Market Overview
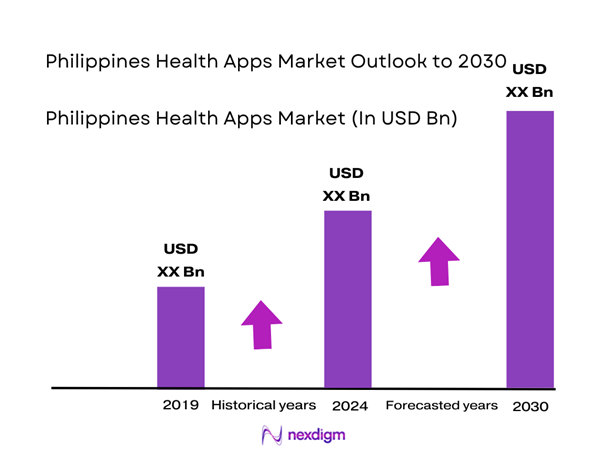
The Philippines Health Apps market (captured within the country’s broader eHealth ecosystem) is valued at USD ~ million in 2024, supported by rising usage of app-based teleconsultation, e-prescriptions, appointment booking, diagnostics scheduling, and medication delivery workflows across major provider networks. In 2023, the Philippines’ healthcare information system market generated USD ~ million, indicating increasing digitization spend that directly expands the addressable base for consumer and provider-facing app deployments (EHR/HIS connectors, e-claims, and patient portals).
Within the Philippines, Metro Manila remains the primary demand and supply hub for health apps due to higher density of tertiary hospitals, specialist networks, corporate payers, and digital health partnerships that accelerate patient acquisition and repeat usage. Cebu and Davao follow as scale cities where urbanization, private hospital expansion, and growing employer coverage support adoption beyond the capital. On the supply side, app ecosystems anchored by Metro Manila–based platforms and nationwide telco distribution relationships improve reach and engagement across islands, enabling stronger conversion outside Tier-1 metros as well.
Market Segmentation
By App Category
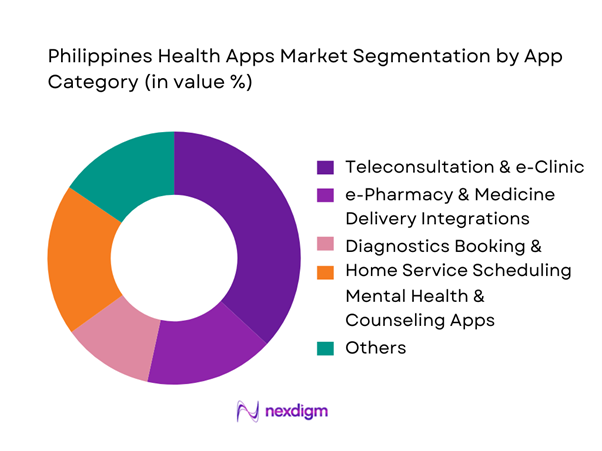
The Philippines Health Apps market is segmented into teleconsultation & e-clinic, e-pharmacy integrations, diagnostics scheduling, mental health, chronic care/adherence, and preventive wellness. Recently, teleconsultation & e-clinic holds the dominant share because it functions as the “front door” for digital care—capturing first contact, triage, follow-up, and referrals while minimizing travel friction across an archipelagic geography. The segment also benefits from expanded provider networks and HMO acceptance workflows inside major platforms that make booking and payment easier for consumers and employers. Platforms such as NowServing position teleconsultation as a core experience while layering labs and medication ordering inside the same journey, improving repeat usage. In parallel, KonsultaMD emphasizes 24/7 consultations with add-ons like medicine delivery and diagnostics, reinforcing teleconsultation’s centrality in the app value proposition.
By Customer / Contracting Model
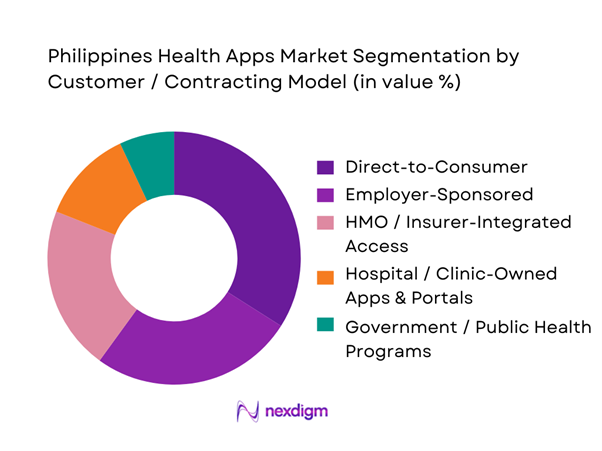
The Philippines Health Apps market is segmented into direct-to-consumer self-pay, employer-sponsored benefits, HMO/insurer-integrated access, hospital/clinic-owned apps, and government-linked programs. Recently, direct-to-consumer adoption leads because it scales fastest through app-store discovery, promos, and “pay-per-consult” simplicity—especially for primary care, minor acute issues, and quick follow-ups. Super-app designs reduce friction by bundling consult + prescription + lab/pharmacy options in one interface, which supports repeat transactions and higher retention. At the same time, DTC is strengthened by telco and ecosystem distribution, where platforms can rapidly onboard users without waiting for long enterprise procurement cycles. Employer and HMO models are growing (notably where HMOs are accepted directly in booking flows), but they typically require deeper integration and contracting, slowing scale relative to DTC.
Competitive Landscape
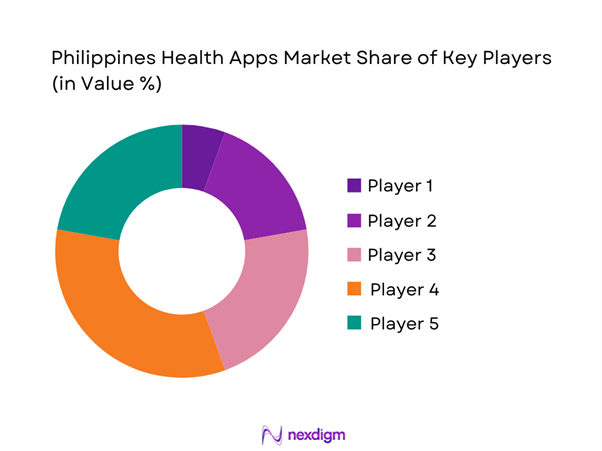
The Philippines Health Apps market is increasingly led by a set of scaled telehealth and integrated-care platforms (teleconsultation-first super apps, provider marketplaces, and telemedicine operators). Consolidation is visible around platforms that can (a) aggregate physician networks, (b) integrate labs/pharmacies/home care, and (c) secure enterprise/HMO distribution, creating a higher barrier to entry for single-feature apps. Examples include KonsultaMD, mWell, NowServing, Medgate, and SeeYouDoc, each differentiated by care breadth, speed-to-consult, and ecosystem partnerships.
| Company | Established | HQ (Primary PH Base) | Core Offering | Care Network Signal | Ecosystem Integrations | Coverage Model | Typical Use-Cases | Differentiation / Positioning |
| KonsultaMD | 2020 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| mWell | 2021–2022 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| NowServing (SeriousMD) | 2018–2019 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Medgate Philippines | 2000s | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SeeYouDoc | 2010s | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Health Apps Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Urban Congestion Impact on Care Access
Metro Manila’s mobility friction directly increases the “value of convenience” for health apps (e-consults, e-prescriptions, booking, and follow-up messaging) because an in-person visit competes with time lost on the road. In Manila’s metro area, the average travel time to drive ~ km is ~ minutes ~ seconds and the “worst day to travel” recorded was ~ minutes ~ seconds for the same ~ km trip—elevating opportunity-cost for clinic visits and repeat follow-ups. At the same time, MMDA’s annual traffic statistics show daily volume at ~ vehicles across major NCR corridors, with ~ motorcycles and ~ private cars recorded per day—intensifying unpredictability for appointment adherence and medication refills. This is occurring in an economy sized at USD ~ (GDP, current US$), so lost productivity time scales quickly in aggregate and pushes employers, families, and individuals toward digital “first-touch” triage, asynchronous chat, and repeatable care pathways. Health apps that reduce ~ physical trips per episode of care (screening, results review, chronic follow-up) become operationally attractive in dense urban cores where time and transport uncertainty act as friction taxes on healthcare access.
Smartphone Penetration and Data Affordability
Health apps scale fastest when (a) a large addressable base already carries an internet-capable device and (b) mobile data usage is behaviorally normalized (video, chat, uploads). The Philippines’ connectivity base is supported by ~ mobile cellular subscriptions, which is larger than the country’s population base and implies multiple SIM ownership that health apps can still monetize through multi-device households (parents + children + caregiver phones). On the “data behavior” side, the Philippines’ ICT performance signals high mobile-broadband activity: the ICT Development Index brief for the Philippines reports ~ mobile broadband internet traffic per subscription (as an indexed/standardized metric used in the IDI framework), consistent with frequent mobile usage patterns that make symptom checkers, chat consults, imaging uploads, and medication reminders workable at scale. Macro conditions also matter: with population at ~ and GDP at USD ~, health apps are selling into a large consumer market where “mobile-first” engagement is one of the few channels that can economically reach both dense cities and fragmented geographies. As telcos and digital infrastructure programs expand, health apps benefit disproportionately because their marginal distribution cost is near-zero compared with physical clinic expansion, and their service model maps naturally to the country’s high-SIM, high-mobile-usage reality.
Challenges
Physician Supply Fragmentation
Even when “total capacity” exists, fragmentation across facility types, islands, and scheduling systems creates access friction that health apps must solve but cannot fully control. Fragmentation shows up as repeat diagnostics, inconsistent follow-up, and a high burden on patients to coordinate records—driving dropout and mistrust if apps cannot ensure continuity. The financing pattern underscores this: household out-of-pocket spending increased from PHP ~ billion to PHP ~ billion, implying that many patients are directly price- and value-sensitive; if an app route results in repeated visits or redundant tests, conversion drops. Meanwhile, total health expenditure increased from PHP ~ trillion to PHP ~ trillion, indicating higher utilization volumes that require stronger coordination to prevent bottlenecks. PhilHealth’s large beneficiary base (e.g., ~ beneficiaries under Direct Contributors) can help standardize eligibility and claims-linked pathways, but provider-side heterogeneity remains: different clinics use different EMR maturity levels, and many still rely on paper-based workflows. In practice, this means health apps must invest in provider enablement (templates, e-prescription flows, referral loops) and patient record portability—not just consumer UI. Macro scale intensifies the coordination need: with population ~, fragmented systems create millions of small failures (missed follow-ups, unfilled prescriptions) that erode trust.
Regulatory Ambiguity for Digital Care
Digital care operators face “moving target” compliance across data privacy, cybersecurity controls, and sector-specific rules—particularly when services span teleconsults, e-prescriptions, e-pharmacy fulfillment, and employer health data. The National Privacy Commission (NPC) requires structured reporting via breach notifications and annual security incident reporting mechanisms, and its DBNMS live statistics provide real-time visibility into incident reporting volumes (e.g., ~ reports shown in the January–August period displayed on the live stats page, along with sector breakdown counts). Separately, NPC’s breach reporting guidance formalizes annual reporting expectations via ASIR (Annual Security Incident Report), which becomes a governance burden for health apps handling sensitive health data across multiple vendors and cloud stacks. The operational risk is amplified by the scale of digital users: mobile subscriptions at ~ means broad reach, but also broad exposure—one misconfiguration can affect large populations quickly. Macro context matters because compliance spend competes with growth investment: in a USD ~ economy, digital health is attractive, but enforcement uncertainty can slow enterprise procurement and insurer/employer rollouts unless vendors can prove audit-readiness.
Opportunities
Employer-Led Digital Care Expansion
The most scalable near-term growth path is employer-led distribution because it reduces CAC, increases utilization through policy nudges, and supports recurring programs (annual physicals, mental health, chronic risk). The payroll-linked health ecosystem is large: PhilHealth reports ~ direct contributor members and ~ dependents (total ~ beneficiaries), with private employed members at ~ and their dependents at ~. This provides a ready-made enrollment infrastructure for app-based triage, e-consults, and navigation. Simultaneously, total health expenditure rose from PHP ~ trillion to PHP ~ trillion, which strengthens the economic case for prevention: employers want fewer avoidable ER visits, faster return-to-work, and reduced absenteeism. Macro conditions support this opportunity: GDP USD ~ indicates a sizable formal sector with recurring HR budgets, while the country’s large population (~) supports multi-site employer rollouts. The opportunity is to package digital health apps not as “teleconsult only,” but as an employer health operating system: eligibility checks, care pathways, e-prescriptions, follow-up adherence, and claims-ready documentation—especially for dependents in provinces who otherwise have weak access. Vendors that integrate with HRIS, offer utilization dashboards (without exposing sensitive personal data), and maintain strong NPC-aligned governance are best positioned to convert employer intent into sustained usage. Importantly, this opportunity is backed by current system scale (coverage and spend) rather than future forecasts—making it actionable now for procurement cycles and benefits redesign.
Provincial Health Access Enablement
The Philippines’ geography makes “provincial enablement” a durable opportunity: apps can extend access without waiting for physical infrastructure to catch up, particularly for follow-ups, chronic monitoring, and navigation. The addressable base is large and not limited to NCR: urban population is ~, which implies tens of millions also reside outside dense urban cores—where provider availability, travel time, and specialist access are often more constrained. Mobile access supports provincial scaling: ~ mobile subscriptions creates a distribution layer that reaches beyond major cities, and OFW-linked households add financing and coordination demand (remittances at USD ~). The system spend environment supports service innovation: total health expenditure at PHP ~ trillion and out-of-pocket at PHP ~ billion indicate both public and private flows that can fund digital-first pathways if they reduce friction. The practical opportunity is to build “hub-and-spoke” digital models: provincial users get triage, repeat prescriptions, care plans, and follow-ups through apps; complex cases are routed to regional centers; labs and pharmacies become fulfillment partners. This can also be aligned with employer dependents and PhilHealth-linked eligibility journeys, creating a unified pathway across cities and provinces.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Philippines Health Apps market is expected to grow through deeper integration of teleconsultation into routine care pathways, expansion of HMO acceptance and corporate coverage, and stronger “care-at-home” service orchestration (labs, pharmacy, home nursing, and chronic monitoring). Growth is also supported by rising provider digitization spend and backend system adoption, which expands interoperability and improves patient experience across multi-visit care journeys. The country’s healthcare information system market outlook indicates ~ CAGR, which is a strong directional indicator for sustained app-layer growth built on expanding digital infrastructure.
Major Players
- KonsultaMD
- mWell
- NowServing
- SeriousMD
- Medgate Philippines
- SeeYouDoc
- Maxicare
- Zennya
- St. Luke’s eHealth Hub App
- MIMS Philippines
- AIDE
- TeleMedC
- Medifi
- The Filipino Doctor
Key Target Audience
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Healthtech operators and digital platform acquirers
- HMOs and private health insurers
- Employer groups / HR benefits decision-makers
- Hospital chains and tertiary care networks
- Diagnostic laboratory networks and home-service lab aggregators
- Pharmacy chains and e-pharmacy operators
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We construct an ecosystem map of the Philippines Health Apps market covering teleconsult platforms, provider networks, labs, pharmacies, payers, and regulators. This is supported by structured desk research using credible industry publications, company disclosures, and app ecosystem evidence. We define revenue drivers such as consultation volumes, subscription/bundled contracts, attach rates for labs/pharmacy, and enterprise/HMO integration depth.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historical indicators for eHealth demand, platform expansion signals, and healthcare IT enablement to build a consistent market model. We analyze how user acquisition and care journeys convert into revenue across DTC and enterprise channels, and how integration (labs/pharmacy/home care) changes monetization per active user.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validate hypotheses through structured expert consultations (CATIs) with platform operators, provider administrators, payer teams, and healthcare IT stakeholders. Interviews focus on operational metrics (doctor availability, consult throughput, cancellation/deflection), contracting models, and product roadmap priorities (interoperability, payments, and e-prescription workflows).
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We triangulate bottom-up signals (platform features, integration breadth, channel access) with top-down market anchors from established research sources to finalize sizing, segmentation, and competitive positioning. We then synthesize findings into actionable decision frameworks for investors, operators, and enterprise buyers.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Scope Boundaries, Philippines Health App Taxonomy, Abbreviation Framework, Market Sizing Logic, Bottom-Up User Monetization Modeling, Platform Revenue Mapping, Primary Stakeholder Interviews, Regulatory Cross-Verification, Data Triangulation, Limitations and Forward-Looking Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Platform Development Timeline and Inflection Points
- Digital Health Business Cycle Dynamics
- Ecosystem and Value Chain Mapping
- Growth Drivers
Urban Congestion Impact on Care Access
Smartphone Penetration and Data Affordability
Physician Density Imbalance
Overseas Filipino Family Health Needs
Employer Preventive Healthcare Spending - Challenges
Physician Supply Fragmentation
Regulatory Ambiguity for Digital Care
Patient Trust and Continuity Barriers
Out-of-Pocket Sensitivity
Data Privacy Compliance Complexity - Opportunities
Employer-Led Digital Care Expansion
Provincial Health Access Enablement
Mental Health Demand Acceleration
Chronic Disease Monitoring Integration
Cross-Selling with Pharmacy and Diagnostics - Trends
AI-Enabled Clinical Triage
Video-First versus Chat-First Care Models
E-Prescription Interoperability
Cloud Hosting Localization
API Integration with HMOs - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Revenue Contribution, 2019–2024
- By Active User Base, 2019–2024
- By Monetization Model, 2019–2024
- By Application (in Value %)
Teleconsultation Apps
Appointment Booking and Provider Discovery Apps
E-Prescription and Medicine Fulfilment Apps
Chronic Care and Disease Management Apps
Mental Health and Wellness Apps - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Individual Consumers
Employer-Sponsored Users
HMO-Covered Members
Overseas Filipino Worker Dependents
Corporate Clinics and Providers - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Standalone Consumer Apps
Marketplace Aggregators
Provider-Owned Platforms
HMO-Embedded Platforms
Super-App Health Modules - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Video-Based Consultation Platforms
Chat and Messaging-Based Platforms
Hybrid Communication Platforms
Asynchronous Care Platforms
AI-Assisted Interaction Platforms - By Region (in Value %)
National Capital Region
Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao
Offshore Filipino Markets
- Market Positioning of Key Players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (active user base, doctor network size, specialty coverage depth, monetization model mix, HMO integration level, employer contracting capability, technology stack scalability, data privacy and compliance readiness)
- Competitive SWOT Benchmarking
- Pricing and Monetization Analysis
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
KonsultaMD
SeriousMD
SeeYouDoc
HealthNow
mWell PH
AIDE App
MyDocNow
Zennya Health
NowServing
MedGrocer Health App
Medifi
Doctor Anywhere Philippines
RecoveryHub PH
Bayanihan Health App
Ayala Healthcare Digital Platforms
- Demand Patterns and Usage Intensity
- Purchasing Power and Payment Behavior
- Compliance and Trust Requirements
- Pain Points and Unmet Needs
- Decision-Making and App Selection Criteria
- By Revenue Contribution, 2025–2030
- By Active Users, 2025–2030
- By Monetization Model Evolution, 2025–2030


