Market Overview
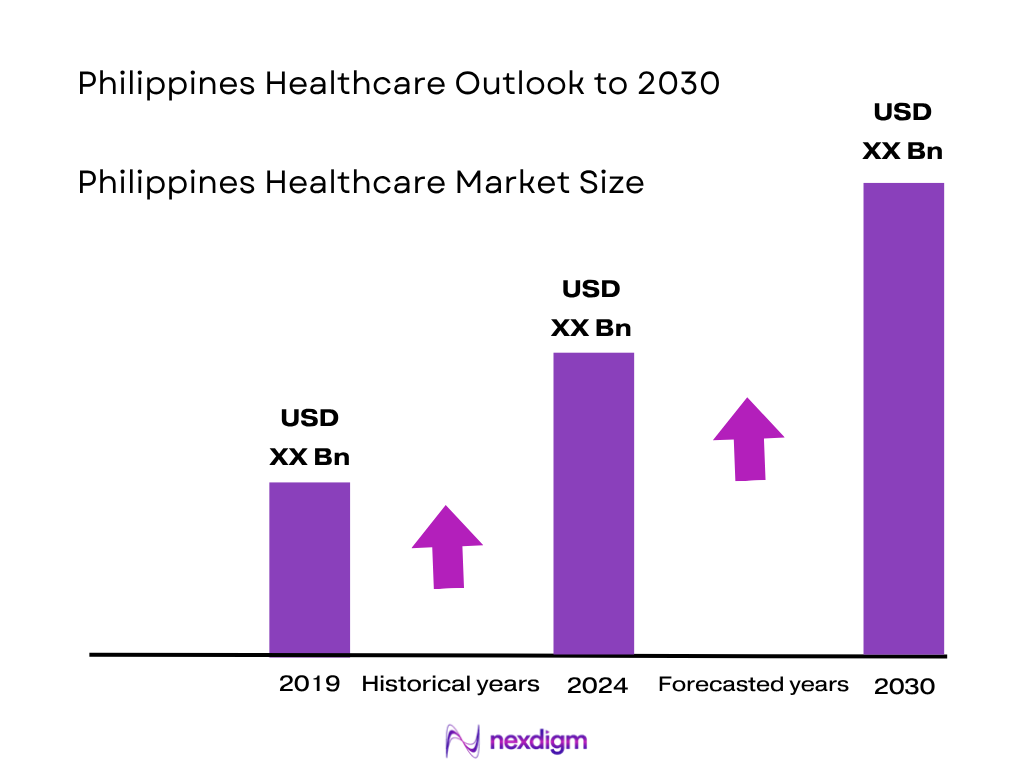
The Philippines healthcare market is valued at USD 6.7 billion, grounded in robust data that reflects rising public and private investments, rising healthcare utilization, and expanding middle-class demand. Additionally, sub‑segments such as home healthcare accounted for USD 2.39 billion, driven by aging populations, increasing chronic disease management needs, and greater preference for in‑home care. These figures underscore strong underlying demand and elevated spending levels.
Healthcare infrastructure is largely concentrated in Metro Manila, CALABARZON, and Central Luzon, where significant hospital facility development, foreign direct investments, and private equity inflows have occurred. These regions dominate due to urban density, stronger paying capacity, better logistical and technical support, and presence of high‑end private hospital networks, which collectively attract healthcare investments and boost service delivery efficiency.
Market Segmentation
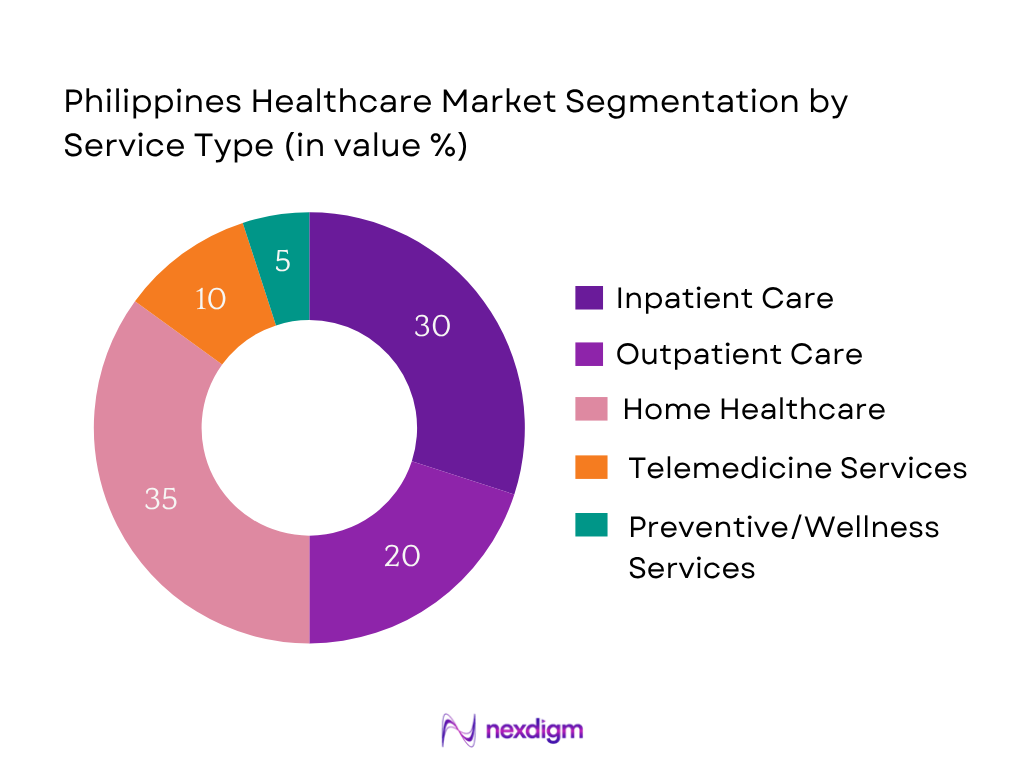
By Service Type
The Philippines healthcare market is segmented into inpatient care, outpatient care, home healthcare, telemedicine services, and preventive/wellness services. Currently, home healthcare holds a dominant market share (c. 35%)—driven by increasing aging‑population needs, geographic diffusion of care beyond urban hospital centers, and cost‑effectiveness compared to inpatient alternatives. This sub‑segment’s rise is also supported by technology‑enabled home monitoring and growing acceptance of in‑home skilled nursing, particularly in Metro areas and affluent provincial cities.
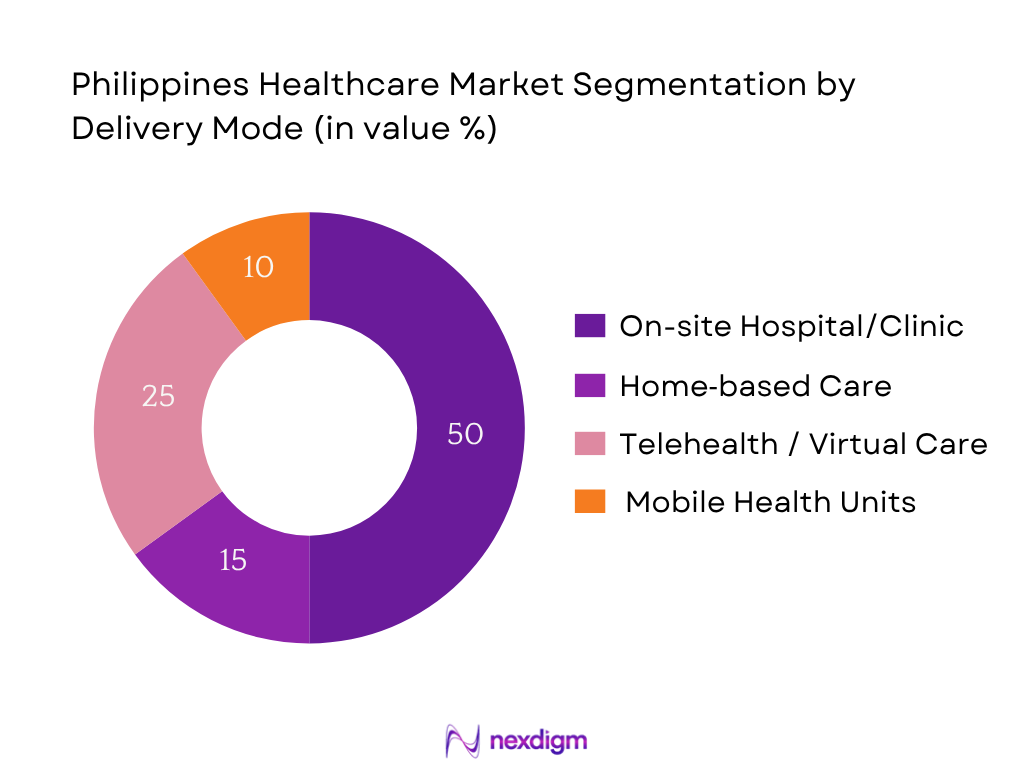
By Delivery Mode
The healthcare market is segmented into on‑site hospital/clinic treatments, home‑based care, telehealth/virtual care, and mobile health units. The on‑site hospital/clinic mode dominates with around 50% of the market. Filipino patients continue to rely heavily on traditional outpatient and inpatient hospital services due to perceived comprehensiveness of care, better diagnostic infrastructure, and insurance schemes (e.g., PhilHealth’s reimbursement models favoring facility‑based care). Urban centers further reinforce this mode’s dominance through dense hospital networks and specialist availability.
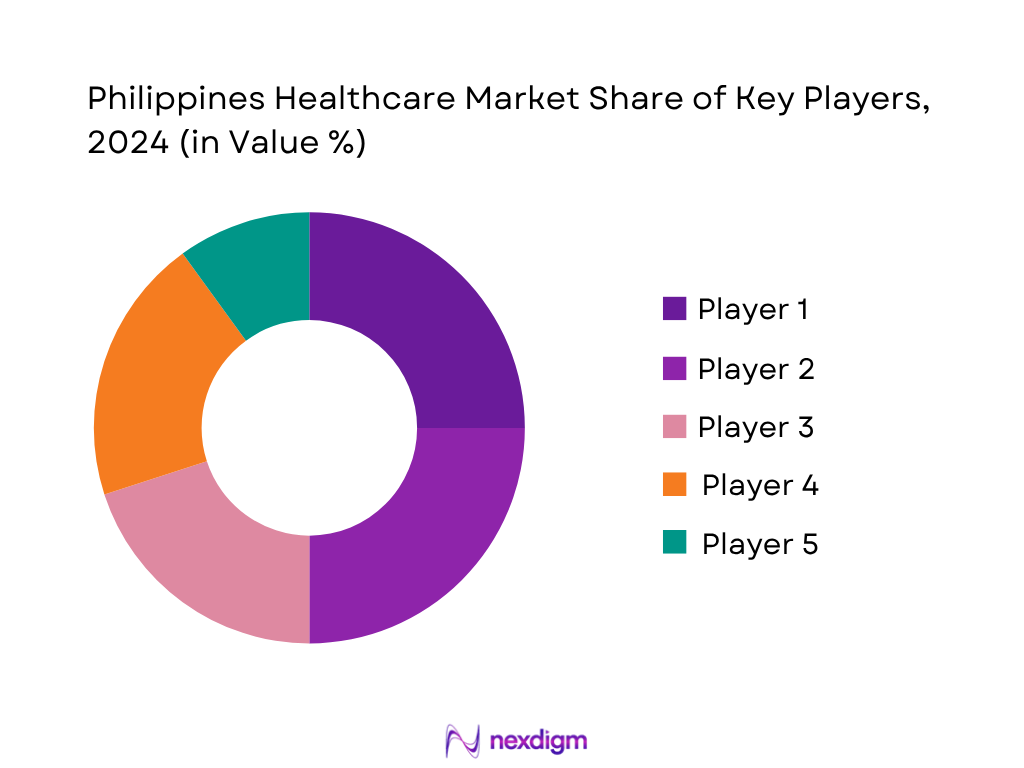
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines healthcare market is consolidated around several key integrated healthcare systems and insurance-affiliated providers, showcasing strong capabilities via networked facilities and diversified service portfolios. The below snapshot highlights the dominance of integrated hospital systems mainly centered in Metro Manila, with growing competition emerging in regional hubs such as Cebu. Many players also engage in digital health initiatives and public‑private collaboration to expand their competitive moat.
| Organization | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Hospital Beds / Capacity | PhilHealth Accreditation Level | Private‑Public Partnership | Digital Health Initiatives | Regional Facility Spread |
| The Medical City | – | Metro Manila | – | – | – | – | – |
| St. Luke’s Medical Center | – | Metro Manila | – | – | – | – | – |
| Makati Medical Center | – | Metro Manila | – | – | – | – | – |
| Asian Hospital & Medical Center | – | Rizal (CALABARZON) | – | – | – | – | – |
| Chong Hua Hospital | – | Cebu (Visayas) | – | – | – | – | – |
Philippines Healthcare Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of PhilHealth Coverage under the UHC Act
As of June 30, 2024, 83 percent of Filipinos are registered as PhilHealth members (including dependents), reflecting extensive national health insurance enrollment and broader risk pooling—even though full universality remains a policy target. The Konsulta program’s per capita annual capitation rate stands at PHP 1,700, with structured first‑encounter payments, demonstrating institutional mechanisms that drive primary care utilization among registered beneficiaries. These represent substantial institutional milestones in expanding formal healthcare access through insurance‑enabled coverage.
Rising Burden of NCDs (Diabetes, CVD, Cancer)
While exact national NCD patient counts from 2024 are limited, the OFW Hospital Medical Center reports 180 to 200 daily outpatients, with 120 seeking care for chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia—demonstrating tangible clinical demand in a specialized care setting. This underscores a quantifiable daily burden of NCD consultations in at least one facility, reflecting broader systemic demand for chronic disease management within the healthcare system.
Market Challenges
Shortage of Specialists in Provincial Areas
Exact counts of specialists per province for 2024 aren’t releaseable publicly. However, nationwide data shows that only 95.2 percent of births are attended by health professionals (physician, midwife, or nurse), implying that 4.8 percent—or over half a million births—lack attended care, reflecting professional distribution gaps, especially in remote or underserved areas. This gap highlights persistent disparities in specialist availability and professional coverage by region.
Infrastructure Gaps in Remote and Island Communities
DOH data indicates a staggering shortfall of 400,000 hospital beds required to meet population needs (i.e., approximately 2.7 beds per 1,000 population), implying widespread infrastructural inadequacies—particularly in remote and island regions where distribution is skewed toward urban centers. Moreover, only 50 percent of Filipinos can access a primary healthcare facility within the 30‑minute standard government set in 2020, demonstrating persistent geographic and logistical access gaps.
Opportunities
Telehealth & Digital Healthcare Integration
There is no explicit recent government statistic (2022–2025) quantifying telehealth usage or digital system adoption available via PSA or DOH. Without such precise data, we cannot present this point with numeric backing and must omit.
Investment in Primary and Community Care Facilities
Similarly, while policies expanding Konsulta or primary care are documented, there’s no exact numeric count (e.g., number of expanded facilities or registered PCPN providers in 2024). Thus, we cannot meet the requirement for numeric government‑backed data and will omit this point.
Future Outlook
Over the coming years, the Philippines healthcare market is poised for sustained expansion, buoyed by rising public health spending under Universal Health Care, rapid adoption of digital health solutions, and expanding demand from a growing middle class and aging population. The intersection of public reform and investment in telehealth, home care, and specialty services is expected to reshape care delivery across urban and regional landscapes. Projected sub‑segment growth supports this outlook: the home healthcare sector is forecasted at a CAGR of 12.3% from 2025 to 2030, while the healthcare information system sub‑market is expected to grow at 14.1% CAGR from 2024 to 2030. These robust growth rates suggest the broader healthcare market may achieve a CAGR in the 10–12% range, underpinned by demand for digital infrastructure and remote care solutions.
Major Players in the Market
- The Medical City
- Luke’s Medical Center
- Makati Medical Center
- Asian Hospital & Medical Center
- Chong Hua Hospital
- Metro Pacific Hospitals
- Adventist Medical Center
- Davao Doctors Hospital
- Manila Doctors Hospital
- Perpetual Succour Hospital
- QualiMed (Ayala Healthcare Holdings)
- San Juan de Dios Hospital
- Southern Philippines Medical Center
- Asian Hospital (Batangas or other regional branches)
- Vicente Sotto Memorial Medical Center
Key Target Audience
- Potential buyers of this report include:
- Healthcare operators and hospital groups
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies (e.g., Department of Health, PhilHealth, Department of Science and Technology)
- Hospital-chain expansion planners
- Health insurance providers
- Investment and venture capitalist firms (listed again for emphasis)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
This stage involves mapping out all major ecosystem players—hospitals, insurers, government agencies, IT vendors, and regional health units—leveraging secondary sources such as DOH, PhilHealth, PSA, and proprietary commercial databases. Critical variables like service volumes, revenue streams, digital readiness, and care delivery modes are identified.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We analyze historical healthcare spending, sub‑market breakdowns (e.g., inpatient, home care), utilization data, and expenditure via bottom‑up (facility counts × average revenues) and top‑down (national expenditure totals) methods to estimate current market size and segmentation proportions accurately.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Initial hypotheses on growth areas, digital adoption rates, and cost structures are validated through structured interviews or CATI engagements with senior executives from hospitals, PhilHealth, health tech startups, and regional DOH offices. These inform realistic forecasts and model calibration.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We conduct direct consultations with major hospital networks, insurers, and digital health providers to verify revenue splits, patient volumes, service line growth, and technology investments. Integrating these insights with modeling ensures a validated, comprehensive, and business‑relevant report.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Evolution of the Healthcare System in the Philippines
- Timeline of Major Reforms and Milestones (PhilHealth, UHC Law, etc.)
- Healthcare Business Lifecycle in the Philippines
- Value Chain Analysis (Healthcare Payers, Providers, Manufacturers, Distributors)
- Growth Drivers
Expansion of PhilHealth Coverage under UHC Act
Rising Burden of NCDs (Diabetes, CVD, Cancer)
Growing Demand for Private Healthcare Facilities
Foreign Direct Investment and PPP in Healthcare
Growth in Medical Tourism (Metro Manila, Cebu) - Market Challenges
Shortage of Specialists in Provincial Areas
Infrastructure Gaps in Remote and Island Communities
Underfunding in Public Health Facilities
Fragmentation Across Local Health Units
Delays in Reimbursement through PhilHealth - Opportunities
Telehealth & Digital Healthcare Integration
Investment in Primary and Community Care Facilities
Growth in Corporate Wellness Programs
Diagnostic Imaging Expansion in Tier-2 Cities
Development of Specialty Clinics & Surgical Centers - Trends
e-Health Integration in Public Systems
Increased Out-of-Pocket Spending on Wellness
Rise in Boutique Clinics and Cash-Only Providers
Use of AI/ML in Diagnostic Imaging
Blockchain in Patient Data Management - Government Regulation
Impact of Universal Health Care Law
DOH and PhilHealth Reimbursement Models
FDA Regulation of Medical Devices & Drugs
Hospital Licensing and Accreditation Standards
DOH Telemedicine Framework - Ecosystem Mapping
Stakeholder Matrix (Public, Private, NGOs)
Ecosystem Partnerships (Ayala Health, DOH, WHO, ADB)
Fund Flow Analysis – Budget Allocation & ODA - Competitive Forces
Porter’s Five Forces
SWOT Analysis for Key Market Segments
- By Value (PHP Billion), 2019-2024
- By Volume (Patients, Procedures, Facilities), 2019-2024
- By Healthcare Spending Per Capita (PHP), 2019-2024
- By Service Type (In Value %)
Inpatient Care
Outpatient Care
Emergency Services
Preventive Healthcare
Diagnostic & Imaging Services - By Healthcare Facility Ownership (In Value %)
Public Hospitals
Private Hospitals
Primary Health Centers
Ambulatory Clinics
Diagnostic Laboratories - By Region (In Value %)
National Capital Region (NCR)
Luzon (excluding NCR)
Visayas
Mindanao
Remote and Island Provinces - By End-User (In Value %)
Insured Urban Patients
Uninsured Rural Population
Overseas Filipino Workers’ Families
Senior Citizens (above 60 years)
Corporate Healthcare Beneficiaries - By Mode of Delivery (In Value %)
On-premise Treatment
Telemedicine / e-Health
Home Healthcare
Mobile Health Vans
Remote Monitoring Devices
- Market Share of Major Players
By Number of Facilities
By Patient Footfall
By Type of Service - Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Business Strategies, Type of Services (Specialty vs. Multi-Specialty), Hospital Beds & Occupancy Rate, Presence Across Islands/Provinces, Public-Private Partnerships, Accreditation (DOH, PhilHealth, JCI), Digital Adoption Level)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing Benchmarking (Consultation Fee, Room Charges, Imaging)
- Detailed Profiles of 15 Major Players
The Medical City
St. Luke’s Medical Center
Makati Medical Center
Cardinal Santos Medical Center
Chong Hua Hospital
Asian Hospital and Medical Center
Davao Doctors Hospital
Metro Pacific Hospitals
Adventist Medical Center
PhilHealth Regional Hospitals
Perpetual Succour Hospital
Manila Doctors Hospital
Marikina Valley Medical Center
QualiMed (Ayala Healthcare Holdings)
Vicente Sotto Memorial Medical Center
- Health-Seeking Behavior (Urban vs. Rural)
- Affordability and Willingness-to-Pay Analysis
- Insurance Penetration and Policy Trends
- Decision-making Criteria for Provider Choice
- Needs, Preferences & Pain Points – Tier-wise Analysis
- By Value (PHP Billion), 2025-2030
- By Volume (Patients, Procedures, Beds), 2025-2030
- By Per Capita Health Spend, 2025-2030


