Market Overview
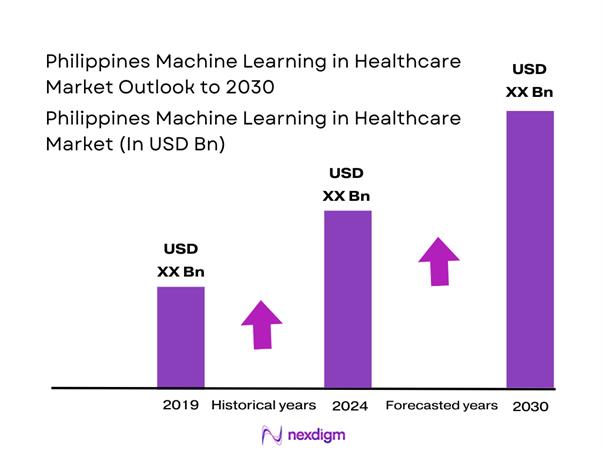
The Philippines Machine Learning in Healthcare market is valued at USD ~ million, driven by increasing healthcare data generation and growing demand for intelligent decision support. Machine learning adoption is expanding across diagnostics, administrative automation, and patient engagement as providers seek to improve clinical accuracy, reduce turnaround times, and optimize operational efficiency. The market’s structural importance lies in its ability to augment limited clinical manpower, standardize care delivery, and enhance outcomes in both public and private healthcare settings through data-driven insights embedded within daily workflows.
Within the Philippines, the National Capital Region dominates adoption due to its concentration of tertiary hospitals, private healthcare groups, diagnostic chains, and technology-ready institutions. These facilities act as early adopters and reference sites for machine learning solutions. CALABARZON and Central Luzon follow, supported by expanding private hospital networks and proximity to Metro Manila-based decision centers. From a global influence perspective, technology and platform capabilities are largely shaped by companies from the United States and other advanced digital health ecosystems, as these countries lead in healthcare AI research, cloud infrastructure, and enterprise-grade machine learning platforms adopted by Philippine providers.
Market Segmentation
By Application Type
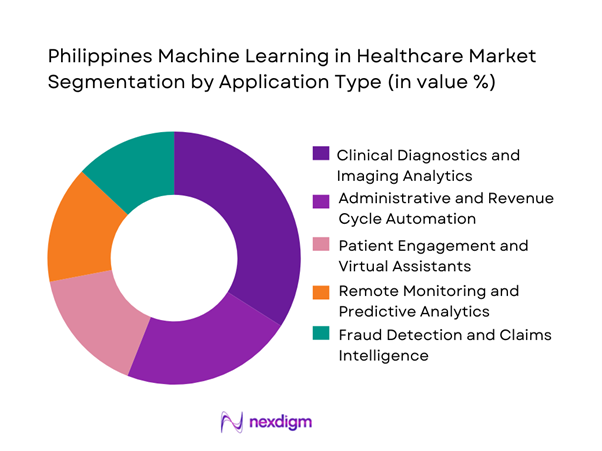
Within application-based segmentation, clinical diagnostics and imaging analytics dominate the Philippines Machine Learning in Healthcare market. This sub-segment benefits from clear clinical use cases such as radiology image interpretation, triage prioritization, and anomaly detection, where machine learning delivers immediate productivity gains. Diagnostic departments face persistent workload pressure, making automation and decision support highly attractive. Imaging-focused ML tools integrate directly into existing PACS and radiology workflows, allowing adoption without significant operational disruption. Additionally, diagnostic applications offer measurable improvements in turnaround time and consistency, making procurement justification easier for hospital administrators. As a result, providers prioritize diagnostic machine learning deployments over more experimental or patient-facing applications.
By Component Type
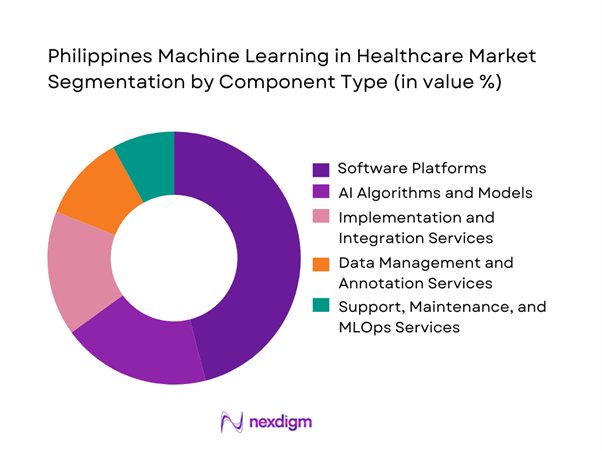
Software platforms represent the dominant component in the Philippines Machine Learning in Healthcare market because healthcare organizations favor scalable, subscription-based solutions that minimize upfront investment. These platforms bundle algorithms, dashboards, and integration layers into configurable products that can be deployed across multiple departments. Hospitals and insurers prefer software-led adoption since it allows phased implementation, easier updates, and faster expansion into new use cases. While services remain essential for integration and customization, software platforms capture the largest value as the core enabler of recurring usage. Their dominance is reinforced by cloud delivery models, which align with the country’s broader shift toward hosted healthcare IT infrastructure.
Competitive Landscape
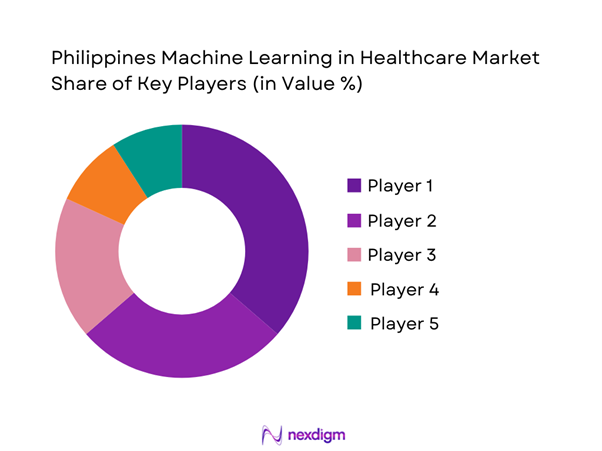
The Philippines Machine Learning in Healthcare market is dominated by a few major players, including IBM and global or regional brands like Microsoft, Google, Philips, and GE HealthCare. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies.
| Company | Established | Headquarters | Primary PH Healthcare ML Focus | Typical Buyer | Deployment Preference | Integration Surface | Data Governance Posture | Go-to-Market in PH |
| IBM (Watson Health ecosystem) | 1911 | Armonk, NY, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Microsoft (Healthcare cloud + AI) | 1975 | Redmond, WA, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Google Health (AI/ML tooling + imaging AI ecosystem) | 1998 | Mountain View, CA, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Philips | 1891 | Amsterdam, Netherlands | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lifetrack Medical Systems | 2012 | Taguig, Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Machine Learning in Healthcare Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Digitization of Clinical Workflows
The accelerating digitization of clinical workflows across hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centers in the Philippines is a foundational driver for machine learning adoption in healthcare. As healthcare providers implement electronic medical records, laboratory information systems, radiology platforms, and integrated hospital information systems, vast volumes of structured and semi-structured data are being generated on a daily basis. This data creates the necessary substrate for machine learning applications to operate effectively. Providers increasingly look beyond basic digitization toward intelligence layers that can interpret data, flag anomalies, and support clinical and administrative decisions. Machine learning enables automation of repetitive tasks, supports clinical decision-making, and improves coordination across departments. Importantly, healthcare organizations aim to extract greater operational and clinical value from their prior investments in digital infrastructure, making machine learning a logical next step in the digital maturity curve rather than a standalone technology adoption.
Rising Diagnostic Workload
Healthcare facilities in the Philippines are experiencing sustained growth in diagnostic workloads due to expanding access to healthcare services, increased utilization of preventive screening programs, and higher patient throughput in both public and private facilities. Diagnostic departments, particularly imaging and pathology units, face mounting pressure to process higher volumes without proportional increases in specialist availability. Machine learning solutions address this challenge by automating image pre-screening, prioritizing high-risk cases, and assisting clinicians in interpretation tasks. These capabilities reduce bottlenecks, improve turnaround times, and support consistent diagnostic quality across facilities. As diagnostic demand grows, providers increasingly view machine learning as an operational necessity rather than an optional enhancement. The technology allows institutions to scale diagnostic capacity, manage clinician fatigue, and maintain service quality even under constrained staffing conditions.
Challenges
Data Fragmentation Across Providers
Data fragmentation remains a significant structural challenge for machine learning deployment in the Philippine healthcare system. Patient data is often distributed across multiple institutions, departments, and platforms, with limited interoperability between systems. Variations in data formats, documentation standards, and legacy systems reduce the availability of clean, unified datasets required for effective model training and deployment. This fragmentation increases the complexity and cost of integration projects and can limit the performance and reliability of machine learning models. For multi-hospital networks and insurers, the inability to aggregate longitudinal patient data constrains the development of advanced analytics and predictive tools. Until interoperability improves and data governance frameworks mature, healthcare organizations must invest additional effort in data harmonization, slowing adoption timelines and reducing near-term returns from machine learning initiatives.
Shortage of AI-Skilled Healthcare Workforce
The limited availability of professionals with combined expertise in healthcare operations, data science, and machine learning poses a major challenge for sustainable adoption. Most healthcare organizations lack in-house teams capable of configuring, validating, and monitoring machine learning systems in clinical environments. This skills gap increases dependence on external vendors and system integrators, which can slow implementation and reduce organizational ownership of AI initiatives. Clinical staff may also lack familiarity with machine learning outputs, leading to hesitation or underutilization of deployed tools. Without sufficient internal capability, hospitals face difficulties in model governance, performance monitoring, and adaptation to evolving clinical needs. Addressing this workforce gap is essential for long-term scalability, but training and talent development require time and sustained investment.
Opportunities
AI-Enabled Diagnostic Decision Support
There is a strong opportunity to extend machine learning capabilities from task-specific automation into broader diagnostic decision support across clinical specialties. Beyond imaging analysis, machine learning models can synthesize patient history, laboratory results, and clinical notes to assist clinicians in risk stratification and differential diagnosis. These tools can act as decision aids, flagging potential conditions, highlighting abnormal trends, and supporting early intervention. In resource-constrained settings, such systems help standardize care delivery and reduce variability in clinical judgment. As clinicians become more familiar with AI-assisted workflows, acceptance of decision support tools is expected to grow. Providers that successfully integrate these solutions into everyday practice can enhance clinical outcomes while improving efficiency and consistency across care settings.
Automation of Claims and Administrative Processes
Administrative inefficiencies remain a persistent burden for healthcare providers and insurers, creating a substantial opportunity for machine learning-driven automation. Claims processing, medical coding, billing validation, and fraud detection involve repetitive, data-intensive tasks that are well suited to machine learning applications. Automation can reduce manual errors, shorten processing cycles, and improve transparency across financial workflows. For hospitals, this translates into faster reimbursements and improved revenue predictability, while insurers benefit from better cost control and reduced leakage. As healthcare organizations face increasing financial pressure, investment in intelligent automation is viewed as a strategic priority. Machine learning enables scalable administrative operations without proportional increases in staffing, making it a compelling solution for both providers and payers.
Future Outlook
The Philippines Machine Learning in Healthcare market is expected to transition from isolated pilot projects to integrated, enterprise-wide deployments. As data standards mature and organizational confidence grows, adoption will expand across both clinical and administrative domains, positioning machine learning as a foundational capability within the national healthcare system.
Major Players
- IBM
- Microsoft
- Philips
- GE HealthCare
- Siemens Healthineers
- Oracle Health
- Amazon Web Services
- NVIDIA
- Qure.ai
- Lunit
- Lifetrack Medical Systems
- SeriousMD
- Zennya
Key Target Audience
- Hospital groups and healthcare networks
- Diagnostic and imaging center chains
- Health insurance providers and HMOs
- Digital health and telemedicine platforms
- Pharmaceutical and life sciences companies
- Medical device distributors
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
This step maps all stakeholders, technologies, and care settings relevant to machine learning adoption in healthcare. Desk research establishes the variables influencing demand, adoption speed, and revenue generation.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical deployment patterns and current usage models are analyzed to construct the market framework. Revenue attribution is aligned with application areas and buyer categories.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions are validated through structured discussions with healthcare administrators, technology vendors, and implementation partners to ensure alignment with operational realities.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are triangulated across sources and synthesized into a coherent market model, ensuring consistency, accuracy, and client usability.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Inclusions/Exclusions, Abbreviations, Topic-Specific Taxonomy, Market Sizing Framework, Revenue Attribution Logic Across Use Cases or Care Settings, Primary Interview Program Design, Data Triangulation and Validation, Limitations and Data Gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Healthcare Usage and Care-Continuum Mapping
- Business Cycle and Demand Seasonality
- Philippines Healthcare Industry and Service Delivery Architecture
- Growth Drivers
Digitization of Clinical Workflows
Rising Diagnostic Workload
Expansion of Telehealth and Remote Care
Operational Efficiency Pressure on Providers
Advancements in Healthcare Data Availability - Challenges
Data Fragmentation Across Providers
Shortage of AI-Skilled Healthcare Workforce
High Implementation and Integration Complexity
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Resistance to Clinical Workflow Change - Opportunities
AI-Enabled Diagnostic Decision Support
Automation of Claims and Administrative Processes
Personalized and Predictive Patient Care Models
AI Integration in Public Health Programs
Cloud-Based ML Platforms for Mid-Sized Hospitals - Trends
- Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Revenue, 2019–2024
- By Solution Mix, 2019–2024
- By Spending Nod, 2019–2024
- By Application Type (in Value %)
Clinical Diagnostics and Imaging Analytics
Administrative and Revenue Cycle Automation
Patient Engagement and Virtual Assistants
Remote Monitoring and Predictive Analytics
Fraud Detection and Claims Intelligence - By Component Type (in Value %)
Software Platforms
AI Algorithms and Models
Implementation and Integration Services
Data Management and Annotation Services
Support, Maintenance, and MLOps Services - By Technology / Platform Type (in Value %)
Deep Learning Models
Natural Language Processing Systems
Computer Vision Platforms
Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics
Hybrid and Ensemble ML Systems - By Deployment Model (in Value %)
Cloud-Based
On-Premise
Hybrid Deployment - By End-Use Customer Type (in Value %)
Public Hospitals
Private Hospitals
Diagnostic and Imaging Centers
Health Insurance Providers
Telehealth and Digital Health Providers - By Region (in Value %)
National Capital Region
CALABARZON
Central Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao
- Competition ecosystem overview
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Clinical validation depth, interoperability readiness, data security architecture, scalability of models, deployment flexibility, local implementation capability, pricing flexibility, post-deployment support maturity)
- SWOT analysis of major players
- Pricing and commercial model benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
IBM
Microsoft
Google
Philips
GE HealthCare
Siemens Healthineers
Oracle Health
Amazon Web Services
NVIDIA
Qure.ai
Lunit
Lifetrack Medical Systems
SeriousMD
Zennya
Advanced Abilities
- Buyer personas and decision-making units
- Procurement and contracting workflows
- KPIs used for evaluation
- Pain points and adoption barriers
- By Revenue, 2025–2030
- By Solution Mix, 2025–2030
- By Spending Nod, 2025–2030


