Market Overview
The Philippines Mobility-as-a-Service market is valued at USD ~, reflecting the structural shift in urban transportation toward digitally enabled, on-demand mobility solutions. The market’s scale is anchored in the daily movement of millions of commuters who rely on app-based ride-hailing, motorcycle taxis, and shared transport to navigate dense urban corridors. Demand is driven by chronic traffic congestion, the rising cost of private vehicle ownership, and the widespread adoption of smartphones and mobile payments. MaaS has evolved from a convenience service into a core urban mobility infrastructure, supporting not only personal travel but also logistics, enterprise mobility, and tourism-related transportation needs.
Within the country, Metro Manila dominates the Philippines Mobility-as-a-Service market due to its concentration of economic activity, extreme traffic density, and the presence of the most mature digital infrastructure. Cebu City and Davao City follow as key regional hubs, benefiting from strong tourism flows, expanding business districts, and proactive local government support for smart mobility solutions. These cities lead because they combine high daily trip volumes with strong platform penetration and wallet-based payment adoption. The market is also shaped by global technology leaders that supply routing algorithms, payment gateways, and platform architecture, enabling local MaaS providers to scale service reliability, safety features, and user experience at a pace that smaller domestic technology ecosystems alone could not sustain.
Market Segmentation
By Service Type
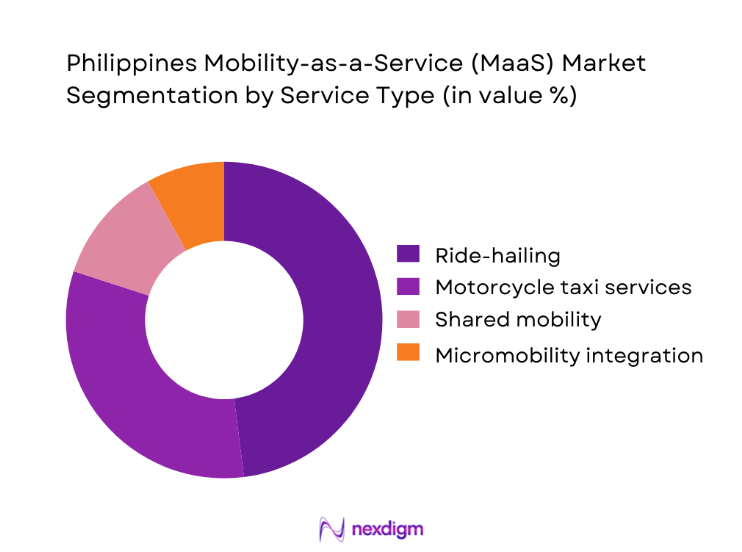
By service type, ride-hailing services dominate the Philippines Mobility-as-a-Service market because they address the most critical urban pain point, which is the lack of reliable, point-to-point transport during peak congestion hours. Ride-hailing platforms offer predictable wait times, transparent pricing, and route flexibility, making them the preferred option for office commuters, business travelers, and tourists alike. Their dominance is reinforced by strong brand recognition, extensive driver networks, and deep integration with digital payment systems that simplify transactions. Corporate mobility programs further strengthen this segment, as companies increasingly outsource employee transport to platform-based providers to improve punctuality and reduce fleet management costs. In addition, ride-hailing services benefit from continuous product innovation such as real-time safety monitoring, in-app insurance coverage, and loyalty programs, which collectively build user trust and repeat usage across daily and occasional travel needs.
By Payment Mode
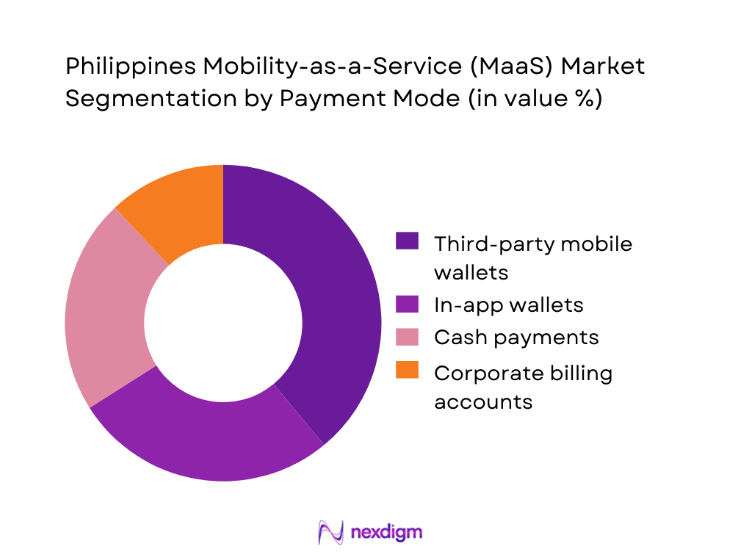
Third-party mobile wallets dominate the Philippines Mobility-as-a-Service market because they have become the default financial interface for urban consumers. Wallet platforms are deeply embedded in daily digital life, supporting not only transport payments but also retail, utilities, and peer-to-peer transfers. Their dominance in MaaS is driven by seamless in-app integration, promotional incentives, and widespread merchant acceptance, which make cashless travel more attractive than traditional payment methods. For MaaS operators, wallet payments reduce cash handling risks, improve transaction traceability, and enable advanced analytics on rider behavior. Government initiatives promoting digital payments further reinforce this trend, encouraging both riders and drivers to transition away from cash. As a result, mobile wallets have evolved into the financial backbone of the MaaS ecosystem, supporting scalability and operational efficiency across platforms.
Competitive Landscape
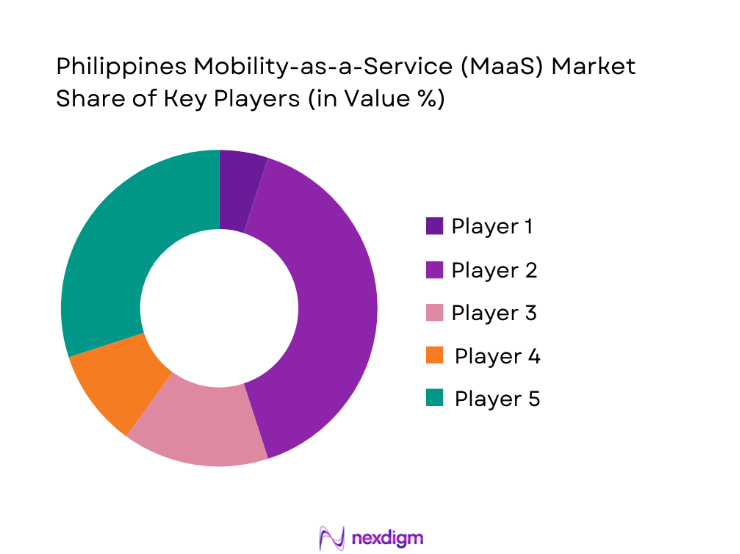
The Philippines Mobility-as-a-Service market is dominated by a few major players, including Grab Philippines and global or regional brands like Angkas, JoyRide, and Move It. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Core MaaS Services | Coverage Cities | Fleet Model | Payment Integration | Regulatory Alignment | Strategic Partnerships |
| Grab Philippines | 2012 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Angkas | 2016 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| JoyRide | 2019 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Move It | 2020 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MiCab | 2013 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Urban congestion intensity
The escalating severity of traffic congestion across major Philippine cities is a primary catalyst for MaaS adoption. Long commute times and unreliable public transport schedules push consumers toward app-based mobility solutions that offer time predictability and route flexibility. As congestion worsens, the perceived value of on-demand transport increases, encouraging habitual use rather than occasional reliance. This dynamic translates into higher trip frequency, stronger platform loyalty, and sustained revenue growth for MaaS providers. Over time, congestion-driven demand is reshaping mobility behavior, positioning MaaS not merely as an alternative but as a necessity for daily urban life.
Smartphone and mobile internet penetration
The rapid diffusion of smartphones and affordable mobile data plans has fundamentally expanded the addressable market for MaaS platforms. Easy access to apps, real-time navigation, and digital payments lowers the barrier to entry for first-time users, especially among younger and lower-middle-income commuters. As mobile internet becomes more reliable, MaaS services gain consistency in booking, tracking, and customer support. This technological accessibility directly supports user acquisition and retention, enabling platforms to scale efficiently across diverse urban and peri-urban demographics.
Challenges
Regulatory uncertainty for motorcycle taxis
Ambiguity in the legal framework governing motorcycle taxis remains one of the most significant constraints on the MaaS market. While demand for two-wheel mobility is high due to speed and affordability, inconsistent licensing and evolving compliance requirements create operational risk for platforms. This uncertainty affects investment planning, fleet expansion, and long-term partnerships. Without stable regulation, companies face challenges in scaling responsibly, which can limit service availability in high-demand corridors and slow overall market growth.
Fragmented public transport systems
The absence of an integrated public transport network makes it difficult for MaaS platforms to fully deliver on the promise of seamless multimodal travel. Disconnected routes, inconsistent fare structures, and limited data sharing between transport operators reduce the effectiveness of mobility integration efforts. This fragmentation increases dependence on private MaaS solutions for end-to-end travel, raising costs for consumers and limiting efficiency gains that could otherwise be achieved through coordinated mobility planning.
Opportunities
Smart city mobility integration
The expansion of smart city initiatives presents a major growth avenue for MaaS providers. As urban planners invest in traffic management systems, sensor networks, and digital infrastructure, MaaS platforms can integrate with these ecosystems to offer predictive routing, congestion-based pricing, and coordinated public transport connections. This alignment enhances service relevance and positions MaaS as a strategic partner in urban development rather than merely a commercial transport service.
Electric vehicle fleet transition
The gradual shift toward electric vehicles in shared mobility fleets creates both a cost and branding advantage for MaaS operators. Electrification reduces long-term operating expenses while aligning platforms with sustainability goals valued by corporate clients and environmentally conscious consumers. As charging infrastructure expands, MaaS providers can differentiate through greener service offerings, strengthening brand equity and unlocking partnerships with clean energy stakeholders.
Future Outlook
The Philippines Mobility-as-a-Service market is set to deepen its role in the national transport ecosystem as urban populations grow and digital infrastructure matures. Over the coming years, MaaS platforms are expected to move beyond point-to-point travel toward fully integrated mobility solutions that connect ride-hailing, public transport, logistics, and enterprise travel management. Strategic alignment with smart city programs, combined with the adoption of electric and low-emission vehicles, will further elevate MaaS from a convenience-driven service to a foundational pillar of urban mobility planning.
Major Players
- Grab Philippines
- Angkas
- JoyRide
- Move It
- MiCab
- Hype Transport Systems
- PeekUp
- Transportify
- Lalamove
- Owto
- Sakay PH
- eJeepney Alliance
- Dash Mobility
- GoGoExpress Mobility
- Mober
Key Target Audience
- Urban mobility platform operators
- Corporate fleet and mobility managers
- Smart city and infrastructure developers
- Digital payment and fintech providers
- Logistics and last-mile delivery companies
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Automotive and electric vehicle ecosystem companies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research begins with mapping the MaaS ecosystem, covering platforms, regulators, payment providers, fleet operators, and end users. Secondary sources and proprietary databases are used to identify adoption drivers, revenue levers, and regulatory influences. This step establishes the foundational variables shaping market behavior.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical service usage patterns, platform penetration, and revenue flows are analyzed to build a structured view of market development. The study evaluates trip frequency, service mix, and monetization models to construct a reliable framework for market sizing and segmentation.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market assumptions are tested through structured interviews with platform executives, fleet partners, and mobility technology providers. These consultations provide operational insights into cost structures, regulatory challenges, and user engagement trends, ensuring practical relevance.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings from primary and secondary research are consolidated into a unified analytical model. Cross-validation across data sources ensures consistency, while expert feedback refines strategic interpretations and market outlook conclusions.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, terminology and abbreviations, MaaS taxonomy across planning booking payment and support layers, market sizing logic by trip volume GMV and platform take rate, revenue attribution across mobility bookings payments ads and subscriptions, primary interview program with operators regulators and integrators, data triangulation and validation approach, assumptions limitations and data gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution of MaaS and Super App Mobility in the Philippines
- Urban Congestion Context and Multimodal Travel Behavior in Metro Manila and Tier 2 Cities
- Public Transport Integration Readiness and Common Ticketing Payment Landscape
- Platform Ecosystem Across Mobility Operators Payment Wallets and Mapping Providers
- Growth Drivers
Smartphone penetration and digital payments adoption
Rising demand for convenient multimodal commuting
Expansion of motorcycle taxi and on demand mobility usage
Growth of delivery and errand mobility adjacent services
Increasing role of wallets rewards and bundling in retention - Challenges
Fragmented public transport operations and limited data standardization
Regulatory uncertainty for app based mobility services
Interoperability gaps across ticketing payments and operator systems
Price sensitivity and promo driven demand volatility
Safety trust and service quality consistency constraints - Opportunities
Deep integration of public transport ticketing with wallets and apps
Unified mobility bundles across rail bus and on demand modes
Corporate MaaS programs for employee commuting and duty travel
Mobility data monetization for planning advertising and partnerships
Expansion into tier 2 cities with formalized operator integrations - Trends
Shift toward super app based mobility ecosystems
Increased use of rewards subscriptions and mobility passes
Growth of multimodal first mile last mile packaging
Rising focus on verification safety features and driver partner quality
Movement toward account based ticketing and contactless acceptance - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Trip Volume and Bookings, 2019–2024
- By Monthly Active Users, 2019–2024
- By Take Rate and Platform Revenue, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Urban daily commuters
Provincial and intercity travelers
Students and campus commuters
Corporate and employee commuters
Tourists and occasional riders - By Application (in Value %)
Multimodal trip planning and routing
On demand ride booking and dispatch
Public transport fare payment and ticketing
First mile last mile connectivity services
Commute benefits and corporate mobility programs - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Super app mobility marketplaces
Dedicated multimodal journey planners
Ticketing and account based fare platforms
Fleet dispatch and booking engines
Mobility data platforms and analytics layers - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone consumer mobility apps
Wallet integrated mobility and payments
Transit operator API integrated platforms
Enterprise and HR integrated commute platforms
Marketplace ecosystems with third party mini apps - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Ride hailing and motorcycle taxi operators
Public transport operators and AFC providers
Payment wallets and fintech partners
Corporate mobility and benefits providers
Local government and transport authorities - By Region (in Value %)
NCR
CALABARZON
Central Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao
- Competitive ecosystem structure across mobility operators payment platforms and transit ticketing providers
- Positioning driven by multimodal coverage reliability and payment integration
- Partnership models between platforms transit operators and wallet ecosystems
- Cross Comparison Parameters (multimodal coverage depth, booking success rate and ETA accuracy, payment acceptance and ticketing interoperability, unit economics take rate and incentive intensity, safety verification and incident handling, customer support resolution time, partner API integration readiness, retention levers rewards passes subscriptions)
- SWOT analysis of major players
- Pricing and commercial model benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Grab Philippines
JoyRide
Angkas
MOVE IT
inDrive
Transportify
Lalamove
Mober
AF Payments Inc beep
GCash
Maya
Sakay ph
Moovit
Google Maps
Waze
- Commuter adoption drivers across time cost and reliability
- Wallet and app preference drivers across trust and rewards
- Corporate buyer requirements for billing policy and reporting
- Operator incentives for platform participation and utilization
- Churn drivers and retention levers across service quality and pricing
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Trip Volume and Bookings, 2025–2030
- By Monthly Active Users, 2025–2030
- By Take Rate and Platform Revenue, 2025–2030


