Market Overview
The Philippines Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) and Care market is valued at USD ~ million, reflecting rising demand for continuous vitals tracking beyond hospital walls and the scaling of home-based monitoring for chronic conditions; a key adjacent indicator is the global RPM market moving from USD ~ billion to USD ~ billion, reinforcing the vendor investment cycle that is also flowing into Southeast Asia device + platform rollouts.
Dominance within the Philippines RPM ecosystem is concentrated in Metro Manila, CALABARZON, and Central Luzon, supported by higher specialist density, private hospital networks, device retail availability, and payer/corporate health programs; outside Luzon, Cebu and Davao stand out due to large tertiary providers, stronger diagnostics footprints, and more mature telehealth partnerships. International vendors dominate enabling layers (devices, cloud, analytics) because of validated hardware portfolios and interoperability toolkits, while local telehealth platforms lead patient acquisition and last-mile care coordination.
Market Segmentation
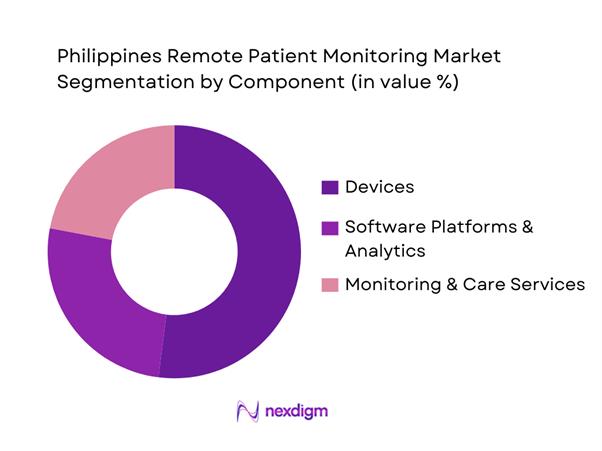
By Component
Philippines RPM is segmented by component into devices, software, and services. Devices dominate because most RPM programs in the country still start with measurable, reimbursable, and operationally “simple” vitals capture (BP cuffs, glucometers, pulse oximeters, weight scales) before scaling into deeper analytics and longitudinal care pathways. Device-led adoption is reinforced by retail and distributor availability in major cities, clinical comfort with validated brands, and program KPIs that prioritize readmission reduction and chronic monitoring compliance—both of which require reliable device data. Software growth is accelerating (integration, dashboards, alerts), but implementation timelines, interoperability readiness, and governance approvals often lag device procurement. Services (nurse monitoring, escalation workflows, onboarding) expand fastest where hospitals run hybrid models and outsource monitoring operations for capacity reasons.
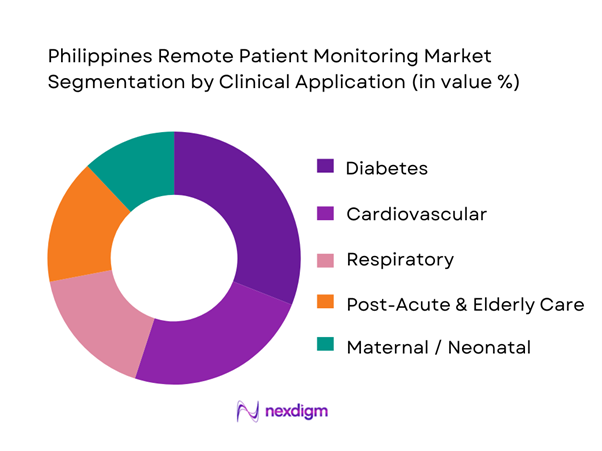
By Clinical Application
Philippines RPM is segmented by clinical application into diabetes, cardiovascular, respiratory, maternal/neonatal, and post-acute & elderly care. Diabetes dominates because RPM aligns tightly with recurring measurement routines (glucose checks), medication adherence support, and remote coaching—creating clear utilization frequency and engagement loops compared to episodic conditions. In practice, diabetes RPM is also easier to operationalize across outpatient settings: clinics can enroll patients continuously, devices are widely available, and telehealth layers can add lifestyle coaching and prescription support. Cardiovascular RPM is strong in tertiary settings (BP, ECG monitoring programs) but tends to be more protocol-heavy and often requires higher clinician oversight. Respiratory monitoring (SpO₂ and related) is growing post-pandemic, while maternal/neonatal RPM remains programmatic (often donor/public-private supported). Post-acute and elderly care is rising with home health models but is constrained by caregiver training and service coverage outside major urban clusters.
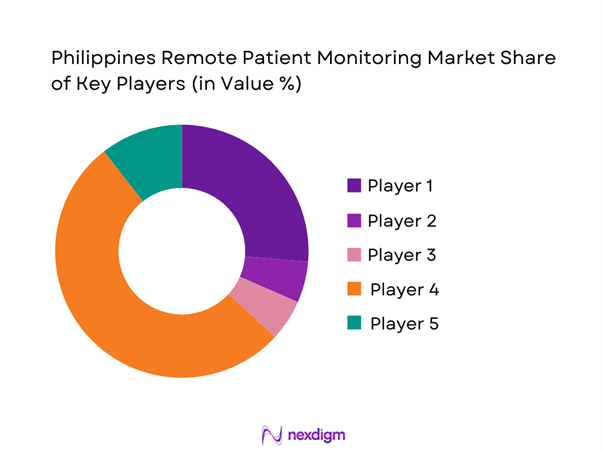
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines RPM market is moderately consolidated at the enabling layer (global device OEMs and platform vendors) while remaining fragmented at the delivery layer (hospitals, clinics, telehealth apps, and monitoring service operators). Programs frequently combine a global device stack, a platform for dashboards and alerts, and local clinical operations for enrollment, adherence, and escalation—creating partnership-heavy competition rather than single-vendor dominance. This is consistent with the broader scaling of telemedicine infrastructure in the country, including national telehealth programs that strengthen referral and remote clinical support networks.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | PH Go-to-Market Motion | RPM Stack Strength | Interoperability Readiness | Typical PH Buyer | Channel Partners in PH | Core Monitoring Focus | Data/Workflow Differentiator |
| Philips (incl. BioTelemetry where relevant) | 1891 | Netherlands | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Medtronic | 1949 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Abbott | 1888 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Roche | 1896 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| VSee | 2008 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Remote Patient Monitoring Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Chronic Disease Burden
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) demand in the Philippines is structurally anchored in the country’s high chronic-disease mortality load that continuously feeds hypertension, diabetes, cardiac, and renal monitoring programs. National mortality reporting shows ~ deaths due to diabetes mellitus in the Philippines, placing it among the top recorded causes of death, while ischemic heart disease and cerebrovascular conditions remain major fatality contributors—conditions where RPM (BP, glucose, SpO₂, weight, ECG) is clinically relevant for continuous tracking and escalation. On the macro side, the Philippines’ economic scale supports sustained healthcare consumption capacity: GDP is USD ~ billion and GDP per capita is USD ~, supporting growing private-sector care utilization and employer health benefits that increasingly bundle chronic monitoring. With an official population count of ~, the absolute pool of chronically managed patients is large enough to keep device replenishment and platform subscriptions structurally “on” for providers and payers.
Hospital Bed Utilization Pressure
RPM adoption accelerates when hospitals and health systems face structural capacity constraints—especially in high-density corridors where occupancy pressure drives earlier discharge and closer post-discharge monitoring. The Department of Health’s national facility planning reference notes the Philippines has ~ hospital beds—a number that illustrates why providers prioritize “care beyond the ward” models such as RPM to reduce avoidable readmissions and stabilize patients at home. Capacity pressure is amplified by the country’s scale: the official population count is ~, meaning hospital-bed availability must stretch across a large national base. In parallel, the macro environment supports continued facility utilization: GDP is USD ~ billion, which matters because higher absolute economic output is typically associated with higher absolute healthcare utilization volumes. RPM becomes a practical operational response: hospitals can monitor vitals remotely to shorten in-facility stays, reduce unnecessary return visits, and prioritize beds for higher-acuity cases—without needing to add immediate physical bed stock.
Challenges
Reimbursement Clarity
RPM scaling is constrained when payer pathways for remote monitoring remain unclear or uneven—because providers hesitate to standardize RPM workflows without predictable payment mechanics. The Philippines has a large, nationally enrolled beneficiary base linked to an official population of ~, which means reimbursement design becomes a system-level determinant of RPM adoption rather than a niche policy issue. PhilHealth’s move to formalize digital service infrastructure through Konsulta-related certifications shows the direction of travel, but RPM reimbursement often requires explicit definitions of eligible monitoring services, clinical thresholds, and reporting standards. In practice, when reimbursement is ambiguous, RPM remains concentrated in private pay programs, corporate health benefits, and hospital-led bundled care models rather than achieving nationwide standardization. Macro capacity matters because payers and providers operate within economic constraints: GDP per capita is USD ~, which influences household ability to pay out-of-pocket and shapes payer pressure to define coverage. The net effect is that reimbursement uncertainty slows broader adoption even when clinical need is clear.
Data Privacy Compliance
RPM programs generate continuous streams of sensitive health data, which raises governance, consent, breach response, and cross-entity data-sharing complexity. The National Privacy Commission anchors enforcement through breach and incident reporting frameworks, documenting formal privacy oversight and reporting mechanisms and emphasizing annual security incident reporting expectations. This regulatory environment is material for RPM because device-to-cloud architectures and platform integrations often cross multiple entities such as hospitals, third-party monitoring services, telecom networks, and app vendors. Compliance cost is not just legal—it affects implementation speed and operational burdens. The scale of the digital ecosystem increases the stakes: with an official population of ~, any large platform deployment potentially touches millions of records. Macroeconomic scale also matters because digitization investments continue: GDP is USD ~ billion, supporting ongoing expansion of connected services while simultaneously raising the need for robust privacy controls. The challenge for RPM is to scale without triggering operational paralysis from governance bottlenecks.
Opportunities
Home-Based Chronic Care Expansion
RPM’s strongest runway in the Philippines is the expansion of home-based chronic care models that reduce facility congestion while keeping clinically meaningful oversight. The chronic load is measurable in mortality statistics, with national reporting showing ~ deaths due to diabetes mellitus, a condition where home monitoring is high-frequency and operationally well-suited to RPM. Facility capacity constraints make home care operationally attractive: DOH planning references cite ~ hospital beds, which strengthens the logic for shifting stable chronic patients into home monitoring to reserve beds for acute needs. The macro environment supports continued expansion: GDP is USD ~ billion and GDP per capita is USD ~, which sustains private hospital investment into hybrid care pathways and employer-funded care programs. Digital channel maturity also supports home-based models, reflecting the scale of consumer comfort with app-driven interactions that complement RPM vitals data. The opportunity is to convert these current realities into scaled RPM programs across discharge-to-home monitoring bundles and chronic care enrollment.
Government-Led Population Health Programs
A major RPM opportunity is alignment with government-led population health pathways that standardize primary care access, digital identity and eligibility flows, and service referrals—because RPM scales faster when it plugs into national programs rather than relying only on single-hospital pilots. PhilHealth’s ecosystem development provides a practical signal of digitization readiness, with certifications being issued that indicate formalized digital service capability supporting structured access, reporting, and patient engagement flows connected to primary care. This opportunity is amplified by national scale, with an official population count of ~ making programmatic population health approaches essential for efficiency. Macroeconomic capacity supports continued public program execution: GDP is USD ~ billion, indicating the economic base within which government and payer modernization efforts operate. Government connectivity efforts also complement population health deployment, with publicly reported Free Wi-Fi for All sites supporting RPM-enabled outreach and monitoring in public spaces and facilities. The near-term opportunity is to embed RPM into chronic disease registries, primary care pathways, and referral networks.
Future Outlook
Over the next planning cycle, the Philippines RPM market is expected to expand steadily as providers shift more chronic care into hybrid pathways, employers embed digital health into benefits, and device and platform bundles become easier to deploy with standardized onboarding and escalation protocols. Provider demand will focus on measurable outcomes such as reduced avoidable admissions, improved adherence, and shorter follow-up cycles, alongside operational resilience and care continuity during disruptions. Growth is also supported by the continued strengthening of telehealth networks connecting underserved areas to specialists, improving the reach component that makes RPM clinically actionable at scale.
Major Players
- Philips
- Medtronic
- Abbott
- Roche
- Dexcom
- GE HealthCare
- Omron Healthcare
- ResMed
- Masimo
- Baxter
- iRhythm Technologies
- Boston Scientific
- Nihon Kohden
- VSee
Key Target Audience
- Hospitals & Integrated Delivery Networks (IDNs)
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) & private payers
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Corporate employers & benefits managers
- Home healthcare operators & post-acute care providers
- Medical device manufacturers & distributors
- Digital health platforms / telehealth operators
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We build a Philippines RPM ecosystem map covering providers, payers, device OEMs, distributors, telehealth platforms, and government programs. Desk research consolidates definitions, regulatory anchors, and channel structures to define variables that move adoption and revenue.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historical demand signals and deployment patterns and translate them into a revenue model by component and use case. We validate assumptions using channel checks on procurement cycles, device mix, and monitoring workflow costs.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validate market hypotheses through structured expert calls with hospitals, HMOs, device distributors, and platform operators. Inputs focus on enrollment funnel metrics, adherence rates, escalation protocols, device replacement cycles, and contracting models.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We synthesize outputs into a triangulated market model and competitive benchmarking. Findings are stress-tested against observed platform partnerships and telehealth network scaling dynamics, ensuring consistency with real-world operational constraints and buyer decision criteria.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, RPM Scope Delineation for Philippines Healthcare System, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Logic, Device vs Platform Attribution Logic, Bottom-Up Patient Installed Base Estimation, Top-Down Healthcare Spend Mapping, Primary Interviews with Providers, Payers, System Integrators and Policymakers, Data Triangulation Framework, Limitations and Forward Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Digital Health Evolution
- RPM Adoption Timeline Across Public and Private Healthcare
- RPM Business Cycle in Philippine Healthcare Delivery
- RPM Care Pathway Mapping
- RPM Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Chronic Disease Burden
Hospital Bed Utilization Pressure
Physician-to-Patient Ratio
Internet and Smartphone Penetration
Public Health Digitization Initiatives - Challenges
Reimbursement Clarity
Data Privacy Compliance
Device Affordability
Patient Adherence
Rural Connectivity Constraints - Opportunities
Home-Based Chronic Care Expansion
Government-Led Population Health Programs
Employer-Sponsored RPM Models
AI-Driven Early Warning Systems - Trends
Shift from Episodic to Continuous Monitoring
Integration with Teleconsultation Platforms
Analytics-Driven Risk Stratification - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Patient Coverage, 2019–2024
- By Active Devices, 2019–2024
- By Care Setting Penetration, 2019–2024
- By Application (in Value %)
Hypertension Management
Diabetes Management
Cardiac Care
Respiratory Monitoring
Post-Acute and Post-Surgical Monitoring - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Bluetooth-Enabled RPM
Cellular-Based RPM
Cloud-Integrated RPM Platforms
AI-Enabled Predictive RPM Systems - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Bluetooth
Cellular
Hybrid Connectivity - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Hospitals
Clinics and Ambulatory Care Centers
Home Healthcare Providers
Health Maintenance Organizations
Government and Public Health Programs - By Region (in Value %)
National Capital Region
Luzon (Non-NCR)
Visayas
Mindanao
- Market Share of Major Players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Device Accuracy Validation, Platform Interoperability, Clinical Workflow Integration, Alert Intelligence Capability, Local Regulatory Compliance, Deployment Scale Capability, After-Sales Clinical Support, Data Security and Hosting Architecture)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Analysis
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Medtronic
Philips Healthcare
Abbott
GE HealthCare
Omron Healthcare
Masimo
ResMed
Boston Scientific
iRhythm Technologies
Honeywell Life Sciences
BioTelemetry
Withings Health Solutions
Dozee
Cloud DX
Care Innovations
- RPM Utilization Patterns by Care Setting
- Budget Allocation and Procurement Decision Flow
- Clinical Workflow Integration
- Pain Points and Unmet Needs
- Decision-Making and Vendor Selection Criteria
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Patient Coverage, 2025–2030
- By Active Devices, 2025–2030
- By Care Setting Penetration, 2025–2030


