Market Overview
The Philippines Vehicle Lighting Electronics Market is valued at USD ~ million, derived from aggregated OEM production, vehicle imports, and aftermarket replacement demand. Growth is driven by rising vehicle registrations exceeding ~ active passenger vehicles, increased adoption of LED lighting as standard fitment, and stricter road safety enforcement. Declining LED component costs and higher lighting electronics content per vehicle have structurally lifted market value across both OEM and aftermarket channels.
The market is dominated by Metro Manila and Greater Luzon, supported by the highest vehicle density, dealership concentration, and nighttime traffic volumes. These regions see faster adoption of LED and DRL systems due to urban safety concerns, higher disposable incomes, and stronger enforcement of lighting compliance. Imported Japanese and Korean vehicles further accelerate demand for advanced lighting electronics due to higher baseline specifications.
Market Segmentation
By Lighting Technology
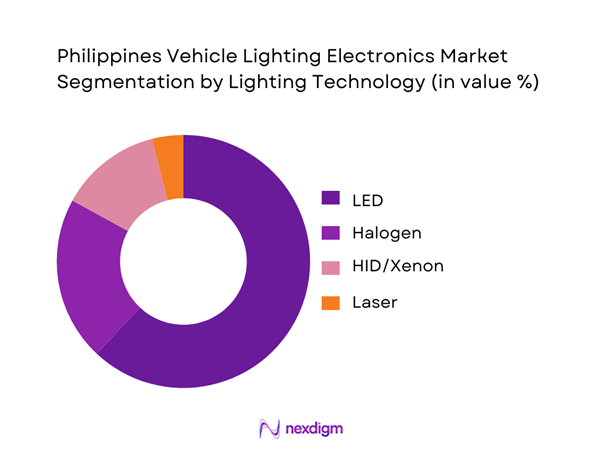
The market is segmented into LED, Halogen, HID/Xenon, and Laser lighting systems. LED lighting dominates with a market share of ~, supported by its longer lifespan, lower power consumption, and compatibility with modern vehicle electronics. OEMs increasingly standardize LED headlamps and DRLs even in mid-segment vehicles, while the aftermarket benefits from widespread LED retrofit demand driven by style and visibility upgrades.
By Vehicle Type
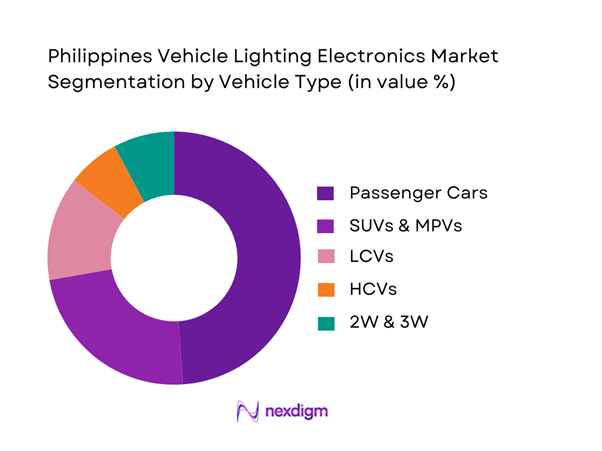
Passenger cars and SUVs & MPVs together command the largest share due to their dominance in the national vehicle parc and higher lighting system complexity. Passenger cars lead the segment, driven by high annual registrations and strong LED penetration across Japanese and Korean models.
Competitive Landscape
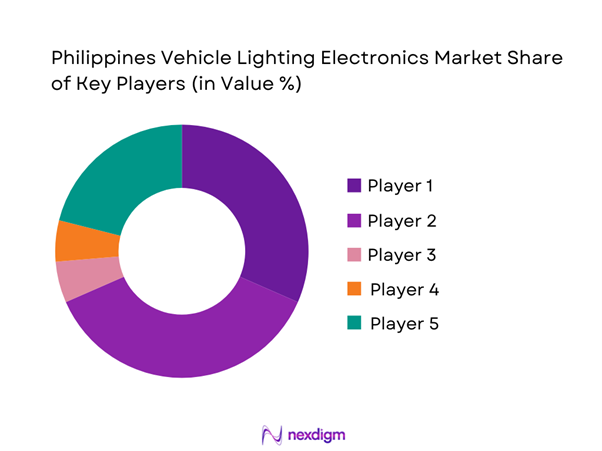
The Philippines Vehicle Lighting Electronics Market is moderately consolidated, dominated by global Tier-1 suppliers aligned with Japanese and Korean OEMs. Companies such as Koito, Stanley, Valeo, and Hella benefit from entrenched OEM relationships, while aftermarket brands compete on price, SKU breadth, and installer networks.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | OEM Presence | LED Capability | Local Presence | Aftermarket Strength |
| Koito | 1915 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Stanley Electric | 1920 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Valeo | 1923 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Hella | 1899 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Marelli | 1919 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Vehicle Lighting Electronics Market Dynamics
Growth Drivers
Vehicle parc expansion
The addressable replacement-and-upgrade base for lighting electronics (LED headlamps/DRLs, tail/stop lamps, turn signal drivers, fog-lamp modules, harness connectors, control units) expands first with the size and utilization intensity of the national vehicle parc. The Philippines recorded ~ registered vehicles (total vehicle stock) in the latest widely cited official-market brief using government-sourced registration data, which directly increases the recurring “lamp failure + upgrade” event pool for both 2W and 4W platforms (bulb burnouts, connector corrosion, ballast/driver failures, heat-soak damage). Macro capacity to sustain parc growth and usage is supported by the economy’s scale: GDP of USD ~ (current US$) and population of ~ (total) underpin continuing vehicle activity (commute trips, logistics runs, delivery fleets) that accelerates wear-out cycles for lighting electronics in tropical humidity and high-traffic corridors. As urban demand concentrates, urban population share of ~ (urban % of total population) typically raises stop-and-go hours and night exposure on arterials—conditions that increase thermal cycling and vibration stress on LED drivers, PCBs, and connectors. This parc-linked scale effect is why lighting-electronics demand in the Philippines is not only OEM-tied but also heavily aftermarket-driven—more vehicles in circulation means more retrofit demand for higher-lumen LED kits, CAN-bus compatible decoders, and upgraded assemblies for visibility and styling.
Safety regulation enforcement
Enforcement pressure raises the “must-fix” rate for defective lighting (non-working headlamps/brake lamps, improper beam patterns, illegal glare kits), converting discretionary spend into compliance spend—especially for public utility vehicles, logistics fleets, and intercity buses where inspections and roadside checks are more frequent. The Philippines’ road-safety backdrop is materially tightening: road-accident fatalities cited at ~ versus ~ reflect a materially higher enforcement and policy focus on preventable crash factors, including visibility and conspicuity at night and in rain. The same communication links the fatality burden with recorded road-crash volumes and vehicle involvement, reinforcing why regulators and transport agencies keep elevating vehicle roadworthiness and safety equipment checks. From a macro ability-to-enforce standpoint, state capacity is also supported by fiscal and economic context: GDP level of USD ~ indicates sustained public-sector resourcing potential for enforcement operations, checkpoints, and digital systems that typically raise compliance rates. For the lighting-electronics market, this translates into higher replacement velocity for compliant assemblies, growing demand for fit-for-purpose commercial-grade modules, and stronger pull for OEM-grade parts in regulated fleets where non-compliance can mean downtime.
Challenges
Import dependency
Vehicle lighting electronics in the Philippines remains structurally import-led across LED chips, drivers/ballasts, automotive-grade PCBs, optics, and many complete lamp assemblies—creating exposure to FX moves, shipping variability, lead-time shocks, and uneven quality across informal supply routes. The macro scale of the domestic economy (USD ~ GDP) and large vehicle base (~ registered vehicles) creates large, steady demand, but local manufacturing depth in automotive lighting sub-assemblies is still limited relative to demand size—so the supply chain relies on imported finished goods and kits to serve both OEM service parts and the aftermarket. This is especially problematic in lighting electronics because quality dispersion is wide: thermal design, ESD protection, conformal coating, connector sealing, and EMI handling differ dramatically across suppliers, and an import-heavy market tends to see higher variance across channels. Import-led sourcing also complicates regulatory consistency—standards compliance is harder to enforce when goods enter via fragmented channels and small consignments. Even when inflation moderates (~ average inflation), the Philippines still faces “import pass-through” risk that can raise replacement costs and encourage low-quality substitution, which in turn increases failure rates and road-safety risk. For market participants, this import dependency makes supply-chain control a key differentiator—especially for fleets and distributors serving high-utilization urban corridors.
Counterfeit penetration
Counterfeit and substandard “look-alike” lighting electronics remain a material channel risk because the market’s size and fragmentation create strong arbitrage incentives. Enforcement data show the scale of the counterfeit economy, with IP-infringing goods seized at PHP ~ billion and PHP ~ billion in successive years—an increase that underscores both market scale and the enforcement push. While these totals span many categories, automotive parts are explicitly included in government and industry enforcement narratives, and the same environment that supports counterfeit apparel and electronics also supports counterfeit auto parts due to high turnover and consumer price sensitivity. For lighting electronics, counterfeit penetration has outsized safety impact: poor thermal management can trigger early LED failure, voltage instability can damage vehicle wiring, and improper optics can create glare that increases crash risk—issues that become more visible and more enforced when road fatalities are elevated (~ versus ~). Net effect: legitimate distributors must invest in authentication, tighter channel governance, and compliance documentation, while fleets increasingly prefer vendor-managed inventories and OEM-grade sourcing to reduce downtime and liability.
Opportunities
Local assembly of LED modules
A practical growth lever is to localize assembly (not necessarily wafer or LED chip fabrication) for sealed LED lamp modules—PCBA population, connector and harness integration, potting and sealing, heat-sink integration, and final photometric validation—because the Philippines already has scale demand signals and congestion-driven utilization that favor reliable assemblies. Demand fundamentals are clear: ~ registered vehicles create recurring replacement cycles, while Metro Manila AADT over ~ vehicles indicates sustained high lighting-on hours and faster wear-out in dense corridors. Safety pressure reinforces the willingness to pay for reliability, with fatalities cited at ~ versus ~ keeping regulators and fleets focused on roadworthiness and visibility. Macroeconomic stability supports investment cases: GDP of USD ~ and moderated inflation reduce planning volatility for inventory-heavy operations. Local assembly can directly address two chronic market pain points without using future statistics: reduce channel quality variance through standardized builds and testing, and improve traceability to combat counterfeit substitution—particularly relevant in an environment where seized counterfeit goods reached PHP ~ billion. If pursued, local assembly nodes positioned near major distribution hubs can shorten lead times for high-turn SKUs and enable fleet-focused service levels, raising the competitiveness of legitimate distributors versus informal imports.
Adaptive lighting adoption
Adaptive lighting (matrix-capable LED arrays, dynamic leveling, cornering lamps, glare-free high beam control, smarter DRL and signature systems) has a Philippines-specific runway because dense urban traffic and night-time congestion increase the safety value of better beam control and conspicuity without requiring future market numbers. The operational context is already heavy: Metro Manila AADT is over ~ vehicles, and national urban population share is ~, meaning a large share of driving happens in complex lighting conditions involving mixed road users, wet roads, and glare. Safety urgency remains elevated, with fatalities cited at ~ versus ~, keeping attention on interventions that reduce night crash risk—an area where adaptive lighting and better rear signaling can matter. Economic capacity also supports premium feature diffusion in higher-end segments and fleets: GDP of USD ~ and inflation moderation improve the affordability environment for feature-upgrade trims and fleet capex cycles. In the near term, adoption can concentrate in SUVs and MPVs in urban families, premium ride-hailing and corporate shuttle fleets, and long-haul logistics operators. For suppliers, the opportunity is less about selling a feature and more about building a compliant ecosystem that can be serviced locally in a market still managing counterfeit risk at scale.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Philippines Vehicle Lighting Electronics Market is expected to grow steadily, driven by continued LED migration, rising SUV penetration, and increasing vehicle safety awareness. Adaptive lighting and smart interior ambient lighting will gain relevance as imported vehicle specifications rise, while localized LED module assembly presents cost-reduction opportunities for OEM suppliers.
Major Players
- Koito Manufacturing
- Stanley Electric
- Hella
- Valeo
- Marelli
- ZKW Group
- Osram Automotive
- Philips Automotive Lighting
- Ichikoh Industries
- Lumileds
- Varroc Lighting
- TYC Brother
- Depo Auto Lamp
- Bosch Mobility Solutions
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEMs and Vehicle Assemblers
- Tier-1 Lighting and Electronics Suppliers
- Automotive Component Distributors
- Aftermarket Lighting Brands
- Electric Vehicle Manufacturers
- Fleet Operators and Leasing Companies
- Investment and Venture Capital Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Mapping OEM production, imports, lighting content per vehicle, and replacement cycles.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Bottom-up aggregation using vehicle parc data, OEM fitment ratios, and aftermarket demand.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Primary interviews with distributors, OEM suppliers, and installers.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Triangulation across OEM data, customs imports, and replacement sales.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Scope Boundaries, Philippines Automotive Lighting Electronics Taxonomy, Abbreviations and Technical Standards, Market Sizing Logic – Bottom-Up & Top-Down, OEM vs Aftermarket Revenue Attribution, Import–Local Assembly Mapping, Primary Interviews with OEMs Tier-1 Suppliers and Distributors, Data Triangulation Framework, Limitations and Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Evolution and Genesis
- Key Technology Inflection Timeline
- Automotive Production and Import Cycle Linkage
- Philippines Automotive Lighting Electronics Value Chain and Supply Chain Mapping
- Growth Drivers
Vehicle parc expansion
Safety regulation enforcement
LED cost deflation
Urban night-time driving density - Challenges
Import dependency
Counterfeit penetration
Price sensitivity
Limited local electronics manufacturing - Opportunities
Local assembly of LED modules
Adaptive lighting adoption
EV lighting integration - Trends
Matrix LED migration
CAN-bus integrated lighting ECUs
Smart ambient lighting - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Unit Shipments, 2019–2024
- By Average System Cost per Vehicle, 2019–2024
- By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
LED Lighting Systems
Halogen Lighting Systems
HID / Xenon Lighting Systems
Laser and Advanced Projection Lighting - By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Cars
SUVs & MPVs
Light Commercial Vehicles
Heavy Commercial Vehicles
Two-Wheelers & Three-Wheelers - By Application (in Value %)
Headlamps
Tail Lamps
Turn Indicators
Fog Lamps
Daytime Running Lamps
Interior Ambient Lighting - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
OEM Installed
Authorized Aftermarket
Independent Aftermarket
Online Automotive Platforms - By Region (in Value %)
National Capital Region (NCR)
Luzon (Ex-NCR)
Visayas
Mindanao
- Market Share Analysis by Value and Volume
- Cross Comparison Parameters (OEM supply footprint in Philippines, local assembly vs import dependency, LED module manufacturing capability, average lighting content per vehicle, product homologation compliance strength, distribution and installer network depth, aftermarket SKU breadth, technology roadmap alignment)
- Competitive SWOT Matrix
- Pricing Architecture Analysis
- Detailed Company Profiles
Koito Manufacturing
Stanley Electric
Hella
Valeo
Marelli
ZKW Group
Osram Automotive
Philips Automotive Lighting
Ichikoh Industries
Lumileds
Varroc Lighting
TYC Brother
Depo Auto Lamp
Bosch Mobility Solutions
Hyundai Mobis
- Purchasing triggers
- Replacement cycles
- Upgrade motivations
- Price vs performance sensitivity
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Unit Shipments, 2025–2030
- By Average System Cost, 2025–2030


