Market Overview
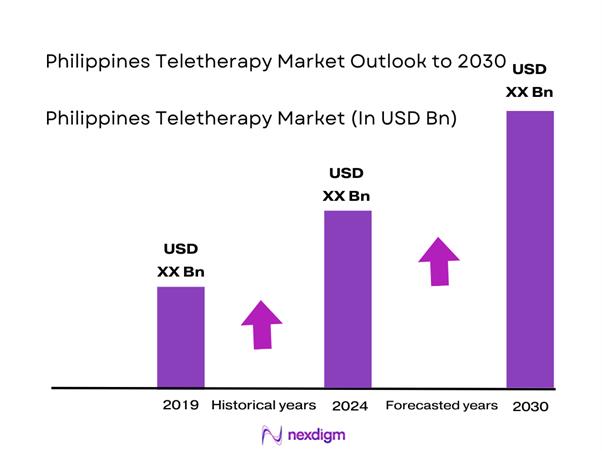
The Philippines Teletherapy Market is valued at USD ~ million. The Philippines telemedicine market is valued at USD ~ million, supported by rising demand for remote consults and platform-based care delivery. On the demand-side, public health resourcing also signals structural pull: government mental health financing reached PHP ~, strengthening referral pathways and awareness that convert into paid therapy utilization.
Dominance in the Philippines Teletherapy Market is concentrated in Metro Manila (largest employer base, corporate wellness budgets, and denser licensed-provider networks), followed by CALABARZON and Central Luzon (spillover of workforce, BPO/IT corridors, and commute-driven preference for online sessions). In practice, the strongest demand nodes align with areas that can sustain EAP-led procurement and recurring digital sessions (large enterprises, BPO parks, multi-site employers), while access expansion into outer provinces is increasingly shaped by distributed service sites (~ access sites) and actual service uptake (~ users) that normalize help-seeking and route patients to tele-consults where in-person capacity is tight.
Market Segmentation
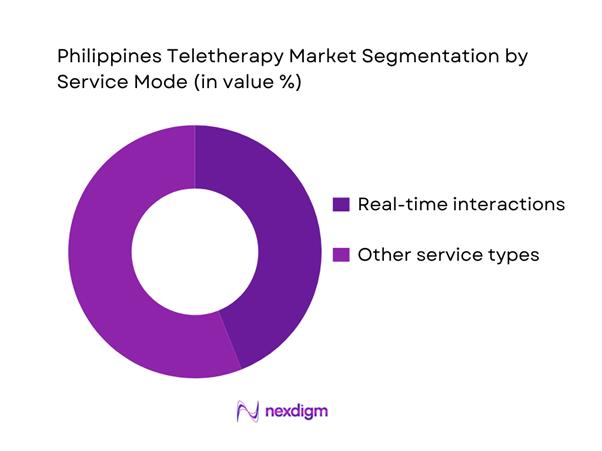
By Service Mode
The Philippines Teletherapy Market can be interpreted by service mode into real-time interactions (scheduled video/voice sessions) and asynchronous / non-real-time models (chat-based counseling, store-and-forward, and blended pathways). Real-time interactions dominate because they match clinical practice expectations for psychotherapy (session structure, therapeutic alliance, risk screening) and are preferred by enterprise EAP buyers who require auditability (appointment logs, utilization reporting, escalation protocols). In the Philippines context, real-time also aligns with the growth of employer-sponsored mental health programs, where HR and HMO-linked flows prioritize booked sessions with licensed psychologists/psychiatrists and documented care pathways over informal support.
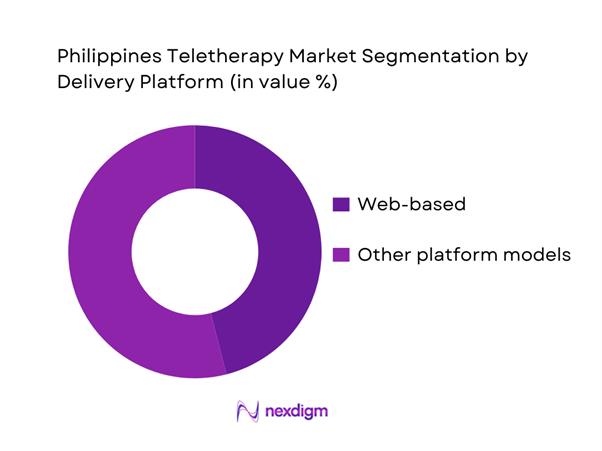
By Delivery Platform
Teletherapy in the Philippines is delivered through web-based access and other infrastructure models (cloud/on-prem variants across provider networks). Web-based dominates because it minimizes friction: users can join sessions without heavy app installs, employers can embed access into HR portals, and providers can run multi-device workflows (desktop notes + video). It also supports faster onboarding for first-time therapy users—critical in a market where stigma reduction and initial access are major conversion gates. For platforms selling to enterprises, web-based reduces IT constraints and eases rollout across multiple worksites and shifts (especially BPO/operations), supporting higher activation and repeat sessions once employees see ease-of-use and confidentiality assurances.
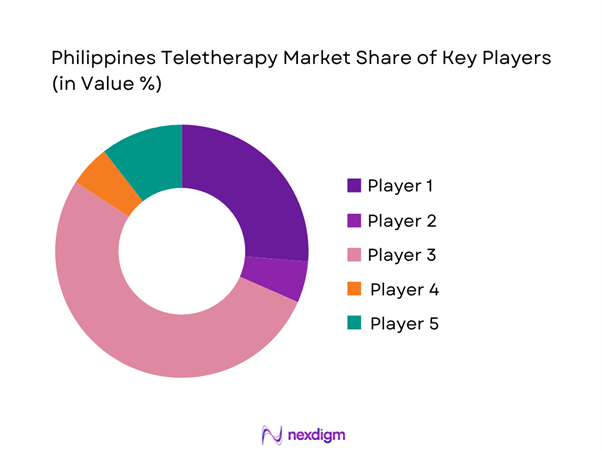
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines Teletherapy Market features a mix of local, mental-health-first providers and broader telemedicine platforms that route to behavioral care. A notable structural pattern is the B2B concentration: many high-volume therapy sessions are contracted through employee assistance programs (EAPs) and corporate wellness bundles, while D2C growth is propelled by app onboarding, bundled assessments, and rapid scheduling.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | Go-to-market focus | Core teletherapy offer | Clinician network model | Enterprise (EAP) readiness | Clinical governance / QA | Typical pricing construct |
| MindNation | 2019 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| KonsultaMD | 2016 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| mWell PH | 2021 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MyPocketDoctor | 2016 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| NowServing (SeriousMD ecosystem) | 2015 | Philippines | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Teletherapy Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Mental Health Law Implementation Impact
The Philippines’ Mental Health Act created the policy foundation that legitimizes demand for structured, confidential counseling pathways—an essential enabler for teletherapy uptake where in-person capacity is thin. On the “need” side, the Department of Health has reported at least ~ Filipinos living with mental, neurological, and substance use disorders, a scale that pushes providers toward scalable remote care models for screening, continuity, and follow-ups. On the “system response” side, government mental health financing has been cited as rising from USD ~ to USD ~, supporting expanded service delivery channels and normalization of help-seeking (including digital touchpoints). This sits within a macro environment where the Philippines’ population reached ~ and GDP per capita reached USD ~, expanding the addressable base for paid teletherapy and employer-sponsored services while increasing demand for productivity-linked mental health support.
Workforce Stress Load
Teletherapy demand rises when work intensity and economic pressure concentrate stress in large employed populations, especially in urban service centers where long commutes and shift work are common. The Philippines’ macro base remains large and consumption-driven, with GDP measured at USD ~ and population at ~, which together translate into large absolute counts of workers exposed to stressors even when prevalence rates vary. Stress load also concentrates where labor is densest, aligning with where teletherapy platforms can acquire users via employer benefits, HMO add-ons, and clinic referral networks. Demand signals for crisis and counseling access are visible through hotlines that continue to receive high call volumes during peak stress periods, showing persistent help-seeking behavior that can convert into teletherapy continuity care after acute events. For teletherapy operators, the workforce stress driver is not only “more people need support,” but “people need support in formats compatible with work schedules”—evening sessions, asynchronous messaging, and hybrid workplace programs—making digital delivery a practical fit for employed adults in dense labor markets.
Challenges
Licensing Fragmentation
Teletherapy compliance in the Philippines is complicated by multi-layer professional licensing, scope boundaries, and differing rules across professions involved in mental healthcare. Providers may include psychologists, psychometricians, guidance counselors, psychiatrists, and allied clinicians—each with distinct credentialing pathways and practice boundaries, creating operational friction for platforms building standardized service protocols. The scarcity context amplifies the problem: when supply is limited, platforms often need to onboard multiple provider types to meet demand, but must ensure each delivers only within their authorized scope and documentation standards. This governance challenge sits in a large macro setting—GDP USD ~ and population ~—where scaled digital distribution can quickly expose compliance gaps if workflows are not tightly controlled. As a result, platform playbooks must include credential verification, scope-based triage routing, clinical escalation rules, and auditable documentation. Fragmentation also affects B2B sales: employers and insurers may demand clarity on who delivers care, under what license, and how supervision is structured. Platforms that cannot demonstrate licensing hygiene and clinical governance face longer procurement cycles and higher legal risk.
Cultural Acceptance Barriers
Even with high need, teletherapy adoption can be constrained by stigma, reluctance to seek help, and fear of being identified—especially in smaller communities where privacy concerns are heightened. Demand indicators show the issue is real: authorities have reported at least ~ Filipinos affected by mental, neurological, and substance use disorders, yet access remains limited, implying a gap between need and utilization that stigma and social barriers can widen. Cultural acceptance interacts with household economics: with GDP per capita at USD ~, many families prioritize immediate necessities, and mental health spending can be deferred unless symptoms become acute. Teletherapy helps by allowing discreet access, but platforms must still invest in trust building—clear confidentiality messaging, culturally aligned therapist matching, and clinical quality assurance. Youth cohorts in particular may prefer digital channels, but family consent dynamics and conservative norms can still block conversion. For business buyers, acceptance barriers also show up as low utilization unless programs are paired with awareness campaigns, manager training, and easy entry points like anonymous self-assessments and brief first sessions.
Opportunities
Corporate Mental Wellness Demand
The strongest near-term growth opportunity for teletherapy in the Philippines is employer-anchored demand: corporate programs convert “need” into funded access, reduce stigma via normalization at work, and deliver scale through repeat cohorts. The macro base supports this: GDP USD ~ indicates a large formal economy footprint, while GDP per capita USD ~ supports paid benefit structures in many sectors even when individual out-of-pocket affordability is uneven. Corporate demand is also structurally linked to urban concentration: with an urban population of ~, HR and HMO procurement hubs are concentrated, enabling faster enterprise sales cycles and program rollouts. Importantly, hotline utilization shows ongoing willingness to seek help when access is easy—teletherapy can position itself as the “continuity layer” after crisis touchpoints. In practice, this opportunity favors platforms that can offer short-wait appointment availability, bilingual therapists, clinical governance and privacy compliance packages, and outcome reporting dashboards that let employers justify renewals. The growth path is to move from reactive counseling to proactive mental wellness programs.
Youth Mental Health Programs
Youth-focused teletherapy expansion is a high-potential opportunity because young people are digitally native, prefer private channels, and can be reached through school-linked and community programs that reduce stigma barriers. The scale of need is underscored by reports of ~ Filipinos living with mental, neurological, and substance use disorders, and by the country’s large population base of ~, which implies very large youth cohorts in absolute terms. Programmatically, youth access is strengthened by smartphone reach and identity formalization, with reported ~ SIM registrants enabling app onboarding at national scale and supporting authentication and continuity features important for safeguarding minors and vulnerable users. This opportunity is best executed through structured pathways: school referrals into teletherapy partners, youth-friendly scheduling, low-bandwidth modes for connectivity constraints, and escalation links to crisis lines and public mental health services. The near-term growth lever is current infrastructure readiness and active privacy oversight that pushes platforms to build trust-first youth services.
Future Outlook
Over 2024–2030, the Philippines Teletherapy Market is expected to expand as enterprise mental health procurement becomes more standardized, therapy access is embedded into broader digital health journeys, and hybrid care models mature. Service design will shift toward measurement-based care, stronger risk triage, and integrated pathways for anxiety, depression, burnout, sleep, and substance-use support. Growth is also supported by the broader telehealth trajectory in the region and the scaling of digital-first access channels.
Major Players
- MindNation
- KonsultaMD
- mWell PH
- MyPocketDoctor
- NowServing
- SeeYouDoc
- Medgate Philippines
- AIDE
- Doctor Anywhere
- MyDoc
- Grab Health / health integrations
- HaloDoc
- BetterHelp
- Talkspace
Key Target Audience
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Health Maintenance Organizations and payers
- Large employers and HR procurement heads
- Hospital groups and integrated delivery networks
- Telehealth platform operators and digital health product owners
- Mental health clinic chains and provider group practices
- Insurance underwriters and corporate benefits administrators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We map the Philippines Teletherapy ecosystem across platforms, provider networks, corporate buyers, and care pathways. Desk research consolidates regulatory context, enterprise procurement norms, and service models. The goal is to define variables that drive utilization, retention, and monetization.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We construct the market using a combined top-down and bottom-up build. We analyze channel flows, conversion points, and repeat-session dynamics to avoid overcounting.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses are validated via structured expert interviews with platform operators, HR benefits leads, licensed clinicians, and payer stakeholders. We test assumptions on buyer selection criteria, clinical governance requirements, unit economics, and churn and retention drivers.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are triangulated across secondary sources, operator inputs, and comparable benchmarks, then synthesized into segment narratives, competitive positioning, and go-to-market implications. Outputs include segmentation logic, player benchmarking, and scenario-based outlook framing for decision makers.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Scope Clarifications, Industry Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Logic, Bottom-Up and Top-Down Validation Framework, Primary Expert Interviews across Psychiatrists, Psychologists, Counselors, Platform Operators, Payers, Regulatory Review Framework, Data Triangulation, Limitations and Forward-Looking Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Evolution of Teletherapy in the Philippines Healthcare System
- Mental Health Care Delivery Landscape
- Teletherapy Business Lifecycle and Maturity Curve
- Teletherapy Value Chain and Stakeholder Mapping
- Growth Drivers
Mental Health Law Implementation Impact
Workforce Stress Load
Urban Density
Smartphone Penetration
Therapist Shortage Ratios - Challenges
Licensing Fragmentation
Cultural Acceptance Barriers
Data Privacy Compliance
Payment Affordability
Therapist Burnout - Opportunities
Corporate Mental Wellness Demand
Youth Mental Health Programs
Rural Access Expansion
Filipino Diaspora Services - Trends
AI-Assisted Triage
Blended Therapy Models
Corporate HR Integration
Crisis-On-Demand Models - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Session Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Consultation Yield, 2019–2024
- By Application (in Value %)
Individual Therapy
Couples Therapy
Family Therapy
Group Therapy
Crisis Counseling - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Anxiety Disorders
Depression and Mood Disorders
Trauma and PTSD
Substance Use Disorders
Behavioral and Stress-Related Conditions - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Video-Based Therapy
Audio-Only Therapy
Text-Based Counseling
Hybrid Therapy Models - By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Individual Consumers
Corporate and Employer Programs
Educational Institutions
Hospitals and Clinics
NGOs and Community Organizations - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Out-of-Pocket Payments
Employer-Sponsored Plans
Insurance-Reimbursed Services
Subscription-Based Therapy Plans - By Region (in Value %)
Metro Manila
Luzon (Excluding Metro Manila)
Visayas
Mindanao
- Market Share of Major Players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Platform Modality Coverage, Licensed Therapist Network Size, Clinical Specialization Breadth, Session Pricing Architecture, Corporate Client Penetration, Insurance Integration Capability, Data Privacy and Security Readiness, Geographic Coverage Depth)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing and Monetization Models Analysis
- MindNation
KonsultaMD
RecoveryHub Philippines
Empath Philippines
The Mind You
MyGolana
GrayMatters Philippines
Ateneo Bulatao Center Telecounseling
Circle of Hope Teletherapy
BetterSteps Psychology
Talk to a Therapist PH
MindCare Club
Lyf Solutions
WeThrive Philippines
Serbisyo Mental Health Network
- Demand Patterns and Session Utilization
- Willingness-to-Pay and Budget Allocation Behavior
- Access Barriers and Adoption Friction
- Decision-Making and Provider Selection Criteria
- Retention, Compliance, and Therapy Continuity
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Session Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Consultation Yield, 2025–2030


