Market Overview
The Philippines EV charging infrastructure market is valued at USD 168.30 million. This valuation reflects the installed base of public and private EV charging stations, fueled by the expanding number of registered EVs—reported to exceed 16,000 units in 2023. The market is driven by renewed zero‑tariff policies on EV imports and components, which have spurred launches like Tesla’s first Supercharging station and large-scale commercial hubs like Mober’s 56‑port Central Charge.
Charging infrastructure development is particularly concentrated in urbanized centers such as Metro Manila and major expressway corridors, where demand and foot traffic are highest. Large operators—SM Supermalls, Shell (Recharge), Tesla, and Mober—have prioritized these zones, enabling easier access, higher utilization, and targeted EV adoption strategies that reinforce their dominance.
Market Segmentation
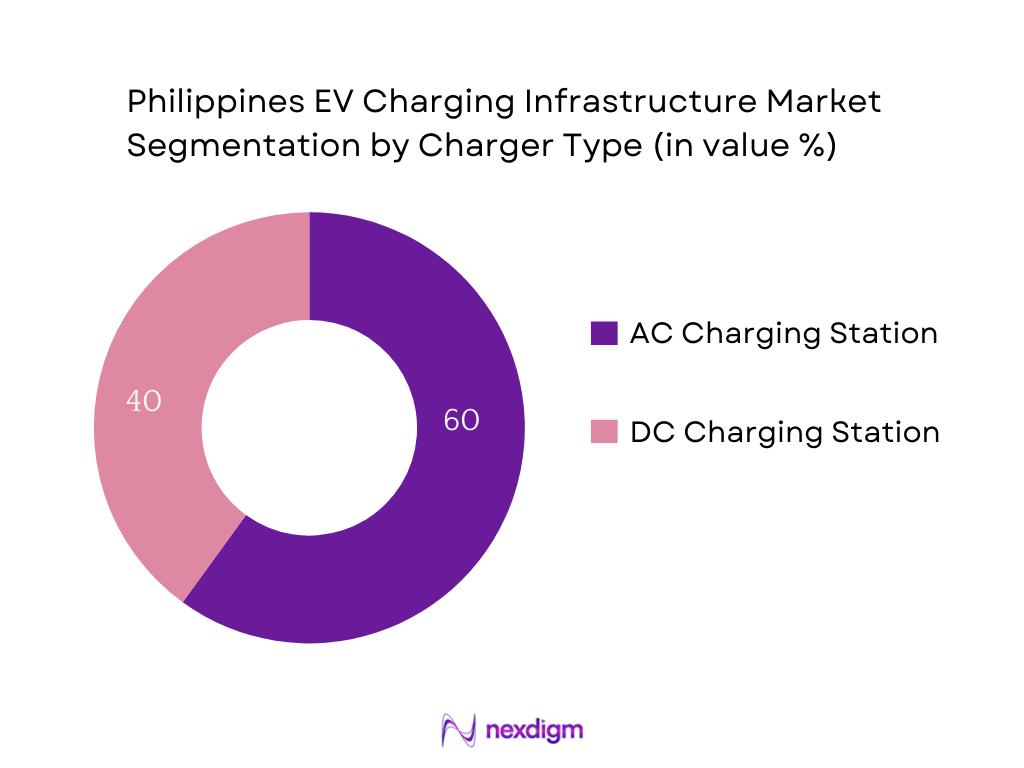
By Charger Type
Sub-segments: AC Charging Stations and DC Charging Stations. Both dominate due to complementary roles: AC chargers are cost-effective, simpler to install, and compatible with standard EVs—making them pervasive in workplaces and residential settings. DC chargers, while more expensive, are essential for fast-charging needs on expressways and high-traffic zones where time savings are critical. The dual availability ensures both convenience and speed, catering to both daily users and long-distance travelers.
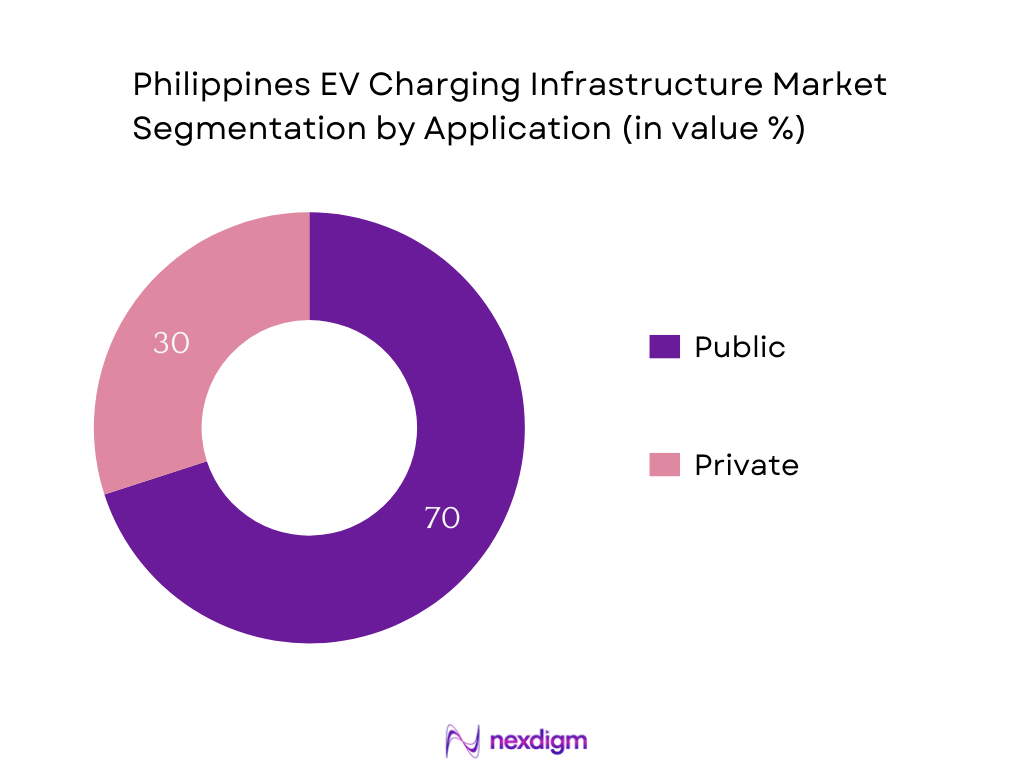
By Application
Sub-segments: Public and Private. Public charging dominates because it addresses range anxiety and supports visibility and accessibility, especially in malls (SM, Robinsons), expressways (TPLEX/Shell Recharge), and high-traffic zones. Users often prefer these public points for convenience, especially outside home charging hours. Private charging, while growing, remains limited due to upfront installation costs and lower prevalence of home EV ownership infrastructure.
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines EV charging infrastructure market is concentrated among a handful of strategic players representing CPOs, mall operators, utilities, and global OEMs. This consolidation highlights their pivotal roles in expanding infrastructure, securing high-visibility locations, and deploying advanced technologies.
| Player | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Vehicle Type Focus | Charger Type Focus | Strategic Strengths | Notable Deployment Focus |
| Shell Pilipinas (Shell Recharge) | — | Philippines | — | — | — | — |
| Tesla Philippines | 2003 (global) | US | — | — | — | — |
| Mober (Central Charge) | — | Philippines | — | — | — | — |
| SM Supermalls | 1958 (SM group) | Philippines | — | — | — | — |
| Meralco / Movem Electric | 1903 / Movem newer | Philippines | — | — | — | — |
Philippines EV Charging Infrastructure Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
The Philippines’ economy saw its GDP rise from USD 437.15 billion in 2023 to USD 461.62 billion in 2024, reflecting strengthening domestic demand that boosts both private and commercial investments in infrastructure. Concurrently, urban electrification reached approximately 98 percent of the population in 2023, which enables reliable deployment and utilization of EV charging stations. Additionally, ADB injected a USD 100 million electric mobility financing package in January 2025 to support installation of EV charging stations and procurement of commercial EVs. These macroeconomic factors—strong GDP growth, near-universal electricity access, and substantial dedicated financing from multilateral bodies—create a fertile foundation for the accelerated roll-out of EV charging infrastructure across urban and semi-urban areas.
Market Challenges
Despite strong economic momentum, several structural challenges impede scaled deployment of EV charging infrastructure. Firstly, the renewable share in installed capacity stood at only 30 percent in 2023, leaving a large base generation mix dependent on conventional sources and hindering grid resilience needed for high-demand charging hubs. Secondly, while overall electrification is high, rural access gaps may persist—though national electrification is improving, off-peak reliability in remote areas can be erratic, affecting charger uptime in less urban localities. Finally, while EV registrations exceeded 16,000 units in 2023, public EV charging stations numbered just 592, indicating a disproportion of approximately one charging station per 27 EVs—a strain on charging availability and site economics. These constraints—low renewable grid share, uneven electrification reliability, and limited station density—pose tangible hurdles to economically viable, resilient network expansion.
Opportunities
The present landscape also furnishes several compelling growth opportunities anchored in macro indicators but framed for future expansion. The Philippines’ GDP per capita rose from USD 3,746 in 2023, with modest improvements underway, signaling growing purchasing power among emerging middle-class segments. Meanwhile, the ADB’s USD 100 million electric mobility financing creates momentum for infrastructure rollout and stimulates private sector involvement. Also, the World Bank is facilitating reforms aimed at increasing the renewable share from 30 percent in 2023 to 42 percent by 2027, which would strengthen grid flexibility and lower operating risks for charging systems. Together, rising per-capita incomes, structured external financing, and energy transition policies provide a robust enabling environment for sustained expansion of EV charging infrastructure, particularly in urban corridors, fleet hubs, and renewable-integrated sites.
Future Outlook
Over the next several years, the Philippines EV charging infrastructure market is poised for robust expansion, supported by sustained government incentives, private-sector investments, and technological advancements. Continued zero-tariff policies and infrastructure projects like large hubs and utility-backed deployments will accelerate network density. Addressing range anxiety and improving charging accessibility will further invigorate EV adoption across private and public segments.
Major Market Players
- Shell Pilipinas (Shell Recharge)
- Tesla Philippines (Supercharging)
- Mober (Central Charge)
- SM Supermalls (SM Prime)
- Meralco / Movem Electric
- ParkNCharge
- EEI Power Corporation
- SysNet Integrators
- Robinsons Land (Robinsons Malls)
- Megaworld Lifestyle Malls
- Unioil (EV charging sites)
- Delta Electronics (Philippines)
- ABB (Philippines)
- QEV Philippines
- ChargeEuropa (Movem-linked network)
Key Target Audience
- Major Energy / Utility Corporations
- Real Estate Developers & REITs with Retail Portfolios
- Oil & Gas Retailers
- Automotive OEMs & EV Importers
- EV Logistics Fleet Operators
- FinTech & Payment Platforms
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We began by mapping the EV charging ecosystem in the Philippines—including public and private charging operators, technology standards (OCPP, ISO 15118), regulatory enablers (zero-tariff policies), and market demand signals (EV registry numbers). This step drew on desk research, industry reports, and policy documents.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Next, we consolidated historical data on charging station rollouts, port counts, EV registrations, and investment announcements. We also assessed pricing structures, site utilization, and adoption catalysts to derive realistic revenue estimations.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Our hypotheses on market growth, operator strategies, and adoption profiles were validated through CATI interviews with stakeholders—CPOs, mall operators, utility executives, and DOE representatives—to refine financial and operational models.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
In the final phase, we engaged with leading operators (e.g., Shell, SM, Mober, Meralco) to corroborate findings. This ensured consistency between our bottom-up model and on-ground realities, producing a thoroughly validated and accurate market narrative.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions; DOE EVCS registry scope; EVIDA compliance; CREVI building code parameters; connector standards OCPP/ISO 15118; bottom-up site audit & power profiling; top-down EV parc & load forecast; tariff structure validation; primary interviews with CPOs/mall operators/utilities; triangulation & cross-verification)
- Definition & Scope
- Evolution & Timeline of Key Market Milestones
- Ecosystem Structure & Stakeholder Map
- Supply Chain & Value Chain Analysis
- Revenue Models & Monetization Pathways
- Growth Drivers
- Market Challenges
- Opportunities
- Trends
- Government & Regulatory Framework (EVIDA IRR, CREVI, DOE unbundling rules, DPWH accreditation)
- Stakeholder Ecosystem (DOE, DOTr, DUs, CPOs, mall/REIT operators, OEMs, fintech/payment gateways)
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Risk & Resilience Factors
- Unit Economics & Sensitivity Analysis
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume (Installed Ports, Sites, kW), 2019-2024
- By Average Charging Fee (Energy + Service Components), 2019-2024
- By Charger Power Class
AC 7–22 kW
DC 30–60 kW
DC 90–180 kW
DC ≥300 kW
Bus/Depot Megawatt-Class Ready - By Connector Standard
Type-2
CCS-2
CHAdeMO
GB/T (legacy/import)
MCS readiness for depots - By Use-Case / Location
Forecourt & Service Stations
Destination / Retail Malls
Workplace / Office Complexes
Fleet Depots / Logistics Hubs
Expressway Corridors (SLEX/NLEX/TPLEX)
Airports, Ports & SEZs
Residential & Condominiums - By Operator Type
Utility-Affiliated
Oil & Gas Forecourt Operators
Mall / REIT-led CPOs
Independent CPOs / Tech Platforms
Government / LGU Sites - By Vehicle / User Segment
Private BEV/PHEV
TNVS / Taxi Fleets
E-Jeepney
E-Bus
2- & 3-Wheel Last-Mile Fleets
Corporate & Institutional Fleets
- Market Share Analysis (Ports, Sites, Installed kW)
- Cross-Comparison Parameters (Public Port Count, DC Share, Max Power Rating, OCPP Version, Payment Integration, Average Charging Fee, Roaming Partnerships, Uptime SLA)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Players
Shell Pilipinas (Shell Recharge)
ACMobility (Ayala Group)
Meralco / Movem Electric
ParkNCharge
EEI Power Corporation
SysNet Integrators
SM Supermalls (SM Prime)
Robinsons Malls (Robinsons Land)
Megaworld Lifestyle Malls
Unioil
Delta Electronics Philippines
ABB (Philippines)
QEV Philippines
ChargeEuropa
V-Green / Green GSM
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Average Charging Fee, 2025-2030


