Market Overview
The Philippines ride-sharing services market is valued at USD ~ billion based on a five-year historical analysis, led by urban expansion, rising smartphone adoption, and commuter preference for on-demand transportation platforms such as app-based ride-hailing and motorcycle taxi services. This valuation reflects adoption trends as commuters increasingly favor convenient, digital mobility solutions amid persistent traffic and gaps in public transport infrastructure. The growth aligns with the continuous shift from traditional transport to app-enabled ride sharing.
Metro Manila, Cebu, and Davao dominate the ride-sharing market due to high population density, severe traffic congestion, and relatively high disposable income, driving strong reliance on digital mobility options. Metro Manila’s urban sprawl limits the efficiency of conventional transport, while Cebu and Davao’s expanding urban economies and tourism appeal increase commuter demand for reliable, flexible transport services. These urban centers also have higher smartphone penetration and digital payment use, underpinning robust ride-sharing adoption.
Market Segmentation
By Service Type
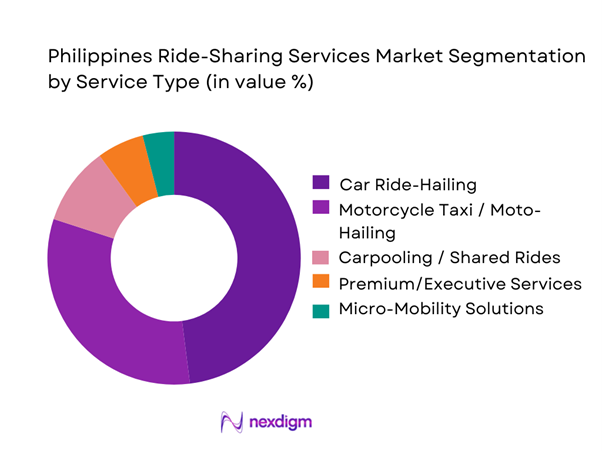
The ride-sharing market is segmented into car ride-hailing, motorcycle taxi (moto-hailing), carpooling or shared services, premium or executive mobility, and micro-mobility such as scooters and smaller on-demand vehicles. In ~, car ride-hailing remains the largest segment, driven by a broad base of consumers using app-based platforms for daily travel across metropolitan areas. This segment’s dominance stems from its versatility in catering to both short and longer intra-city journeys, offering comfort and safety compared with traditional transport. Additionally, car ride-hailing’s integration with digital payment systems and mapping technologies enhances user convenience, further reinforcing its market share. Meanwhile, motorcycle taxi services also hold a substantial share due to their ability to navigate congested urban streets quickly, especially in Metro Manila and Cebu, offering lower fare alternatives and fast point-to-point mobility for commuters seeking time-efficient travel.
By Payment Mode
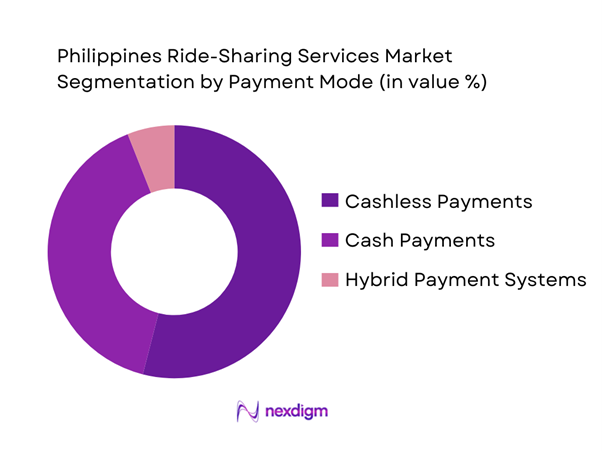
The Philippines ride-sharing market is segmented into cashless payments, cash payments, and hybrid systems. In ~, cashless payments dominate, largely due to the rapid growth of digital wallets which are widely used by riders for their convenience and security. Integration of digital wallets into ride-sharing apps has enabled frictionless transactions, reduced cash handling risks, and shortened boarding times, making them the preferred payment method for urban commuters. Merchants and platforms have also incentivized cashless usage through promotions and loyalty rewards, further driving acceptance. Conversely, cash payments remain significant, especially among occasional users and non-urban commuters who may have limited access to banking or digital payment tools, preserving cash as a familiar and trusted transaction method. Hybrid systems that allow both cash and cashless options cater to diverse user preferences but capture a smaller share as the digital infrastructure strengthens.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment in the Philippines ride-sharing market is concentrated among a mix of regional heavyweights and local operators. Grab Philippines remains a dominant force, with a strong brand presence and integrated service offerings that include car and motorcycle options. Emerging players like Angkas and inDrive have increased competitive intensity by leveraging specialized services and flexible pricing. Overall, consolidation among key platforms underscores their influence on mobility trends and consumer preferences.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Active User Base | Service Types | Geographic Coverage | Revenue Growth | Customer Satisfaction |
| Grab Philippines | 2012 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Angkas | 2016 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| JoyRide | 2019 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| inDrive | 2012 | Russia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Move It | 2019 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Ride-Sharing Services Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Escalating urban traffic congestion and daily mobility demand
Ride-sharing demand in the Philippines is structurally underpinned by a very large, fast-moving daily mobility base concentrated in dense urban corridors. The country’s total population is ~ people, and the urban population alone is ~, a scale that compresses commuting, errands, and service trips into limited road space and fixed peak periods. The macro backdrop also matters because ride-hailing usage tracks disposable income and employment intensity in large cities, signaling the size of the formal and informal economic activity that must move people around every day. In parallel, public investment to expand capacity is ongoing but incremental relative to demand, improving certain bottlenecks but not eliminating citywide congestion frictions that make door-to-door on-demand trips valuable. In this context, ride-sharing becomes a practical congestion hedge, as users convert time uncertainty into app-managed dispatch, dynamic routing, and multi-option fulfillment across major urban centers. The large urban base also supports high trip frequency for work, education, and services, reinforcing habitual demand patterns even when total road capacity improvements lag overall city growth.
High smartphone penetration and digital payment adoption
Ride-sharing in the Philippines scales because discovery, booking, and payment are now largely digital. A core enabler is broad mobile data reach, indicating a huge addressable base for app-based mobility. On the payments side, national measurement shows monthly retail payments are increasingly cash-lite, with large digital retail payment value and transaction volume. This matters directly for ride-sharing because frictionless checkout supports repeat usage, subscription and loyalty mechanics, and lower cancellation risk at pickup. The operational proof is visible in fast payment rails that power in-app top-ups and peer-to-peer settlement behaviors, reflecting very large-scale real-time transfers that normalize pay-by-phone behavior alongside mobility use cases. Together, high mobile broadband reach plus deepening digital payments create a market where platforms can scale dispatch, identity, and refunds while keeping unit operations efficient, which is critical for dense cities where trip frequency is high and consumer tolerance for checkout delays is low.
Challenges
Regulatory complexity under transport network vehicle service frameworks
Philippine ride-sharing operates inside an evolving, highly managed regulatory perimeter where capacity, operator accreditation, and compliance expectations directly shape supply availability and platform economics. The reported approval of multiple ride-hailing companies illustrates both market opening and oversight complexity, as more accredited entities require increased compliance monitoring, differentiated operating conditions, and broader stakeholder coordination across cities and service types. On the supply side, how many vehicles can legally operate is administratively governed rather than purely market-driven, showing that legal authorization is a hard gate to scale. Regulators also make tactical capacity adjustments ahead of peak-demand seasons, underscoring that supply expansion is often episodic and decision-led rather than continuous. For operators, this environment raises costs in documentation, compliance workflows, driver onboarding, and audit readiness, while for consumers it influences availability and service consistency across metro areas and second-tier cities. The net impact is that regulatory pathway design becomes a primary market variable rather than a background constraint.
Safety, insurance, and rider-driver trust issues
Trust is a core constraint because ride-sharing is an instant access service where consumers accept unknown counterparties and time-sensitive pickups. The formal accreditation of multiple operators expands consumer choice but also increases the need for consistent, auditable safety governance across platforms, including screening standards, incident reporting pathways, and service quality controls. The authorized TNVS base is large, raising the operational burden of ensuring standardized insurance coverage, driver compliance, and passenger protection across thousands of vehicles and driver partners. Digitalization helps but also introduces new trust surfaces, as rapid digital payment flows increase the importance of dispute handling, resolution processes, and fraud controls around mobility wallets and top-ups. At the macro level, the size of the population suggests that even low-incidence safety events can materially affect user perception when amplified through social channels. As a result, safety and insurance are not merely compliance items but brand-defining operating systems influencing repeat usage, driver retention, and regulator confidence.
Opportunities
Electric vehicle integration and sustainable mobility models
The strongest near-term pathway for EV-linked ride-sharing growth in the Philippines is not future EV counts, but the readiness of the country’s digital rails and regulated mobility supply to support new vehicle models, charging-linked payments, and fleet-grade controls. The legal TNVS foundation is already sizable, creating a realistic base for phased electrification through fleet operators, driver-partner financing programs, and city-led pilots. On payments infrastructure, high-volume digital retail payment flows and fast payment systems demonstrate that app-linked transactions are normalized at scale. Urban density strengthens the EV business case because electric vehicle total cost advantages are most meaningful in dense, stop-and-go duty cycles with high daily utilization. Infrastructure upgrades also matter operationally, as improved route continuity supports more predictable EV energy planning for fleets. The opportunity lies in building EV-ready ride-sharing bundles now using current-scale digital and regulatory foundations.
Corporate ride programs and enterprise mobility contracts
Enterprise mobility represents a high-leverage opportunity in the Philippines because it converts volatile consumer demand into contracted trip volumes with tighter service-level control over pickup reliability, safety standards, and reporting. The macro base supports this through a large, formalizing economy with expanding service sectors that generate predictable commuting and client-visit travel needs. Urban concentration strengthens the contractability of demand by creating dense clusters of offices, industrial parks, hospitals, and education hubs where enterprises can standardize mobility corridors and budgets. On the supply side, a regulated TNVS base enables platforms to segment supply for corporate tiers without operating outside the regulatory perimeter. Payment and reconciliation, often the biggest friction in corporate mobility, has become easier due to normalized digital payment infrastructure and real-time fund movement. These conditions allow ride-sharing platforms to sell enterprise contracts that bundle policy controls, duty-of-care features, and consolidated billing, turning mobility into a managed service line item for employers and institutions in major urban centers.
Future Outlook
The Philippines ride-sharing market is expected to grow steadily, propelled by expanding smartphone penetration, increasing preference for cashless transactions, and persistent urban mobility challenges. Operators are likely to enhance platform capabilities through route optimization, in-app safety features, and partnerships with local governments to align with regulatory frameworks. Expansion into tier-two and tier-three cities and service diversification, including electric vehicle integration and corporate mobility solutions, will further broaden user adoption and revenue streams. Evolving consumer expectations around speed, safety, and affordability will drive competitive innovation across platforms, making ride-sharing an integral component of urban transport ecosystems.
Major Players
- Grab Philippines
- Angkas
- JoyRide
- inDrive
- Move It
- Hype
- U-Hop
- Micab
- TaxiGo
- EasyTaxi
- Biyahero
- OWTO
- GoJek
- Lalamove
Key Target Audience
- Ride-Sharing and Mobility Platform Investors
- Transportation Network Companies Strategy Teams
- Public Transport Authorities
- Local Government Units
- Fleet Operators and Vehicle Providers
- Insurance and Financial Services
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial research phase involved mapping major stakeholders within the ride-sharing ecosystem, including digital platforms, driver partners, and commuter segments. Secondary sources such as industry reports, government statistics, and app usage data were collected to define core market variables influencing revenue and utilization.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical data was compiled to assess revenue generation, service adoption rates, active user growth, and trip volumes. Payment modes, vehicle types, and geographic penetration were examined to derive a comprehensive market overview and ensure accuracy.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses were developed and validated through interviews with industry practitioners, transportation policymakers, and mobility platform specialists to refine data accuracy. These interviews provided insights on operational trends and regulatory impacts.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Final insights were synthesized by reconciling primary and secondary findings, cross-verified against published market valuations and industry growth forecasts. This ensured a validated, precise analysis of market dynamics and competitive positioning.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Market Scope & Ride-Sharing Service Criteria, Abbreviations & Industry Terms, Market Sizing Framework, Service Adoption & Utilisation Modeling, Mobile App Penetration & Digital Payment Integration Assumptions, Primary & Secondary Data Sources, Research Limitations & Assumptions)
- Industry Definition and Scope
- Genesis & Evolution of Ride-Sharing in the Philippines
- Transportation Ecosystem in the Philippines
- Ride-Sharing Value Chain & Ecosystem
- Demand-Supply Dynamics & Business Models
- Growth Drivers
Escalating urban traffic congestion and daily mobility demand
High smartphone penetration and digital payment adoption
Shift from traditional public transport to on-demand mobility
Smart mobility initiatives and transport modernization programs - Challenges
Regulatory complexity under transport network vehicle service frameworks
Safety, insurance, and rider-driver trust issues
Price competition and commission pressure on platforms
Urban infrastructure constraints and road congestion - Opportunities
Electric vehicle integration and sustainable mobility models
Corporate ride programs and enterprise mobility contracts
Expansion into tier-2 and tier-3 cities
Advanced data monetization and personalization engines - Trends
Professionalization of motorcycle taxi services
Bundling of mobility, delivery, and financial services
Increased adoption of cashless and wallet-based payments
AI-driven routing and surge pricing optimization - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- Installed Base, 2019–2024
- Service Revenue Mix, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Standard Cars
SUVs and Premium Cars
Motorcycle Taxis
EV and Hybrid Fleets
Accessible and Special Needs Vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Daily Commuting
Airport Transfers
Corporate and Business Travel
Night-Time and Leisure Travel
On-Demand Parcel and Logistics - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
App-Based Aggregator Platforms
AI-Based Dynamic Pricing Platforms
Route Optimization and Navigation Engines
Data Analytics and Demand Forecasting Systems
Safety and Verification Technology Stacks - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Mobile Internet-Based Platforms
Integrated Digital Wallet Ecosystems
Cloud-Based Dispatch Systems
API-Integrated Super Apps
Standalone Ride-Hailing Applications - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Individual Consumers
Corporate Enterprises
Hospitality and Tourism
Retail and E-Commerce
Logistics and Last-Mile Delivery - By Region (in Value %)
Metro Manila
Metro Cebu
Metro Davao
Other Urban Clusters
Emerging Small Cities and Semi-Urban Areas
- Market Share Analysis by Revenue, Trips, and Active Users
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Service portfolio breadth, active driver fleet size, city coverage footprint, average rider ratings and safety scores, app downloads and user growth, customer retention metrics, fare structure and pricing strategy, regulatory compliance strength)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing and Surge Strategy Benchmarking
- Detailed Company Profiles
Grab Philippines
Angkas
Move It
JoyRide
MiCab
U-Hop
Hype
OWTO
TaxiGo
Biyahero
inDrive
EasyTaxi
TNC
Owlto
- Ride usage patterns and commuter behavior
- Rider cohort profiling and spending bands
- Price sensitivity and loyalty determinants
- Service quality, safety perception, and satisfaction drivers
- Decision-making criteria and platform selection factors
- By Value, 2025–2030
- Installed Base, 2025–2030
- Service Revenue Mix, 2025–2030


