Market Overview
The Philippines engine control units (ECU) market sits within a rapidly expanding automotive ecosystem where light-vehicle sales have risen from roughly ~ units to about ~ units over the most recent two-year window, supported by strong growth in passenger cars, which climbed from around ~ to more than ~ units. Globally, automotive ECU revenue is estimated at over USD ~ billion, with Asia-Pacific contributing close to USD ~ billion, underscoring the region’s electronics intensity. Based on these benchmarks and local vehicle volumes, this study models the Philippines ECU market at around USD ~ million, driven by rising ECU content per vehicle and growing adoption of electronic powertrain and safety systems.
The Philippines engine control units (ECU) market is concentrated around the National Capital Region (NCR) and adjoining industrial corridors in CALABARZON (notably Laguna, Batangas and Cavite). NCR accounts for the largest share of national economic output and vehicle demand, with its gross regional domestic product exceeding PHP 8.2 trillion, while Region IV-A, NCR and Region III together contribute close to three-fifths of national GDP. Major assembly and component facilities for brands such as Toyota, Mitsubishi and Yazaki are clustered in Santa Rosa, Calamba and Lipa, anchoring ECU fitment, diagnostics and after-sales activity in these automotive belts.
Market Segmentation
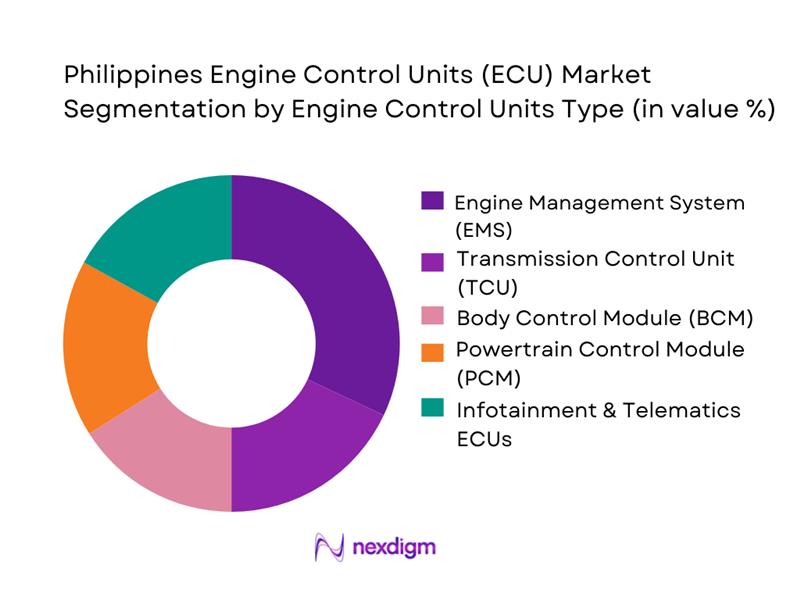
By Engine Control Units Type
The Philippines engine control units (ECU) market is segmented by ECU type into engine management systems (EMS), transmission control units (TCU), body control modules (BCM), powertrain control modules (PCM), and infotainment & telematics ECUs, along with emerging ADAS/domain controllers. Recently, engine management systems hold the dominant share under this segmentation, as virtually every locally-sold passenger car and commercial vehicle now relies on electronically managed fuel injection and ignition. Rising emissions and fuel-efficiency requirements push OEMs to specify more sophisticated EMS units even on entry-segment models, while imported Japanese and Korean nameplates sold through large dealer networks come with EMS as standard. The growing parc of modern vehicles and rising diagnostic sophistication in NCR and CALABARZON further entrench EMS as the core ECU category in the country.
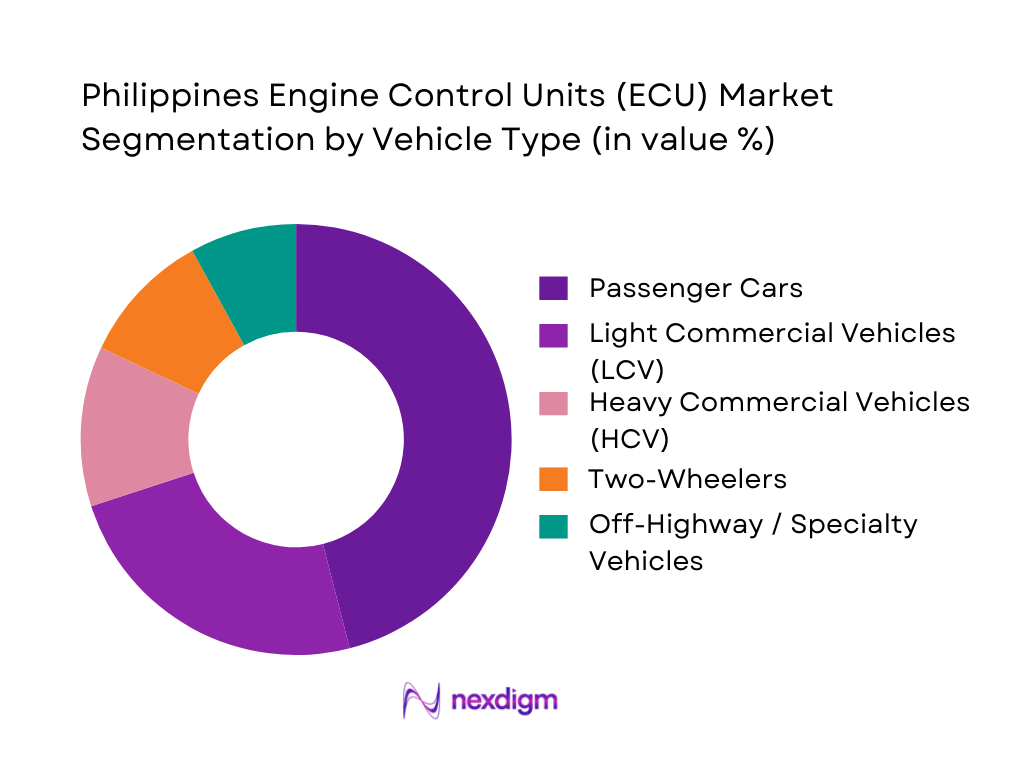
By Vehicle Type
The Philippines engine control units (ECU) market is segmented by vehicle type into passenger cars, light commercial vehicles (LCV), heavy commercial vehicles (HCV), two-wheelers, and off-highway / specialty vehicles. Passenger cars currently dominate ECU demand under this segmentation, reflecting their large and fast-growing parc within total vehicle sales and their higher ECU density per unit. Light vehicles in the country have recently reached around ~ annual sales, with passenger cars forming a substantial portion of incremental growth. Compact sedans and crossovers from Japanese and Korean OEMs typically integrate multiple ECUs for powertrain, body electronics and infotainment, while premium imports add ADAS controllers. This combination of volume and electronics intensity ensures that passenger cars remain the anchor segment for ECU demand in the near term.
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines engine control units (ECU) market is strongly influenced by global Tier-1 suppliers that integrate into Japanese, Korean and increasingly Chinese OEM supply chains. The landscape is moderately consolidated, with multinational vendors such as Bosch, Denso, Continental, Delphi/BorgWarner and Hitachi Astemo providing the bulk of EMS, TCU, BCM and safety-related ECUs embedded in locally assembled and imported vehicles. These firms compete on calibration expertise for ASEAN driving conditions, cybersecurity and functional-safety compliance, as well as the availability of diagnostics interfaces and training for dealer and independent workshops. Local value capture sits primarily in wiring harnesses and electronics assembly, with deeper ECU design and silicon still largely imported.
| Company | Establishment Year | Global HQ | Core ECU Focus in PH | Primary OEM Linkages in PH | Local Presence Model | Technology & Safety Focus | Diagnostics & Service Support | Notable Differentiator in PH Context |
| Bosch | 1886 | Gerlingen, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Denso | 1949 | Kariya, Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Continental | 1871 | Hanover, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Delphi / BorgWarner | 1880s (legacy brands) | Auburn Hills, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Hitachi Astemo | 2021 (merger of Hitachi Automotive + Keihin + Showa + Nissin) | Tokyo, Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Engine Control Units (ECU) Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Increasing powertrain electronics penetration
The Philippines is scaling up vehicle assembly and road motorization, which directly lifts demand for engine and powertrain ECUs. International motor-vehicle production statistics show the country produced ~ units in the latest reported year, up from ~ units a year earlier, marking its highest output on record and reflecting OEM investment in more electronically-controlled platforms. Road motorization is also rising, with ~ registered vehicles in operation, indicating a sizeable parc that increasingly shifts from purely mechanical control to electronically managed engines, transmissions, and emissions systems. In parallel, the electronics manufacturing ecosystem is strong—Philippine exports of electronics reached USD ~ billion out of USD ~ billion total merchandise exports, underscoring deep capabilities in electronic components, PCBs, and control hardware that can be leveraged for ECU localization.
FI mandate trajectory
Stricter emissions and fuel-quality rules are pushing OEMs and importers toward fuel-injected, electronically-controlled engines, structurally expanding the ECU content per vehicle. The Philippine Clean Air Act and its implementing rules require tighter automotive emissions limits, while fuel standards have been upgraded to Euro 4-equivalent gasoline and diesel, backing electronic injection and closed-loop control technologies rather than carbureted setups. At the same time, the Philippines records relatively low per-capita CO₂ emissions of 1.4 tons and 98% access to electricity, which supports electrified auxiliaries and onboard diagnostics as regulators pursue cleaner growth. These environmental and fuel-quality policies effectively lock in FI-plus-ECU architectures as the default for new internal-combustion vehicles, from passenger cars to jeepneys and light trucks.
Market Challenges
Import dependency on Tier-1s
The Philippines remains structurally dependent on imported automotive electronics and control assemblies from global Tier-1 suppliers, exposing ECU supply to currency volatility and external shocks. Trade statistics based on UN Comtrade show that imports of “electrical machinery and equipment” (HS 85) reached around USD ~ billion in recent years, forming one of the largest single import categories as the country sources semiconductors, control boards, and harnesses from East Asian hubs. NTRC’s EV-related tax analysis alone records PHP ~ billion in customs collections from EVs, parts and components from 2018–2022, including sizeable flows of control boards under HS 85.37. With limited local Tier-1-grade ECU manufacturing, Philippine assemblers and distributors must align with foreign suppliers’ lead times, pricing cycles, and platform roadmaps, constraining bargaining power and localization potential.
Calibration complexity
Growing engine diversity—ranging from small gasoline units in compact cars to diesel powertrains in jeepneys and light trucks—raises the complexity and cost of ECU calibration in a market with relatively limited local testing resources. Public data show the Philippines has around ~ million registered vehicles, spanning motorcycles, private cars, UVs, and commercial fleets, each with distinct duty cycles and load patterns that require specific ECU calibration strategies for fuel economy, emissions, and drivability. Yet R&D spending remains structurally low; a Congressional research paper notes public R&D expenditure of just 0.2% of GDP, well below regional peers, underscoring constrained capabilities for advanced powertrain and emissions-bench testing. This mismatch—rising engine variety and emissions requirements versus modest R&D and testing investment—makes in-country development and calibration of engine maps, OBD strategies, and drive-by-wire control logic more challenging.
Opportunities
Local remanufacturing clusters
The Philippine vehicle parc of ~ units represents a sizable installed base for ECU diagnostics, repair, and remanufacturing, particularly as vehicles age and owners seek lower-cost alternatives to new parts. National statistics show ongoing growth in motor-vehicle registrations and strong activity in transportation and storage services, indicating sustained utilization of light-commercial vehicles, jeepneys, and buses that depend heavily on reliable engine and transmission ECUs. At the same time, EVIDA and related industrial policies explicitly encourage the establishment of EV-related testing centers, battery facilities, and support infrastructure—policy levers that could be extended to include remanufacturing hubs for powertrain electronics. Given the country’s electronics manufacturing base and engineering talent pool, localized ECU remanufacturing clusters in industrial zones such as Calabarzon and Central Luzon could capture value from failed or obsolete controllers, reduce import dependence, and support circular-economy targets through component reuse and refurbishment.
ECU reprogramming services
Emerging EV and hybrid fleets, combined with rising connectivity, create a strong base for value-added ECU reprogramming and software-update services in the Philippines. LTO data summarized by NTRC show ~ registered electric motor vehicles, including new BEVs and hybrid SUVs and UVs, while CAMPI-based figures in the same study report ~ EV sales in just the first quarter of a recent year, pointing to accelerating adoption. On the digital side, the World Bank reports 117.3 mobile-cellular subscriptions per 100 people and 84% internet usage, indicating that most vehicle owners and fleet managers can support connected diagnostics and over-the-air update models. As EV incentives under EVIDA prioritize the manufacture of electronic parts, testing facilities, and charging infrastructure, the installed base of programmable controllers will grow, opening space for local specialists in ECU reflashing, power-limit updates, emissions-strategy revisions, and feature unlocks tailored to Philippine driving conditions and regulations.
Future Outlook
Over the coming years, the Philippines engine control units (ECU) market is expected to benefit from the steady expansion of the automotive sector and the shift toward more electronics-rich vehicles. National light-vehicle sales are on an upward trajectory, with recent performance surpassing earlier projections and targets, while new economic plans still place transport and infrastructure among key growth pillars. As OEMs standardize advanced ECUs even on entry models, local ECU content per vehicle will trend higher.
Policy support for cleaner and more efficient transport, including incentives for eco-friendly vehicles, strengthens the case for higher sophistication in EMS, TCU and hybrid/EV domain controllers. Concurrently, rapid development of wiring harness and electronics supply chains in the country—already valued in the billions of dollars—creates a foundation for future localization of certain ECU sub-assemblies and test functions.
Major Players
- Bosch
- Denso
- Continental
- Delphi Technologies / BorgWarner
- Hitachi Astemo
- Marelli
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Valeo
- Hella / Forvia
- Autoliv Electronics
- Nidec Mobility
- Renesas Automotive Solutions
- Visteon
- ZF Friedrichshafen (Electronics & ADAS Modules)
Key Target Audience
- Global and regional ECU manufacturers
- Automotive OEMs and assemblers operating in the Philippines
- Component importers and tier-2 distributors
- Automotive dealer groups and service networks
- Fleet operators and mobility service providers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Telematics, diagnostics and automotive software providers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves constructing an ecosystem map for the Philippines engine control units (ECU) market, covering OEMs, assemblers, Tier-1 suppliers, distributors, workshops and regulators. Extensive desk research is conducted using industry reports, government statistics, customs data and credible news sources to identify critical variables such as vehicle parc evolution, ECU content per vehicle, import dependence, regulatory mandates and electrification trends. These variables form the foundation for quantitative sizing and qualitative analysis.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, historical data on automotive sales, vehicle registrations and electronics content is compiled and normalized. Global and Asia-Pacific ECU benchmarks are combined with local light-vehicle volumes and wiring harness/electronics indicators to approximate ECU revenues specific to the Philippines. The analysis also considers the split between OEM and aftermarket channels, penetration of different ECU types and the role of passenger versus commercial vehicles to construct a coherent bottom-up and top-down market model.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses on ECU penetration, pricing bands, growth drivers and constraints are validated through structured interviews and consultations with industry experts. These include professionals from OEM technical teams, Tier-1 sales and application engineering, large dealer workshops, diagnostics tool providers and logistics fleets. Insights gathered through these interactions help refine assumptions on calibration requirements, failure rates, replacement cycles and future electrification, ensuring that the model reflects on-ground practices and not just desk-based extrapolation.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final step synthesizes quantitative findings and expert insights into a cohesive narrative and set of deliverables. Market sizing and segmentation outputs are reconciled with import/export trends, power electronics and wiring harness indicators, and ASEAN ECU dynamics. Scenario analysis is then performed to generate a base, optimistic and conservative view of growth through 2030, with explicit articulation of risks and triggers. The end result is a validated, decision-oriented view of the Philippines engine control units (ECU) market, tailored for business professionals and investors.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions & assumptions, ECU typology, ASIL framework references, automotive electronics penetration benchmarks, market sizing approach, consolidated research model, validation by OEM–tier interactions, primary interviews with assembler networks, limitations & forward-looking considerations)
- Definition and Scope
- Industry Evolution & Technology Genesis
- Diagnostic Standards Evolution
- Automotive Value Chain & Import Dependency Structure
- Local Assembly, CKD/SKD Dynamics & Integration Depth
- Growth Drivers
Increasing powertrain electronics penetration
FI mandate trajectory
EV/hybrid adoption curve
Fleet telematics expansion
Rising average ECU count per vehicle - Challenges
Import dependency on Tier-1s
Calibration complexity
Lack of local testing labs
Chip supply vulnerabilities
Counterfeit ECUs in aftermarket - Opportunities
Local remanufacturing clusters
ECU reprogramming services
Diagnostics-as-a-service
ADAS domain controller integration opportunities - Trends
Shift toward centralized computing
OTA-enabled ECU platforms
Cybersecurity-tight architectures
Model-based software integration - Government Regulation
- SWOT Analysis
- Stake Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Average ECU Realization Value, 2019-2024
- By ECU Type (In Value %)
Engine Management System
Transmission Control Unit
Body Control Module
Powertrain Control Module
ADAS/Advanced Domain Controllers - By Vehicle Type (In Value %)
Passenger Cars
Light Commercial Vehicles
Heavy Commercial Vehicles
Two-Wheelers
Off-Highway & Specialty Vehicles - By Propulsion Type (In Value %)
Internal Combustion Engine
Hybrid Powertrain
Battery Electric Vehicles
Mild Hybrid 48V Systems
Alternative Fuel Vehicles (LPG/CNG) - By Sales Channel (In Value %)
OEM Assembly (CKD/SKD)
Tier-1 Direct Supply
Independent Aftermarket
Authorized Dealer Service Network
Fleet & Telematics Integrators - By Communication Protocol (In Value %)
CAN
LIN
FlexRay
Ethernet Automotive
Proprietary OEM Networks - By Region (In Value %)
NCR
Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao
- Market Share of Major Players
Market Share by ECU Type - Cross Comparison Parameters (ECU architecture capability, Calibration & tuning depth for tropical driving conditions, Compliance with OBD-II, cybersecurity & ISO 26262 ASIL levels, Embedded software stack maturity, Hardware robustness under high humidity/high temperature, Local dealer/assembler integration support, Lead time resilience & semiconductor sourcing model, Diagnostics ecosystem compatibility)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Price Architecture & SKU Benchmarking
- Detailed Company Profiles
Bosch
Denso
Continental
Delphi Technologies / BorgWarner
Hitachi Astemo
Marelli
Mitsubishi Electric
Valeo
Hella / Forvia
Autoliv Electronics
Nidec Mobility
Renesas Automotive Solutions
Visteon
ZF Friedrichshafen
- OEM & Assembler Requirements
- Fleet Operator ECU Usage Behavior
- Dealership & Service-Center Dependency
- Regulatory Compliance & OBD Validation Needs
- End-User Pain Point Analysis
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Average ECU Realization Value, 2025-2030


