Market Overview
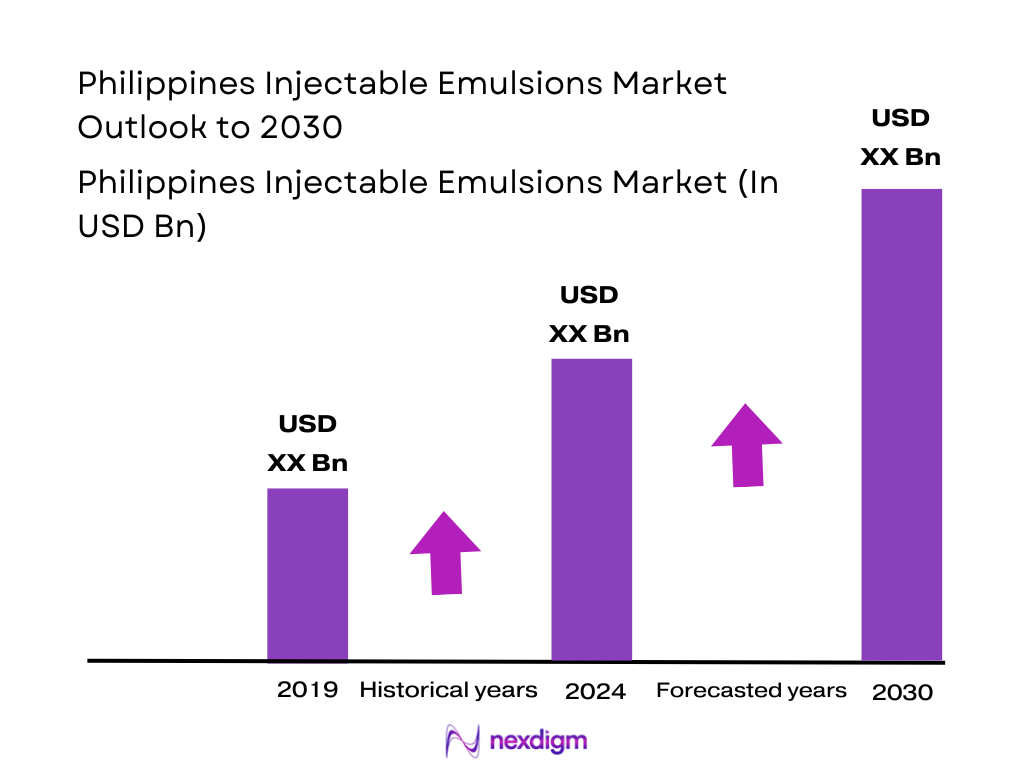
The Philippines injectable emulsions market is closely aligned with the parenteral nutrition and anesthesia injectable ecosystem. The Philippines parenteral nutrition market values at about USD ~ million, based on a five-year historical analysis, with growth driven by chronic disease burden and expanding hospital infrastructure. Globally, the parenteral nutrition market has advanced from roughly USD ~ billion in the preceding period to USD ~ billion in the latest base period, indicating steady structural expansion in intravenous nutrition demand. Given that lipid injectable emulsions are a core PN cost component and also used in anesthesia, this global trend underpins rising value for injectable emulsions in the Philippines.
Metro Manila, Cebu, and Davao form the demand core for injectable emulsions in the country. These cities already dominate parenteral nutrition usage due to dense tertiary hospital clusters, specialist ICUs, and higher rates of complex surgeries. This pattern is reinforced by large distributors like Zuellig Pharma investing in additional cold-chain chambers in Manila, Cebu, and Davao and expanding medical-grade storage capacity nationwide, enabling reliable supply of temperature-sensitive injectable emulsions to referral centers and satellite facilities.
Market Segmentation
By Therapeutic Indication
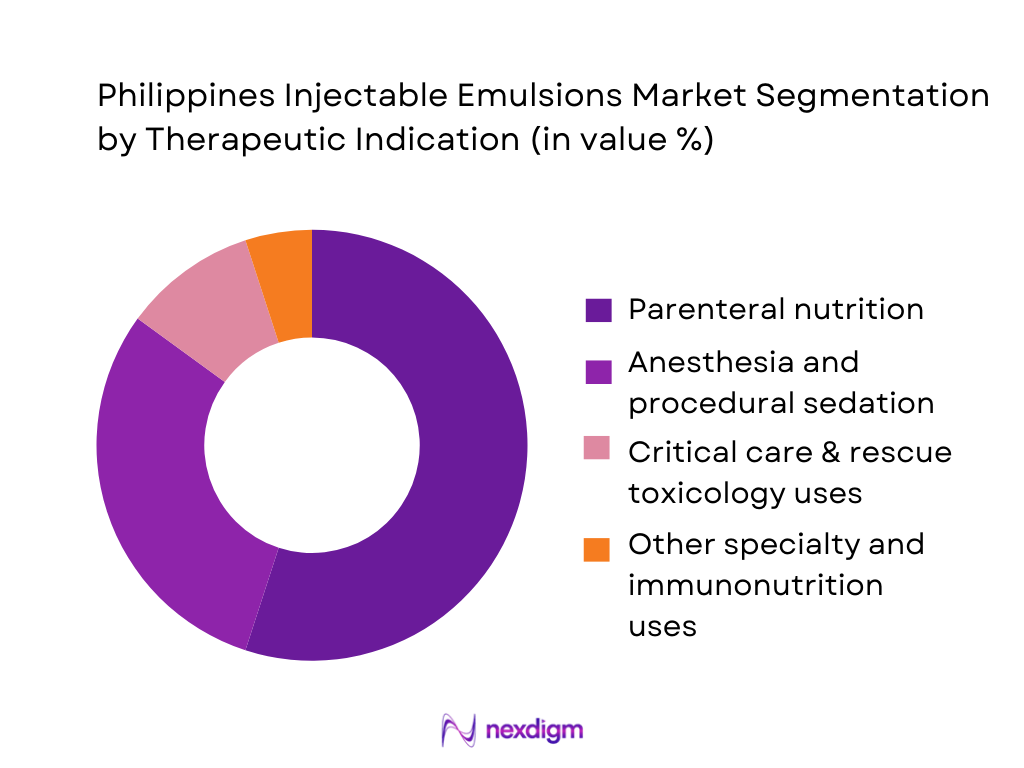
The Philippines injectable emulsions market is segmented by therapeutic indication into parenteral nutrition, anesthesia and procedural sedation, critical care and rescue toxicology, and other specialty uses (e.g., immunonutrition and oncology adjuncts). Parenteral nutrition currently dominates because lipid injectable emulsions are a mandatory macronutrient and energy source in PN regimens, as highlighted in clinical literature and ASPEN guidance. Multichamber PN bags from players such as Fresenius Kabi (SmofKabiven) and Baxter (OliClinomel/ClinOleic) couple amino acids, glucose and lipid emulsions in a single system, locking emulsions structurally into every PN bag used in Philippine ICUs, oncology wards and surgical units.
By End User
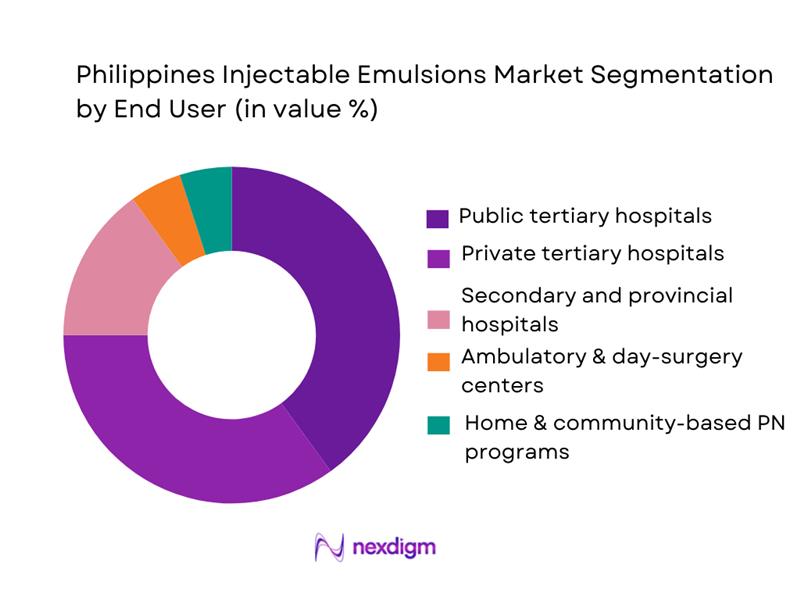
The Philippines injectable emulsions market is segmented by end user into public tertiary hospitals, private tertiary hospitals, secondary and provincial hospitals, ambulatory/day-surgery centers, and home and community-based PN programs. Public tertiary hospitals lead market share because they handle the highest volumes of critical care, complex surgeries and oncology cases funded under national health financing schemes, concentrating PN and anesthetic emulsion use. Hospitals as the primary end-user cluster for parenteral nutrition, with home PN still nascent. Public referral centers in Metro Manila and regional hubs (Cebu, Davao) run large ICUs and NICUs, consume high numbers of PN bags and lipid emulsions per bed, and are integrated into national procurement programs, reinforcing their dominance over private and ambulatory settings.
Competitive Landscape
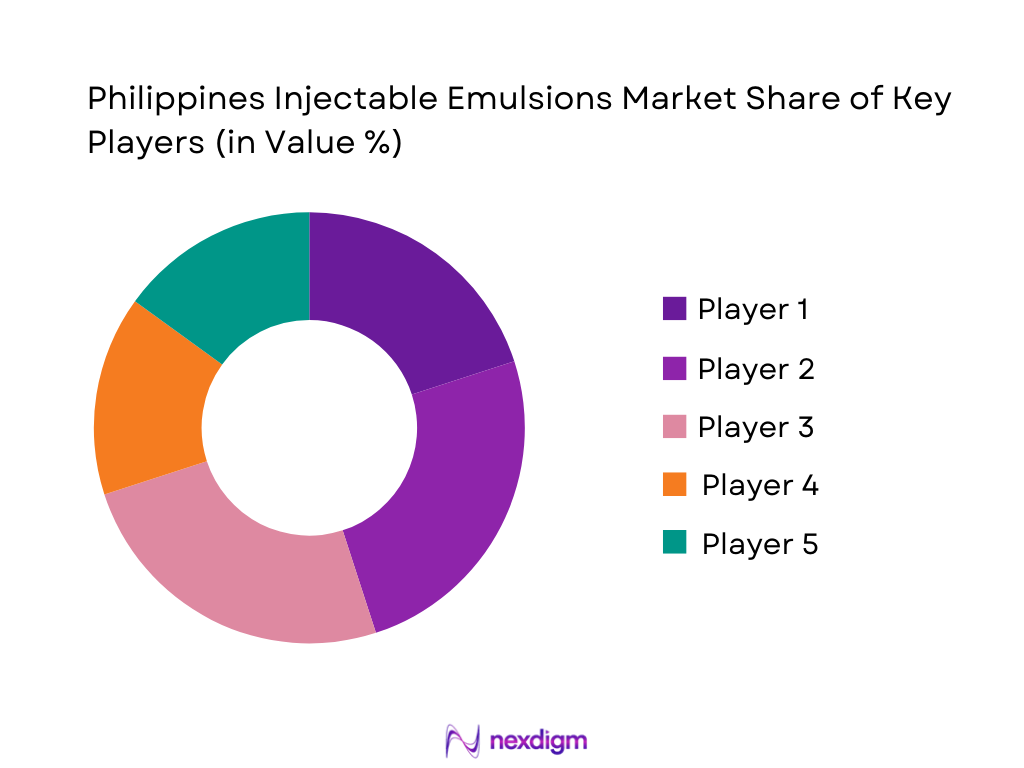
The Philippines injectable emulsions market is shaped by a concentrated group of multinational parenteral nutrition leaders and strong local distributors. Baxter International, Fresenius Kabi, B. Braun Melsungen, Otsuka Pharmaceutical and major local channel partners such as Zuellig Pharma and United Laboratories are among the key participants in the Philippines parenteral nutrition space. These companies bring proprietary lipid injectable emulsions (e.g., SMOFlipid, ClinOleic, Lipidem), multi-chamber PN bags and anesthetic emulsions, supported by robust cold-chain logistics and relationships with tertiary hospitals, enabling them to influence formularies, protocols and long-term PN contracting.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Key Injectable Emulsion Focus | Flagship Emulsion / PN Brands Relevant to PH | Core Therapeutic Segments Served in PH (PN / Anesthesia / ICU) | Presence Type in Philippines | Recent Strategic / Portfolio Focus in Emulsions & PN |
| Baxter International Inc. | 1931 | Deerfield, Illinois, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Fresenius Kabi AG | 1999 (group PN arm) | Bad Homburg, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| B. Braun Melsungen AG | 1839 | Melsungen, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. | 1964 | Tokyo, Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| United Laboratories (Unilab) | 1945 | Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Injectable Emulsions Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising Critical Illness, ICU Admissions and Surgical Volumes
The Philippines’ growing and ageing population, now above 111 million people, is putting sustained pressure on acute and critical care services, which directly fuels demand for injectable emulsions used in parenteral nutrition (PN), anesthesia and sedation. Strong economic momentum underpins higher utilization of tertiary hospitals: national GDP has risen from about US$ ~ billion to roughly US$ ~ billion over the last two years, expanding fiscal room for health spending and elective procedures. At the same time, the Department of Health (DOH) budget rose to about ₱ ~ billion under the latest General Appropriations Act, with a sizable share earmarked for hospital services and critical care, structurally lifting the base of ICU admissions and surgical volumes that rely on PN and anesthetic emulsions.
Increasing Recognition of Hospital Malnutrition and Nutrition Therapy
Macro-level nutrition indicators show why hospital teams in the Philippines are paying more attention to malnutrition and hence to PN with lipid emulsions. The country’s Global Hunger Index (GHI) score improved from 14.8 to 14.4 over the last two assessments, but still signals a “moderate” level of hunger and undernutrition, implying millions of nutritionally at-risk adults who can deteriorate rapidly when hospitalized. Filipino policymakers have formally analyzed these GHI results in congressional briefings, linking them to priorities in the national food and health agenda. As clinicians increasingly screen for malnutrition and sarcopenia in medical, surgical and oncology wards, more patients qualify for PN support, reinforcing structural demand for safe, stable injectable emulsions in tertiary hospitals.
Market Challenges
Import Dependence for Lipid Emulsions and Propofol Emulsions
Despite growing local pharmaceutical capacity, the Philippines remains structurally dependent on imported pharmaceutical products for many sterile injectables, including lipid and anesthetic emulsions. UN trade statistics show that imports of pharmaceutical products reached about US$ ~ billion in the most recent year, underscoring the scale of external reliance for finished and bulk formulations. Complementary UN-based data series on “medicinal and pharmaceutical products” show annual import values above US$ ~ million in 2023 and more than US$ ~ billion in 2022, highlighting how volatile global supply and exchange rates can directly affect availability and landed costs of PN and propofol emulsions. For hospitals that depend on these imports for critical care, any disruption in logistics or foreign exchange liquidity can translate into formulary gaps, stock-outs or forced substitution to older, less optimal formulations.
Pricing Pressure from Public Tenders and Formulary Restrictions
Macroeconomic and fiscal dynamics in the Philippines exert strong downward pressure on injectable emulsion pricing through centralized public procurement. The proposed DOH budget for one recent fiscal year was initially pegged at around ₱ ~ billion, a reduction from roughly ₱~ billion the year before, before being increased to about ₱~ billion in the final General Appropriations Act after legislative negotiations. In a wider context, the total “health sector” allocation sits near ₱~ billion, competing with large outlays for education and infrastructure. These constraints drive DOH and PhilHealth to emphasize lowest-evaluated bid tenders and strict formulary management to stretch public funds. For high-value injectable emulsions, this environment often results in intense price competition, narrow tender awards and limited reimbursement categories, challenging the ability of suppliers to introduce newer mixed-lipid or fish-oil–containing emulsions at sustainable margins.
Opportunities
Upgradation from Conventional Soy-Based to Mixed and Omega-3–Containing Emulsions
Stronger macro fundamentals and hospital budgets are enabling Philippine centers to move away from older, pure soy-oil emulsions towards mixed-lipid and omega-3–containing emulsions that support better inflammatory and liver profiles. With GDP climbing to about US$ ~ billion and GDP per capita approaching US$4,000, the country is transitioning into an upper-middle-income profile, allowing tertiary hospitals to allocate more resources per ICU and oncology patient. Pharmaceutical imports, at around US$ ~ billion annually, already reflect the presence of multiple high-value parenteral products from global suppliers. As DOH capital budgets and HFEP funds improve infusion pumps, laminar flow hoods and PN compounding areas, clinicians in ICUs and cancer centers gain both the clinical justification and operational capability to standardize higher-grade emulsions, positioning this as a clear upgrade opportunity in the injectable emulsions market.
Expansion of Home Parenteral Nutrition and Outpatient Infusion Services
Gradually improving human-development and income indicators create a viable base for home PN and outpatient infusion models that rely on stable, easy-to-handle injectable emulsions. Sub-national HDI data show Metro Manila with an index of 0.753 and a national average around 0.720, indicating relatively advanced education and income levels in key urban regions where complex home-based therapies can be supported by caregivers. At the same time, out-of-pocket spending still accounts for a large share of household health expenses, encouraging hospitals and payers to explore cost-efficient care pathways that reduce prolonged inpatient stays. In this context, ready-to-infuse PN emulsions and standardized bags suitable for home or ambulatory infusion centers can help tertiary hospitals free high-cost ICU and ward beds while maintaining adequate nutritional support, making injectable emulsions central to emerging chronic-care models.
Future Outlook
Over the next several years, the Philippines injectable emulsions market is expected to grow steadily on the back of rising non-communicable disease burden, increasing ICU and oncology caseloads, and broader access to modern parenteral nutrition regimens. Government spending on health and expansion of tertiary infrastructure are improving access to PN and anesthetic services across Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao, gradually extending demand beyond Metro Manila. At the same time, innovation in multi-chamber PN bags, omega-3–enriched lipid emulsions and immunonutrition is likely to shift hospital protocols toward higher-value formulations, lifting average value per patient and supporting mid-single-digit to high-single-digit annual market growth aligned with regional PN trends.
Major Players
- Baxter International Inc.
- Fresenius Kabi AG
- B. Braun Melsungen AG
- Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
- Grifols S.A.
- Terumo Corporation
- Pfizer Inc.
- ICU Medical Inc.
- Sanofi S.A.
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC
- Sandoz (a Novartis division)
- Astellas Pharma Inc.
- Zuellig Pharma Philippines
- United Laboratories, Inc. (Unilab)
- Metro Drug Inc.
Key Target Audience
- Hospital procurement and pharmacy leadership
- Critical care, NICU and oncology department heads
- Anesthesiology and peri-operative services leadership
- Manufacturers of injectable emulsions and parenteral nutrition products
- Pharmaceutical distributors and cold-chain logistics providers
- Health insurance companies and HMOs
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The first phase involved mapping the full injectable emulsions ecosystem in the Philippines, including PN bag manufacturers, lipid emulsion producers, anesthesia suppliers, distributors, and tertiary care providers. Philippines parenteral nutrition report, global PN and lipid emulsion market studies, regulatory databases (FDA Philippines) and scientific literature on lipid injectable emulsions was used to identify critical demand drivers, usage patterns by indication and hospital-level decision variables.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, we synthesized historical global and regional parenteral nutrition and lipid emulsion market data to construct a top-down view of injectable emulsions demand, then aligned it with Philippines market valuation as a local anchor. Hospital bed counts, ICU penetration, surgical procedure volumes and DOH budget trends were layered in to benchmark per-bed PN and anesthetic emulsion usage. This enabled derivation of the Philippines injectable emulsions market size, segment splits by indication and end user, and a forward view consistent with Asia–Pacific PN growth trajectories.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Working hypotheses on segment dominance (parenteral nutrition vs anesthesia), public vs private hospital weightage, and adoption of advanced lipid emulsions were validated against published interviews, case studies and company disclosures for key global PN players (Fresenius Kabi, Baxter, B. Braun, Otsuka) and leading Philippine distributors. Their reported PN portfolios, geographic coverage and cold-chain investments were cross-checked with FDA product registrations and local market reports to refine estimates of hospital coverage, emulsion mix and emerging home-PN adoption.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Finally, we synthesized macro-level PN and lipid emulsion evidence with Philippines-specific competitive and regulatory insights into a cohesive market model. Particular attention was given to aligning the injectable emulsions narrative with clinical evidence on lipid emulsions’ role in PN and ICU outcomes and with local dominance of Metro Manila, Cebu and Davao in PN usage. The resulting report integrates top-down and bottom-up perspectives, framing a defensible view of current market size, projected CAGR, leading segments and strategic opportunities for manufacturers, distributors and investors in the Philippines injectable emulsions market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definition, Product Taxonomy and Scope, Assumptions, Exclusions and Normalisations, Data Collection Approach, Market Sizing and Forecasting Framework, Pricing, Volume and Revenue Estimation Methodology, Validation Through Key Opinion Leader Interactions, Study Limitations and Future Research Directions)
- Definition, Clinical Scope and Product Boundaries
- Therapeutic Genesis of Injectable Emulsions in Philippines Clinical Practice
- Evolution of Key Molecules, Lipid Systems and Indications in Hospital and Critical Care Settings
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Structure – From API and Lipid Oils to Bedside Administration
- Stakeholder Ecosystem – Regulators, Payers, Hospital Systems, Distributors and Manufacturers
- Positioning of Injectable Emulsions within Overall Parenteral Therapy and Injectable Drugs Landscape
- Growth Drivers
Rising Critical Illness, ICU Admissions and Surgical Volumes
Increasing Recognition of Hospital Malnutrition and Nutrition Therapy
Expansion of Tertiary Care, NICU/PICU and Oncology Infrastructure
Adoption of Advanced Lipid Emulsions and Multi-Chamber PN Bags - Market Challenges
Import Dependence for Lipid Emulsions and Propofol Emulsions
Pricing Pressure from Public Tenders and Formulary Restrictions
Safety, Stability and Compatibility Concerns
Limited Local Manufacturing Capacity for Sterile Emulsions - Opportunities
Upgradation from Conventional Soy-Based to Mixed and Omega-3 Containing Emulsions
Expansion of Home Parenteral Nutrition and Outpatient Infusion Services
Local Contract Manufacturing, Compounding and Custom PN Solutions
Value-Added Service Bundles – Stability Testing, Compatibility Tools and Clinical Education - Trends
Shift Toward Four-Oil Emulsions and Personalised PN Regimens
Rising Use of Ready-to-Use Multi-Chamber PN Emulsions vs Pharmacy-Compounded Bags
Integration with Smart Infusion Pumps, EMR and Dose-Error Reduction Systems
Emulsion Use in Rescue Therapies and Specialised Indications - Regulatory and Policy Landscape
Philippines FDA Registration Pathways and Pharmacopoeial Standards for Injectable Emulsions
Philippine National Formulary / Essential Medicines Inclusion for PN and Propofol Emulsions
PhilHealth Case Rates, Reimbursement Treatment of PN and Anesthesia Emulsions
ASEAN Harmonisation, Labelling, Stability and Quality Documentation Requirements - Technology and Formulation Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Emulsion Type, Indication and Pack Size, 2019-2024
- By Therapeutic Indication (in Value %)
Parenteral Nutrition
General Anesthesia and Procedural Sedation
Critical Care and ICU Support
Oncology, Haematology and Transplant Support
Other Indications - By Emulsion Chemistry and Lipid Source (in Value %)
Soybean-Oil Based Lipid Emulsions
MCT/LCT Mixed Lipid Emulsions
Olive-Oil Based and Olive-Containing Lipid Emulsions
Fish-Oil Containing Four-Oil Lipid Emulsions
Nanoemulsions, Submicron Emulsions and Emerging Structured Lipid Systems - By Patient Group and Clinical Profile (in Value %)
Neonatal and Paediatric PN and Sedation Cohorts
Adult Medical Inpatients Requiring PN and Sedation
Adult Surgical, Perioperative and Day-Surgery Patients
Geriatric, Long-Term Care and Palliative Care Patients
Home Parenteral Nutrition and Outpatient Infusion Patients - By Care Setting (in Value %)
DOH and Government Tertiary Hospitals
Private Tertiary and Specialist Hospitals
Secondary and Level-One Hospitals
Ambulatory Surgery Centres and Diagnostic Centres
Homecare Providers, Compounding Pharmacies and Infusion Clinics - By Distribution and Procurement Channel (in Value %)
DOH Central and Regional Tenders / PhilGEPS-Led Procurement
PhilHealth-Accredited Public and Private Hospitals
Group Purchasing Organisations and Private Hospital Chains
Independent Hospital Purchasing and Direct Manufacturer Contracts
Distributor / Depot-Led and Online B2B Procurement Platforms - By Region (in Value %)
National Capital Region (NCR)
North and Central Luzon
South Luzon and Bicol
Visayas
Mindanao
- Market Share of Major Players on the Basis of Value and Volume
Market Share by Therapeutic Indication - Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Injectable Emulsion Portfolio by Indication, Emulsion Chemistry and Lipid Source Mix, Philippines FDA-Registered SKUs and PNF Listing Status, Hospital and ICU Coverage Across Regions, Tender and PhilHealth Reimbursement Engagement, Local Manufacturing / Compounding and Sterility Capabilities, Clinical Evidence and Guideline Alignment for Emulsion Safety and Outcomes)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing and Pack-Size Analysis
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Fresenius Kabi Philippines Inc.
B. Braun Medical Supplies Inc.
Baxter Healthcare Philippines Inc.
Otsuka (Philippines) Pharmaceutical Inc. and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Factory
Aspen Philippines Inc.
Delex Pharma International Inc.
Bambang Pharmaceutical Depot Inc.
Euro-Med Laboratories Phil., Inc.
United Laboratories, Inc.
Pascual Laboratories, Inc.
Pascual Pharma Corp.
Lloyd Laboratories, Inc.
JN Carlo Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Bachem AG
- End User Segmentation and Utilisation Patterns
- Procurement, Formulary and Tender Decision-Making
- Clinical Guidelines and Protocol Adoption
- Pain Points and Unmet Needs
- Patient Journey and Outcomes Metrics
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Emulsion Type, Indication and Pack Size, 2025-2030