Market Overview
The Philippines pharmaceutical packaging market is valued at about USD ~ million, based on a multi-year historical analysis of demand across primary, secondary, and tertiary formats. Packaging represents close to 30% of medicine cost in the country, making efficiency and materials choice a key profitability lever for manufacturers and distributors. Using global benchmarks where tertiary packaging (corrugated shippers, pallets, insulated boxes) typically contributes a mid-teens share of total pharmaceutical packaging value, this study estimates the Philippines pharmaceutical tertiary packaging market at roughly USD ~ million in the current base year.
Tertiary pharmaceutical packaging activity in the Philippines is heavily concentrated around Metro Manila, CALABARZON and Central Luzon, where more than 400 licensed pharmaceutical manufacturing and packaging businesses are clustered, alongside export processing zones and logistics hubs. These regions host the main warehouse and distribution infrastructure, including Zuellig Pharma’s network of distribution centres offering about 59,000 square metres of space across seven warehouses and extensive cold-chain capacity for vaccines and biologics. Their dominance stems from dense hospital networks, proximity to ports and airports, and the co-location of generic manufacturers, importers and third-party logistics providers.
Market Segmentation
By Tertiary Packaging Format
The Philippines Pharmaceutical Tertiary Packaging Market is segmented into corrugated shippers and master cartons, palletized stretch-/shrink-wrapped loads, insulated shippers and thermal pallet boxes, returnable plastic crates and totes, and other formats such as wooden pallets, metal bins and specialized bulk containers. Corrugated shippers and master cartons currently hold a dominant share because they are the default tertiary pack for both ambient and controlled-room-temperature medicines distributed through wholesalers, hospital pharmacies and retail chains. The country’s pharma packaging industry relies heavily on paper and paperboard, identified as a key material segment in national packaging analyses, and corrugated shippers integrate well with existing warehouse racking, manual handling practices and outbound truck-load optimization, allowing low-cost scaling for both domestic distribution and export consignments.

By Application / Use Case
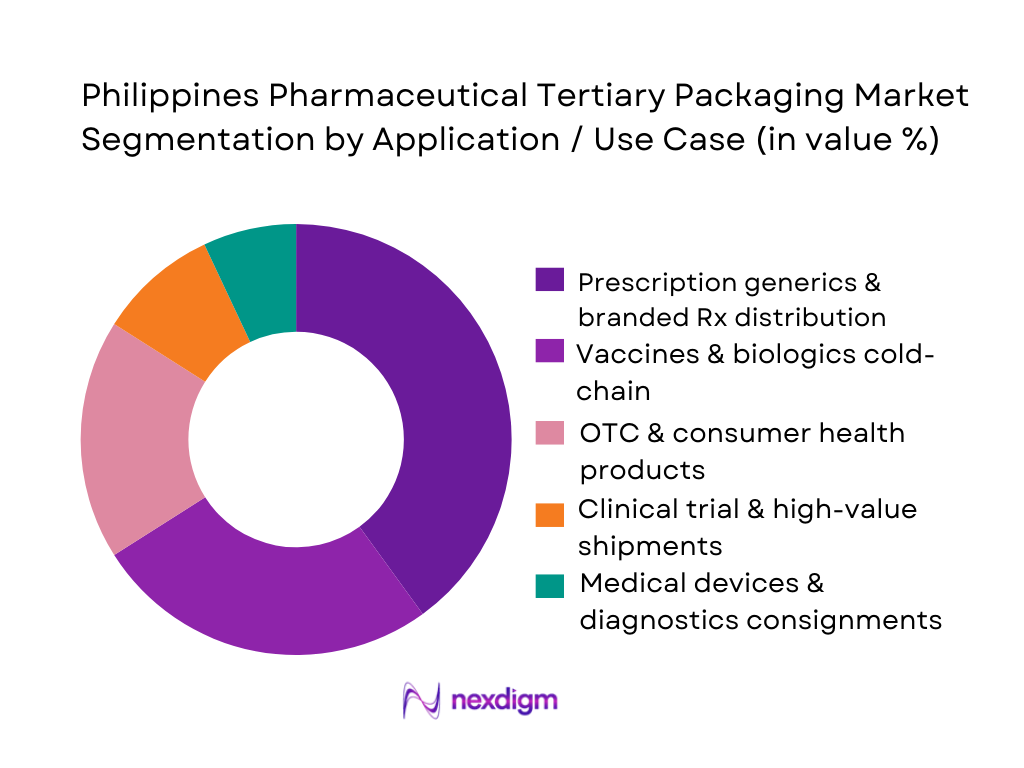
The Philippines Pharmaceutical Tertiary Packaging Market is segmented into prescription generics and branded Rx distribution, vaccines and biologics cold-chain, OTC and consumer health products, clinical trial and high-value shipments, and medical devices and diagnostics consignments. Prescription generics and branded Rx distribution dominates because the national pharma market is still primarily driven by oral solid dose generics and branded generics sold through over 6,000 pharmacies, supermarkets, hospitals and clinics covered by leading distributors such as Zuellig Pharma. These flows require large volumes of ambient tertiary packaging—standard cartons on pallets—that can be handled in high-throughput warehouses. While vaccines and biologics demand sophisticated insulated shippers, their shipment volumes remain smaller than mass-market generics, so their tertiary packaging spend, though fast-growing, is still secondary in share.
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines Pharmaceutical Tertiary Packaging Market is characterized by a mix of global pharmaceutical packaging majors, regional cold-chain packaging specialists and local corrugated and flexible packaging converters. The broader pharmaceutical packaging market is relatively fragmented but anchored by players such as Amcor, Berry Global and several domestic firms, while tertiary packaging for pharma logistics is increasingly influenced by cold-chain innovators like Zuellig Pharma’s eZCooler and global temperature-controlled packaging specialists. Competition centres on validated temperature-controlled shippers, lane-qualification capabilities, sustainability credentials (reusable systems, recyclable materials) and the ability to serve both domestic distribution and export flows under Philippine FDA Good Distribution Practice (GDP) requirements.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Core PH Pharma Focus (Tertiary Layer) | Tertiary Portfolio Focus (PH-Relevant) | Cold-Chain / Thermal Validation Capability | Local Presence Model in PH | Key PH Client Segments | Sustainability / Circular Initiatives (Tertiary) |
| Amcor Plc | 1860s | Zurich, Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Berry Global Group Inc. | 1967 | Evansville, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Bestpak Packaging Solutions, Inc. | 1959 | Metro Manila, Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Netpak Phils., Inc. | 1980s | Laguna, Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ` |
| Zuellig Pharma Corporation | 1922 | Manila, Philippines (APAC HQ) | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Pharmaceutical Tertiary Packaging Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Macroeconomic and healthcare expenditure growth
The Philippines’ macro and fiscal backdrop is expanding the volume of medicines that must move through tertiary cartons, shippers and pallets. National output rose from about USD ~ billion to USD ~ billion in successive recent years, with World Bank data placing GDP at roughly USD ~ billion in the latest reading, sustaining strong consumer, government and private healthcare demand. At the same time, Total Health Expenditure climbed from around PHP ~ trillion to PHP ~ trillion and then PHP ~ trillion, according to official National Health Accounts, indicating an expanding pool of reimbursed medicines and vaccines that require compliant tertiary packaging for hospital, retail and inter-island distribution.
Expansion of pharma manufacturing
Local manufacturing and packaging capacity is deepening the need for standardized pallets, corrugated shippers and export-ready tertiary units. An official pharmaceuticals sector guide notes that up to 435 pharmaceutical manufacturing and packaging businesses had been licensed to operate in the country by the medicines regulator, with clustering in the National Capital Region, CALABARZON and Central Luzon—regions that anchor most export processing zones and road–port corridors. Meanwhile, the regulator’s human-drug product database reports over 32,700 registered drug products as of the latest update, reflecting a broad SKU base spanning generics, branded molecules, injectables and biologics presentations. Each incremental product and line extension adds complexity in warehousing, palletization patterns, labeling and shipper cube optimization, pushing manufacturers and toll-packers to invest in higher-spec tertiary solutions aligned with Good Distribution Practice and export carton test standards.
Challenges
Archipelagic geography
The Philippines’ geography severely complicates tertiary packaging flows. The country comprises about 7,641 islands grouped into three main island clusters, with health facilities scattered across hundreds of provinces and municipalities. Disaster-risk assessments place the Philippines first globally on the World Risk Index, with a score of 46.82 in one recent edition and 46.9 in the latest update, reflecting extreme exposure to natural hazards combined with vulnerability in infrastructure and social systems. This risk profile is reinforced by an average of roughly 20 tropical cyclones entering the national area of responsibility each year, with eight or nine typically crossing land. Such fragmentation and hazard exposure demand tertiary packaging that can endure repeated loading and unloading across small ports, bancas and roll-on/roll-off ferries, while also ensuring cartons and pallets resist moisture, compression and impacts during rerouting in adverse weather.
Fragmented logistics
Even as logistics performance improves, fragmentation across ports, carriers and inland networks inflates damage risk for tertiary packs. Philippine Ports Authority data show domestic containerized cargo volumes rising from about ~ million TEUs to approximately ~ million TEUs in consecutive years, pointing to dense inter-island flows through multiple secondary ports with varying material-handling capabilities. In the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index, the Philippines climbed to 43rd out of 139 economies with an overall score of 3.3, up from 2.9 previously, reflecting progress in customs, tracking and timeliness but also highlighting gaps versus best-in-class peers. In practice, this means many pharma shipments still transit through facilities with limited mechanization, inconsistent pallet standards and variable warehouse conditions, increasing the likelihood of crushed corners, punctured cartons and over-stacking on mixed-load trucks—especially for heavy bottled liquids and corrugated shippers stacked beyond tested compression limits.
Opportunities
PUR and PCM-based shippers
The installed base of cold-chain assets and biologics demand offers strong headroom for advanced polyurethane (PUR) and phase-change material (PCM)–based tertiary shippers. National COVID-19 vaccination data from the regulator show about ~ million doses administered by mid-2024, with more than ~ million people fully vaccinated and large booster and pediatric campaigns still underway. At the same time, health-expenditure statistics indicate total health spending climbing from PHP ~ trillion to PHP ~ trillion over recent years, with vaccines and biologics accounting for a rising share of budgets. Many of these products require 2–8 °C or frozen conditions during multi-day inter-island journeys from central warehouses in Luzon to Visayas and Mindanao ports and onward to rural health units. PUR panel and PCM shipper systems that can hold temperature for 72–120 hours in high-ambient tropical conditions—without relying solely on powered reefers—are therefore well-positioned. They allow consolidation of mixed biologic loads (routine plus COVID-19 and newer products) onto fewer lanes while maintaining qualification data for audits by DOH, LGUs and global partners.
Standardization of lane-qualified tertiary packs
Rising container flows and digital-economy growth support a push to standardize “lane-qualified” tertiary packs across major pharma corridors. Ports authority statistics show domestic containerized cargo volumes growing from roughly ~ million TEUs to about ~ million TEUs in consecutive years, while international container traffic also increased, indicating heavier use of multimodal lanes linking industrial clusters in Luzon with Visayas and Mindanao cities. In the Logistics Performance Index, the Philippines’ score of 3.3 and rank of 43rd out of 139 economies reflect improved but still uneven logistics performance. At the same time, official digital-economy estimates place its value at PHP ~ trillion in 2023 and around PHP ~ trillion in 2024, underscoring the scale of data-rich, trackable shipments. These conditions create a clear opportunity to define standard tertiary pack formats—carton dimensions, pallet footprints, stacking heights and test profiles—certified for specific “lanes” such as NCR–Cebu–Davao or NCR–Iloilo–Zamboanga. For pharma and third-party logistics providers, adopting such lane-qualified packs can reduce damage, optimize truck and container fill, and streamline qualification dossiers for regulators and multinational principals.
Future Outlook
Over the next several years, the Philippines Pharmaceutical Tertiary Packaging Market is expected to expand steadily, tracking both the national pharmaceutical market (which stands at over USD ~ billion) and the dedicated cold-chain packaging market, valued at roughly USD ~ billion across food, pharma and e-commerce. Rising biologics and vaccine volumes, stronger pro-generic policies and incentives for local pharma manufacturing are set to increase palletized and insulated shipment flows from key clusters in Metro Manila, CALABARZON and Central Luzon. At the same time, investments in reusable insulated systems, digital condition monitoring and sustainable corrugated solutions will reshape buying criteria, favouring suppliers that can combine GDP compliance with cost-efficient, low-carbon tertiary packaging.
Major Players
- Amcor Plc
- Berry Global Group Inc.
- Bestpak Packaging Solutions, Inc.
- Netpak Phils., Inc.
- GL Otometz Corp.
- Merfel Plastic Manufacturing Inc.
- Versa Group Philippines Corporation
- Swiss Pac Philippines
- Zuellig Pharma Corporation
- Sonoco ThermoSafe
- Cold Chain Technologies (CCT)
- Peli BioThermal
- Sealed Air Corporation
- DHL Supply Chain
Key Target Audience
- Local generic and branded pharmaceutical manufacturers
- Global and regional pharmaceutical companies operating in the Philippines
- Contract packaging organizations (CPOs) and contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs)
- Third-party logistics (3PL) and cold-chain logistics providers
- Retail pharmacy chains and drugstore groups
- Hospital, clinic and institutional pharmacy procurement departments
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves mapping the full ecosystem of the Philippines Pharmaceutical Tertiary Packaging Market, covering medicine manufacturers, importers, CPOs/CDMOs, packaging converters, cold-chain specialists, 3PLs and regulatory bodies such as DOH and FDA Philippines. Extensive desk research using secondary and proprietary databases is conducted to identify critical variables such as pharma output, cold-chain penetration, packaging material mix and logistics intensity.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, historical data for the Philippines pharmaceutical market, pharmaceutical packaging market and cold-chain packaging market are compiled and harmonized. Ratios such as packaging spend per unit of pharma sales, cost contributions of packaging (notably the ~30% share of medicine cost in the Philippines) and global primary/secondary/tertiary packaging splits are used to construct a bottom-up estimate of tertiary packaging value. Adjustments are made for the country’s specific distribution structure, export flows and regional clustering of manufacturers and warehouses.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses on tertiary packaging share, growth rates and segment weights (format and application splits) are validated through structured interviews with supply-chain managers at local pharma companies, procurement teams at large hospital groups, regional packaging suppliers and cold-chain logistics providers. Where direct interviews are not available, the study leverages published case studies from Zuellig Pharma, global cold-chain packaging firms and logistics providers operating in Asia, focusing on actual pallet counts, shipper fleet sizes, validated lane volumes and service models.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final step involves reconciling top-down market data (e.g., total pharmaceutical sales and total pharmaceutical packaging value) with bottom-up estimates derived from packaging format usage, application-level shipment patterns and warehouse throughput metrics. Scenario analysis is applied to reflect different growth trajectories in generics, biologics and vaccine shipments, and their corresponding impact on tertiary packaging demand. The output is a fully triangulated, transparent and documented view of the Philippines Pharmaceutical Tertiary Packaging Market, including base-year size, 2024-2030 CAGR, segment splits and a structured view of the competitive landscape.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definition and taxonomy for tertiary packaging, packaging-level coverage, pharma sub-segment coverage, value and volume units, top-down and bottom-up sizing, inter-island lane mapping, expert interviews with converters, 3PLs and MAHs, data triangulation, assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and Functional Scope of Tertiary Packaging in Pharma
- Role of Tertiary Packaging in the Philippines Pharma Supply Chain
- Pharma and Biologics Supply Chain Structure in the Philippines
- Tertiary Packaging Within Corrugated and Temperature-Controlled Packaging Ecosystem
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Macroeconomic and healthcare expenditure growth
Expansion of pharma manufacturing
Cold-chain investments
Vaccine and biologics uptake
Rise of e-pharmacies and organized retail - Challenges
Archipelagic geography
Fragmented logistics
Inter-island transit risk
Carton and pallet damage rates
Skill gaps in cold-chain handling - Opportunities
PUR and PCM-based shippers
Standardization of lane-qualified tertiary packs
Outsourcing to GDP-compliant 3PLs
Route optimization - Trends
Eco-designed corrugated
Right-weighting
FSC-certified paper
Reduction of single-use plastics
Recyclability of insulated shippers - Regulatory, Quality and Compliance Landscape
- Technology and Digitalization in Tertiary Packaging
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- Average Price Metrics by Tertiary Pack Type, 2019-2024
- Split by Ambient vs Temperature-Controlled Tertiary Packaging, 2019-2024
- Split by Captive vs Outsourced / Contract Tertiary Packaging, 2019-2024
- By Packaging Format (in Value %)
Corrugated Shipping Cartons and Master Cases
Pallet Boxes, Gaylords and Bulk Bins
Insulated Shippers and PUR Containers
Wooden and Plastic Pallets, Crates and Totes
Other Tertiary Packaging Formats - By Material (in Value %)
Corrugated Board and Paperboard
Rigid and Flexible Plastics
Wood and Wood-Based Materials
Foams, PUR and Advanced Insulation Materials
Other Materials and Hybrids - By Temperature-Controlled Lane (in Value %)
Ambient and Controlled Room Temperature Tertiary Packaging
Cold Chain Tertiary Packaging for +2 to +8 Degrees Shipments
Frozen and Deep-Frozen Tertiary Packaging
Mixed-Temperature and Multi-Compartment Solutions - By Shipment Type and Load Unit (in Value %)
Parcel and Case-Level Shipments
Full-Pallet and Mixed-Pallet Shipments
Containerized and Cross-Dock Shipments
Clinical Trial and Sample Logistics - By End User Type (in Value %)
Research-Based and Multinational Pharma Companies
Local Branded Generics and Contract Manufacturers
Vaccine and Biologics Importers and Program Managers
Hospital and Clinic Networks
Retail Pharmacies, Drugstore Chains and E-Pharmacies - By Region and Logistics Corridor (in Value %)
Metro Manila and Luzon Manufacturing & Distribution Cluster
Visayas Distribution Hubs
Mindanao Corridors
Export-Oriented Gateways and Freeport Zones
- Market Share of Major Players by Value and Volume
Market Share by Packaging Format Cluster
Market Share by End-User Segment Served - Cross Comparison Parameters (Company overview and ownership structure; Philippines pharma tertiary packaging portfolio breadth by format and temperature lane; Philippines manufacturing and distribution footprint across carton plants and cold-chain hubs; quality and regulatory certifications including GDP, ISO and relevant approvals; key pharma, vaccine and biologics customer segments served; sustainability and circular packaging initiatives including recycled content and returnable pools; integration with cold-chain logistics providers and monitoring platforms; service performance indicators including lead time, on-time delivery and damage/temperature excursion records)
- Strategic and Operational SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Analysis
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Amcor Flexibles Philippines Corp.
San Miguel Yamamura Packaging Corporation
Bestpak Packaging Solutions, Inc.
Netpak Phils., Inc.
Robicel Trading
GL Otometz Corporation
Plastic Container Packaging Corporation
APO International Marketing Corporation
Versa Group Philippines Corporation
Zuellig Pharma Corporation
Pharmaserv Express
FAST Logistics Group
DHL Supply Chain Philippines
UPS Healthcare Philippines
- Procurement Models and Decision-Making Units
- Service-Level, Quality and Compliance Expectations
- Budgeting, Total Cost of Ownership and Trade-Offs
- Needs, Pain Points and Unmet Requirements
- End-User Segmentation and Priority Accounts
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- Average Price Metrics by Tertiary Pack Type, 2019-2024
- Split by Ambient vs Temperature-Controlled Tertiary Packaging, 2019-2024
- Split by Captive vs Outsourced / Contract Tertiary Packaging, 2019-2024


