Market Overview
The automotive seat adjuster market (which includes electric seat adjustment systems: motors/actuators, tracks, gearboxes, ECUs, switches, and seat memory modules) is valued at USD ~ million, with the prior-year value at USD ~ million, as reported in an automotive seat adjuster market sizing dataset. Growth is primarily driven by rising fitment of powered seats in higher-trim passenger cars and SUVs, plus wider adoption of comfort/safety functions such as multi-way adjustment, lumbar support, and memory seats that increase electronics/actuator content per seat.
Within the broader seat-adjuster ecosystem, China, Japan, and South Korea dominate production scale and technology depth because they anchor major OEM platforms and Tier-1 seating supply chains, supporting high volumes of electromechanical adjusters and seat ECU/module integration. In Southeast Asia, Thailand and Indonesia are the key regional assembly hubs that attract vehicle production programs (and therefore OEM seat-system sourcing), while the Philippines demand base is concentrated in major metro purchasing clusters where higher-trim imported/assembled models more frequently include powered seat packages.
Market Segmentation
By Component Type
The Philippines electric seat adjustment systems market is segmented into seat motors & linear actuators, seat tracks/rails & mechanical transmission, seat control modules & memory modules, switch packs & HMI, and sensors & wiring sub-harness. Seat motors & linear actuators dominate because every powered-seat function ultimately scales with actuator count—way systems add motors for slide, recline, height, cushion tilt, lumbar, and sometimes headrest/bolster movement. OEM “comfort packages” typically increase the number of actuators per seat faster than they increase other electronics, and replacement demand also concentrates here due to wear on drive units, gear wear, and exposure to dust/humidity (common in daily urban commuting). This makes motors/actuators the highest “content-per-vehicle” line item within electric adjustment, particularly for front seats in SUVs and premium variants.

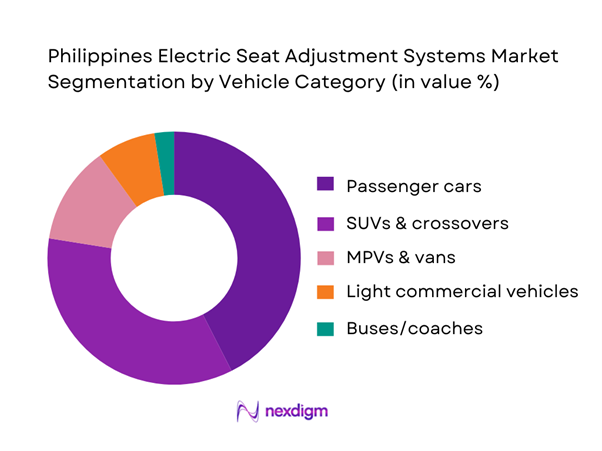
By Vehicle Category
The Philippines electric seat adjustment systems market is segmented into passenger cars, SUVs & crossovers, MPVs & vans, light commercial vehicles, and buses/coaches. SUVs & crossovers dominate because trim ladders in this body style more frequently bundle powered driver seats (and increasingly powered passenger seats) as part of “mid-high” variants that compete on comfort, perceived premium positioning, and family usability. SUVs also tend to carry higher average transaction values, allowing OEMs to absorb the bill-of-materials of multi-motor systems and memory modules. In Metro Manila and other urban centers where stop-and-go driving and longer daily commutes are common, consumer preference shifts toward comfort features (power adjustment, lumbar support) and convenience (memory seating for multi-driver households). This combination pushes higher powered-seat penetration in SUVs compared with entry-level passenger cars and utilitarian fleets.
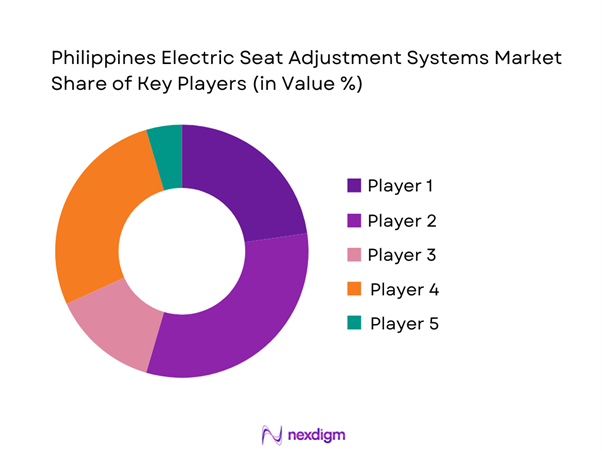
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines electric seat adjustment systems landscape is shaped by global seat-system Tier-1 suppliers (platform-level integration), actuator/motor specialists (mechatronics), and aftermarket distributors supplying replacement motors, switches, and control modules. In practice, market influence is concentrated among Tier-1 groups that win OEM seating platform awards, while component specialists compete on noise/vibration, durability, packaging (thin motors), and electronics integration.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | Primary Role in Electric Seat Adjustment | Core Technologies | OEM Platform Penetration | APAC Manufacturing Footprint | Quality/Compliance Stack | Aftermarket Presence |
| Adient | 2016 | USA | Seating Tier-1 integrator | Seat structures + adjuster integration | High (global OEM programs) | Strong | OEM-grade validation | Medium |
| Lear Corporation | 1917 | USA | Seating Tier-1 + electronics integration | Seat systems, comfort electronics | High | Strong | OEM-grade validation | Medium |
| FORVIA (Faurecia) | 1997 | France | Seating Tier-1 + interiors | Mechatronic seat functions | High | Strong | OEM-grade validation | Medium |
| Brose | 1908 | Germany | Mechatronics specialist | Seat drives, motors, modules | High | Strong | Functional safety/process rigor | Medium |
| Bosch | 1886 | Germany | Electronics/mechatronics enabler | Motors, sensors, ECUs | Medium–High | Strong | Automotive electronics compliance | Medium–High |
Philippines Electric Seat Adjustment Systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Shift Toward Feature-Rich Vehicles
Philippine demand for electric seat adjustment systems is rising as new-vehicle buyers increasingly “trade up” to trims that bundle power seat motors with comfort, safety, and infotainment packages—especially in commuter-heavy metros. New vehicle sales reached ~ units and then ~ units, expanding the addressable OE-fit base for powered seats. Macro capacity to pay for feature-rich variants is supported by an economy sized at USD ~ billion with GDP per capita of USD ~, while population expanded, sustaining household formation and replacement demand for newer vehicles where power-adjust seats are more common.
SUV and MPV Sales Mix
The Philippines’ market mix structurally favors body styles (SUVs/MPVs/AUVs and “commercial vehicle” classifications) where buyers value higher seating comfort, multi-row ergonomics, and adjustable driving positions—features that frequently include powered seat adjusters in mid-to-upper variants. Industry reporting shows commercial vehicle sales of ~ units and passenger car sales of ~ units, reinforcing a CV-heavy market where family and fleet use-cases amplify seat comfort expectations. This mix is reinforced by urban concentration: the country’s urban population was ~ alongside a total population of ~, meaning a large share of users drive in dense stop-and-go conditions that make powered adjustability more valued in daily use.
Challenges
High Import Dependence
A key constraint is reliance on imported seat motors, control modules, and seat mechanism sub-assemblies, exposing OEMs and distributors to lead-time and FX volatility. Product-level trade profiling shows the Philippines imported USD ~ million of motor vehicle parts and accessories, highlighting the import-heavy nature of the components ecosystem that would include powered seat system inputs. This sits against local production scale: motor vehicle production was reported at ~ units and then ~ units, far below new-vehicle demand of ~ units, implying a continued dependence on imported CBUs/CKDs and parts content. With inflation moving from ~ down to ~, cost shocks may moderate, but import exposure remains a structural challenge for stable sourcing of seat electronics and motors.
Cost Sensitivity in Mass-Market Vehicles
Even as comfort expectations rise, mass-market buyers remain highly price sensitive, limiting how far OEMs can push powered seats into entry trims. This is visible in the structure of demand: passenger car sales were ~ units versus ~ commercial vehicle units, indicating that a large volume sits in value-optimized configurations where feature content is carefully rationed. Macro conditions matter: while GDP per capita of USD ~ supports gradual premiumization, affordability is still constrained in a population that grew, where many first-time buyers prioritize monthly payment. Inflation cooling helps, but OEMs still face a margin trade-off—adding seat motors, switches, and wiring increases BOM complexity. As a result, electric seat adjustment often remains concentrated in mid and upper variants, slowing penetration into the largest unit pools unless OEMs redesign seats to reduce motor count, wiring, and controller cost.
Opportunities
Local Assembly Localization
A credible pathway to future growth is increasing localization around seat assembly (frames, foam, trim) and progressively localizing electromechanical sub-assemblies (tracks, gear sets, small motors) as OEM volumes and supplier programs mature. Current data supports the business case without using future projections: domestic motor vehicle production rose, while new-vehicle sales reached ~ units, indicating an expanding activity base for CKD assembly, supplier warehousing, and localized sub-assembly. The macro backdrop—GDP of USD ~ billion and inflation easing from ~ to ~—also supports investment planning and cost predictability for localization programs. As localization expands, seat adjustment systems benefit because they are high-touch interior modules where OEMs can tune features to local trim strategies while reducing logistics friction and improving service parts availability.
Mid-Segment Feature Upselling
The strongest near-term upside is “mid-segment upselling,” where OEMs push powered driver seats (and, selectively, powered passenger seats) into high-volume variants rather than limiting them to top trims. The market’s volume foundation is already proven: new vehicle sales increased from ~ to ~ units, while passenger car sales reached ~ units and commercial vehicles ~ units, providing multiple high-throughput nameplates where a single-feature change can scale quickly. The country’s urban base (~ people) and congestion indicators strengthen the consumer value proposition for comfort upgrades without relying on future statistics. With inflation easing from ~ to ~, OEMs have more room to market “comfort packages” at manageable monthly payment deltas—supporting higher take-rates for electric seat adjusters, switches, and seat control modules in mainstream models.
Future Outlook
Over the next planning cycle, the Philippines electric seat adjustment systems market is expected to expand steadily as OEMs intensify feature differentiation in mid-trim variants, and as SUVs/crossovers remain the preferred upgrade path for urban households. Technology direction will move toward quieter and lighter actuators, modular seat ECUs, and smarter HMI (integrated switch packs), while Tier-1 suppliers push more integration between seat motion, occupant sensing, and safety/comfort features. Electrification and platform standardization in APAC will also favor scalable seat modules that can be deployed across multiple nameplates.
Major Players
- Adient
- Lear Corporation
- FORVIA
- Brose
- Bosch
- Denso
- Johnson Electric
- Nidec
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Magna International
- Aisin
- ZF
- Valeo
- Continental
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEMs & national sales companies
- Tier-1 seating system integrators & module suppliers
- Tier-2 actuator/motor, switch, and ECU manufacturers
- Automotive parts importers, distributors & aftermarket retail chains
- Vehicle fleet operators & corporate mobility buyers
- Insurance & extended-warranty providers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We map the Philippines seat-adjustment ecosystem—OEM programs, Tier-1 seat suppliers, component makers, and aftermarket channels—then define variables such as powered-seat fitment rate by vehicle class, actuator count per seat, and replacement incidence drivers.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historical indicators from vehicle sales mix, trim/package benchmarking, and supplier shipment signals to structure a bottom-up view by vehicle category and component content, separating OEM-fit demand from service/aftermarket replacement.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses on fitment trends, failure modes, and channel pricing structures are validated via CATI-style interviews with distributor executives, workshop networks, and regional supplier managers to confirm real-world sourcing and service patterns.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We consolidate findings into segment models (component and vehicle category), reconcile against available industry datasets, and finalize insights on platform-level competition, supply-chain risks, and procurement levers relevant to the Philippines.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Scope Boundaries, Abbreviations and Acronyms, Seat Adjustment System Taxonomy, Market Sizing Logic, Bottom-Up OEM Feature Penetration Modeling, Import–Assembly Normalization Approach, Primary Interview Framework, Demand-Side Validation, Limitations and Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Evolution of Seat Electrification in the Philippines Passenger Vehicle Market
- Key Milestones in Comfort and Power Seat Adoption
- Automotive Business Cycle Impact on Interior Feature Uptake
- Automotive Seating System Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Shift Toward Feature-Rich Vehicles
SUV and MPV Sales Mix
Consumer Comfort Expectations
Rising Urban Commute Durations
OEM Interior Differentiation Strategies - Challenges
High Import Dependence
Cost Sensitivity in Mass-Market Vehicles
Limited Local Seat Motor Manufacturing
Aftermarket Integration Complexity - Opportunities
Local Assembly Localization
Mid-Segment Feature Upselling
EV-Specific Interior Packages
Dealer-Level Customization - Trends
Seat Memory Bundling
Lightweight Motor Adoption
Integration with ADAS and Driver Profiles
Modular Seat Platforms - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average System Price, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
2-Way Electric Adjustment
4-Way Electric Adjustment
6-Way Electric Adjustment
8-Way and Above (Multi-Axis)
Memory-Enabled Electric Seats - By Application (in Value %)
Entry-Level Passenger Cars
Mid-Segment Sedans and Hatchbacks
SUVs and Crossovers
MPVs and Family Vehicles
Premium and Luxury Vehicles - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
ICE Vehicles
Hybrid Vehicles
Battery Electric Vehicles - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Driver Seat
Front Passenger Seat
Second-Row Seats
Third-Row Seats - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Factory-Installed OEM Fitment
Dealer-Installed Accessories
Aftermarket Retrofit Systems
- Market Share of Key Players by Value and Volume
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Adjustment Axis Coverage, Motor Torque Rating, Noise and Vibration Levels, Memory Module Integration, Seat ECU Compatibility, Weight per Actuator Set, OEM Platform Penetration, Aftermarket Retrofit Readiness)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis by Vehicle Segment and Adjustment Level
- Detailed Company Profiles
Adient plc
Lear Corporation
Faurecia (Forvia)
Toyota Boshoku Corporation
Magna Seating
Brose Fahrzeugteile
Bosch Mobility Solutions
Nidec Corporation
Denso Corporation
Aisin Corporation
Johnson Electric
TS Tech Co., Ltd.
Hyundai Transys
Shanghai Yanpu Automotive
- OEM Feature Adoption Strategy
- Dealer-Level Feature Upsell Dynamics
- Consumer Comfort vs Cost Trade-Off Analysis
- Pain Points Across Vehicle Segments
- Purchase Decision and Feature Selection Funnel
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average System Price, 2025–2030


