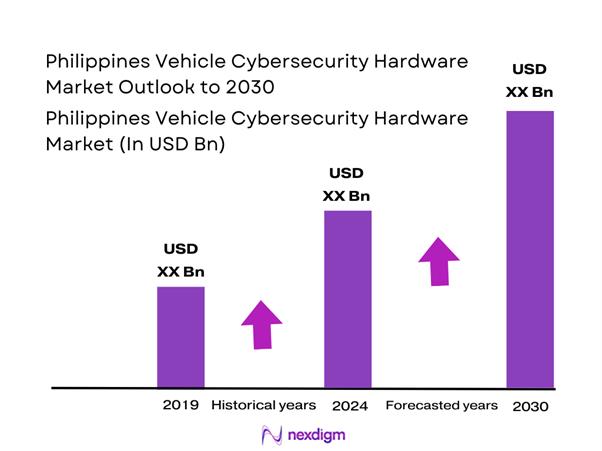
Market Overview
The automotive cybersecurity market is valued at USD ~ billion in the prior year and USD ~ billion in the latest year, based on widely cited global automotive cybersecurity benchmarks. This expansion is driven by the rapid increase in connected-vehicle functions (telematics, infotainment-cloud pairing, remote diagnostics, OTA enablement) and by regulation-driven cybersecurity-by-design programs across OEMs and Tier-1s. Hardware demand rises when OEMs harden ECUs using secure elements/HSM-capable MCUs and secure gateways.
Within the Philippines, adoption intensity is anchored in Metro Manila and adjacent industrial corridors because these areas concentrate OEM/dealer service networks, commercial fleets, and telematics integrators—making secure retrofit gateways, hardened TCUs, and hardware-backed identity more deployable at scale. On the supply side, Japan, South Korea, and China shape the country’s cybersecurity hardware content because they dominate the Philippines’ imported vehicle base and OEM platform standards, and their Tier-1 supply chains decide whether secure gateways/HSM-ready compute ships by default.
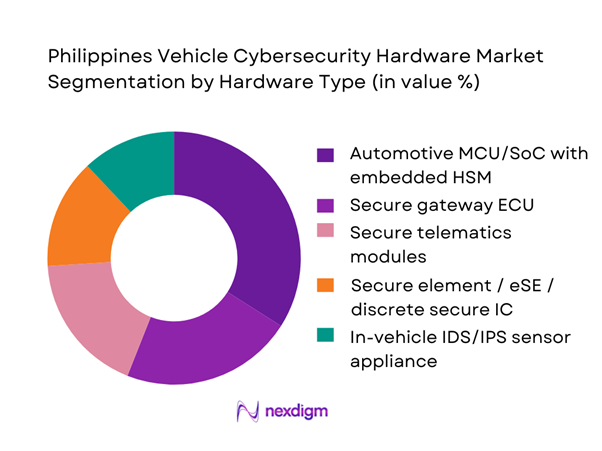
Market Segmentation
By Hardware Type
The Philippines Vehicle Cybersecurity Hardware Market is segmented by hardware type into secure elements/eSE, automotive MCUs/SoCs with embedded HSM, secure gateway ECUs (CAN/CAN-FD ↔ Ethernet), in-vehicle IDS/IPS sensor appliances, and secure telematics modules (TCU security add-ons). Recently, automotive MCUs/SoCs with embedded HSM dominate because OEM and Tier-1 design choices increasingly embed cryptography, secure boot, and key storage into the primary compute silicon rather than adding multiple discrete security chips. This reduces BOM complexity, improves latency for secure communications, and supports compliance-aligned development flows (security-by-design). In the Philippines, the dominance is reinforced by importer-led vehicle platform carryover: models already designed for multi-market compliance ship with HSM-capable controllers, while fleets and integrators typically retrofit at the edge (TCU/gateway) only when mandated by risk exposure.
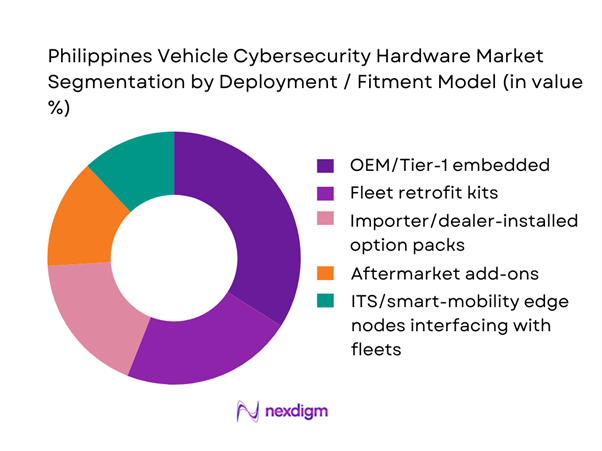
By Deployment / Fitment Model
The Philippines Vehicle Cybersecurity Hardware Market is segmented by deployment model into OEM/Tier-1 embedded (factory fit), importer/dealer-installed option packs, fleet retrofit kits, and aftermarket add-ons, plus ITS/smart-mobility edge nodes interfacing with fleets. Recently, OEM/Tier-1 embedded dominates because cybersecurity hardware is most cost-effective and defensible when it is designed into ECUs and gateways at platform level—where secure boot chains, key injection, and hardware-backed identity are integrated into manufacturing and homologation processes. In the Philippines, importer economics also favor factory-fit security: dealers prefer solutions that do not create post-sale calibration liability, and fleet operators prefer warranty-safe configurations for high-uptime assets. Retrofits still grow, but are concentrated in fleets with higher cyber exposure (telematics-heavy operations, cashless in-vehicle workflows, or safety-critical routing) and where integrators can provide provisioning and RMA support.
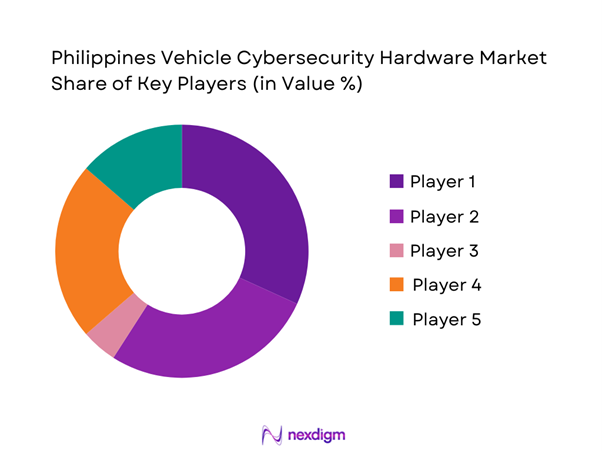
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines Vehicle Cybersecurity Hardware Market is characterized by platform-led consolidation: silicon vendors (secure MCU/SoC and secure element providers) influence the core hardware root-of-trust, while Tier-1s (gateways/domain controllers/TCUs) determine how security is integrated into vehicle architectures delivered into the country via import channels. Competition is therefore decided by reference designs, automotive qualification depth, provisioning toolchains, and local channel capability (inventory + RMA + engineering support).
| Company | Est. Year | Headquarters | Primary PH Route-to-Market | Core Cybersecurity Hardware Focus | Vehicle Network Coverage | Hardware Root-of-Trust Approach | Provisioning Model | Automotive Qualification Depth | After-sales Enablement |
| NXP Semiconductors | 2006 | Netherlands | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Infineon Technologies | 1999 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| STMicroelectronics | 1987 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Bosch (incl. ETAS ecosystem) | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Continental | 1871 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Vehicle Cybersecurity Hardware Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Connected vehicle penetration
The baseline driver for in-vehicle cybersecurity hardware is the Philippines’ rapidly expanding “connected surface area” across drivers, passengers, and vehicles—because every additional connected endpoint increases exposure for IVI/telematics/ECU networks and pushes OEMs, importers, and fleets toward hardened gateways, secure elements, and authenticated in-vehicle communications. The Philippines’ population is ~ and GDP is USD ~ billion, which supports continued scaling of the digital economy and connected mobility services across Metro Manila and other high-traffic corridors. Internet adoption is also structurally high: ~ (internet users, percent of population) is the latest reading, which translates to a very large online base when applied to a population above ~—meaning more app-based navigation, ride-hailing, e-commerce logistics, and remote fleet operations that depend on connected vehicles. On the automotive side, new-vehicle throughput is large and still expanding: total new motor vehicle sales of ~ units followed by ~ units, widening the installed base of newer, more electronically complex vehicles that are more likely to feature networked infotainment, telematics, advanced gateways, and software-defined functions that require hardware-rooted trust.
Telematics device deployment across fleets
Fleet digitalization increases demand for cybersecurity hardware because commercial operations rely on always-on telematics and back-office integration—turning the vehicle gateway/TCU into a high-value attack path that must be protected with secure boot, hardware security modules/secure elements, tamper resistance, and credential lifecycle controls. The Philippines’ macro backdrop supports this digitization: GDP per capita is USD ~ and consumer price inflation is ~ (annual, percent), which together signal a large consumption economy where logistics and mobility services compete heavily on utilization, routing efficiency, and uptime—conditions that encourage fleets to instrument vehicles with connected trackers and telemetry. On the demand side, commercial vehicle movement is consistently the larger slice of monthly sales: in a peak month, total sales reached ~ units with ~ units commercial vehicles versus ~ units passenger vehicles—an operating reality that naturally expands the addressable base for fleet-grade telematics and, by extension, vehicle cybersecurity hardware protecting TCUs/gateways and in-vehicle networks. Even early-year momentum is strong: total sales in the first two months reached ~ units, reinforcing that fleets and SME operators are continuously adding vehicles that increasingly plug into dispatch, tracking, and digital payment workflows. As telematics becomes embedded into route compliance, driver behavior programs, and preventive maintenance, hardware security becomes mandatory—not optional—because a compromised TCU or gateway can create operational disruption (vehicle immobilization, falsified telemetry, or ransomware-style lockouts), regulatory exposure, and safety risk.
Challenges
Cost sensitivity and ASP constraints
A key constraint for cybersecurity hardware adoption is affordability pressure across fleet buyers and consumers, because hardware-rooted security adds BOM and integration workload that must be justified against operating margins, financing costs, and total cost-of-ownership targets. The Philippines’ GDP per capita is USD ~, which anchors the reality that many vehicle purchases are cost-managed and that aftermarket “security add-ons” compete with essential spend (maintenance, tires, fuel, insurance). Inflation is ~ (annual, percent) in the latest snapshot, which, even when moderate, can tighten procurement thresholds and slow the willingness to pay for invisible security features. At the same time, the market is adding vehicles at high volumes—~ units of new vehicle sales in the latest full year—so even small per-vehicle security cost increments translate into large absolute procurement decisions for OEM import programs and large fleets. This creates a “value proof” challenge: cybersecurity hardware must be positioned not as an optional accessory but as a risk-control mechanism that prevents downtime, liability, and data compromise. Without credible incident-driven ROI framing, cost sensitivity can push buyers toward minimum compliance, partial protection (software-only), or postponing gateway/TCU hardening until after a security event.
Limited local automotive-grade supply chain
The Philippines’ vehicle market is large in sales throughput, but local availability of automotive-grade cybersecurity hardware (secure elements, HSM-enabled gateways, certified cryptographic components) can be constrained by reliance on imported platforms, qualification requirements, and limited local depth in AEC-Q/automotive-grade electronics ecosystems. This becomes challenging when the installed base expands quickly—~ units then ~ units of new sales in successive periods—because local service networks and parts channels must scale secure replacements (genuine gateway modules, authenticated diagnostic interfaces, secure key injection services) without relying on informal grey supply. On the macro side, foreign direct investment net inflows are ~ (percent of GDP, latest snapshot), which matters because scaling a local, quality-controlled automotive electronics supply chain typically requires sustained investment into testing, compliance, and secure manufacturing/provisioning processes. As the market absorbs more connected vehicles, supply constraints surface in long lead times for genuine parts, limited local availability of security-certified modules, and fragmentation between OEM channels and aftermarket sourcing—each of which slows cybersecurity hardware penetration beyond factory-fit solutions.
Opportunities
Secure gateway retrofits for fleets
Fleet retrofits represent a near-term growth lever because the Philippines has a large and expanding base of commercially used vehicles and digitally managed operations, creating immediate demand for retrofit-grade secure gateways, hardware security modules/secure elements, and hardened telematics interfaces. Commercial vehicle sales are consistently heavy—one high-volume month shows ~ commercial units versus ~ passenger units—indicating a steady stream of vehicles entering duty cycles where telematics and remote operations are economically valuable. Early-year sales also show scale: ~ units in the first two months in one reported period, reinforcing that fleet and SME operators are continuously adding vehicles. These operating conditions reward security hardware that reduces operational risk: secure gateways that segment in-vehicle networks, authenticate diagnostic sessions, and protect cryptographic keys can prevent telemetry manipulation, unauthorized immobilization, and data leakage that disrupts dispatch and compliance. The macro base supports rapid diffusion of retrofit programs: GDP is USD ~ billion, and mobile cellular subscriptions are ~, providing the connectivity conditions that make secured telematics and secured OTA-like maintenance workflows practical for fleets.
OEM security content expansion
An important opportunity is deeper OEM “security content” shipped by default into vehicles delivered to the Philippines—more secure elements, HSM-enabled gateways, and hardware-assisted intrusion detection—because global regulatory and engineering baselines are converging and OEMs increasingly standardize platforms across regions. Cybersecurity regulation frameworks set expectations around cybersecurity management and technical controls that cascade into vehicle architectures worldwide, including markets supplied primarily through global platforms and imports. Locally, the vehicle market’s sustained scale—~ units followed by ~ units annual new sales—means OEM content decisions translate into large hardware volumes even without local market-share dominance numbers. The national risk environment supports stronger OEM defaults: ~ incidents handled in a seven-month period signals persistent threats across the same digital infrastructure vehicles rely on (telecom, cloud, identity). With a population of ~ and high internet use (latest value ~ as percent of population), OEMs have commercial incentives to protect connected services (apps, remote features, infotainment accounts) using hardware-rooted trust that reduces fraud and account takeover risks that damage brand trust and aftersales revenue.
Future Outlook
Over the next five to six years, the Philippines Vehicle Cybersecurity Hardware Market is expected to accelerate as vehicles transition to software-defined architectures, higher telematics penetration, and broader OTA readiness. Fleet operators will push for hardware-backed identity, anti-tamper controls, and secure remote access to reduce downtime and cyber incidents. Meanwhile, global compliance pull from UN R155 / ISO-aligned cybersecurity engineering will increasingly influence the baseline security content of imported models, raising demand for secure gateways, HSM-enabled compute, and secure provisioning toolchains.
Major Players
- NXP Semiconductors
- Infineon Technologies
- STMicroelectronics
- Renesas Electronics
- Texas Instruments
- Microchip Technology
- Qualcomm Technologies
- NVIDIA
- Bosch
- Continental
- Aptiv
- DENSO
- HARMAN
- Thales
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEM regional offices and importer/distributor groups
- Commercial fleet operators and fleet management heads
- Telematics and IVMS solution integrators
- Automotive electronics distributors / authorized semiconductor distributors
- Insurance providers and underwriting teams for connected fleets
- Payments/fintech + mobility platform operators
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We construct an ecosystem map covering OEM/importer channels, Tier-1 electronics pathways, semiconductor distribution, fleets, and integrators in the Philippines. Desk research is used to define hardware categories (secure elements, HSM-enabled compute, secure gateways, IDS appliances) and the variables that drive adoption.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historical adoption signals across connected features, telematics penetration in fleets, and ECU architecture trends. This phase links “security hardware content” to vehicle categories and deployment models (factory-fit vs retrofit) to structure demand pools.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses are validated through CATI-style interviews with distributors, fleet integrators, and automotive electronics stakeholders. These discussions validate procurement behavior, provisioning constraints, certification requirements, and service/RMA realities.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are synthesized using triangulation across channel checks, OEM platform intelligence, and integrator deployment patterns. The output is stress-tested for internal consistency across fitment models, hardware function mapping, and buyer decision flows.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (market definitions and scope boundaries, hardware-only inclusion and exclusion logic, Philippines vehicle parc linkage approach, OEM–importer–aftermarket triangulation, bill of materials mapping and secure-component attribution, distributor and channel validation, expert interview framework, regulatory and standards assessment, assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis
- Ecosystem Timeline
- Vehicle Technology Stack Evolution
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Mapping
- Growth Drivers
Connected vehicle penetration
Telematics device deployment across fleets
OTA enablement requirements
Increasing ECU and gateway complexity
Rising cybersecurity incident exposure - Challenges
Cost sensitivity and ASP constraints
Limited local automotive-grade supply chain
Calibration and service capability gaps
Counterfeit and grey-market risks
Secure provisioning skill shortages - Opportunities
Secure gateway retrofits for fleets
OEM security content expansion
EV cybersecurity hardware integration
ITS and fleet convergence opportunities
Hardware-backed provisioning services - Trends
Zonal gateway architectures
Migration toward automotive Ethernet
Hardware-backed identity adoption
Secure diagnostics access control
Post-quantum readiness indicators - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price and Security Content, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Vehicles
Commercial Vehicles
Buses and Public Utility Fleets
Two and Three Wheelers with Connectivity Kits
Electric and Hybrid Vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Secure Boot and Runtime Integrity
Cryptographic Acceleration
Key Management and Secure Provisioning
Network Segmentation and Firewalling
Intrusion Detection and Prevention - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Discrete Secure Elements and eSE
Automotive MCU or SoC with Embedded HSM
Trusted Platform Modules
Secure Gateway ECUs
Dedicated In-Vehicle IDS Hardware - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
CAN and CAN-FD
LIN
Automotive Ethernet
Cellular Telematics Connectivity
Wi-Fi Bluetooth and V2X Interfaces - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
OEM and Vehicle Importers
Fleet Operators and Logistics Providers
Public Transportation Authorities
Ride-Hailing and Mobility Platforms
Smart City and ITS Operators - By Region (in Value %)
National Capital Region
CALABARZON
Central Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao
- Competitive Benchmarking Framework
- Cross Comparison Parameters (automotive-grade qualification and safety alignment, hardware root-of-trust strength, cryptographic acceleration throughput and latency, secure boot and OTA verification depth, in-vehicle network coverage, integration footprint and toolchain support, provisioning model and anti-cloning controls, Philippines channel capability)
- Market Share Assessment
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and BOM Positioning
- Company Profiles
NXP Semiconductors
Infineon Technologies
STMicroelectronics
Renesas Electronics
Texas Instruments
Microchip Technology
Qualcomm Technologies
NVIDIA
Bosch
Continental
Aptiv
DENSO
HARMAN
Thales
- OEM and importer decision frameworks
- Fleet operator adoption dynamics
- Public mobility procurement models
- Vendor selection and validation process
- Buyer pain point assessment
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Selling Price and Security Content, 2025–2030


