Market Overview
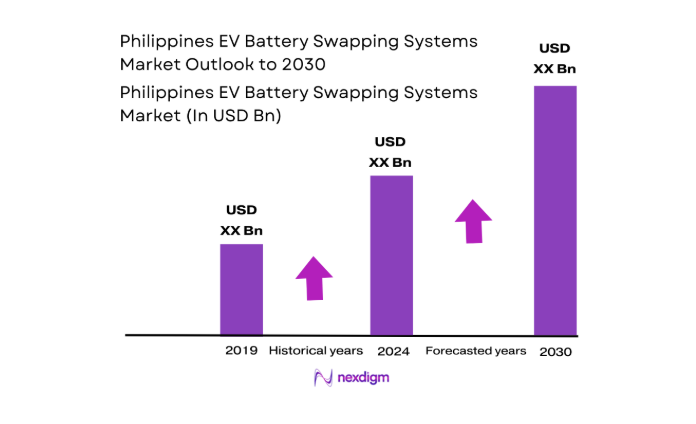
The Philippines EV Battery Swapping Systems market is valued at USD ~ in 2024, driven by growing consumer demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and government support for green infrastructure. This market is integral to the country’s transition to sustainable mobility, providing a flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional EV charging methods. The growth of battery swapping infrastructure, backed by both public and private investments, allows users to quickly exchange depleted batteries, addressing range anxiety and reducing EV downtime. The market’s adoption is heavily influenced by policies such as the Electric Vehicle Industry Development Act (EVIDA), as well as regional EV adoption trends.
The Philippines market is centered around urban areas such as Metro Manila, Cebu, and Davao, where high vehicle density, pollution concerns, and traffic congestion are prominent. These cities are experiencing the rapid deployment of battery swapping stations, primarily due to the government’s push for cleaner transportation solutions. Additionally, international players such as Gogoro and local firms like Voltai are driving the market with their advanced battery swapping technologies. These dominant regions are fueling the Philippines’ drive to increase EV infrastructure and promote sustainable urban mobility.
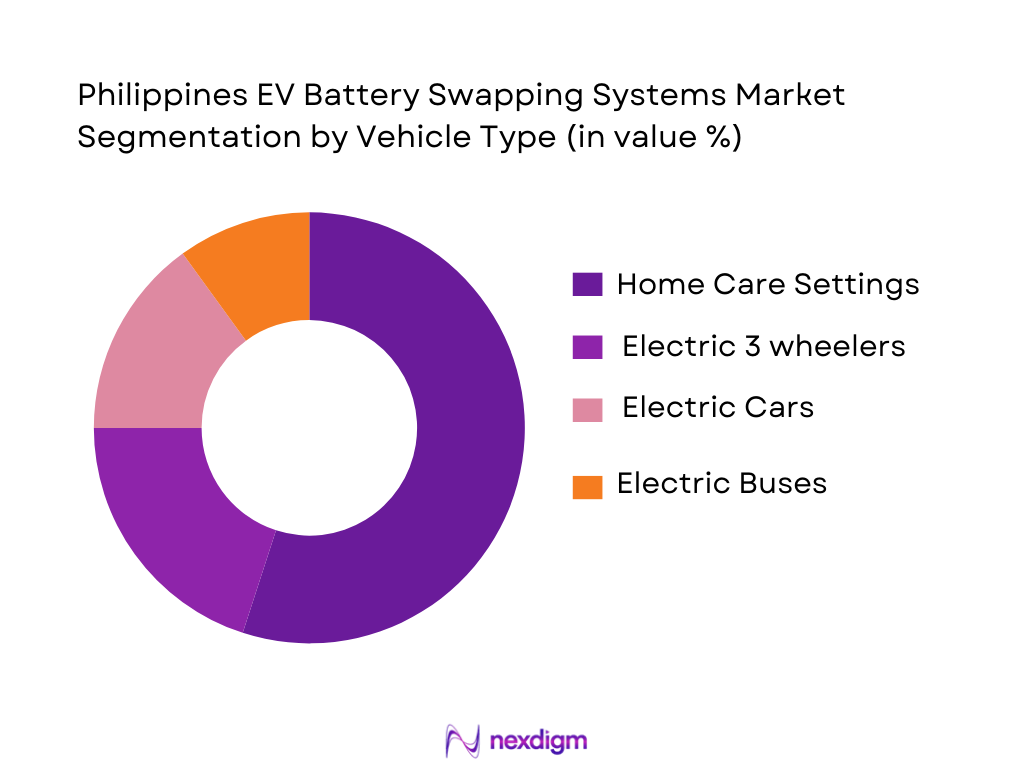
Market Segmentation
By Vehicle Type
The Philippines EV Battery Swapping Systems market is segmented by vehicle type, with electric 2-wheelers holding the largest share. This segment leads the market due to the affordability, practicality, and convenience of electric scooters and motorcycles, which are well-suited for the Philippines’ dense urban areas. As traffic congestion remains a significant concern in cities like Metro Manila, electric 2-wheelers offer a more efficient alternative for commuters, further propelling their market share. With lower initial investment costs compared to electric cars and buses, electric 2-wheelers are becoming the go-to solution for short-distance, high-frequency urban travel.
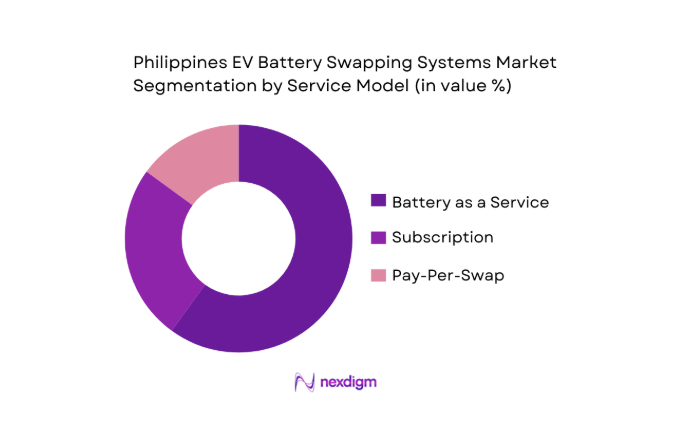
By Service Model
In the service model segmentation, the Battery as a Service (BaaS) model leads the market. This model allows consumers to pay for battery use on a subscription or pay-per-swap basis, eliminating the need for upfront battery costs. The BaaS model is particularly attractive in the Philippines, where consumers are more inclined toward cost-effective, flexible solutions. BaaS facilitates the use of electric vehicles by providing affordable access to fully charged batteries, while also addressing concerns about battery lifespan and obsolescence. This model is gaining ground across urban areas with frequent battery exchanges and lower operational costs.
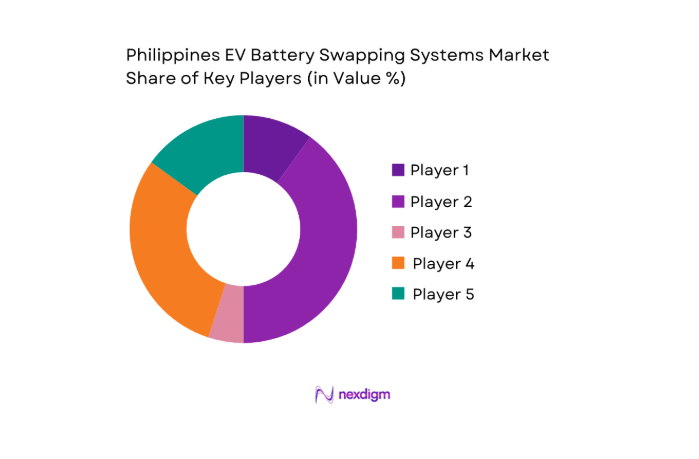
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines EV Battery Swapping Systems market is dominated by a few major players, including Voltai and global or regional brands like Gogoro, Oyika, Pilipinas Shell, and NIO. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies. These players are key drivers of market growth, contributing through their investments in infrastructure, innovative technology, and strategic partnerships with local players to expand service networks across major cities.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Parameter 1 | Parameter 2 | Parameter 3 | Parameter 4 | Parameter 5 | Parameter 6 |
| Voltai | 2022 | Metro Manila, PH | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Gogoro | 2011 | Taiwan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Oyika | 2015 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Pilipinas Shell | 1914 | Makati, PH | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| NIO | 2014 | Shanghai, China | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines EV Battery Swapping Systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Last Mile Delivery Growth and Rider Fleet Electrification
The rapid expansion of last-mile delivery services and the electrification of rider fleets are significant growth drivers for the electric vehicle (EV) and battery sector. With the rise of e-commerce and increasing consumer demand for faster deliveries, companies are adopting electric delivery bikes, scooters, and other vehicles to improve efficiency and reduce emissions. Electrification offers lower operating costs, such as reduced fuel expenses and fewer maintenance needs, compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. As last-mile delivery fleets transition to electric power, the demand for reliable and efficient battery solutions, particularly those that can be quickly recharged or swapped, will continue to grow.
High Daily Utilization Needs That Favor Rapid Energy Replenishment
The growing demand for electric vehicles in high-utilization sectors, such as delivery fleets, urban transportation, and logistics, requires rapid energy replenishment solutions. Vehicles used for these purposes often have high daily mileage requirements, which necessitate fast and efficient recharging or battery swapping systems to minimize downtime. The need for quick energy replenishment options is driving the development of more advanced charging technologies and battery swap stations. This trend presents a substantial opportunity for the battery sector, as companies seek solutions that can support high turnover, ensuring that vehicles stay in operation for longer periods without facing prolonged charging delays.
Challenges
Fragmented Battery Formats and Weak Interoperability
One of the primary challenges in the electric vehicle and battery sector is the fragmentation of battery formats and the lack of interoperability between different battery systems. As various manufacturers and service providers use proprietary technologies, users face difficulties in finding compatible batteries across different vehicle types and charging infrastructure. This lack of standardization leads to inefficiencies, as vehicles may require specific batteries or charging stations, complicating the process for fleet operators, consumers, and infrastructure developers. The absence of universal standards creates operational hurdles and impedes the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and battery swapping solutions.
Site Acquisition Constraints and Power Upgrade Requirements
The expansion of charging and swapping stations is hindered by site acquisition constraints and the need for power grid upgrades. Identifying and securing locations for charging or swapping stations, especially in densely populated urban areas, can be challenging due to space limitations, zoning regulations, and high real estate costs. Additionally, the installation of charging infrastructure often requires significant upgrades to local power grids to handle the increased electricity demand. These logistical and technical challenges can slow down the rollout of the necessary infrastructure, limiting the growth of EV fleets and battery swapping solutions, and making it difficult to meet rising demand.
Opportunities
Standardization Alliances for Battery Packs and Connectors
The development of standardization alliances for battery packs and connectors represents a significant opportunity for the electric vehicle and energy sectors. By creating universal standards for battery packs and charging connectors, manufacturers and service providers can improve interoperability, reduce costs, and enhance the convenience of EV usage. Standardized systems would allow electric vehicles from different manufacturers to use the same battery types and charging stations, simplifying fleet management and boosting the adoption of EVs. This standardization would also make it easier for battery swapping and charging infrastructure providers to expand, as they can target a broader range of electric vehicles without worrying about compatibility issues.
Swap Enabled Financing and Battery as a Service Programs
The rise of battery-as-a-service (BaaS) and swap-enabled financing programs presents a new avenue for growth in the electric vehicle market. These innovative business models allow customers to purchase or lease electric vehicles while separately renting or swapping batteries, reducing the upfront cost of EV ownership. BaaS programs also ensure that users always have access to fully charged, high-performance batteries, while vehicle manufacturers can focus on the vehicle itself, rather than the battery technology. Swap-enabled financing, where the cost of battery leasing is integrated into the vehicle’s operating costs, makes EV adoption more affordable and convenient for businesses and consumers alike, helping to accelerate the transition to electric fleets.
Future Outlook
The Philippines EV battery swapping market is expected to witness continued growth as government support, technological advancements, and growing consumer demand for eco-friendly transport solutions converge. Expanding infrastructure networks, particularly in underserved regions, and enhancing interoperability between different EV brands will be key to sustaining this growth. Strategic partnerships and collaborations between local and international players are expected to drive technological innovation and improve market penetration, creating a competitive landscape conducive to long-term success.
Major Players
- Voltai
- Gogoro
- Oyika
- Pilipinas Shell
- NIO
- GreenPack
- Sun Mobility
- Pushme
- Frot & Sullivan
- Aboitiz Power
- Kymco
- Tata Power
- Vivo Energy
- BYD
- Tesla
Key Target Audience
- EV Fleet Operators
- Electric Vehicle Manufacturers
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
- Battery Swapping Service Providers
- Automotive Industry Regulators
- Energy & Utility Companies
- Infrastructure Development Companies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
This step involves defining all critical market variables that will influence the Philippines EV battery swapping market. It will include an ecosystem map that covers stakeholders such as battery suppliers, service providers, and regulatory bodies.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, data from historical sources will be analyzed to establish market size, growth trends, and adoption rates. This data will be used to create forecasts and models for market expansion.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses will be tested through consultations with industry experts, stakeholders, and thought leaders. Insights from these discussions will validate assumptions and refine data models.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final analysis will incorporate both quantitative and qualitative data, synthesizing the results to provide a detailed and actionable report on the Philippines EV battery swapping market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, terminology and abbreviations, battery swapping system taxonomy, market sizing logic by swap stations and swap events, revenue attribution across hardware software and service plans, primary interview program with operators OEMs utilities and regulators, data triangulation and validation approach, assumptions limitations and data gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution of Swapping Models in the Philippines
- Two Wheeler and Three Wheeler Electrification Context
- Battery Swapping Value Chain and Operating Model Map
- Power Availability Site Access and Permitting Realities
- Growth Drivers
Last mile delivery growth and rider fleet electrification
High daily utilization needs that favor rapid energy replenishment
Total cost of ownership pressure from fuel price volatility - Challenges
Fragmented battery formats and weak interoperability
Site acquisition constraints and power upgrade requirements
Battery asset ownership risk and cycle life uncertainty - Opportunities
Standardization alliances for battery packs and connectors
Swap enabled financing and battery as a service programs
Partnerships with convenience stores fuel stations and malls - Trends
Shift from pilot deployments to corridor density buildout
Rising use of data analytics for routing and station placement
Bundling of swapping with telematics and fleet productivity tools - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Swap Station Count, 2019–2024
- By Battery Pack Circulation Base, 2019–2024
- By Swap Events Volume, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Consumer two wheelers
Commercial delivery rider fleets
E tricycles and three wheelers
Light commercial fleet vehicles
Public mobility and transport operators - By Application (in Value %)
Last mile delivery and logistics
Ride hailing and on demand mobility
Commuter urban transport
Campus and industrial estate mobility
Intercity corridor operations - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Standardized modular battery packs
Proprietary OEM locked battery formats
Smart cabinet based swap stations - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone swapping networks
App enabled user and station management
Cloud fleet dashboard and dispatch integration - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
E motorcycle and e scooter OEMs
Logistics and courier companies
Retail and FMCG distribution fleets
Shared mobility operators
- Market share of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (swap time per event, station throughput capacity, battery interoperability readiness, battery cycle life management approach, safety certifications and thermal monitoring, pricing model flexibility, software fleet integration capability, network uptime and service coverage)
- SWOT analysis of major players
- Pricing and benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Gogoro
Oyika
Sun Mobility
Ample
NIO Power
CATL EVOGO
Aulton New Energy
Geely Swapping Services
Honda Mobile Power Pack Solutions
Yamaha Battery Swapping Programs
Kymco Ionex
Silk Road Energy
Numocity
Bolt Earth
Swap Mobility Philippines
- Fleet procurement logic and electrification decision triggers
- Rider economics and willingness to pay for swapping convenience
- Service reliability expectations and uptime sensitivity
- Battery subscription acceptance and churn drivers
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Swap Station Count, 2025–2030
- By Battery Pack Circulation Base, 2025–2030
- By Swap Events Volume, 2025–2030