Market Overview
The Philippines Mobile Health Solutions market is valued at USD ~ billion, reflecting a consolidated view of mobile-first care delivery (telemedicine workflows, remote monitoring, and mHealth applications) within the broader digital health ecosystem. This value is anchored in published market sizing that links growth to rising virtual consultation use cases, chronic disease management needs, and platform-led care access expansion across major urban hubs. Supporting the commercial scale of healthcare digitalization, AC Health recorded PHP ~ billion in revenue in the latest disclosed annual performance, reinforcing strong enterprise push for digitally enabled healthcare delivery.
Metro Manila leads adoption due to its dense hospital and clinic footprint, higher concentration of private payers, and faster rollout of tech-enabled patient journeys (booking, e-prescriptions, and follow-ups). Cebu and Davao are the next most influential hubs because they combine large urban catchments with improving connectivity, increasing private provider investments, and strong demand for remote access in surrounding provinces. The market’s dominance is reinforced by multi-site provider networks and corporate health programs that cluster in these cities, where care capacity constraints and convenience-led demand accelerate mobile-first engagement.
Market Segmentation
By Solution Type
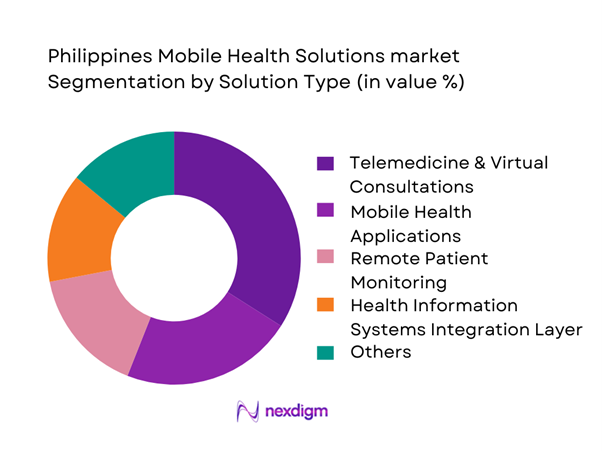
Philippines Mobile Health Solutions can be segmented by solution type into telemedicine & virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring (RPM), mobile health applications, e-prescription services, and patient engagement platforms. Telemedicine & virtual consultations are dominant because they convert unmet access into immediate transactions: faster consult throughput, lower friction than in-person visits, and strong consumer pull for convenience. Telemedicine also sits at the center of bundled journeys—triage → consult → eRx → referral—making it the highest-frequency paid interaction and the first “entry product” for many platforms and hospital networks. This dominance is reinforced by provider marketplace density in urban hubs and employer/HMO partnerships that channel members into digital-first pathways.
By End User
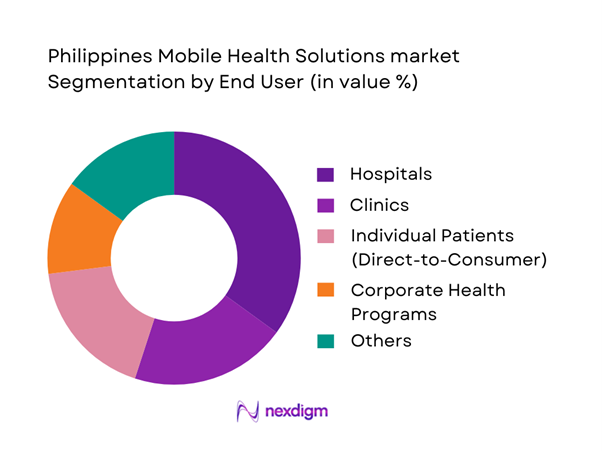
The market is segmented into hospitals, clinics, individual patients, corporate health programs, and insurance providers/HMOs. Hospitals dominate because they control clinical governance, referral pathways, and data-heavy workflows that benefit most from digitization (appointments, clinical notes, diagnostics routing, follow-ups). They also have the strongest need to reduce congestion and improve operational efficiency, making them the most consistent institutional buyers and integrators of mobile health solutions. Additionally, hospitals can scale solutions through their physician networks and satellite clinics, creating faster adoption than purely consumer-led app growth. As a result, hospital-led programs (own apps or partner platforms) become the anchor channel for repeat utilization and enterprise-grade integrations.
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines Mobile Health Solutions market is increasingly shaped by a mix of provider-network-linked platforms and consumer-first apps that compete on physician access, care journey completeness (consult → eRx → labs → follow-up), and enterprise integrations (HMO/corporate). The competitive structure is consolidating around players that can secure partnerships with large provider groups and payers, while differentiating through fast consult access, regulated data handling, and deeper clinical pathways for chronic and mental health use cases.
| Company | Est. Year | Headquarters | Primary Offer | Care Delivery Model | Key User Channels | Integration Depth (eRx/Labs/Payments/EHR) | Core Differentiation | Compliance Posture (Data Privacy, Clinical Governance) |
| KonsultaMD | 2015 | Taguig | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Medgate Philippines | 2016 | Makati | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| HealthNow | 2020 | Taguig | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| AIDE | 2016 | Makati | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MyHealth Clinic | 2009 | Makati | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Mobile Health Solutions Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Smartphone Penetration
The Philippines’ mobile health (mHealth) demand base is fundamentally enabled by a large, digitally reachable population of ~ people and a middle-income consumption profile reflected in GDP of USD ~ billion and GDP per capita of USD ~—conditions that support app-based services at scale. On the access side, digital reach is already mainstream: ~ (of every ~ people) are counted as internet users under national indicator reporting. On the telecom foundation, the Philippines recorded ~ mobile-cellular subscriptions per ~ inhabitants, which indicates multi-SIM behavior and high addressability for app onboarding, OTP authentication, and teleconsult workflows. This “always-on” base directly supports high-frequency mHealth use cases—teleconsult follow-ups, medication reminders, chronic care check-ins, and digital triage—because engagement does not rely on a single channel (a user can access via data, Wi-Fi, or multiple mobile lines). In practical rollout terms, higher subscription density reduces the marginal cost of patient acquisition for provider marketplaces and payer-linked apps: onboarding can be pushed through SMS + app stores + in-app reactivation without requiring facility visits. It also strengthens the viability of “hub-and-spoke” models (urban specialists + remote patients) because the first constraint becomes clinical capacity and connectivity quality—not basic device availability.
Healthcare Access Gaps
Healthcare access gaps remain a structural driver for mHealth because the country must serve ~ people across a complex geography while sustaining service delivery capacity. The same macro context—GDP of USD ~ billion and GDP per capita of USD ~—creates a dual reality: demand for healthcare increases with income and urban lifestyles, but service supply is uneven due to facility clustering in major metros. A key “coverage proxy” for primary-care-linked digital access is the national primary care accreditation network, which illustrates that organized primary care entry points exist but must still scale relative to national population needs. In this context, mHealth becomes the operational bridge between high-demand communities and a finite number of accredited touchpoints—through appointment booking, remote triage, e-referrals, and continuity-of-care messaging that extends each facility’s effective reach. The access gap is not only distance to hospital; it is also the friction of navigating the system (where to go, what to prepare, how to pay, how to follow up). Telemedicine, e-pharmacy coordination, and digital patient navigation reduce drop-offs in the care cascade by replacing multiple physical steps with a single mobile workflow.
Challenges
Regulatory Ambiguity
Regulatory ambiguity is less about no rules and more about overlapping obligations across health service delivery, data protection, payments, and professional practice—creating compliance design complexity for mHealth platforms. The Philippines’ scale (~ people) and macro footprint (USD ~ billion GDP) mean regulators must balance innovation with systemic risk controls, and the resulting guidance evolution can create moving targets for product teams. The compliance environment is demonstrably active, signaling ongoing scrutiny relevant to patient data flows, cloud hosting choices, consent capture, and breach response playbooks. For mHealth operators, ambiguity shows up in real operational decisions: what clinical activities can be performed asynchronously; how to structure teleconsult versus health information features; how to store and transmit sensitive health information; and how to manage third-party integrations without creating uncontrolled data-sharing. Enforcement intensity also increases the cost of getting it wrong. With economic activity growing, regulators face higher transaction volumes and more digital services, which can translate into more frequent policy updates and supervisory actions. The result is that platforms often build conservatively—over-documenting consent, limiting automation, and slowing feature rollouts—unless they have legal and clinical governance mature enough to interpret evolving guidance quickly.
Data Privacy Compliance
Data privacy compliance is a hard constraint for Philippine mHealth because health information is sensitive by nature and the regulator’s operating tempo is measurable. The market operates at national scale—~ people—in an economy of USD ~ billion, meaning even low incident rates can translate into large absolute event volumes and high reputational risk. Regulatory reporting underscores that breaches are not hypothetical and that audits and verification activity is ongoing. For mHealth platforms, this shapes architecture and operating models. Platforms must implement privacy-by-design: role-based access control for clinicians and call center staff; encrypted data at rest and in transit; secure identity verification; and carefully scoped third-party access for labs, pharmacies, and payment processors. The compliance load also interacts with the country’s digital adoption curve, meaning more patients are generating digital traces (appointment histories, chat logs, e-prescriptions) that must be handled under strict governance. Additionally, higher digital payments usage expands the surface area for payment-linked data handling inside health apps—especially where apps support in-app settlement, refunds, and reconciliation for providers.
Opportunities
AI-Enabled Diagnostics
AI-enabled diagnostics is a high-potential opportunity because the Philippines’ disease burden creates large, repeatable diagnostic workloads—precisely the environment where AI-assisted triage and decision support can raise throughput and consistency without adding proportional clinician hours. On the macro side, the country’s scale (~ people) and economy (USD ~ billion) support continued expansion of digital health delivery models that can reduce avoidable costs from late-stage care. On the clinical burden indicators, government releases show very large volumes for cardiovascular mortality proxies and communicable disease notifications, implying sustained screening and follow-up needs. These volumes create multiple near-term AI entry points that do not require future adoption assumptions: clinical triage bots that reduce inappropriate referrals; image-assisted decision support for screening and imaging workflows; risk stratification models for chronic disease follow-up; and automated documentation and coding support for teleconsults to reduce clinician administrative load. The opportunity is reinforced by digital reach, enabling data exhaust (symptoms, adherence, follow-up outcomes) that can power continuous model improvement—subject to strong privacy governance.
Rural Telemedicine Expansion
Rural telemedicine expansion is the most actionable growth opportunity because the country already has the demand-side scale (~ people) and digital reach to support remote care journeys—while infrastructure and accredited provider networks are improving but not yet fully saturating demand. The macro base—USD ~ billion GDP—means both public and private sectors have incentives to reduce productivity losses from untreated conditions and long travel times for basic consultations. On the system readiness side, the Konsulta infrastructure provides a structured set of entry points that can be digitized via remote appointment booking, eligibility checks, and e-referrals. Infrastructure expansion strengthens this case, increasing the feasible footprint for voice and video consults and asynchronous messaging models, even if fixed broadband remains constrained. The opportunity is not to wait for perfect connectivity, but to design rural-first telemedicine stacks that fit current constraints: low-bandwidth triage, store-and-forward consults, remote prescription authorization, lab coordination, and referral routing to the nearest accredited primary care site.
Future Outlook
Over the next planning cycle, the Philippines Mobile Health Solutions market is expected to expand through deeper integration of teleconsultation, e-prescriptions, diagnostics routing, and follow-up care into single mobile journeys. Growth will be supported by stronger payer participation, employer-led healthcare programs, and hospital networks using mobile health to manage capacity constraints. Platform differentiation will increasingly depend on clinical depth (chronic and mental health pathways), interoperability with provider systems, and trust factors such as privacy assurance and service reliability.
Major Players
- KonsultaMD
- AIDE
- SeeYouDoc
- HealthNow
- Medifi
- Doctor Anywhere Philippines
- mWell PH
- SeriousMD
- Medgate Philippines
- MyPocketDoctor
- MyHealth Clinic
- MediCard
- Zennya
- Docquity
Key Target Audience
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Hospital groups and integrated provider networks
- Large private clinic chains and ambulatory care operators
- Insurance providers and HMOs
- Corporate employers and workforce health benefits buyers
- Pharmacy chains and e-prescription fulfillment partners
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Health-tech platform operators and digital health product owners
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We map the Philippines mobile health ecosystem across patients, providers, payers, pharmacies, diagnostics, and platform operators. Desk research is used to define variables such as consult volumes, user acquisition channels, payer participation, and integration depth. The objective is to isolate the structural factors that determine monetization and scale within mobile-first healthcare delivery.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historical and current indicators tied to digital health adoption—teleconsultation enablement, remote monitoring expansion, and enterprise program deployments. Market sizing is constructed through triangulation of published market values and validation through ecosystem logic (platform revenues + enterprise program flows + provider-network digital revenue streams).
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses are validated using structured interviews with hospital administrators, telehealth operators, payer-side product leaders, and corporate benefits buyers. These interviews pressure-test pricing models, adoption barriers, channel economics, and utilization patterns. Findings are used to refine segment-level assumptions and competitive benchmarking.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We consolidate insights across solution categories (telemedicine, RPM, mHealth apps, eRx enablement) and validate ecosystem behavior using cross-references from major published sources. The final output synthesizes market sizing anchors, segment structure, competitive positioning, and forward-looking opportunity areas into a decision-ready report format.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Scope Boundaries, Philippines Healthcare Digitalization Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Engineering Logic, Demand–Supply Mapping Framework, Primary Interviews with DOH-Affiliated Providers, Telehealth Operators & Insurers, Bottom-Up & Top-Down Validation, Data Triangulation Model, Research Limitations and Forward-Looking Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Evolution and Genesis
- Timeline of Mobile Health Adoption in the Philippines
- Healthcare Delivery Cycle and Digital Touchpoint Integration
- Mobile Health Value Chain and Stakeholder Flow Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Smartphone Penetration
Healthcare Access Gaps
Doctor-to-Patient Ratio Stress
Insurance Digitization
Government Telehealth Push - Challenges
Regulatory Ambiguity
Data Privacy Compliance
Fragmented Healthcare Infrastructure
Low Rural Connectivity - Opportunities
AI-Enabled Diagnostics
Rural Telemedicine Expansion
Employer Health Programs
Insurance-Embedded Platforms - Trends
AI Triage Tools
Remote Monitoring Adoption
Mental Health App Uptake
Integrated Health Super-Apps - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Active User Base, 2019–2024
- By Service Utilization Economics, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Remote Patient Monitoring Solutions
Teleconsultation and Virtual Care Platforms
Chronic Disease Management Apps
Mental Health and Behavioral Therapy Apps
Preventive Health and Wellness Applications - By Application (in Value %)
Primary Care
Chronic Disease Care
Mental Health and Psychiatry
Maternal and Child Health
Lifestyle and Preventive Care - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Cloud-Based Platforms
On-Premise Solutions
Hybrid Deployments - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Hospitals and Health Systems
Diagnostic Centers and Clinics
Insurance Providers and HMOs
Corporate Wellness Programs
Individual Consumers - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Subscription-Based
Pay-Per-Consultation
Employer-Sponsored Access
Insurance-Integrated Payments
Freemium and Upsell Models - By Region (in Value %)
National Capital Region
Luzon (Outside NCR)
Visayas
Mindanao
- Market Share Analysis by Platform Type
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Clinical Coverage Breadth, AI and Analytics Capability, Integration with PhilHealth and HMOs, Data Security Architecture, Mobile App UX and Engagement Metrics, Provider Network Size, Geographic Coverage, Monetization Strategy)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing and Monetization Benchmarking
- Detailed Company Profiles
KonsultaMD
AIDE App
SeeYouDoc
HealthNow
Medifi
Doctor Anywhere Philippines
mWell PH
SeriousMD
Medgate Philippines
MyPocketDoctor
MedifiCare
AVA Telehealth
Pulse Health
eKonsulta
- Demand Patterns and Usage Frequency
- Budget Allocation and Willingness to Pay
- Regulatory Compliance Expectations
- Pain Points and Service Gaps
- Decision-Making Hierarchy and Adoption Triggers
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Active User Base, 2025–2030
- By Service Utilization Intensity, 2025–2030


