Market Overview
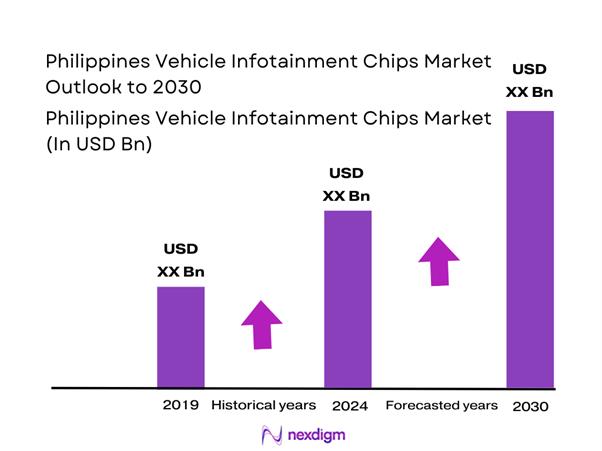
The Philippines Vehicle Infotainment Chips Market is valued at USD ~ million. As a practical benchmark for decision-making, the global Automotive Infotainment SoCs market is reported at US$ ~ million. Demand in the Philippines is fundamentally pulled by new-vehicle installations (OEM) and retrofit upgrades (aftermarket), with total new-vehicle sales rising from ~ units to ~ units, expanding the addressable base for head units, cockpit domain compute, connectivity modules, and memory content.
The Philippines market is demand-led locally but supply-led offshore. On the demand side, infotainment chip consumption concentrates around the country’s highest vehicle throughput and dealer networks—Metro Manila (NCR) and adjacent growth corridors in CALABARZON/Central Luzon—because these regions account for a disproportionate share of new registrations, financing activity, and dealership/service density (where higher-trim infotainment adoption is strongest). On the supply side, chip platforms and reference designs are dominated by Taiwan and Mainland China (fab + ecosystem scale), South Korea (memory/display ecosystems), Japan (automotive-grade MCU/SoC and Tier-1 ecosystems), and the United States (compute + connectivity IP/platforms), reflecting where the automotive semiconductor value chain is anchored and where infotainment SoC roadmaps are set.
Market Segmentation
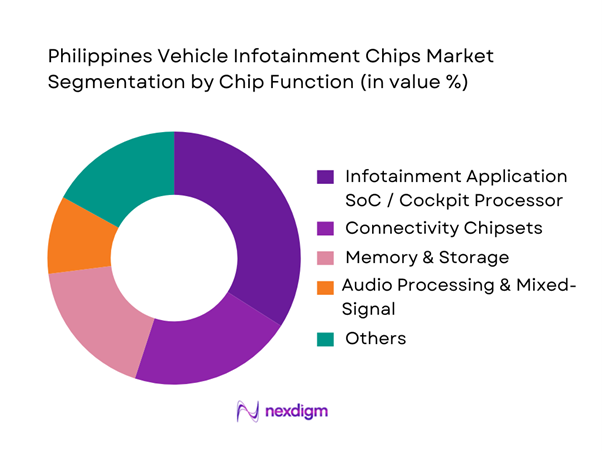
By Chip Function
Infotainment Application SoCs / cockpit processors lead because they anchor the entire infotainment bill-of-materials: once an OEM or major aftermarket brand selects a compute platform, the design typically “pulls through” the rest of the chip stack (memory density targets, connectivity companions, display interfaces, audio DSP choices, and PMIC rails). The Philippines’ demand profile favors feature-rich but cost-controlled trims—touch display, phone projection, navigation-ready hardware, and connected services—so integrators prioritize SoCs that consolidate CPU/GPU, multimedia encode/decode, hardware security, and automotive-grade thermal behavior. This consolidation reduces board complexity and speeds homologation across multiple vehicle nameplates commonly sold in the country. As the installed base rises with vehicle sales increasing from ~ units to ~ units, platform standardization becomes more attractive for distributors and installers who service mixed fleets and want stable chip availability and software support.
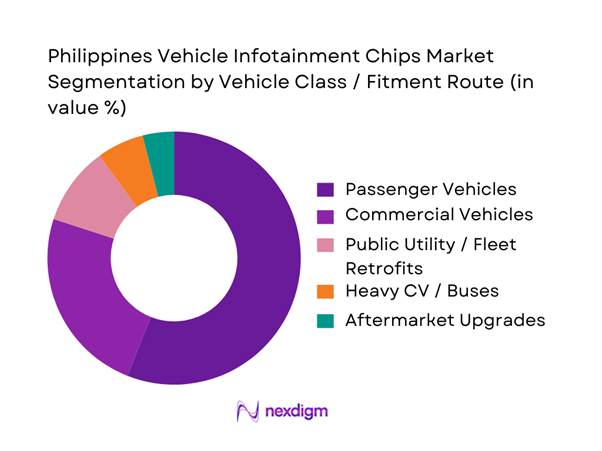
By Vehicle Class / Fitment Route
Passenger Vehicles dominate because infotainment is now a primary “sell feature” in private purchases: larger displays, phone integration, camera interfaces, and voice features are strongly associated with perceived vehicle modernity and resale value. This segment also sees faster refresh cycles—facelifts and trim updates frequently add screen size or connectivity features, which directly increases semiconductor content per vehicle. In addition, passenger vehicles are more likely to carry higher head-unit variants (greater DRAM/NAND needs, more GPU capability, and richer connectivity), while commercial fleets often prioritize durability and basic functionality. The Philippines’ growing total sales volume—moving from ~ units to ~ units—expands the base for OEM-fit infotainment chips and also increases spillover demand for service, replacements, and upgrades that are more common among passenger owners.
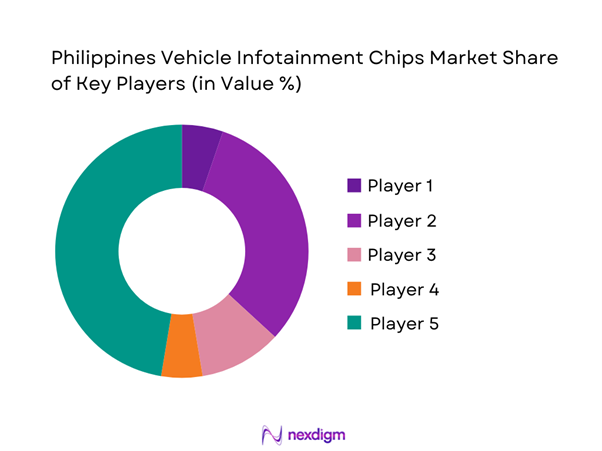
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines vehicle infotainment chips ecosystem is platform-driven: a small number of global silicon vendors set the compute and connectivity roadmaps, and local demand is realized through OEM import programs, Tier-1 modules, distributor channels, and aftermarket brands. Competitive differentiation is most visible in time-to-automotive qualification, platform software support, thermal performance, multimedia quality, and long-term availability.
| Company | Est. year | HQ | IVI compute portfolio breadth | Connectivity integration strength | Automotive-grade qualification focus | Software ecosystem maturity | Reference design / Tier-1 adoption | Supply assurance approach | Local PH channel visibility* |
| Qualcomm | 1985 | San Diego, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MediaTek | 1997 | Hsinchu, Taiwan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| NXP Semiconductors | 2006 | Eindhoven, Netherlands | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Renesas Electronics | 2010 | Tokyo, Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Texas Instruments | 1930 | Dallas, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Vehicle Infotainment Chips Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Vehicle parc expansion
The Philippines’ installed base of passenger cars and light commercial vehicles keeps widening, which mechanically expands the “addressable socket count” for infotainment SoCs/MCUs (head unit, display controller, connectivity companion chips, audio DSP/amp ICs, tuner, GNSS). CAMPI–TMA reported ~ new vehicle sales (units) in the country on a full-year basis, and the market later reached ~ new vehicle sales (units), meaning hundreds of thousands of incremental vehicles that typically ship with factory infotainment or are upgraded via dealer/OEM accessory programs. In metro-driven usage, high daily utilization accelerates replacement/upgrade cycles for head units and display stacks (thermal stress, USB wear, touchscreen failures), which increases downstream chip demand in the service ecosystem (replacement boards/modules). On the macro side, the World Bank reports the Philippines’ total population at ~, supporting a large and still-growing base of mobility demand that sustains vehicle parc growth and, by extension, the recurring requirement for infotainment silicon across OEM fitment and aftermarket replacements.
Infotainment feature adoption
Feature-content per vehicle is increasing: larger touch displays, multi-screen cockpits, higher camera counts, DSP-rich audio, and tighter integration with telematics, ADAS display overlays, and steering-wheel controls—each raising semiconductor content and performance requirements (higher TOPS/CPU/GPU headroom, more memory bandwidth, stricter thermal envelopes). This is visible even in near-term sales mixes: CAMPI–TMA’s ~ vehicle sales (units) recorded in a single month window show how fast new “feature-bearing” vehicles are entering the parc, and CAMPI’s breakdown highlights commercial vehicles at ~ units and passenger cars at ~ units—segments where buyers increasingly expect at least a screen-based head unit (especially for navigation prompts, reverse camera, Bluetooth/USB, and smartphone projection). Macro conditions also matter for feature adoption: external trade scale and electronics import intensity determine what infotainment modules and subassemblies are available and how quickly features diffuse through the fleet; the Philippines’ goods trade in a single month reached USD ~ billion, reflecting a high-throughput import environment that supports continuous inflow of electronics-heavy vehicles and components.
Challenges
Import dependency
The Philippines vehicle infotainment chip supply chain is structurally import-reliant: automotive-grade SoCs, PMICs, memory, and RF chipsets are largely sourced from overseas fabs and OSAT ecosystems, and even “local” assembly still depends on imported silicon and subcomponents. This is visible in national trade composition: a government release put total external trade in goods at USD ~ billion for a single month, and electronics imports were reported at USD ~ billion—figures consistent with heavy reliance on inbound electronics flows. For infotainment chips, this translates into longer procurement lead times, FX exposure, and dependence on global allocation decisions (automotive vs consumer electronics prioritization). When port congestion, customs processes, or upstream shortages occur, local assemblers, distributors, and installers can face abrupt SKU unavailability, which disrupts service levels for dealers and aftermarket channels. In a large domestic demand base (World Bank population ~), even short disruptions can ripple quickly across dealers and installers because the installed vehicle base creates constant demand for replacement boards, harnesses, and head units.
Supply allocation risks
Automotive infotainment chips compete for wafer capacity with consumer devices (phones, tablets, TVs), and allocation often prioritizes long-term contracted OEM volumes—creating “spillover volatility” for smaller markets and for aftermarket-grade head units. The Philippines’ demand signal is clear in unit volumes: CAMPI–TMA recorded ~ new vehicles (units) on a full-year basis, and monthly run-rates like ~ units imply sustained inflow of vehicles that will need infotainment silicon either at factory fitment or via upgrades. When global supply is tight, importers and distributors may see partial shipment fulfillment or forced substitutions (different SoC family, different memory configuration), which then triggers software revalidation costs and slows installation throughput. The broader import environment also signals how exposed the market is to shipping cadence: electronics imports of USD ~ billion in a month show the scale of dependence on consistent inbound electronics logistics. A large consumer base (World Bank population ~) also means consumer electronics demand remains strong, intensifying competition for shared silicon supply.
Opportunities
Premium cockpit compute adoption
Even without using forward-looking market-size claims, current indicators show why higher-compute infotainment silicon has runway: the Philippines is adding vehicles at scale (~ new units in a year), and consumers increasingly expect multi-screen UX, faster boot times, better voice capture, and stable wireless projection—capabilities that typically require newer automotive-grade SoCs and upgraded memory configurations. Connectivity infrastructure supports this shift: Globe added ~ new sites and reported over ~ devices connected to its network in a month, while DITO cited over ~ cell sites across over ~ cities. As more towns and cities sustain high-bandwidth use, OEMs can justify richer cockpit compute to deliver smooth media, navigation, calling, and OTA updates. On the supply side, electronics imports of USD ~ billion in a month signal active import channels for higher-end head units, displays, and subassemblies—making it feasible for dealers and distributors to expand premium infotainment lineups. The opportunity, therefore, is to capture incremental silicon content per vehicle via higher-tier cockpit platforms already supported by today’s unit volumes and network conditions.
AI-enabled HMI
AI-enabled human–machine interfaces (voice-first control, in-cabin noise suppression, intent-based navigation prompts, driver-aware UI adaptation) are a chip-driven opportunity because they increase compute (NPU/CPU), memory, and audio DSP requirements inside the head unit. Current scale conditions already justify productization: the Philippines’ vehicle market added ~ new units in a year, creating a large base for OEMs and accessory channels to standardize AI-capable head units across multiple trims. Network signals reinforce feasibility: Globe reported over ~ devices connected to its network in a month and expanded coverage to ~ towns with ~ new sites, while DITO reported over ~ cell sites across over ~ cities. This matters because AI HMIs increasingly blend on-device inference with cloud-backed services (speech-to-text improvements, map intelligence, streaming), and dependable connectivity improves user-perceived reliability. Finally, counterfeit pressure (e.g., PHP ~ counterfeit seizure value reported by authorities) strengthens the case for trusted, certified AI-HMI platforms—because AI UX failures (mic issues, latency, crashes) are more visible and damaging than “basic” infotainment failures, pushing buyers toward validated silicon/platform stacks.
Future Outlook
Over the next cycle of platform refreshes, the Philippines vehicle infotainment chips market should shift toward cockpit-domain consolidation, where infotainment, cluster, and driver monitoring features increasingly share compute resources. Global benchmarks indicate continued expansion in the underlying infotainment technology stack: the global in-car infotainment market is reported at US$ ~ billion with a projected rise to US$ ~ billion by the end of the forecast window, indicating sustained OEM feature adoption momentum. For the Philippines specifically, rising vehicle sales volumes and greater feature bundling in mainstream trims are expected to increase chip content per vehicle (more memory, better GPUs, more connectivity companions), while the aftermarket will increasingly focus on certified integration, camera/ADAS interfaces, and software-driven personalization.
Major Players
- Qualcomm
- MediaTek
- NXP Semiconductors
- Renesas Electronics
- Texas Instruments
- STMicroelectronics
- Infineon Technologies
- NVIDIA
- Samsung Electronics
- Micron Technology
- SK hynix
- Broadcom
- Marvell
- Analog Devices
Key Target Audience
- Vehicle OEMs & national sales companies
- Tier-1 infotainment and cockpit module suppliers
- Aftermarket head-unit brands, distributors & large-format installers
- Fleet owners & fleet management operators
- Automotive dealer groups & dealership service networks
- Semiconductor distributors and electronics component importers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We construct a Philippines-specific ecosystem map covering OEM import flows, Tier-1 module channels, distributor structures, and aftermarket installation networks. Desk research consolidates platform families, qualification standards, and bill-of-material drivers that determine chip content per infotainment configuration.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historical vehicle throughput and fitment patterns (OEM vs dealer-fit vs aftermarket) and translate them into infotainment unit volumes by vehicle class and price band. Chip attach rates and content multipliers are applied at subsystem level (SoC, memory, connectivity, audio, display interface, PMIC).
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validate assumptions through CATIs with local importers/distributors, Tier-1 partners, major installers, and fleet maintenance heads, focusing on platform selection criteria, failure/returns patterns, lead times, and substitution behavior during supply disruptions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We triangulate top-down demand indicators (vehicle sales and parc growth) with bottom-up channel checks (installer throughput, distributor sell-in, platform shipment proxies) to finalize segment shares, competitive positioning, and forward-looking adoption themes.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and assumptions, abbreviations, scope boundaries, market sizing approach, triangulation logic, primary interview plan, OEM and aftermarket mapping approach, validation checkpoints, limitations and key conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution of In-Car Infotainment Compute
- Infotainment ECU Architecture Evolution
- Business Cycle and Demand Seasonality
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Vehicle parc expansion
Infotainment feature adoption
Smartphone projection demand
Connectivity readiness
Dealer accessory economics - Challenges
Import dependency
Supply allocation risks
Counterfeit and gray market exposure
RF certification barriers
Price sensitivity - Opportunities
Premium cockpit compute adoption
AI-enabled HMI
Fleet infotainment upgrades
Local module assembly
Higher connectivity attach rates - Trends
Domain controller transition
SoC consolidation
Larger display integration
Advanced audio DSP usage
Wi-Fi 6 readiness
In-vehicle cybersecurity enhancement - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- Supply Risk and Resilience
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Unit Shipments, 2019–2024
- By ASP Waterfall, 2019–2024
- By Compute Class, 2019–2024
- By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Infotainment Application Processors and Cockpit SoCs
Connectivity Chips
Memory
Audio Chips
Display and Touch Interface ICs - By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Cars
SUVs and MPVs
Light Commercial Vehicles
Buses and Coaches
Two and Three Wheelers with Connected Displays - By Application (in Value %)
Basic Audio and Bluetooth
Smartphone Projection Systems
Embedded Navigation Systems
Telematics and Connected Services
Multi-Display and Premium Infotainment - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Factory-Fit OEM Systems
Dealer-Installed Accessories
Independent Aftermarket Systems
Fleet-Installed Systems
E-commerce Installer Supply - By Region (in Value %)
NCR
CALABARZON
Central Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao
- Market Share Assessment Framework
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Infotainment SoC performance tier, connectivity stack breadth, automotive-grade compliance, software ecosystem enablement, security capabilities, power and thermal efficiency, Philippines channel footprint, supply assurance)
- Player SWOT Snapshot
- Pricing and BOM Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Qualcomm
MediaTek
NXP Semiconductors
Renesas Electronics
Texas Instruments
Infineon Technologies
STMicroelectronics
Samsung Electronics
NVIDIA
Broadcom
Marvell Technology
Realtek Semiconductor
Cirrus Logic
Analog Devices
Microchip Technology
- Demand and Utilization Patterns
- Purchase Decision Criteria
- Installer and Dealer Influence
- Fleet Requirements
- Pain Points and Unmet Needs
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Unit Shipments, 2025–2030
- By ASP Waterfall, 2025–2030
- By Compute Clas, 2025–2030


