Market Overview
The Philippines In-Car Payment Systems Market sits within a rapidly expanding global in-vehicle payment services space, which is valued at about USD ~ billion in earlier benchmarking and rises to roughly USD ~ billion in the latest global assessment. Complementing this, other studies place global in-vehicle payment services at around USD ~ billion in the most recent year, underscoring multi-billion-dollar scale. In this context, Nexdigm estimates the Philippines in-car payment systems market at roughly USD ~ million in 2024, driven by fast digital wallet uptake and expanding RFID-enabled toll and mobility payments.
The Philippines In-Car Payment Systems Market is heavily concentrated in Metro Manila and the surrounding Luzon growth corridors, where vehicle density, expressway length, and digital payments adoption are highest. Metro Manila alone accounts for nearly four out of every ten vehicles in the country’s stock, making it the primary locus of congestion and toll-road demand. The central bank reports that digital payments now account for over half of monthly retail transaction volume and close to three-fifths of value, with monthly digital transaction value at about USD ~ billion, anchoring wallet-based in-car payments along expressways, fuel stations, and parking facilities.
Market Segmentation
By Payment Use Case
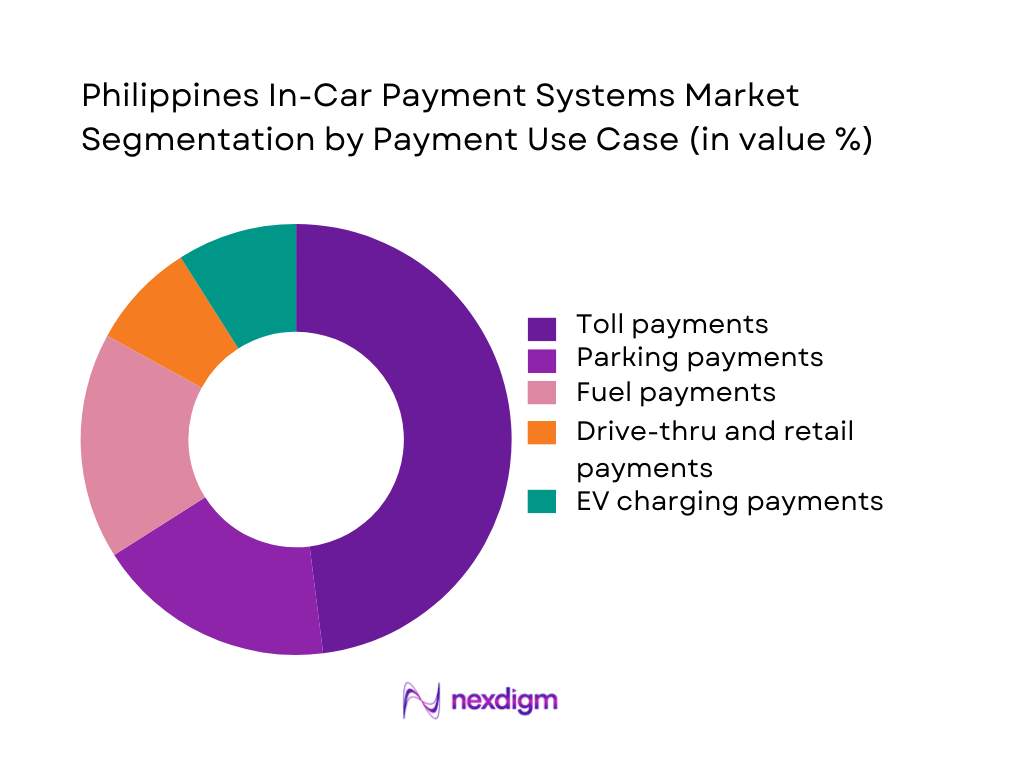
The Philippines In-Car Payment Systems Market is segmented by payment use case into toll payments, parking payments, fuel payments, EV charging payments, drive-thru and retail payments. Today, toll payments dominate the market share under this segmentation because most high-value car journeys in and out of Metro Manila traverse RFID-enabled expressways such as NLEX, SLEX, CALAX and Skyway, where interoperable electronic toll collection is being rolled out. RFID tags are already mandatory for seamless passage on multiple corridors, and recurring commuter and freight traffic generates high transaction frequency. These lanes are typically linked to pre-paid wallets or bank channels, making them the anchor use case for in-car and near-car payments, well ahead of still-emerging parking, drive-thru and EV-charging applications.
By Integration / Channel Type
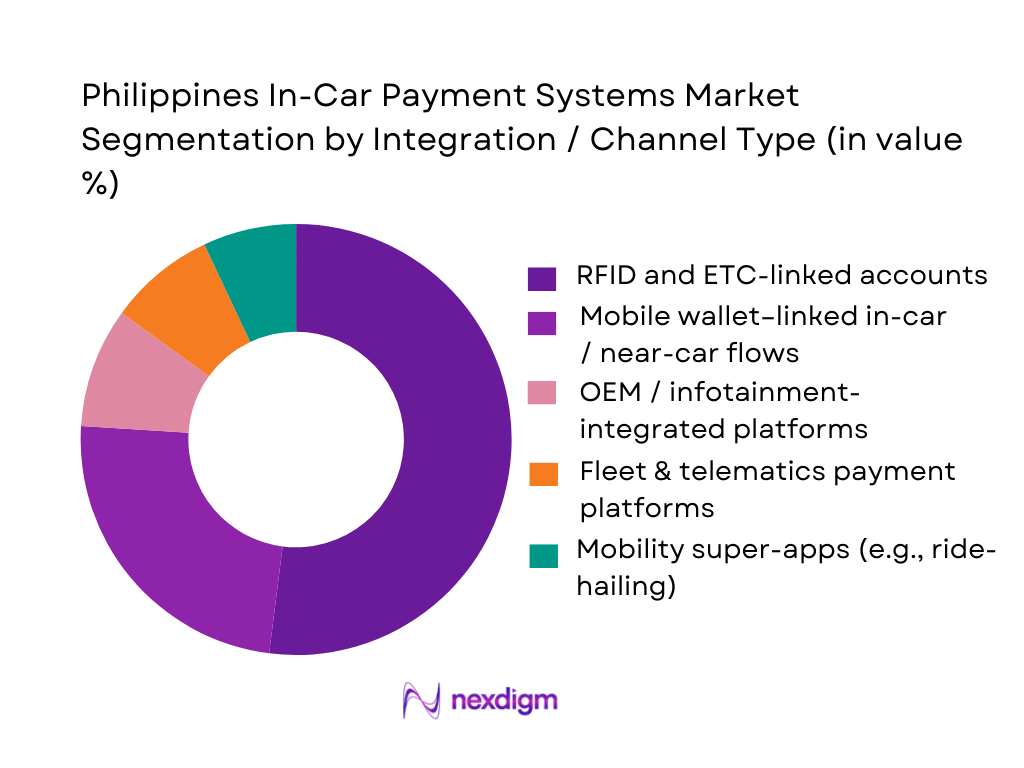
The Philippines In-Car Payment Systems Market is segmented by integration type into RFID and ETC-linked accounts, mobile wallet–linked flows, OEM and infotainment-integrated payment platforms, fleet and telematics platforms, and mobility super-apps. At present, RFID and ETC-linked accounts hold a dominant market share under this segmentation because toll operators under Metro Pacific Tollways and San Miguel Corporation have rolled out interoperable RFID systems across most major Luzon expressways, creating a de facto standard for vehicle-linked identifiers and payment credentials. These tags are often funded through over-the-counter loads, mobile banking and e-wallet top-ups, but the underlying control of the vehicle-level account lies with the ETC operators, giving this integration layer the deepest penetration in active in-car payment flows today.
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines In-Car Payment Systems Market is shaped by a hybrid ecosystem of toll-road conglomerates, mobile wallet super-apps, and telecom-backed digital platforms rather than traditional automotive OEMs alone. Toll operators under Metro Pacific Tollways and San Miguel Corporation control most expressway corridors, while digital payments are dominated by GCash and Maya, each serving tens of millions of wallet users. Telcos like PLDT/Smart act as connectivity and IoT enablers for connected-car services. This creates a concentrated but multi-layered landscape where a few anchor platforms exert outsized influence over how in-car transactions are initiated, routed, and settled.
| Player | Establishment Year | Headquarters (City, Country) | Core Role in In-Car Payments | Primary Mobility Use Cases | Key Technology Stack | Notable Mobility / Automotive Partnerships | Regulatory / Licensing Anchor | Ecosystem Strengths |
| GCash (Mynt) | 2004 | Taguig, Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Maya | 2000 (Smart Money legacy) | Mandaluyong, Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Metro Pacific Tollways Corporation (MPTC) | 2008 | Makati, Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| San Miguel Corporation (Autosweep RFID) | 1890 | Mandaluyong, Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| PLDT / Smart (Connected Car & IoT) | 1928 | Makati, Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ` |
Philippines In-Car Payment Systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of Expressways & ETC Infrastructure
The backbone for in-car payments in the Philippines is a rapidly expanding toll and road network. The national highway network reached ~ km by October 2023, combining ~ km of concrete and ~ km of asphalt roads. A 2023 factsheet estimates ~ km of national roads and ~ km of local roads, for ~ km in total, underscoring the scale of road-based mobility that can be digitized for tolling and fuel payments. Expressway and toll projects like South Luzon Expressway Toll Road 5 deepen the use case for electronic toll collection and RFID-based in-car payments as traffic is channeled into controlled-access, cashless corridors. With GDP in current US dollars surpassing roughly ~ in 2023 and population at ~ in 2024, the scale of demand for frictionless toll, parking, and fuel payments along this network provides a strong macro foundation for in-car payment systems.
Increasing Connected-Car Penetration
In-car payments rely on connected vehicles operating over dense digital networks, and the Philippines now has ~ million internet users, with ~ of the population online at the start of 2024. Mobile connectivity is even deeper: there were ~ million cellular mobile connections at the start of 2023, well above the total population, supporting embedded SIM, telematics units, and smartphone-tethered infotainment platforms in vehicles. A 2025 telecom analysis notes that Smart’s 4G and 5G networks now collectively cover around 97 of the population, indicating that most urban and highway corridors used by cars are within high-speed coverage for real-time authorization and tokenization of in-car transactions. Urban residents – ~ people in 2023 and ~ in 2024 – are concentrated in Metro Manila, Central Luzon and CALABARZON, which are also major vehicle and expressway markets, making them primary hotspots for connected-car adoption and payment experimentation.
Challenges
Interoperability Between Wallets & Toll Systems
The Philippines’ in-car payment opportunity is constrained by fragmented toll systems and heterogeneous payment rails. The expressway network is organized into multiple concessions and six discontinuous expressway groups, all under the broader Philippine expressway network, which historically evolved with different toll operators and RFID systems. At the same time, BSP-supervised financial institutions reached 30,655 units in 2024, including 13,384 bank outlets, illustrating the diversity of issuers and acquirers whose QR, card, and real-time payment products must interoperate with each toll operator. While QR Ph and InstaPay promote interoperability in retail payments, in-car toll payments still often tie a specific RFID tag to an operator wallet, limiting seamless nationwide driving. Mapping these 30,000+ financial access points to multiple expressway operators without unified tokenization or open-loop standards remains a core challenge for achieving a truly interoperable in-car payment ecosystem.
Limited OEM-Embedded Payment Readiness
Most of the Philippines’ vehicle fleet consists of legacy models without embedded connectivity or native payment capabilities. DTI notes that in 2022 roughly ~ million registered businesses exist in the country, 99.59 of which are MSMEs employing over ~ million people, many relying on cost-sensitive fleets and second-hand vehicles rather than premium, connected models. While macro indicators show a growing economy – nominal GDP reaching about ~ US dollars in 2023 and unemployment rates trending down through 2024 – disposable income for households and small firms still favours lower-cost vehicles without built-in telematics or app ecosystems. As a result, in-car payments must often piggyback on smartphones mounted on dashboards instead of OEM-embedded systems, creating UX friction and limiting the scale of direct, hardware-integrated payment partnerships between automakers, fuel retailers, and toll operators.
Opportunities
Open-Loop Payment Enablement
The Philippines already has a robust base of bank accounts, cards, and e-money accounts that can be leveraged for open-loop in-car payments rather than closed, operator-specific wallets. World Bank data show a population of ~ in 2024, while IMF estimates GDP in current prices near ~ US dollars, implying a large and increasingly banked consumer base for interoperable, scheme-agnostic payment tokens. BSP statistics list 30,655 BSP-supervised financial institutions (head offices and outlets) as of 2024, including 13,384 bank touchpoints, showing the breadth of issuers that can participate in open-loop tokenization for in-car payments instead of siloed operator accounts.
The InstaPay ACH already has 82 sender/receiver participants as of late 2025, ranging from universal banks to EMIs, establishing an interoperable real-time backbone which, once linked to license plates, RFID tags, or vehicle IDs, can enable in-car payments that pull from any bank account or wallet across the ecosystem, rather than tying users to a single toll operator or issuer.
Super-App Partnerships with OEMs
The Philippines has one of ASEAN’s most digitally engaged populations, making it highly attractive for super-app and OEM partnerships around in-car payments. There are ~ million internet users and ~ internet penetration in early 2024, with mobile devices as the dominant access channel – exactly the environment where ride-hailing, delivery, and mobility super-apps scale rapidly. Real-time payments infrastructure has already shown its ability to support high-frequency, low-value transactions: InstaPay processed ~ million transactions in 2022, worth ₱~ trillion, creating a mature foundation for in-app transport fares and merchant payments that can be extended to vehicle dashboards through API integrations. BSP’s open finance pilot, launched in 2023 as a collaborative undertaking of banks and third-party providers, further opens the door for secure data-sharing between banks, wallets, and mobility platforms. Together, this creates a near-term opportunity for OEMs to embed super-app payment buttons and mobility services directly in head units, localizing global connected-car payment models to the Philippines’ super-app-centric consumer behaviour.
Future Outlook
Over the coming six-year horizon, the Philippines In-Car Payment Systems Market is expected to expand rapidly as three structural forces converge: aggressive digital payments growth, ongoing expressway and urban parking infrastructure build-out, and the gradual introduction of connected-car and infotainment platforms by global OEMs. Global research projects robust double-digit growth in in-vehicle payment services, with forecasts of the market reaching USD ~ billion globally by the mid-next decade. Parallel to this, national data shows digital payments already accounting for the majority of retail transaction value, providing a strong baseline for vehicle-linked payments.
Nexdigm’s bottom-up analysis—anchored in global in-vehicle payment benchmarks, BSP digital payments statistics, and Philippines vehicle-stock growth—suggests that the Philippines In-Car Payment Systems Market is around USD ~ million in 2024 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of roughly 20% between 2024 and 2030. This projection assumes continued expansion of RFID interoperability, increased integration of GCash and Maya with mobility ecosystems, and nascent roll-out of OEM-embedded payment interfaces for tolls, fuel, parking, and drive-thru transactions.
Major Players
- Toyota Mobility Services Philippines Services
- Honda CONNECT Philippines
- Hyundai Bluelink
- Kia Connect
- GCash
- Maya
- Metro Pacific Tollways Corporation / Easytrip RFID ecosystem
- San Miguel Corporation / Autosweep RFID network
- PLDT / Smart IoT and Connected Car Services
- Globe Telecom
- Grab
- Shell Philippines
- Caltex / Chevron Philippines
- Unioil
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEMs and Importers
- Toll Road and Expressway Concessionaires
- Fuel Retail Chains and Mobility Service Stations
- Parking and Urban Mobility Infrastructure Operators
- Fleet and Logistics Operators
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
- Digital Wallets, Banks and Payment Service Providers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves constructing an ecosystem map encompassing all major stakeholders within the Philippines In-Car Payment Systems Market, including toll concessionaires, digital wallets, banks, OEMs, telcos, parking operators, and EV-charging networks. Extensive desk research is conducted using secondary databases, regulatory filings (BSP, TRB, LTO), and global in-vehicle payment market reports to identify critical variables such as vehicle-linked transaction value, RFID penetration, wallet usage, and connected-car readiness.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, historical and current data on digital payments, toll traffic, vehicle registrations, and expressway coverage are compiled and synthesized. This includes analysing metrics such as the share of digital payments in retail transactions, the value processed through RFID toll systems, and the ratio of connected-capable vehicles to overall vehicle stock. Using a combination of top-down and bottom-up approaches, we construct revenue pools by use case and by integration channel.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses around segment growth, penetration rates, and monetization models are validated through structured interviews and computer-assisted calls with toll-road operators, digital wallet providers, telco IoT teams, and mobility-platform executives. These consultations provide insight into adoption timelines, interchange fees, interoperability initiatives, and OEM connectivity roadmaps. Feedback from these experts is used to refine key assumptions, cross-check adoption curves, and stress-test the initial revenue and CAGR estimates.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase integrates quantitative estimates with qualitative insights to produce a cohesive market narrative and forecast. Direct engagement with OEMs, fleet operators, and payment providers helps verify volumes by use case, user behaviour (commuter vs. fleet), and the practical readiness of in-car interfaces. This synthesis is used to calibrate forecasts for 2024–2030 market size, segment shares, and growth drivers, culminating in a validated and decision-ready view of the Philippines In-Car Payment Systems Market for investors, operators, and policymakers.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions & Scope, Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Data Triangulation, Connected-Vehicle Payments Architecture Mapping, Payment Rail Assessment, Primary Stakeholder Interviews – OEMs / PSPs / Telcos / Mobility Operators, Secondary Data Validation, Limitations and Future Considerations)
- Definition and Scope
- Technology & Evolution Path (Connected Vehicle Payments Stack)
- Market Genesis – OEM, PSP, Telco & Smart-Mobility Integration
- Timeline of Introduction by Major Ecosystem Players
- Supply Chain & Value Chain Mapping (OEM – TCU – Connectivity Provider – Payment Gateway – Merchant Network – Aggregators – Fleet Integrators)
- Growth Drivers
Expansion of Expressways & ETC Infrastructure
Increasing Connected-Car Penetration
Rise of Digital Wallet Adoption
Fleet Electrification & Charging Integrations
Mobility Digitalization - Challenges
Interoperability Between Wallets & Toll Systems
Limited OEM-Embedded Payment Readiness
Data Privacy & Cybersecurity Gaps
Fragmented Merchant Integration
High Cost of Real-Time Connectivity - Opportunities
Open-Loop Payment Enablement
Super-App Partnerships with OEMs
Integration with EV Charging Infrastructure
Merchant Loyalty Automations
Fleet Payment Optimization - Trends
Voice-Activated Payments
Usage-Based Insurance Payment Sync
Real-Time Transaction Scoring
Vehicle Identity Tokens
Blockchain-Based Payment Authentication - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stake Ecosystem Mapping
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Transaction Volume, 2019-2024
- By Verified Connected-Vehicle Base, 2019-2024
- By Average Revenue Per Vehicle (ARPV), 2019-2024
- By Payment Use Case (in Value %)
Toll Payments
Parking Payments
Fuel Payments
EV Charging Payments
Quick-Service Restaurants / Retail Drive-Thru Payments - By Payment Integration Layer (in Value %)
Embedded OEM Wallet
Smartphone-Linked Wallet
Vehicle OS-Linked Pay Layer
Third-Party Connected-Car Aggregators
Fleet Platform Integrations - By Vehicle Type (in Value %)
Passenger Cars
Light Commercial Vehicles
Ride-Hailing Fleet Cars
Delivery Fleets
Premium/Connected Models - By Technology Architecture
NFC-Vehicle
RFID/ETC
Vehicle-Embedded Wallet
Cloud-Linked Payment Engines
API-Based Merchant Integrations - By Distribution Channel
OEM-Integrated
Aftermarket Telematics Service Providers
Payment Service Providers
Telco-Backed Connected Car Platforms
Mobility Super-Apps - By Region
NCR
Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao
- Market Share Analysis by Value / Transactions
Market Share by Payment Use Case - Cross Comparison Parameters (Connectivity Architecture Strength, Merchant Network, Payment Rail Integration, Vehicle OS Integration Depth, Security & Authentication Stack, Fleet Payment Features, Local Partnership Ecosystem, Scalability of API & Developer Framework (Merchant Integration Readiness)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing & Monetization Model Analysis
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Toyota Mobility Services Philippines
Honda CONNECT Philippines
Hyundai Bluelink
Kia Connect
PLDT Smart IoT Connected Car
Globe Connected Vehicle Platform
Easytrip / MVP Infra
Autosweep RFID
PayMaya/Maya Mobility Payments
GCash Automotive & Merchant Integrations
Shell Mobility Pay Solutions
Caltex / Chevron Mobile Payments
Unioil Pay Systems Integration
GrabFleet Car Payments Ecosystem
- Consumer Behaviour Mapping
- Fleet & Mobility Operator Requirements
- Regulatory & Compliance Considerations for End-Users
- Pain Point Analysis
- End-User Decision Journey
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Transaction Volume, 2025-2030
- By Verified Connected-Vehicle Base, 2025-2030
- By Average Revenue Per Vehicle (ARPV), 2025-2030


