Market Overview
The Philippines Garage Management Software market is valued at USD ~ million, supported by the rapid expansion of the national vehicle parc, which crossed ~ registered vehicles, and the formalization of automotive aftersales operations. Market expansion is driven by increasing digitization of independent garages, rising labor costs in urban workshops, and growing demand for billing transparency. The market recorded revenues of USD ~ million previously, reflecting rising adoption of SaaS-based workshop tools across passenger car, motorcycle, and fleet service centers, supported by expanding smartphone and broadband penetration.
The market is dominated by Metro Manila, Cebu, and Davao, due to vehicle density concentration, higher workshop digitization readiness, and the presence of dealership service networks. Metro Manila leads owing to high passenger car ownership, fleet operators, and dealership clusters requiring standardized workflows. Cebu benefits from regional logistics fleets and motorcycle repair density, while Davao’s dominance is driven by agricultural transport vehicles and expanding commercial vehicle service infrastructure. Urban labor costs and compliance pressure accelerate software adoption in these regions.
Market Segmentation
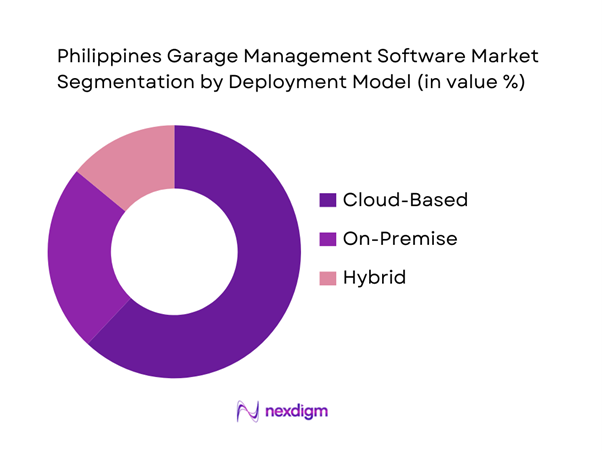
By Deployment Model
The Philippines Garage Management Software market is segmented by deployment model into cloud-based, on-premise, and hybrid systems. Among these, cloud-based deployment dominates, accounting for the largest share due to affordability, scalability, and mobile accessibility. Cloud platforms eliminate upfront infrastructure costs, a key advantage for small and mid-sized garages. SaaS platforms also enable automatic updates, tax-compliant invoicing, and remote monitoring, aligning well with the fragmented workshop ecosystem. Increasing smartphone-led operations and unreliable local IT support further reinforce cloud dominance.
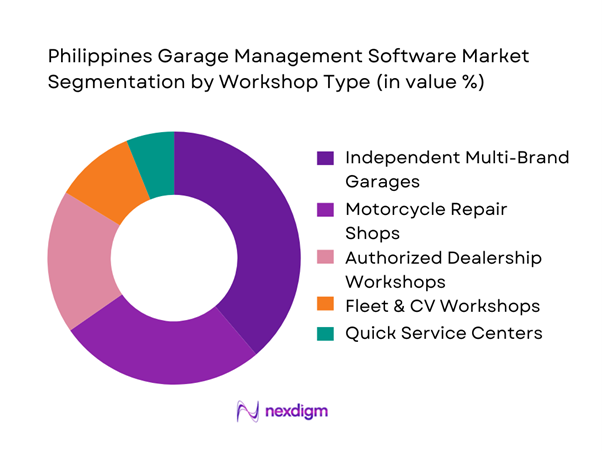
By Workshop Type
The market includes independent multi-brand garages, authorized dealership workshops, motorcycle repair shops, fleet & commercial vehicle workshops, and quick service centers. Independent multi-brand garages dominate due to their sheer volume and increasing need for inventory control and billing automation. These workshops face margin pressure, making cost-efficient software essential. Motorcycle repair shops follow closely, driven by the Philippines’ two-wheeler-heavy vehicle mix. Dealer workshops adopt advanced systems, but their limited count reduces overall share compared to independent operators.
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines Garage Management Software market shows moderate fragmentation, with global SaaS providers competing alongside regionally deployed platforms. International vendors lead in functional depth and integrations, while regional players compete on pricing and localization. Entry barriers remain low, but customer switching costs are rising as garages embed software deeply into workflows. Competitive advantage increasingly depends on mobile usability, compliance readiness, and customer onboarding efficiency.
| Company | Established | Headquarters | Core Deployment | Key End-User Focus | Mobile Capability | Localization Strength | Pricing Model | Integration Capability |
| AutoLeap | 2020 | US | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Shopmonkey | 2016 | US | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Tekmetric | 2015 | US | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GaragePlug | 2018 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| OmniAuto | 2017 | Asia-Pacific | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Garage Management Software Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Digitalization of informal garages
The Philippines’ vehicle service ecosystem is dominated by micro and informal operators, and the macro push toward digitization is making basic shop systems (job cards, customer history, parts issuing, and digital payments) operationally “necessary,” not optional. On the demand side, the economy’s scale supports more transactions moving through small enterprises: nominal GDP at USD ~ billion and output at PHP ~ billion typically increase the number of repair orders, walk-ins, and parts purchases that benefit from digital recording and reconciliation. On the enabler side, households’ ability to transact and communicate online has expanded, with ~ households having internet access at home, which matters because informal garages often depend on messaging for approvals and quotations. On the payments layer, digital payments’ share rose from ~ to ~ out of every ~ retail payment transactions, widening acceptance of QR and e-wallet settlement for repairs and parts—one of the fastest entry use-cases for garage software in small shops.
Expanding national vehicle parc
A growing and aging vehicle base increases service frequency (preventive maintenance, wear-and-tear replacements, diagnostics), which raises the value of structured workflows such as appointment queues, inspection checklists, parts reservation, and warranty or return tracking. Macroeconomically, nominal output reported at USD ~ billion and then USD ~ billion signals expanding mobility and logistics activity that translates into higher utilization and more repair events across urban corridors. At the household level, population scale also matters for two-wheel and four-wheel density, with the population listed at ~ and then ~, expanding the base of drivers and riders who depend on workshops for upkeep. In practice, high-concentration urban markets create operational complexity for service centers where even low-cost garage systems become valuable. The same concentration also increases repeat-customer value, as software that preserves service history and reminders improves retention when customers have many nearby substitutes.
Challenges
Price sensitivity of small workshops
A large share of workshops operate on thin cashflow and prefer “pay-as-you-go” tools, while upfront software commitments can be hard to justify when demand is volatile. Macroeconomic conditions shape that sensitivity, with average inflation at ~ for the year, squeezing discretionary spending for both consumers deferring repairs and micro-entrepreneurs delaying software spend. At the same time, operational inputs change frequently, with price adjustments such as a PHP ~ per liter move in key fuels raising logistics and supplier delivery costs and making owners prioritize immediate working capital over digitization. Even where digitization value is clear, the decision threshold is high, as the software must show fast payback through fewer comebacks, better parts control, and higher bay utilization. The adoption hurdle is especially acute outside major urban cores where transaction volume is lower and customers are highly price-driven.
Low IT literacy among operators
Many shop owners and foremen are excellent technicians but have limited comfort with structured data entry, accounting categories, or workflow enforcement, leading to partial adoption and eventual churn. The macro environment shows why this persists, as while the economy is large with nominal GDP at USD ~ billion, the informal sector remains significant and skill acquisition is uneven across regions. Digital access is improving, but access does not automatically translate to operational competence, with ~ households having home internet access also implying millions of households still operate without reliable connectivity, limiting continuous practice with digital tools. Payment digitization helps but can also confuse operators if not integrated, as digital payment shares moved from ~ to ~ out of every ~ retail payment transactions, while many small garages still struggle to reconcile e-wallet inflows with job tickets. Without strong UX design and hands-on training, IT literacy remains a binding constraint.
Opportunities
Motorcycle workshop digitization
Motorcycles drive a large share of everyday mobility, and the workshop landscape is highly fragmented, creating a sizeable digitization opportunity for lightweight garage systems that fit quick-turn jobs such as oil and filter changes, brake service, tire replacement, and chain or sprocket work. The macro backdrop supports this opportunity, with population scale increasing from ~ to ~, sustaining high commuter demand and frequent maintenance cycles for two-wheelers. Digital readiness is also improving, with ~ households having home internet access expanding the addressable base for messaging-based approvals, digital receipts, and service reminders that motorcycle shops can deliver with minimal process change. Payments behavior is shifting as well, with digital payment share moving from ~ to ~, supporting simple scan-to-pay settlement for low-ticket repairs and often serving as the first compelling workflow to digitize.
Fleet and telematics software integration
Commercial fleets such as delivery vans, service vehicles, shuttles, and contracted transport are increasingly managed through digital tools including dispatch, route planning, and in some cases telematics, creating a strong integration opportunity for GMS platforms. The macro context supports this, with nominal GDP at USD ~ billion and output at PHP ~ billion consistent with large-scale logistics and services activity where fleet uptime is directly tied to revenue. Fuel volatility reinforces maintenance discipline, as frequent pump price adjustments including PHP ~ per liter changes push fleets to reduce inefficiencies like unplanned breakdowns and repeat repairs. On the payments and documentation side, digital payments expanded from ~ to ~, enabling cleaner business-to-business settlement and audit trails that fleets require for internal controls.
Future Outlook
The Philippines Garage Management Software market is expected to expand steadily, driven by increasing vehicle ownership, rising workshop formalization, and government-mandated digital invoicing. The shift toward mobile-first platforms will accelerate adoption among micro and single-bay garages. Integration with spare-parts distributors, digital payments, and fleet telematics will emerge as key growth levers. Software vendors offering localized compliance, training support, and affordable tiered pricing will be best positioned to capture incremental demand across secondary cities.
Major Players
- AutoLeap
- Shopmonkey
- Tekmetric
- GaragePlug
- OmniAuto
- Mitchell 1
- AutoFluent
- RAMP Garage Management
- Torque360
- Protractor Garage Software
- GEM-Car
- Workshop Software
- AutoRepair Cloud
- Busy Workshop
Key Target Audience
- Independent automotive garage owners and service chains
- Authorized vehicle dealership workshop operators
- Fleet management and logistics companies
- Motorcycle service and repair networks
- Spare parts distributors with workshop tie-ups
- Automotive software vendors and platform providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research begins with ecosystem mapping of the Philippines automotive aftermarket, identifying workshops, dealers, fleet operators, and software providers. Secondary research sources include industry databases, transport authority statistics, and software adoption benchmarks to define key revenue and usage variables influencing market structure.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical data on workshop density, vehicle parc growth, and software adoption rates is analyzed to build the market model. Revenue normalization is conducted across deployment models, workshop sizes, and subscription tiers to ensure consistency.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market assumptions are validated through structured interviews with garage owners, dealership service managers, and SaaS vendors. These interactions provide insight into pricing tolerance, feature demand, and onboarding challenges, strengthening data accuracy.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Final estimates are synthesized using bottom-up workshop-level revenue mapping and cross-validated through vendor inputs. Findings are consolidated into a coherent market framework reflecting operational realities and adoption barriers.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Scope Boundaries, Market Sizing Logic, Bottom-Up Workshop-Level Estimation, Top-Down Vehicle Parc Mapping, Primary Interviews with Independent Garages and Dealer Workshops, SaaS Revenue Normalization Framework, Data Validation and Triangulation, Limitations and Research Constraints)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Digital Adoption Evolution
- Industry Timeline and Software Penetration Milestones
- Automotive Aftermarket Business Cycle Mapping
- Automotive Workshop Value Chain and Software Touchpoint Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Digitalization of informal garages
Expanding national vehicle parc
Rising labor cost pressures
Need for inventory shrinkage control
Standardization requirements in dealer workshops - Challenges
Price sensitivity of small workshops
Low IT literacy among operators
Internet reliability issues
Resistance to workflow standardization
Data migration and onboarding barriers - Opportunities
Motorcycle workshop digitization
Fleet and telematics software integration
Spare parts distributor software partnerships
Mobile-first SaaS adoption
Embedded payments and workshop financing - Trends
Cloud-first deployment preference
Mobile job card usage
Messaging-app-based customer engagement
Subscription bundling models
Open API integrations with POS and parts suppliers - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- Installed Base by Active Workshop Deployments, 2019–2024
- Average Revenue per Workshop, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Independent multi-brand garages
Authorized dealership workshops
Motorcycle repair shops
Fleet and commercial vehicle workshops
Quick service and lube centers - By Application (in Value %)
Job card and work order management
Inventory and spare parts management
Billing and invoicing systems
Customer relationship management and service reminders
Technician productivity and bay utilization - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Cloud-based SaaS platforms
On-premise software solutions
Hybrid deployment models - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Web-based systems
Mobile-first applications
Offline-capable systems with sync - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Passenger vehicle servicing
Two-wheeler servicing
Commercial vehicle maintenance
Fleet operations and logistics servicing - By Region (in Value %)
Metro Manila
Luzon (non-Metro)
Visayas
Mindanao
- Market share by active installations
- Cross Comparison Parameters (deployment model, core functional coverage, mobile application capability, localization and tax compliance, pricing model structure, average onboarding time, parts supplier integration, customer support and training depth)
- SWOT analysis of major players
- Pricing and packaging analysis by bay, user, and workshop
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
AutoLeap
Shopmonkey
Tekmetric
GaragePlug
OmniAuto
Workshop Software
AutoFluent
Mitchell 1
Autosoft
RAMP Garage Management
Torque360
AutoRepair Cloud
Busy Workshop
GEM-Car
Protractor Garage Software
- Workshop demand and usage intensity
- Budget allocation and willingness to pay
- Buying decision hierarchy
- Pain point and workflow gap assessment
- Software switching and churn dynamics
- By Value, 2025–2030
- Installed Base by Workshop Adoption, 2025–2030
- Average Revenue per Workshop, 2025–2030


