Market Overview
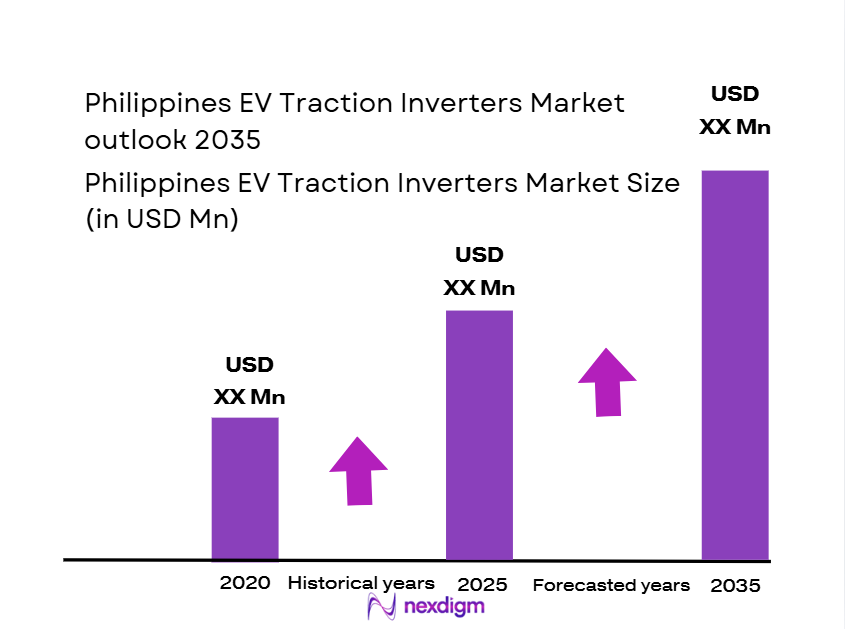
The Philippines electric vehicle (EV) traction inverter market is growing rapidly, driven by a combination of government initiatives, rising environmental awareness, and increased adoption of electric mobility. The market is valued at ~USD million in 2024, with continued growth projected due to the expanding local automotive ecosystem and the push towards clean transportation. The market’s dynamics are heavily influenced by local policy support such as the EV industry roadmap, and government incentives, which aim to boost EV adoption across various segments, including passenger vehicles and public transportation.
Metro Manila, Cebu, and Davao are the dominant cities driving the EV traction inverter market in the Philippines. Metro Manila, as the nation’s capital, leads the market with the highest vehicle fleet and transportation demand. The government’s green transportation initiatives in these urban areas encourage electric vehicle uptake, including EV buses and electric jeepneys. Cebu, a vital hub for trade and commerce, is also witnessing rising EV adoption, while Davao’s growing focus on sustainable development contributes to its increased role in the market.
Market Segmentation
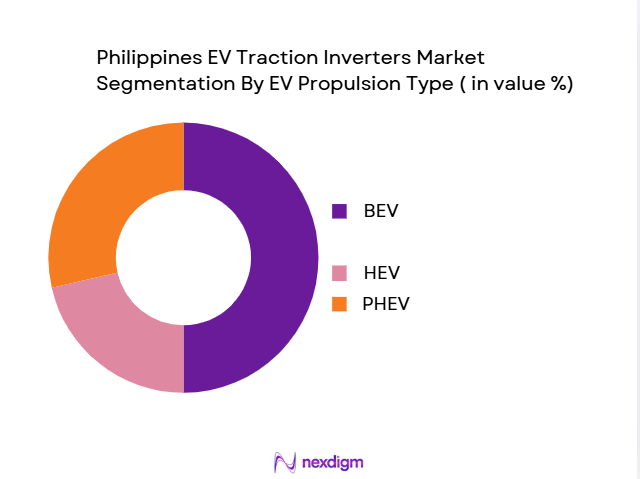
By EV Propulsion Type
The Philippines EV traction inverter market is segmented by EV propulsion types into Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV), Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV), and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV). Among these, Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) have dominated the market share in 2024. This is attributed to the increasing preference for fully electric, zero-emission vehicles, particularly in urban areas like Metro Manila where EV policies, government incentives, and the growing infrastructure for charging stations are promoting BEV adoption. The transition to BEVs is also supported by advancements in battery technologies that improve driving range and reduce overall vehicle costs.
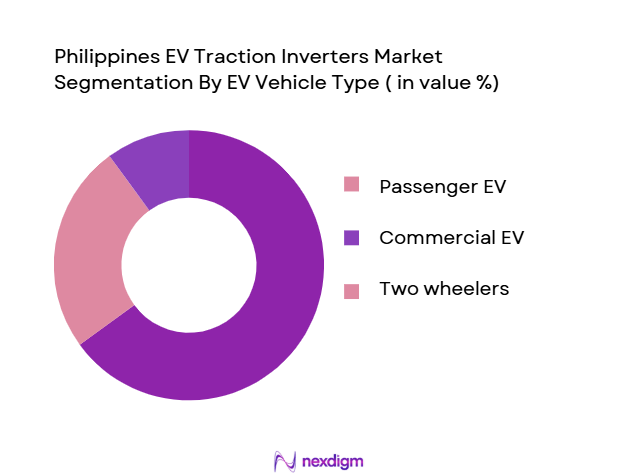
By EV Vehicle Type
The market is further segmented by vehicle types, which include passenger EVs, two-wheelers, and commercial EVs. In 2024, passenger EVs dominate this segment. The increase in consumer interest for electric sedans and SUVs, particularly in larger cities like Metro Manila, is attributed to the growing trend of environmentally conscious consumers. With the ongoing development of EV-friendly infrastructure, such as charging stations and financing options, passenger EVs are expected to continue capturing the majority of the market. The government’s push to electrify public transport further supports this dominance by introducing electric buses and jeepneys.
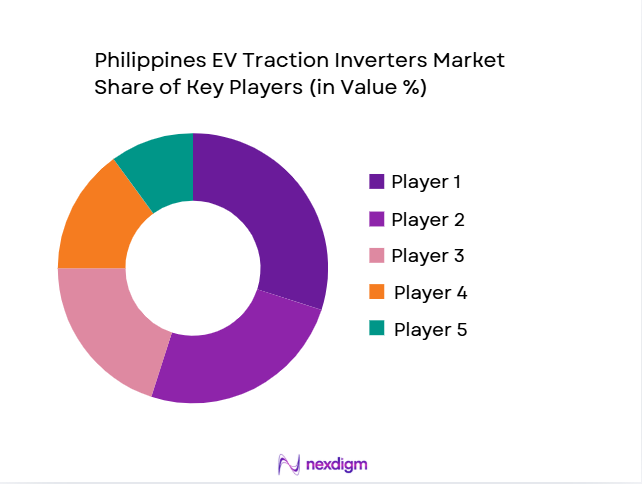
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines EV traction inverter market is competitive, with several local and international players striving to cater to the growing demand for electric vehicles and supporting technologies. Major players include established power electronics companies, OEMs, and Tier-1 suppliers that provide traction inverters and related components for EV applications. The market is dominated by major international suppliers such as Infineon Technologies, Bosch, and Mitsubishi Electric, who are driving technological advancements, including the transition to SiC and GaN-based inverters, crucial for high-performance EV powertrains.
| Company | Year Established | Headquarters | Product Range | R&D Focus | Market Presence | Key Clients |
| Infineon Technologies | 1999 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Mitsubishi Electric | 1921 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Bosch Automotive | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| STMicroelectronics | 1987 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Continental AG | 1871 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines EV Traction Inverters Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Urbanization
Philippines urban population has been steadily increasing, contributing to rising air pollution levels in major cities. As of 2022, more than ~% of Philippines population lives in urban areas, a figure projected to rise to ~% by 2035, according to the World Bank. This rapid urbanization exacerbates the demand for air quality monitoring systems (AQMS) as more industrial activities, transportation, and waste generation increase air pollution. Cities like Jakarta, Bandung, and Surabaya are particularly affected by high levels of particulate matter (PM2.5), making real-time air quality data crucial to mitigating health risks. This surge in urban population drives the need for more effective monitoring solutions to ensure public health and safety.
Industrialization
Indonesia’s industrial output has been growing rapidly, with the manufacturing sector contributing ~% to GDP in 2022, per the World Bank. Industrial activities such as mining, energy production, and transportation contribute heavily to air pollution in regions surrounding industrial zones. In response to these activities, air quality monitoring systems are critical for measuring pollutants like sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and particulate matter (PM). The industrial sector’s continued growth will drive the demand for advanced AQMS to assess and mitigate environmental and health impacts, especially as stricter emission regulations are enforced by the government.
Restraints
High Initial Costs
The high initial costs of implementing advanced air quality monitoring systems pose a significant barrier to market growth in Indonesia. AQMS infrastructure, including sensors, data collection systems, and software platforms, requires substantial capital investment. For example, setting up a single air quality monitoring station can cost upwards of USD ~, with ongoing maintenance and calibration costs. For many local governments and small businesses, these upfront costs are prohibitive, especially when compared to the ongoing operating costs of such systems. As a result, this is delaying the widespread adoption of AQMS, particularly in smaller municipalities and rural areas.
Technical Challenges
Technical challenges related to the accuracy, calibration, and maintenance of air quality monitoring systems are another key restraint. In 2023, Indonesia faced significant challenges with the deployment of low-cost air monitoring devices that were often found to have calibration issues or inaccuracies. The tropical climate and high humidity levels in Indonesia can affect sensor performance, leading to lower reliability of the data collected. As AQMS technologies evolve, ensuring system durability and accuracy in harsh environments remains a technical challenge that must be overcome for more widespread adoption.
Opportunities
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in air quality monitoring systems present significant opportunities for the Indonesian market. The rise of low-cost, high-precision sensors and real-time data analytics has made AQMS more accessible and accurate. In particular, the integration of IoT technologies allows for the seamless monitoring of air quality through connected devices. As these innovations reduce costs and increase efficiency, more businesses and local governments will be incentivized to adopt AQMS. Additionally, AI and machine learning are enhancing predictive capabilities, enabling better forecasting of pollution events. These advancements are likely to fuel further growth in the AQMS market.
International Collaborations
Indonesia’s increasing collaboration with international organizations and governments to improve air quality presents another growth opportunity for AQMS. In 2023, Indonesia partnered with the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the World Health Organization (WHO) to enhance air quality monitoring frameworks across major cities. These partnerships have enabled the country to access advanced technologies and financial support to strengthen its air quality management systems. Such collaborations open up the potential for further investment in monitoring systems, as well as sharing best practices from countries with more advanced air quality monitoring infrastructure.
Future Outlook
Over the next few years, the Philippines EV traction inverter market is expected to show significant growth. The government’s support for sustainable transportation through tax incentives and funding will continue to drive demand for EVs and, in turn, for traction inverters. The adoption of cutting-edge technologies such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) semiconductors in traction inverters will likely improve the performance and efficiency of electric vehicles. Additionally, as local manufacturers begin to focus on scaling up EV production, the need for localized inverter solutions will rise, contributing to market expansion.
Major Players
- Infineon Technologies
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Bosch Automotive
- STMicroelectronics
- Continental AG
- Nidec Corporation
- Denso Corporation
- Eaton Corporation
- Valeo
- Delphi Automotive
- LG Electronics
- Hitachi Ltd.
- Fuji Electric
- Siemens AG
- ABB Group
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers)
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Electric Vehicle Component Suppliers
- Energy & Infrastructure Companies (EV Charging Stations)
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Department of Energy, Philippines)
- Transportation Companies (Electric Bus Operators, Fleet Owners)
- Automotive Tier-1 Suppliers
- EV Manufacturers and Startups
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research begins with the identification of key market variables, including electric vehicle adoption rates, technology integration in traction inverters, and local infrastructure developments. This phase utilizes both secondary data and market reports to gain a comprehensive understanding of the variables driving the market.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Next, the analysis of market trends, historical performance, and the influence of key drivers such as government policies and technological innovations is conducted. This helps in creating an accurate construction of market projections and segment-specific demand analysis.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses regarding the future growth and market challenges are validated through interviews with industry experts, government representatives, and major EV manufacturers in the Philippines. These consultations provide deeper insights into future market scenarios.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase integrates all gathered data, including expert opinions and primary research findings, to synthesize a comprehensive analysis. This stage validates all projections and market assumptions through real-time industry feedback.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions & Component Scope, Assumptions & Data Normalization, Secondary & Primary Research Framework, EV Adoption Indicators & Policy Drivers Used for Forecasting, Limitations & Confidence Intervals)
- Traction Inverter Market Context (Link to Powertrain & EV markets in Philippines)
- Technology Evolution & Genesis
- From IGBT ↔ MOSFET ↔ Gallium Nitride (GaN) Technologies
- Compact Integrated Drive Unit (IDU) Trends
- EV Powertrain Adoption Lifecycle (Philippines Focus)
- BEV, HEV, PHEV Adoption & Impact on Inverter Demand
- Traction Inverter Functional Value Chain
- Input Semiconductors → Power Modules → Inverter Packaging → EV OEM Integration
- Growth Drivers
Government Clean Mobility Incentives & Emission Roadmaps
Increasing EV Registrations / Fleet Electrification
Component Localization and Supplier Development
- Challenges
Limited Local Manufacturing Scale
Raw Material & Semiconductor Supply Constraints
High Initial Cost of Advanced Inverter Platforms - Market Opportunities
SiC/GaN Technology Adoption Premium
Aftermarket Electrification & Retrofit Growth
Local EV OEM Partnerships & Assembly Plans - Emerging Trends
Smart Inverter Integration (Connectivity + Diagnostics)
Thermal / Efficiency Enhancements
Tier‑1 / System Supplier Collaboration Patterns - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
EV Tax Incentives, Import Duty Structures
Energy Efficiency & Safety Certifications
Local Automotive Standards Convergence - SWOT & Competitive Positioning
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity and Entry Barrier Assessment
- Value (USD) Metrics 2019- 2025
- Volume (Units Shipped / Installed) 2019- 2025
- Average Selling Price (ASP) Dynamics 2019- 2025
- Regional Volume Split (Metro Manila, Cebu, Davao) 2019- 2025
- By EV Propulsion Type (In value %)
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV) [Component Integration Levels]
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV)
Plug‑in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV)
- By Vehicle Application (In value %)
Passenger EVs (Cars, SUVs)
Two‑Wheelers (Scooters, Motorbikes)
Commercial EVs (E‑Trucks, Buses)
- By Power Rating Band (In value %)
kW (Light EV & 2‑Wheeler)
kW (Mid‑Range Passenger)
kW (Commercial / Heavy EV) - By Semiconductor Technology (In value %)
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field‑Effect Transistor
Silicon Carbide
Gallium Nitride
- By System Integration Type (In value %)
OEM Integrated Inverter Solutions
Aftermarket / Retrofit Systems
Modular Platform Inverters
- Market Share of Major Players
- Cross Comparison – Key Vendors
(Company Overview, Product Portfolio Breadth, Revenue & Growth, R&D Intensity, Regional Footprint, Pricing Strategy, Technology Leadership, OEM & Tier‑1 Partnerships) - SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing Analysis of Major Players
- Detail Profiles of Major Philippines EV Traction Inverters
Infineon Technologies AG
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
BorgWarner Inc.
Continental AG
ZF Friedrichshafen AG
Hitachi Astemo, Inc.
STMicroelectronics N.V.
Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Delphi / BorgWarner Subsidiaries
Magna International Inc.
Dana Incorporated
ABB Ltd.
Eaton Corporation Plc
GKN Automotive (Traction Components)
- Demand Drivers by EV Segment
- OEM Procurement & Qualification Criteria
- Aftermarket Demand Signals
- Pricing Sensitivity & TCO Analysis
- Pain Points, Priorities & Purchase Criteria
- By Value Forecast (USD), (2026–2030)
- By Volume Forecast (Units), (2026–2030)
- By ASP & Technology Mix Projection, (2026–2030)


