Market Overview
The Philippines hydrogen refueling stations market is projected to witness significant growth, driven by the government’s push for cleaner energy solutions and the increasing adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCEVs). With investments in infrastructure and increasing fuel demand, the market size has seen a steady rise. By 2024, the market size is expected to reach USD ~ million, primarily driven by hydrogen production and refueling infrastructure expansion. The market growth is also aided by the favorable policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions and fostering the green energy transition. Growing consumer interest in eco-friendly transportation further accelerates the demand for hydrogen refueling stations.
The dominance of key cities and countries in the Philippines hydrogen refueling station market is largely attributed to their early adoption of clean energy and electric vehicle infrastructure. Metro Manila, Cebu, and Davao are significant contributors due to their high population density, rising pollution levels, and government initiatives focusing on sustainable transport. These cities have seen greater investment in hydrogen infrastructure, owing to their central economic roles. Their commitment to reducing carbon emissions and embracing renewable energy solutions positions them as major drivers of hydrogen refueling station growth in the region.
Market Segmentation
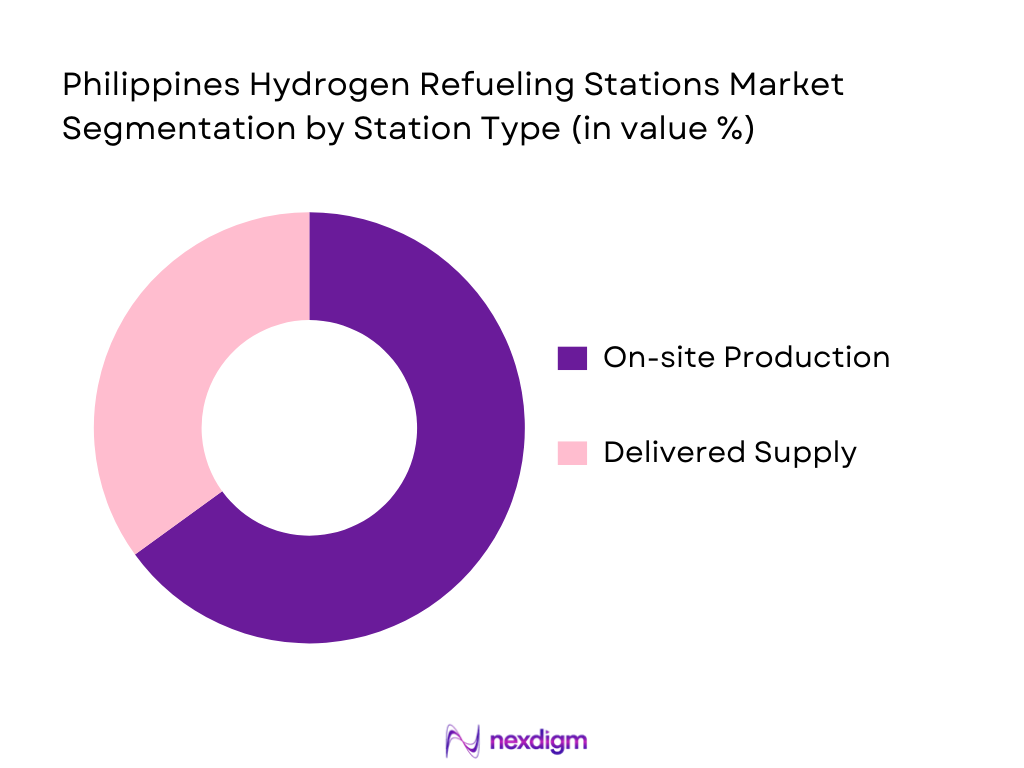
By Station Type
The Philippines hydrogen refueling stations market is segmented by station type into on-site production and delivered supply models. On-site production models are dominating the market in recent years due to the growing trend of integrating hydrogen generation systems at the refueling stations themselves. This model supports sustainability by utilizing green hydrogen production methods like electrolysis, which reduces dependency on external hydrogen suppliers. Delivered supply models also contribute significantly to the market by ensuring that hydrogen is distributed efficiently, especially in more remote or industrial areas where on-site production may not be viable.
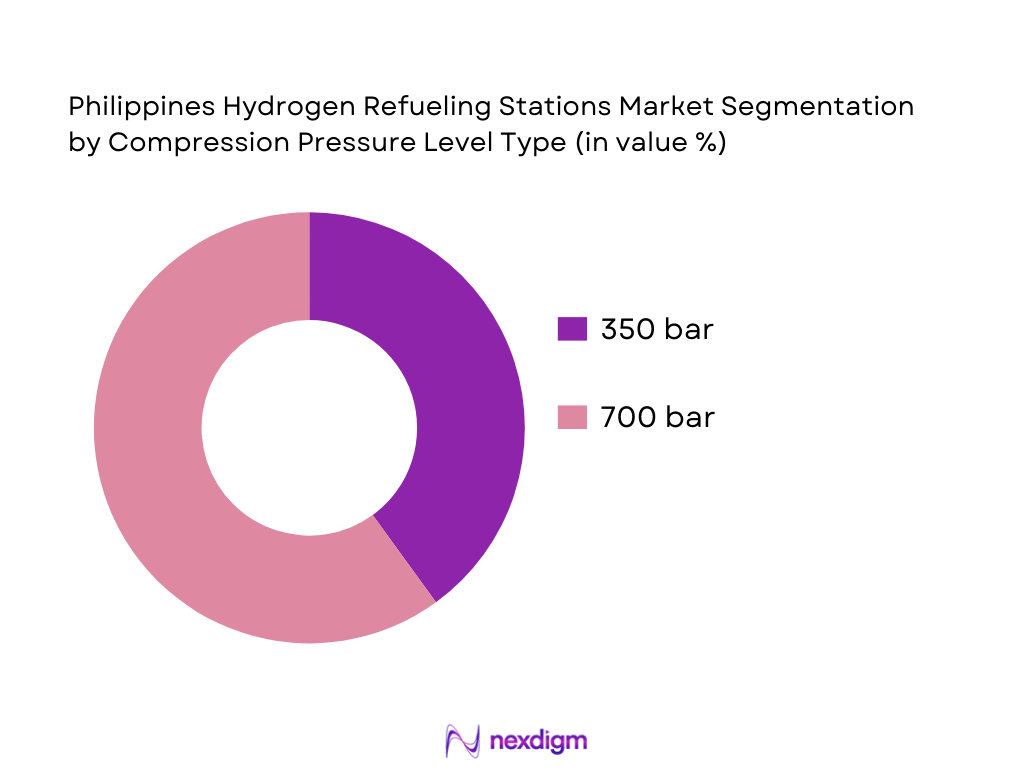
By Compression Pressure Level
The compression pressure level market segment in the Philippines is divided into 350 bar and 700 bar stations. The 700 bar segment currently holds the dominant share due to the increasing adoption of high-performance hydrogen fuel cell vehicles that require higher pressure to ensure better storage efficiency and longer driving ranges. These stations are most commonly found in metropolitan areas where FCEV adoption is growing. However, the 350 bar stations continue to maintain a significant presence, particularly in regions where the demand for hydrogen is still in its early stages, and fuel cell vehicles are less common.
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines hydrogen refueling station market is dominated by a mix of local and international companies that provide hydrogen fuel infrastructure and services. Major players include global leaders in the clean energy sector such as Air Liquide, Linde, and Toyota Tsusho, as well as local firms committed to sustainable energy solutions. These companies are investing in the country’s hydrogen infrastructure to meet the growing demand for clean fuel, driven by government initiatives and increasing FCEV adoption. The market also sees several collaborations between the public and private sectors, which help accelerate hydrogen infrastructure development across the Philippines.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Market Share | Production Capacity | Partnerships | Revenue | Technology |
| Air Liquide | 1902 | Paris, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Linde | 1901 | Munich, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Toyota Tsusho | 1948 | Aichi, Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Nel ASA | 1927 | Oslo, Norway | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| McPhy Energy | 2008 | La Motte-Fanjas, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Hydrogen Refueling Stations Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Urbanization
The acceleration of urbanization in the Philippines is a significant driver for the adoption of hydrogen refueling infrastructure. In 2024, the Philippines had an urban population of approximately ~ people, representing about ~ of the total population, indicating a nearly half concentration of residents in urban centers such as Metro Manila, Cebu, and Davao where transport demand and pollution pressures are high. This urban concentration increases demand for cleaner mobility alternatives, including hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, due to intensified traffic and air quality concerns. Urban hubs also host more economic activities and higher vehicle density, creating environments where hydrogen refueling stations become more viable and strategically necessary to support evolving energy and transport needs. Urban dwellers in these cities engage more in commuting, logistics, and goods transport—further amplifying the pressure to develop refueling infrastructure that supports low-emission technologies.
Industrialization
Industrialization in the Philippines is another growth driver for hydrogen refueling stations as energy demand from industrial sectors grows alongside clean energy ambitions. Data from the World Bank shows that the industry sector (including manufacturing and construction) contributed ~ % of GDP in 2024, with specific manufacturing value added at ~ % of GDP—a notable indicator of industrial expansion and economic diversification. Industrial zones across Luzon, CALABARZON, and Central Visayas support heavy transport and logistics operations, which increasingly explore hydrogen as a cleaner energy alternative to diesel and gasoline to reduce emissions and energy costs. Industrial growth increases freight movement and corporate fleet needs, making hydrogen refueling stations strategically relevant for medium to heavy-duty operations. Furthermore, with the Philippines producing over ~ exajoules of primary energy consumption in 2023 and continuing to depend heavily on imported fossil energy, cleaner fuels like hydrogen align with industrial decarbonization priorities to reduce energy imports and pollution.
Restraints
High Initial Costs
One of the foremost restraints on the growth of hydrogen refueling infrastructure in the Philippines is the high initial capital requirement for building stations. Establishing a hydrogen refueling station includes costs for land acquisition, high‑pressure storage systems, electrolyzers or delivery logistics, and advanced safety systems that meet international technical standards. Philippines infrastructure projects also face heightened cost pressures from imported equipment due to the country’s significant reliance on energy and technology imports, as reflected in the fact that domestic energy production only meets around ~ % of primary energy consumption, with the remainder requiring import. This dependency amplifies capital requirements and the economic burden on developers investing in hydrogen stations. Furthermore, the broader power sector grapples with reliability issues, with over ~ million consumer-hours lost to power outages as of 2021 due to grid challenges, underscoring the need for stable supporting infrastructure that can sustain hydrogen production and station operations. These upfront expenses deter some investors from committing significant resources toward hydrogen station proliferation until cost efficiencies improve and supportive financing mechanisms are more widely accessible.
Technical Challenges
Technical challenges also restrain the development of hydrogen refueling stations in the Philippines. The country’s energy infrastructure is still heavily reliant on traditional energy sources, with renewable share only about ~ of total installed electricity generation capacity and fossil fuels dominating the energy mix. Integrating hydrogen production systems—such as electrolyzers connected with intermittent renewables—requires advanced grid stability and technical coordination that currently remain underdeveloped. With electricity infrastructure issues persisting across more than 120 small islands and isolated grids, establishing consistent hydrogen supply and reliable refueling operations becomes complex. Moreover, the nascent stage of hydrogen and fuel cell adoption in the Philippines means there is limited local technical expertise, standardized safety codes, and established best practices, which further complicate scaling hydrogen refueling systems nationwide. These technical barriers must be overcome through training, regulatory frameworks, and grid modernization to support widespread hydrogen station deployment.
Opportunities
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements present a compelling opportunity for the Philippines hydrogen refueling stations market. Progressive developments in hydrogen electrolyzer technology, high‑pressure storage systems, and automated dispensing units are making hydrogen refueling more efficient and safer. Global initiatives have driven down the costs of advanced electrolyzers and made modular hydrogen production systems more adaptable to local renewable energy inputs. Meanwhile, partnerships between the Philippine government and international clean hydrogen innovators, such as collaborations with hydrogen technology leaders, create pathways for knowledge transfer and infrastructure deployment. The discovery of significant natural hydrogen seepage with over 800 tonnes of annual hydrogen outgassing in the Zambales region demonstrates potential resource advantages that may support technology experimentation and renewable‑integrated hydrogen production. These technology shifts can unlock cost efficiencies, enable localized production, and support a broader ecosystem where hydrogen stations serve not just transport but industrial and distributed power applications.
International Collaborations
International collaborations are a major opportunity for scaling hydrogen refueling infrastructure in the Philippines. In recent years, multilateral financing mechanisms—such as the establishment of clean hydrogen market support with World Bank funding mechanisms—have started directing substantial capital toward clean energy transition initiatives, including hydrogen energy projects globally. These collaborative frameworks provide platforms for knowledge exchange, co‑funding of pilot infrastructure projects, and integration of global best practices into the Philippines’ policy environment. Engaging in international technology partnerships supports the transfer of technical expertise in station design, safety standards, and operational protocols that are essential for building public confidence and operational reliability. As global networks increasingly prioritize hydrogen in decarbonizing transport and energy sectors, the Philippines can leverage these partnerships to attract capital investments, harmonize standards, and accelerate the rollout of dependable refueling stations across key economic corridors and urban centers.
Future Outlook
Over the next few years, the Philippines hydrogen refueling station market is poised to experience robust growth driven by government support for green energy initiatives and the increasing adoption of hydrogen vehicles. The government’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions and bolstering renewable energy infrastructure will be key growth drivers. Additionally, the expansion of FCEVs in commercial and public transport sectors will increase hydrogen demand, further accelerating the buildout of refueling stations across the nation. As the technology matures and costs decline, hydrogen stations are expected to become more widely available, contributing to a cleaner, greener transportation ecosystem in the Philippines.
Major Players
- Air Liquide
- Linde
- Toyota Tsusho
- Nel ASA
- McPhy Energy
- Plug Power
- Hydrogenics
- Shell Hydrogen
- Ballard Power Systems
- Cummins Inc.
- ITM Power
- Hydrogen Europe
- Snam
- Gulf Oil
- HDF Energy
Key Target Audience
- Hydrogen Infrastructure Developers
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Energy and Utility Providers
- Automobile OEMs (Electric Vehicle Manufacturers)
- Logistics and Transportation Companies
- Government Agencies (DOE – Department of Energy)
- Regulatory Bodies (Philippine Environmental Management Bureau)
- Private Sector Investors in Clean Energy
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The first phase involves mapping out the key stakeholders in the Philippines hydrogen refueling station market, including government entities, energy suppliers, station operators, and technology providers. This process is supported by secondary data collection from credible industry sources, including government publications and energy reports.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, historical data is collected and analyzed to assess the growth of hydrogen fuel stations, including station deployment numbers, fuel throughput, and technological advancements. Trends in fuel demand and government incentives are also reviewed to project future market trends.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
To validate the initial hypotheses, interviews and consultations will be conducted with market experts, infrastructure developers, and government officials. These insights will help refine market dynamics and ensure the accuracy of forecasts and assumptions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Finally, market insights will be cross-referenced and verified through direct engagements with stakeholders across the hydrogen ecosystem. This ensures the data’s reliability, providing a comprehensive market analysis for the Philippines hydrogen refueling stations sector.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Data Sources & Validation, Analytical Frameworks, Forecast Modeling, Primary Research & Market Calibration)
- Definition and Scope
- Industry Genesis in the Philippines
- Timeline of Key Infrastructure Milestones
- Value Chain & Supply Chain Dynamics (Hydrogen Supply Routes, On‑Site vs Delivery, Compression & Dispensing Value Nodes)
- Technology Ecosystem
- Market Drivers
Deployment Incentives & Regulatory Targets (National Clean Energy + Zero Emission Vehicle Support)
Rising FCEV Fleet Adoption (Light & Heavy‑Duty)
Energy Security & Low‑Carbon Fuel Transition Strategies - Challenges & Constraints
High CapEx for Station Build‑Out
Technical Barriers (Compression, Storage, Safety Codes)
Supply Chain Fragmentation - Opportunity Landscape
Renewable Energy Coupled Electrolysis Integration
Long‑Distance Hydrogen Corridor Builds
Industrial & Logistics Hub Refueling Concentrations - Market Trends
Standardization of Station Design
Digital & IoT‑Enabled Operations
Multi‑Modal Hydrogen Refueling Integration - Government Regulation & Policy Framework
Clean Energy Mandates
Incentive Structures
Safety & Technical Codes - Ecosystem Mapping
Government Bodies, Energy Producers, OEMs, Infrastructure Developers, Logistics Operators - Porter’s Five Forces & Risk Matrix
Supplier Power, Buyer Power, Substitution Risk, Competitive Rivalry
- By Value, 2019-2025
- By Volume, 2019-2025
- By Average Price of Platforms/Services, 2019-2025
- By Station Type (In Value %)
In Value & Installed Count
On‑Site Production
Delivered Supply Model
- By Compression Pressure Level (In Value %)
350 bar
700 bar
- By Mobility Application (In Value %)
Light‑Duty FCEVs
Heavy‑Duty Buses & Trucks
Logistics Fleets
- By Hydrogen Supply Source (In Value %)
Green Hydrogen
Blue Hydrogen
Gray Hydrogen
- Market Share Landscape (Installed Stations, Throughput Capacity)
- Cross‑Comparison Parameters (Company Profile, Regional Footprint, Refueling Network, CapEx Intensity, Deployment Speed, Strategic Partnerships, Tech Maturity, Safety Record)
- Competitive SWOT Analysis
- Pricing Benchmark – Station Build & Service Rates
- Detailed Company Profiles
Air Liquide
Linde plc
Air Products and Chemicals
Cummins Inc. (Hydrogen Station Solutions)
Nel ASA
ITM Power
Ballard Power Systems
FuelCell Energy, Inc.
Hexagon Purus
Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions
Toyota Tsusho / H2 Mobility Partnerships
Hyundai Hydrogen Mobility
Siemens Energy (Hydrogen Solutions)
McPhy Energy
HDF Energy Philippines Partnership Vehicle
- Refueling Demand Profiles
- Fleet Adoption Patterns & Capital Budget Allocations
- Fleet Owner Decision Drivers & Pain Points
- Safety Perception & Adoption Resistance Metrics
- Purchasing / Procurement Funnel Dynamics
- Future Market Size by Value, 2026-2030
- Future Market Size by Volume, 2026-2030
- Average Frame Cost Outlook, 2026-2030


