internationally, creating vulnerability to supply disruptions and longer replenishment cycles. While the market-specific import bill for welding equipment varies by classification and supplier mix, the macro trade footprint shows an economy deeply integrated into global flows, where workshop equipment availability is influenced by port throughput, distributor inventory policies, and FX-driven reorder timing. External debt stocks total ~ and GDP is ~, underscoring sensitivity to external financing conditions and imported-input continuity for tool-and-equipment channels. For welding buyers, this translates into periodic scarcity for certain torches and consumables, uneven availability of compatible spares across brands, and a practical preference for models with the strongest local service network and interchangeable consumables.
Counterfeit and Gray Market Presence
Counterfeit and gray-market circulation is enabled when a large tool-and-equipment ecosystem meets fragmented retail channels, creating risks around fake consumables, re-labeled torches, substandard cables, and non-compliant power sources. Market conditions that support this include high-volume trade exposure and a large base of small, price-sensitive workshops. The Philippines’ population of ~ expands the addressable base for low-priced equipment, while GNI per capita of ~ indicates wide dispersion in purchasing power, often leading micro-shops to prioritize lowest upfront outlay. In welding, the consequences are operational: inconsistent wire chemistry or low-quality electrodes can increase spatter and rework; substandard torches can overheat; counterfeit PPE and cables increase safety risks. This challenge elevates the importance of traceability, verified warranty channels, and distributor-led training.
Opportunities
Collaborative Welding Cells for SMEs
A major growth opportunity is SME-friendly collaborative welding set-ups—standardized jigs and fixtures, repeatable process settings, and compact cell layouts that raise productivity without requiring large-scale automation budgets. The Philippines has strong conditions for this kind of upgrade because the economic base can support toolcapex diffusion: personal remittances received of ~ contribute to consumer and small-enterprise spending power, while GNI of ~ signals broad economic scale that supports equipment distribution into secondary cities. In the automotive context, collaborative cells are most relevant for repetitive repair and fabrication tasks where cycle-time consistency matters. The current opportunity is visible in the installed base dynamics, where adding basic fixtures, documented weld procedures, and more stable inverter MIG platforms can lift throughput immediately.
Lightweight Material Repair Solutions
Lightweighting and mixed-material vehicle fleets create a near-term opportunity for specialized repair solutions—improved MIG/MAG control for thinner steels, better heat input management, and accessory ecosystems that help body shops execute repairs more cleanly. This opportunity is supported by continued expansion in the vehicle user base and spending capacity: population of ~ alongside GNI per capita of ~ increases the number of vehicles maintained over longer lifecycles. Current workshop economics favor faster, cleaner repairs, where distortion control reduces rework and paint correction and improved bead quality supports structural integrity expectations. As modernization progresses, workshops increasingly value equipment that can handle thin-gauge work with stable arcs and reduced spatter.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Philippines automotive welding equipment market is expected to expand as workshops modernize toward higher duty-cycle inverters, safer operations, and repeatable weld quality driven by insurer expectations, fleet uptime pressures, and tighter tolerances in body fabrication. Adoption of automation-ready platforms should rise first among Tier suppliers and larger body builders, while the mass workshop base continues to refresh arc platforms and plasma cutting capacity. Supply-side competition will intensify through dealer service differentiation, faster spare-parts availability, and bundled training that reduces rework and consumable waste.
Major Players
- Lincoln Electric
- ESAB
- Miller Electric (Illinois Tool Works)
- Fronius International
- Panasonic Welding Systems
- OTC Daihen
- Kemppi
- Hypertherm
- Colfax / ESAB group solutions
- Kobe Steel
- ABB
- FANUC
- Yaskawa Motoman
- Ador Welding
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEMs and vehicle assemblers
- Tier-1 and Tier-2 automotive component manufacturers
- Commercial vehicle body builders and upfitters
- Collision repair networks and large multi-branch body shops
- Fleet owners and maintenance depots
- Industrial distributors, welding equipment dealers, and service partners
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We begin by mapping the automotive welding ecosystem across OEMs, suppliers, body builders, collision repair chains, and distributors. Desk research consolidates technology variables, buyer specifications, and channel structures to define the market boundaries.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile trade-linked and channel indicators to construct demand baselines, linking equipment categories to end-use intensity. We also evaluate the alignment of product mix with buyer tiers.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validate assumptions through structured expert calls with distributors, service engineers, and workshop owners to confirm buying triggers, replacement cycles, service pain points, and the practical dominance of specific technologies across automotive job profiles.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We synthesize findings into segmentation and competition views, triangulating technology adoption, channel behavior, and buyer requirements. Final outputs emphasize actionable implications related to portfolio positioning, route-to-market, and capability priorities.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Scope Boundary Conditions, Market Sizing Approach, Bottom-Up Demand Modeling, Top-Down Trade and Production Proxy Modeling, Primary Interview Framework, Expert Validation, Data Triangulation, Sensitivity Analysis, Limitations and Forward Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Ecosystem Timeline of Key Brands, Channel Partners, and Service Networks
- Business Cycle and Demand Seasonality
- Automotive Welding Value Chain
- Growth Drivers
Vehicle Parc Servicing Load
Body Repair Demand
Local Fabrication Expansion
Workshop Modernization - Challenges
Import Dependence
Counterfeit and Gray Market Presence
Skilled Labor Shortage
After-Sales and Spare Parts Latency - Opportunities
Collaborative Welding Cells for SMEs
Lightweight Material Repair Solutions
Bundled Fume Control Systems
Rental-to-Own and Leasing Models - Trends
Pulse MIG Adoption for Thin Gauge Welding
Aluminum and Advanced Steel Repair
EV Safety-Compliant Welding Practices
Digitally Logged Welding Programs - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- Supply Chain, Pricing, and Procurement Analysis
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Unit Shipments, 2019–2024
- By Installed Base, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price Bands, 2019–2024
- By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Inverter MMA and Stick Welders
MIG and MAG Power Sources
TIG Systems
Resistance Spot Welding Systems
Stud Welding Systems
Plasma Cutting Systems - By Application (in Value %)
Panel Repair and Body Welding
Structural Frame Welding
Auto Parts Fabrication
Bus and Truck Body Building
EV Battery and Lightweight Component Welding - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone Analog Welding Systems
Digitally Controlled Welding Systems
Synergic and Pulse-Controlled Systems
Data-Logging Enabled Welding Systems
IoT-Ready and Network-Integrated Systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
OEM Vehicle Assembly Plants
Tier 1 and Tier 2 Auto Parts Manufacturers
Collision Repair and Body Shops
Fleet Maintenance Workshops
Bus, Truck, and Special Vehicle Builders - By Region (in Value %)
NCR
CALABARZON
Central Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao
- Competitive Positioning Matrix
Go-to-Market Models - Cross Comparison Parameters (Product Coverage Depth, Performance Envelope, Arc Quality Toolset, Automation Readiness, After-Sales Capability, Consumables and Torch Ecosystem, Safety and Compliance Stack, Commercial Strength)
- Company SWOT Snapshots
- Pricing Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Lincoln Electric
ESAB
Fronius
Panasonic Welding Systems
OTC Daihen
Miller Electric
Kemppi
Hyundai Welding
Denyo
Hobart
Hypertherm
Jasic
EWM
GYS
Lorch
- OEM and Tier Supplier Requirements
- Collision Repair Workshop Requirements
- Bus and Truck Body Builder Requirements
- Fleet Workshop Requirements
- Purchasing Criteria and Vendor Shortlisting
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Unit Shipments, 2025–2030
- By Installed Base, 2025–2030
- By Average Selling Price Bands, 2025–2030


