Market Overview
The Philippines engine blocks market is underpinned by the country’s expanding automotive base and regional trade in engine components. The economy is now worth about USD ~ billion in nominal terms, with population at roughly 115.8 million, providing a broad demand base for vehicles and service parts. New motor vehicle sales reached 475,094 units, up from roughly 441,000 units in the prior year, reinforcing steady internal-combustion engine demand that anchors engine block consumption, while ASEAN imports of engine parts (HS 8409) total about USD ~ billion, signalling strong regional component flows into which the Philippines is integrated.
Engine block demand is concentrated around key industrial and automotive hubs. Metro Manila and nearby CALABARZON (Laguna, Cavite, Batangas) dominate due to the clustering of Toyota Motor Philippines in Santa Rosa, Mitsubishi Motors Philippines in Santa Rosa, Isuzu Philippines in Biñan and Hino Motors Philippines in Laguna, all of which assemble ICE vehicles and rely on imported or regionally sourced engine castings and blocks. Central Luzon and Cebu follow as secondary centres, supported by logistics corridors, port access and dense commercial-vehicle usage in construction, logistics and provincial transport, which sustains a sizeable replacement and remanufacturing engine block segment.
Market Segmentation
By Material Type
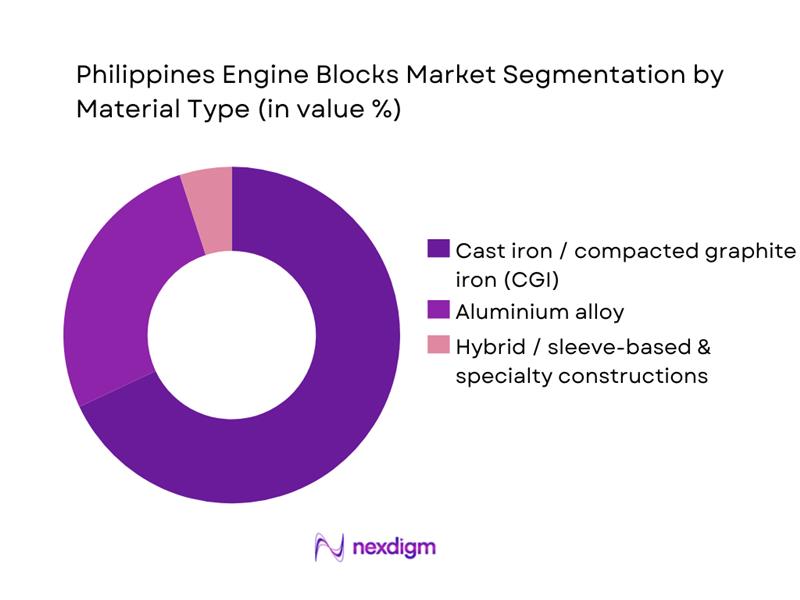
The Philippines Engine Blocks Market is segmented by material type into cast iron / compacted graphite iron, aluminium alloy and hybrid or sleeve-based specialty constructions. Cast iron and CGI engine blocks hold a dominant position because the domestic vehicle parc is heavily skewed towards durable diesel light trucks, jeepneys and buses, which prioritise robustness and tolerance to fuel and maintenance variability over weight reduction. CAMPI–TMA data show that commercial vehicles account for the majority of the 475,094 vehicles sold, reflecting strong demand in logistics, construction and provincial transport where long-life diesel engines with thick-walled grey-iron blocks are preferred to minimise downtime. Local rebuilders and machine shops are also tooled primarily for boring, sleeving and surfacing cast-iron blocks, reinforcing this installed base advantage over aluminium units, which require more specialised equipment and often arrive as complete imported assemblies.
By End-Use Vehicle & Engine Category
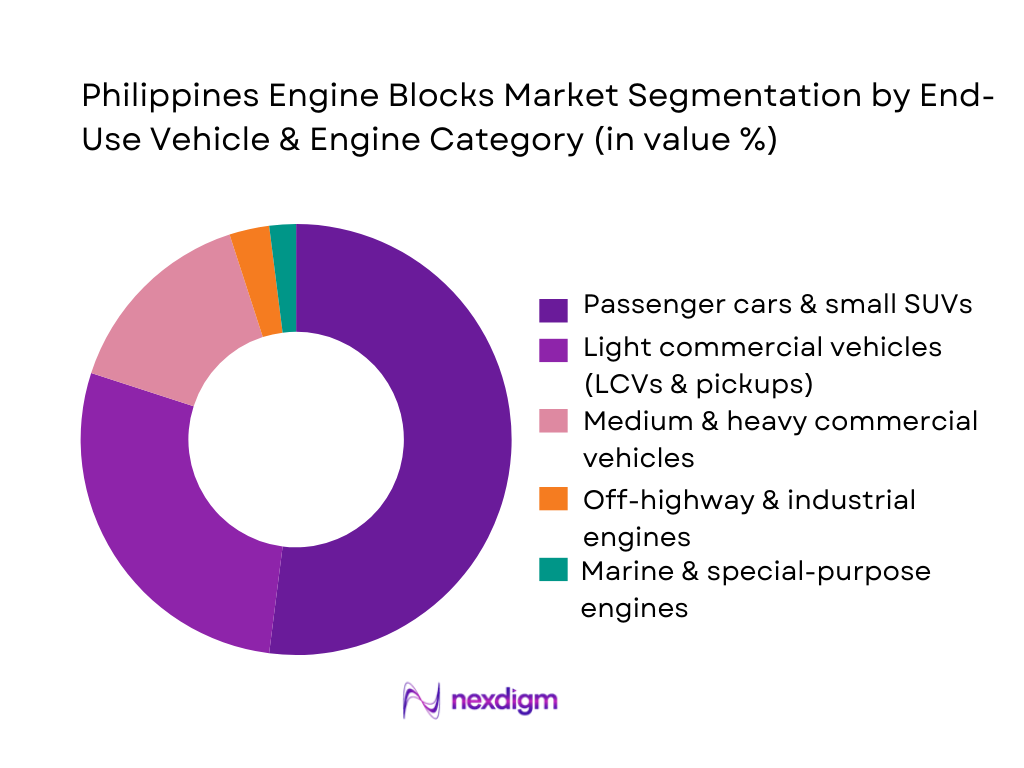
The Philippines Engine Blocks Market is segmented into passenger cars and small SUVs, light commercial vehicles, medium and heavy commercial vehicles, off-highway and industrial engines, and marine or special-purpose engines. Passenger cars and small SUVs lead by value despite commercial vehicles dominating volumes, because global OEMs such as Toyota, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Hyundai and Honda focus their local line-ups around higher-value compact sedans, crossovers and multipurpose vehicles whose powertrains embed more expensive aluminium and high-precision multicylinder blocks. These models benefit from regional engine sourcing out of Thailand and Indonesia, where ASEAN engine parts imports reach USD 3.4 billion, and are increasingly specified with downsized turbocharged engines that command a higher unit value per block. At the same time, the proliferation of financing and rising urban middle-class incomes tilt engine-block value pools towards metro-based passenger platforms.
Competitive Landscape
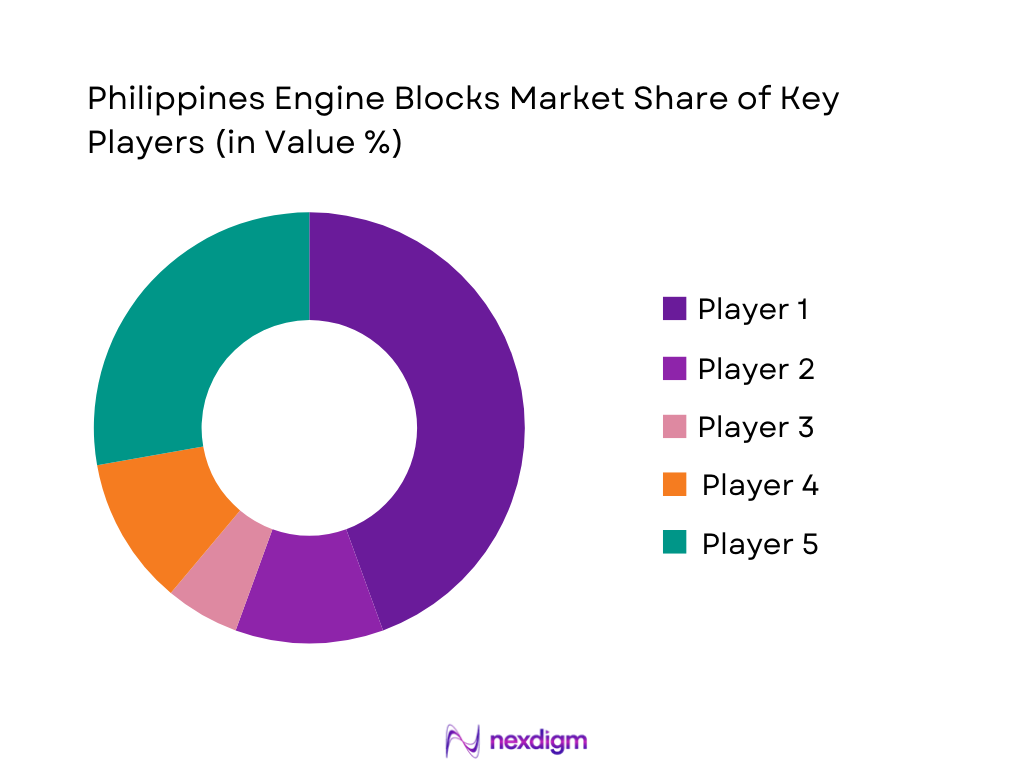
The Philippines engine blocks market is shaped by a limited number of large OEM assemblers and global engine suppliers that control the bulk of ICE vehicle production and high-value replacement engines. Toyota Motor Philippines, Mitsubishi Motors Philippines, Isuzu Philippines, Hino Motors Philippines and Cummins Sales and Service Philippines form the core of this ecosystem, with concentric rings of distributors for Hyundai, Nissan, Ford, Honda, Foton and agricultural engine brands. The concentration of assembly plants in Laguna and neighbouring provinces creates strong bargaining power on engine sourcing, while a fragmented landscape of independent rebuilders, machine shops and importers of surplus Japanese engines competes more on price and service coverage than on technology leadership.
| Company | Establishment Year (Local) | Headquarters (Local) | Core Engine / Block Focus in PH | Key Vehicle / Engine Segment | Local Assembly or Import Model | Engine Plant / Foundry Footprint (PH & ASEAN) | Key Customer / Channel Focus | Notable Strength in Engine Blocks Value Chain |
| Toyota Motor Philippines Corporation | 1988 | Santa Rosa, Laguna | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Mitsubishi Motors Philippines Corporation | 1963 (predecessor) | Santa Rosa, Laguna / Taguig | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Isuzu Philippines Corporation | 1995 | Biñan, Laguna | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Hino Motors Philippines Corporation | 1975 | Laguna | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Cummins Sales & Service Philippines | Early 2000s (Distributor presence) | Metro Manila | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Engine Blocks Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Engine Parc Expansion
The engine blocks market in the Philippines is underpinned by a rapidly expanding vehicle parc. The Land Transportation Office and industry sources report about ~ million registered motor vehicles in the country, with 372,083 new units sold in one recent year and over 429,000 units the following year as the market recovered. Total registrations have risen to over 14.3 million units, while the population is around 115 million, indicating intensive motorization and sustained demand for ICE engines. This growing parc translates directly into long-term demand for new and replacement engine blocks across passenger cars, light commercial vehicles, and public-transport fleets.
Rebuild Cycles
A large, intensively used vehicle parc drives frequent overhaul and rebuild cycles, supporting strong aftermarket demand for engine blocks and short blocks. With over 14 million registered vehicles versus annual new sales of roughly 0.4–0.45 million units, most vehicles remain in service for many years, making heavy reliance on engine rebuilds economically rational. Final energy consumption in the country reached ~ million tons of oil equivalent, with the transport sector alone using 12.9 MTOE, and road transport accounting for 11.6 MTOE, reflecting high annual mileage and engine wear. This combination of a large parc, relatively modest replacement with new units, and high usage intensity underpins a sizeable market for rebored and remanufactured blocks, sleeves, and related machining services.
Market Challenges
Foundry Capacity Limits
Despite a manufacturing share of about 16% of GDP, the Philippines still lacks large-scale ferrous foundries dedicated to automotive castings, forcing engine-block buyers to depend on imports or small jobbing foundries. Industrial energy data show that total industry consumption is around 7.0 MTOE, with manufacturing at 5.8 MTOE, while transport energy use alone is 12.9 MTOE, underscoring how demand from the vehicle parc outpaces the development of heavy-metal processing capacity. Merchandise imports reached about USD ~ billion in a recent year, down from USD 145 billion the year before, yet the country continues to run persistent trade deficits partly due to imported intermediate goods and capital equipment that include cast and machined components. These structural imbalances highlight constraints for scaling domestic engine-block casting.
Machining Tolerance Gaps
High-precision cylinder block machining relies on advanced CNC equipment and metrology, but much of the Philippines’ industrial base is composed of small and medium enterprises. MSME statistics show over ~ million business establishments, of which about ~ million are MSMEs; manufacturing MSMEs number around 133,504, indicating a fragmented supplier landscape with limited capital per firm for state-of-the-art machine tools. The manufacturing sector’s final energy consumption of 5.8 MTOE, compared with 11.6 MTOE for road transport, points to a still-developing industrial backbone relative to vehicle usage. Imports of capital goods reached roughly USD 35.7 billion, accounting for about 28.33% of total merchandise imports, underlining that many precision machines and tooling needed for tight-tolerance boring, honing, and line-boring of blocks are still sourced from abroad, constraining local machining depth and consistency.
Opportunities
Local Casting Investments
While current foundry capacity is limited, macroeconomic conditions and industrial policy create a clear opportunity to localize engine-block casting. The Philippines’ GDP in current US dollars is estimated at around USD ~ billion rising to roughly USD ~ billion and then USD ~ billion over a three-year period, indicating a steadily expanding domestic market that can support capital-intensive casting operations. Merchandise trade totals close to USD ~ billion, with capital goods imports around USD ~ billion, demonstrating the scale of current investment in industrial equipment. Manufacturing’s share of GDP at roughly 16% and industrial energy use of 7.0 MTOE point to an ecosystem large enough to absorb dedicated ferrous foundries for engine blocks, especially if anchored by commercial-vehicle OEMs, large rebuilders, and export-oriented machine shops. Fiscal and investment liberalization measures—such as widening sectors open to full foreign ownership and streamlining incentives—further strengthen the case for domestic casting clusters supplying both local and regional engine markets.
HEV-Compatible Lightweight Blocks
The emerging shift to hybrids and stricter fuel-efficiency norms opens a niche for locally produced lightweight blocks designed for range-extender and downsized turbocharged engines. EV-industry data show 47,231 EVs sold in a single recent fiscal year alone (across BEV, HEV, PHEV and L-category vehicles), on top of 1,200 units the prior year, indicating rapid acceleration from a low base. At the same time, total motor-vehicle registrations exceeding ~ million and cumulative EV sales of 48,521 confirm that ICE platforms will remain dominant for many years, but with increasing pressure to improve efficiency and emissions. Under RA 11697, requirements such as a 5% minimum EV share in select fleets and zero import duties on EVs and certain parts create a policy environment where OEMs and local tier-1 suppliers can invest in aluminum and compacted-graphite iron block programs tailored to hybrid powertrains, capturing value in both domestic and export supply chains.
Future Outlook
Over the next planning horizon the Philippines Engine Blocks Market is expected to expand steadily, anchored by macroeconomic growth, infrastructure spending and a still-ICE-heavy national vehicle parc. The World Bank projects the Philippine economy to remain on a roughly mid-single-digit growth trajectory, with GDP already around USD ~ billion, supporting rising vehicle ownership and freight demand. CAMPI-TMA data indicate that new vehicle sales already surpassed 475,000 units, with commercial vehicles accounting for the bulk of growth, ensuring sustained demand for diesel engine blocks in both OEM fitment and replacement cycles. At the same time, progressive but gradual electrification and hybridisation imply that pure ICE block demand will eventually plateau, pushing local suppliers and rebuilders to upgrade machining, balancing and remanufacturing capabilities while exploring hybrid-ready and range-extender engine platforms tailored to Philippine duty cycles.
Major Players
- Toyota Motor Philippines Corporation
- Mitsubishi Motors Philippines Corporation
- Isuzu Philippines Corporation
- Hino Motors Philippines Corporation
- Nissan Philippines, Inc.
- Honda Cars Philippines, Inc.
- Hyundai Motor Philippines, Inc.
- Suzuki Philippines, Inc.
- Ford Group Philippines, Inc.
- Foton Motor Philippines
- Cummins Sales and Service Philippines, Inc.
- Yanmar engine distributors in the Philippines
- Kubota Philippines
- Perkins engine distributors
Key Target Audience
- ICE engine and powertrain OEMs
- Automotive OEM subsidiaries and assemblers
- Tier-1 and Tier-2 engine component suppliers
- Independent engine rebuilders and machine-shop networks
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Logistics, construction and fleet operators
- Genset, marine and industrial engine OEMs/assemblers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves mapping the Philippines Engine Blocks Market ecosystem across OEM assemblers, engine suppliers, foundries, importers, rebuilders and fleet operators. This is carried out using extensive desk research, aggregating statistics from multilateral databases (World Bank, TrendEconomy, UN trade data), CAMPI–TMA vehicle sales releases and corporate disclosures. The objective is to isolate variables such as engine-equipped vehicle sales, diesel share, import reliance and rebuild intensity that drive engine block demand.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase we construct the historical and current market size for the Philippines Engine Blocks Market through a bottom-up approach. Vehicle sales by segment are combined with benchmark engine-block values per unit and expected replacement cycles, calibrated against ASEAN engine-parts trade values and powertrain value-add ratios. We also incorporate macro indicators such as GDP level, manufacturing value added and infrastructure spending to validate whether the implied engine-block intensity is consistent with broader industrial activity.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Working hypotheses on engine-block material mix, OEM versus aftermarket shares and segment-wise growth are validated through structured interviews and computer-assisted telephone interactions with OEM technical teams, distributors, large machine shops and fleet maintenance managers. These discussions focus on practical issues such as failure modes, typical overhaul intervals, sourcing preferences for complete engines versus bare blocks, and evolving views on aluminium versus cast-iron platforms. The insights are used to refine our penetration assumptions and reconcile discrepancies across secondary data sources.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final stage integrates the quantitative model with qualitative intelligence to produce a coherent view of the Philippines Engine Blocks Market. Forecasts are generated by aligning engine-block demand drivers with GDP projections, vehicle-sales outlooks and prospective policy changes around emissions and electrification. Cross-checks are made against regional comparators to ensure plausibility of the derived CAGR and segment shares. The result is a fully documented market model, accompanied by competitive mapping, opportunity analysis and scenario-based recommendations for investors, OEMs and policymakers.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions & Metallurgical Classifications, Assumptions, Abbreviations, Engine Block Sizing Logic, Foundry Capacity Mapping, OEM–Aftermarket Rebuild Ratio Analysis, Tolerance-Band Benchmarking, Consolidated Research Approach, Primary Interviews with OEMs/Engine Rebuilders/Foundries, Limitations & Inferences)
- Definition & Scope
- Industry Genesis & Evolution
- OEM vs Aftermarket Engine Block Ecosystem
- Engine Block Supply Chain & Value Chain
- Local vs Imported Engine Block Dynamics
- Growth Drivers
Engine Parc Expansion
Rebuild Cycles
Diesel Dependence
Foundry Localization
LCV Fleet Modernization - Market Challenges
Foundry Capacity Limits
Machining Tolerance Gaps
High Import Dependency
HEV Shift - Opportunities
Local Casting Investments
HEV-Compatible Lightweight Blocks
CNC Machining Hubs
Tier-2/3 Supplier Development - Trends
CGI Adoption
Aluminum Block Penetration
Rebuild-Grade Blocks
Imported Semi-Finished Blocks - Government & Regulatory Environment
- SWOT Analysis of Market
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces for Engine Block Ecosystem
- Competition Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Average OEM Block Value, 2019-2024
- By Block Material Type (in Value %)
Grey Cast Iron
Ductile/Nodular Iron
Compacted Graphite Iron
Cast Aluminum Blocks
Hybrid Composite/Alloy Blocks - By Engine Displacement Category (in Value %)
<1.2L
1.2L–1.6L
1.6L–2.5L
2.5L–4.0L
>4.0 - By Vehicle Category (in Value %)
Passenger Cars
SUVs/MPVs
Light Commercial Vehicles
Heavy Commercial Vehicles
Agricultural/Construction/Marine Engines - By Manufacturing Route (in Value %)
Sand Casting
High-Pressure Die Casting
Gravity Die Casting
Low-Pressure Casting
CNC Machined Imported Semi-Finished Blocks - By Distribution Channel (in Value %)
OEM Supply (assembled engines)
CKD/SKD Engine Programs
Authorized Engine Rebuilders
Independent Machine Shops
Imported Blocks & Parallel Imports - By End-Use Engine Category (in Value %)
Gasoline Engines
Diesel Engines
Mild Hybrid Engines
HEV/Series-Parallel Hybrid Blocks
Industrial Engines - By Region (in Value %)
NCR & Central Luzon
CALABARZON
Northern Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao
- Market Share of Major Players
By Block Material
By Vehicle Category
By Distribution Channel - Cross-Comparison Parameters (Metallurgy Capabilities, Foundry Melting Capacity, Machining Tolerance Accuracy, Engine Displacement Coverage, Heat Treatment Infrastructure, OEM Program Integration, Block Durability/Failure Rate Benchmarks, Local Supply Chain & Import Dependence Ratio)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis of Engine Blocks
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Toyota Motor Philippines
Mitsubishi Motors Philippines
Isuzu Philippines
Nissan Philippines
Hyundai Motor Philippines
Kia Philippines
Ford Philippines
Mazda Philippines
Foton Philippines
Hino Motors Philippines
Cummins Philippines
Yanmar Philippines
Kubota Philippines
Guangxi Yuchai / Chinese Engine Block Importers
- Engine Block Demand Patterns
- Fleet Operator Requirements & TCO Mapping
- Rebuilder Procurement Behaviors
- Pain Point Analysis
- Decision-Making Framework
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Average OEM Block Value, 2025-2030