Market Overview
The Philippines Connected Glucose Meters market (covering connected self-monitoring blood glucose meters and continuous/flash glucose monitoring devices, along with key monitoring consumables) is valued at USD ~ million, anchored by rising diabetes management intensity and a fast-maturing “monitor-to-app-to-care team” workflow across private hospitals, diabetes clinics, and homecare settings. Momentum is reinforced by expanding public health funding capacity—PhP ~ billion in government health expenditure and PhP ~ billion in primary healthcare spending—supporting higher screening, treatment continuity, and device utilization through stronger primary care touchpoints.
Market activity is most concentrated in Metro Manila (NCR) and the broader Luzon corridor, where specialist density, large private hospital networks, and higher purchasing power accelerate adoption of connected meters and CGM/FGM, while provincial growth tracks improving infrastructure and rising chronic disease burden. On the supply side, the United States and Germany remain important supplier countries for medical devices due to deeper technology portfolios and established regulatory and channel relationships in the Philippines. Demand intensity is also supported by an expanding older population base, with ~ people aged ~+ and a rising elderly share (from ~ to ~ of the population).
Market Segmentation
By Product Category
The Philippines Connected Glucose Meters market is segmented by product category into Connected SMBG (Bluetooth glucometers + strips/lancets), CGM/FGM Sensors, and CGM/FGM Durables (readers/transmitters). Recently, Connected SMBG holds the dominant market share due to its lower entry cost, strong retail pharmacy availability, and entrenched physician/patient familiarity—especially for type ~ diabetes self-management where fingerstick confirmation remains common. Bluetooth syncing, trend summaries, and shareable logs make connected SMBG a “step-up” upgrade from basic meters without the recurring sensor cost profile of CGM. At the same time, CGM/FGM is expanding quickly in intensive insulin users, pregnancy care pathways, and high-variability cases, supported by specialist adoption and private pay uptake.

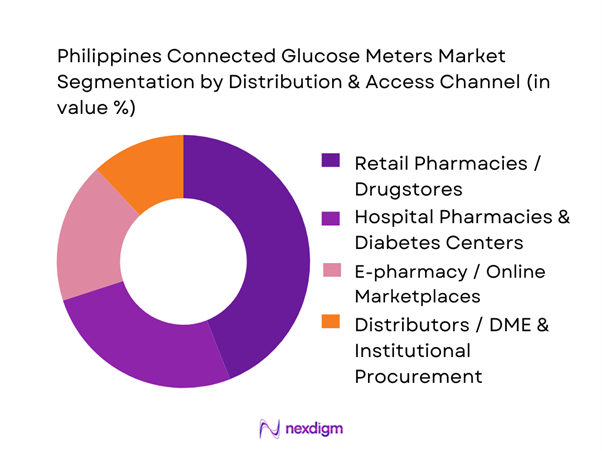
By Distribution & Access Channel
The market is segmented by distribution & access channel into Retail Pharmacies/Drugstores, Hospital Pharmacies & Diabetes Centers, E-pharmacy/Online Marketplaces, and Distributors / DME & Institutional Procurement. Retail pharmacies/drugstores dominate market share because they are the default refill point for strips/lancets, enable repeat purchases with minimal friction, and sit closest to day-to-day patient demand. Major chains in urban hubs further amplify product education and brand visibility, while hospital pharmacies and diabetes centers concentrate CGM starts through endocrinology guidance and device training. E-pharmacy is rising fastest for replenishment and price discovery, but trust, after-sales support, and authenticity concerns keep many users anchored to physical channels—especially for higher-ticket CGM components.
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines Connected Glucose Meters market is influenced by a mix of global leaders and value-focused meter brands, with competition shaped by app ecosystem quality, consumables availability, channel access (drugstores vs hospital starts), and after-sales/service confidence. Across the broader diabetes care devices context, the market is described as semi-consolidated with several major multinational players shaping product standards and partnerships.
| Company | Established | Headquarters | Core Connected Glucose Portfolio | App / Data Ecosystem | Clinical Positioning | Philippines Channel Strength | Training & After-Sales Model | Typical Buyer Focus |
| Abbott | 1888 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Roche Diabetes Care | 1896 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Dexcom | 1999 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| LifeScan | 1981 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Ascensia Diabetes Care | 2016 | Switzerland (global operations) | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |

Philippines Connected Glucose Meters Market Dynamics and Industry Analysis
Growth Drivers
Diabetes monitoring intensity
The Philippines’ monitoring intensity is fundamentally anchored in a large and active diabetes base: the adult population is ~, with ~ adults living with diabetes—creating a sustained need for repeat testing (strips/lancets) and more frequent, data-rich tracking via connected meters and CGM/FGM ecosystems. The clinical and public-health burden is also visible in mortality reporting: the Philippine Statistics Authority recorded ~ deaths due to diabetes mellitus, keeping diabetes among the top causes of death and reinforcing physician insistence on better home logs and adherence support.
On the macro capacity side, the Philippine economy posted USD ~ billion in GDP (current prices), which matters because out-of-pocket chronic care purchases rise as household income pools expand and formal employment improves access through corporate programs. These demand forces are concentrated in highly connected urban regions where routine follow-ups are common and patients can integrate readings into mobile health routines—an adoption pattern amplified by digital access scale: ~ million people (aged ~+) used the internet under the national ICT household survey results, providing the baseline for app-based monitoring, reminders, and caregiver sharing that connected glucose meters rely on.
Shift to connected self-care
Connected self-care is rising because the Philippines now has both the health need and the digital rails to make app-led monitoring practical at scale. On health need, diabetes prevalence data show ~ adults living with diabetes, while PSA mortality tallies include ~ diabetes deaths—two hard indicators that intensify demand for structured self-management beyond occasional clinic visits. On the digital rails, national ICT results report ~ million internet users (aged ~+), enabling core connected-meter behaviors such as Bluetooth sync, photo-based meal logging, time-stamped readings, and family caregiver access—features that convert episodic SMBG into usable longitudinal data.
Macro capacity matters because connected self-care still requires discretionary spend and smartphone access: data place the Philippines at USD ~ billion GDP (current prices), and GDP per capita at USD ~ (current US$), which helps explain why uptake is strongest in Metro Manila and higher-income Luzon corridors where patients can sustain strip replenishment and (for some cohorts) CGM consumables.
Challenges
Device affordability
Affordability remains a major constraint because connected SMBG is recurring-cost heavy (strips) and CGM/FGM is both device- and consumable-intensive, while a large share of demand is still out-of-pocket in practice. The macro indicators show why affordability is uneven across geographies: GDP per capita at USD ~ (current US$), which implies many households must prioritize essential spending and may delay upgrades from basic meters to connected ones, or from SMBG to sensor- Based monitoring. This is particularly important in a market where diabetes burden is large (~ adults living with diabetes), meaning the affordability barrier affects a very large cohort and directly shapes segment mix (connected SMBG tends to scale faster than CGM where benefits coverage is limited).
On the system side, even when public capacity expands, funds must stretch across many needs: Philippine budget documentation for the Department of Health shows P~ billion total available appropriations for FY ~, which must cover broad programs beyond diabetes—so connected devices are not automatically de-risked by public spending. Meanwhile, employment gains (~ employed) help, but employment alone doesn’t guarantee device support unless employers or payers explicitly include glucose monitoring in benefits.
Strip/sensor continuity
Continuity is a structural challenge because glucose monitoring is replenishment-driven; any disruption to strips (SMBG) or sensors (CGM/FGM) immediately breaks adherence and reduces trust in the technology. The scale of the problem is proportional to the diabetes base: ~ adults living with diabetes creates heavy, steady demand for consumables and increases the stakes of even short disruptions. The Philippines’ geography and distribution reality add friction: ensuring consistent supply across island clusters requires strong distributor planning and last-mile coverage, and continuity becomes more complex for sensor-based products that require specific SKUs and sometimes training-linked activation. Macro signals underline why distributors prioritize high-volume corridors first: GDP USD ~ billion (current prices) and the concentration of purchasing power in NCR/Luzon typically pull inventory toward urban demand, which can leave provincial users dependent on online replenishment or periodic restocking. The good news is that payments infrastructure is strong enough to support recurring refills: data shows ~ million digital merchant-payment transactions and ~ million P2P transfer transactions, which helps patients purchase from authorized online pharmacies or send money for refills.
Opportunities
RPM programs
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is a high-potential opportunity because the Philippines now has the disease burden, digital access, and payment infrastructure to scale structured monitoring beyond clinic walls—without needing to cite future projections. The disease base is substantial: ~ adults living with diabetes, and PSA-reported ~ diabetes deaths reinforce the need for tighter monitoring and earlier intervention pathways.
Digitally, the RPM backbone exists: ~ million internet users (aged ~+) enables app-based readings upload, care-team dashboards, and caregiver sharing that can be standardized into RPM workflows. On the transaction layer, data reports ~ million digital merchant-payment transactions and a monthly digital payments value of USD ~ billion, which supports recurring purchases of strips/sensors and potential RPM service fees collected through digital channels.
Payer-led adherence models
Payer-led adherence models are an attractive opportunity because they can reduce churn and improve outcomes by turning “device purchase” into a structured care journey—supported by today’s employment scale and primary-care contracting expansion efforts. The labor base is large: ~ employed persons and a ~ labor force create a sizeable addressable pool for employer-linked payers/HMOs to sponsor adherence interventions (reminders, coaching, refill automation) tied to connected logs.
On the public-side payer ecosystem, circulars show ongoing operational strengthening of provider networks and outpatient benefit pathways (including Konsulta-related circular actions), which supports broader primary-care engagement where glucose monitoring can be embedded into routine follow-ups. The demand-side justification is straightforward and current: ~ adults living with diabetes and ~ diabetes deaths recorded by PSA indicate that adherence improvements are not optional; they are a practical lever to reduce complications and stabilize long-term costs.
Future Outlook
Over the next five to six years, the Philippines Connected Glucose Meters market is expected to expand steadily as diabetes screening and long-term management increase, and as connected monitoring becomes more routine in private care pathways. CGM/FGM adoption will rise through specialist prescribing, better patient education, and broader availability of sensors and onboarding support. Growth will also be driven by a continued shift to hybrid care models—clinic initiation plus home monitoring—where app-linked logs and data sharing improve adherence and therapy adjustments. The key “make-or-break” factors will remain affordability, authenticity assurance, and channel execution.
Major Players
- Abbott
- Roche Diabetes Care
- Dexcom
- LifeScan
- Ascensia Diabetes Care
- Medtronic
- Insulet
- Tandem Diabetes Care
- Ypsomed
- i-SENS
- Sinocare
- ARKRAY
- Terumo
- AgaMatrix
Key Target Audience
- Medical device manufacturers & brand principals
- Philippines medical device distributors / importers
- Retail pharmacy chains & drugstore buying teams
- Private hospital networks & hospital pharmacy procurement heads
- Diabetes clinics / endocrinology centers
- Digital health & chronic care platform operators
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We build a Philippines-specific ecosystem map covering manufacturers, authorized distributors, pharmacy chains, hospitals/clinics, and regulators. Secondary research is combined with structured variable mapping to define the key demand and supply drivers for connected glucose monitoring adoption. This step clarifies scope, product definitions, and channel pathways.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historical market direction across device sales, consumables velocity, and channel mix to construct the market baseline. The model separates connected SMBG and CGM/FGM economics, and tests assumptions against observed replenishment patterns and typical onboarding routes (hospital start vs retail purchase).
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses are validated via expert consultations with distributors, pharmacists, diabetes educators, and clinicians across NCR and major provincial hubs. These interactions validate product movement, brand preference logic, availability constraints, and the practical barriers that shape patient switching behavior.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We triangulate findings across bottom-up channel checks and top-down healthcare context signals to finalize sizing, segmentation, and competitive insights. Final outputs are stress-tested for consistency across product category dynamics, channel realities, and regulatory/compliance considerations relevant to connected devices.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Device Classification and Scope Boundary, Market Sizing Approach, Triangulation Framework, Primary Research Approach, Secondary Research Sources, Pricing/Channel Checks, Data Validation and Outlier Treatment, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Adoption Flywheel
- Industry Timeline
- Demand Drivers Context
- Ecosystem Map
- Growth Drivers
Diabetes monitoring intensity
Shift to connected self-care
E-commerce penetration
Clinician demand for logs
Workplace wellness - Challenges
Device affordability
Strip/sensor continuity
Counterfeit/parallel imports
Data privacy expectations
Adherence drop-off - Opportunities
RPM programs
Payer-led adherence models
Pharmacy-led diabetes coaching
Bundled vitals kits
Clinic digital pathways - Trends
CGM-to-SMBG ecosystem convergence
App coaching
Simplified onboarding
QR-based education
Interoperability push - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Unit Shipments, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019–2024
- By Recurring Consumables Revenue Mix, 2019–2024
- By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
SMBG connected meters
Flash glucose monitoring
Real-time CGM
Hybrid bundles
- By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Bluetooth
NFC/scan-based
Cloud-synced
Offline-to-sync
Multi-user sharing
- By Application (in Value %)
Type 1 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes on insulin
Type 2 diabetes non-insulin
Gestational diabetes
Prediabetes/high-risk
- By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Hospital pharmacy
Retail pharmacy chains
Independent drugstores
E-pharmacy
Marketplaces
- By Region (in Value %)
NCR
North/Central Luzon
South Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Out-of-pocket
HMO/insurer support
Employer wellness
Clinic subscription
Device+consumable bundles
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Philippines FDA authorization status, Authorized channel partners, App ecosystem strength, Data-sharing features, Interoperability, Consumables continuity, Anti-counterfeit controls, After-sales & education, customer support footprint)
- Pricing and Pack Architecture Benchmarking
- Go-to-Market Strategy Review
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Abbott
Dexcom
Medtronic
Roche Diabetes Care
Ascensia Diabetes Care
LifeScan
i-SENS
Sinocare
ForaCare
ACON Laboratories
Terumo
B. Braun
MedExpress
Watsons Philippines
- Use-Case Mapping
- Purchasing Journey and Decision-Making Unit
- Adoption Barriers and Drop-Off Points
- Channel Preferences
- Needs, Desires, and Pain Point Analysis
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Unit Shipments, 2025–2030
- By Average Selling Price , 2025–2030
- By Recurring Consumables Revenue Mix, 2025–2030


