Market Overview
The Philippines Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market is valued at USD ~, reflecting its early but structurally important position within the country’s evolving energy and mobility ecosystem. The market is anchored in the rapid buildout of electric vehicle charging infrastructure, smart grid investments, and growing demand for flexible power resources that can stabilize supply and demand imbalances. As utilities face rising peak loads and renewable energy penetration, bidirectional charging solutions are becoming strategically relevant for grid resilience, ancillary services, and distributed energy management.
Within the Philippines, metropolitan regions such as the National Capital Region, Calabarzon, and Central Visayas dominate early V2G readiness due to higher electric vehicle density, stronger utility digitalization, and greater commercial fleet electrification. These regions benefit from advanced distribution networks and higher energy demand concentration, making V2G applications commercially viable sooner. At the technology and solution level, global innovation leaders continue to shape local adoption pathways by setting hardware standards, software platforms, and grid integration models that local utilities and mobility operators increasingly reference when designing pilot programs and future-scale deployments.
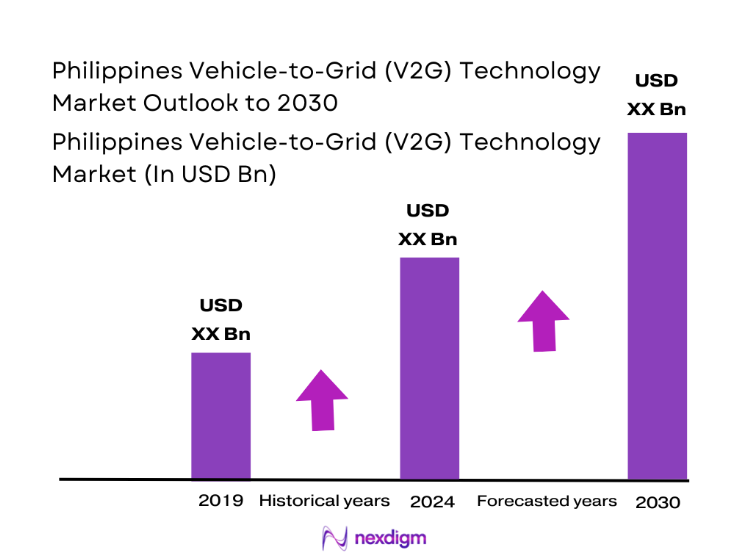
Market Segmentation
By Application Segment
The Philippines Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market is segmented by application into grid frequency regulation, peak load shaving, renewable energy firming, backup power and resilience, and microgrid and campus energy support. Among these, grid frequency regulation dominates due to the growing need for fast-response energy balancing solutions as renewable generation expands across the country. Intermittent solar and wind resources place pressure on utilities to maintain stable voltage and frequency levels, and V2G-enabled electric vehicles offer a distributed, responsive asset base that can inject or absorb power in near real time. Utilities view this use case as the most immediate operational value of V2G, since it directly supports grid reliability without requiring large centralized storage investments. Commercial and public fleets parked for extended hours provide predictable availability windows, strengthening the practicality of this segment and reinforcing its leadership position in the market.
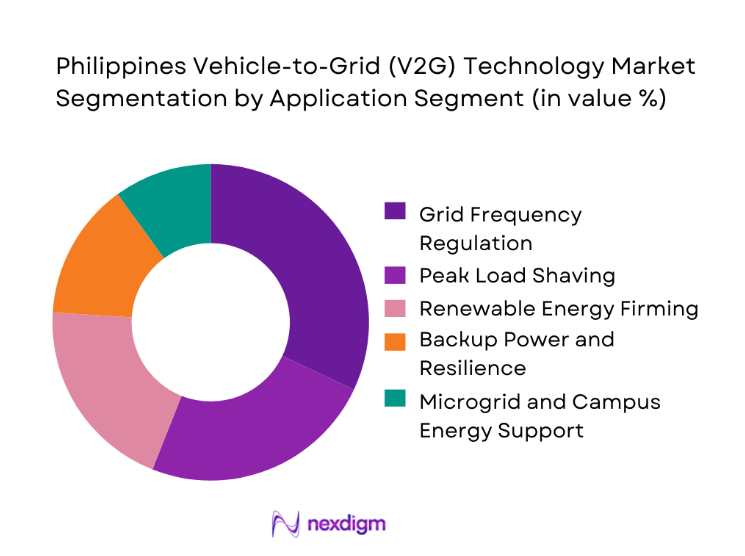
By Technology Platform Type
The market is segmented into AC bidirectional charging, DC fast bidirectional charging, onboard inverter-based V2G, offboard inverter-based V2G, and software-centric aggregation platforms. AC bidirectional charging currently dominates as it aligns well with existing residential and workplace charging infrastructure, offering a lower-cost and easier entry point for early V2G adoption. This technology integrates smoothly with standard charging equipment upgrades rather than full system replacements, making it attractive to utilities, fleet operators, and property developers seeking incremental deployment strategies. In the Philippine context, where charging networks are still scaling, the flexibility and affordability of AC-based solutions enable faster market penetration. Their compatibility with a wide range of electric vehicle models also supports broader user participation, reinforcing this segment’s leadership as the foundational layer of the V2G ecosystem.
Competitive Landscape
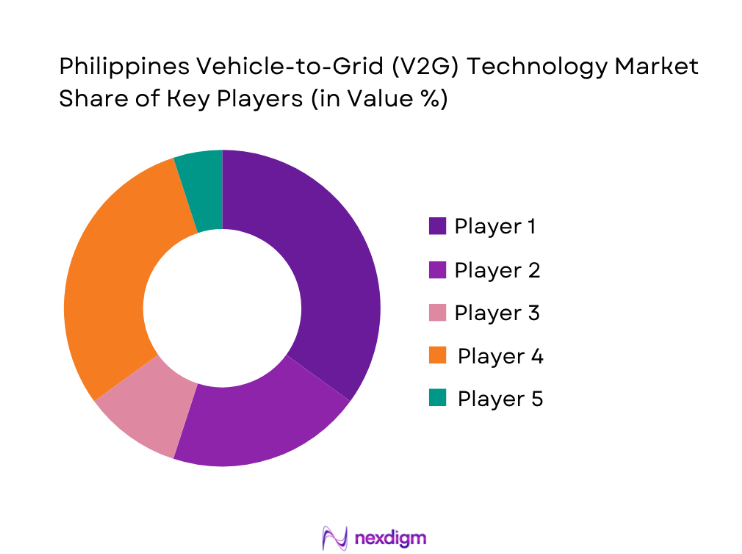
The Philippines Vehicle-to-Grid Technology market is dominated by a few major players, including Nissan Motor Corporation and global or regional brands like ABB, Schneider Electric, and Nuvve. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies.
| Company | Est. Year | Headquarters | V2G Tech Deployment | Grid Partnership Footprint | EV Fleet Integration | Software & Analytics | Charging Hardware Capability | Service & Support Network |
| Nissan | 1933 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ABB | 1988 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Schneider Electric | 1836 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Nuvve | 2010 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Enel X | 2008 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Philippines Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Grid modernization and smart infrastructure expansion
The expansion of smart grid technologies across the Philippines is creating a strong foundation for the adoption of Vehicle-to-Grid solutions. Utilities are investing in advanced metering, distribution automation, and digital control systems to improve power quality and reduce outages. These upgrades enable the two-way energy flows required for V2G operations, transforming electric vehicles into active grid assets rather than passive loads. As digital infrastructure matures, utilities gain the operational confidence to integrate distributed energy resources at scale. This shift accelerates demand for V2G platforms that can coordinate thousands of vehicles simultaneously, positioning the technology as a strategic component of long-term grid resilience and operational efficiency.
Rising electric vehicle adoption
The accelerating uptake of electric vehicles across personal, commercial, and public transport segments is expanding the addressable base for V2G participation. As more vehicles with bidirectional charging capability enter the market, the cumulative storage potential grows significantly. This expanding fleet base enhances the economic logic of V2G by lowering per-unit infrastructure costs and increasing aggregated energy capacity available to utilities. In the Philippines, fleet electrification programs in logistics, ride-hailing, and public transport create concentrated nodes of V2G readiness. These clusters allow early commercial models to emerge, demonstrating financial viability and encouraging broader adoption across the mobility ecosystem.
Challenges
Regulatory uncertainty and interconnection standards
One of the most significant barriers to V2G deployment in the Philippines is the lack of clearly defined regulatory frameworks governing bidirectional power flow between vehicles and the grid. Utilities and technology providers face ambiguity around interconnection rules, metering requirements, and compensation mechanisms for energy exported from vehicles. Without standardized protocols, project developers encounter delays in approvals and higher compliance costs. This uncertainty slows pilot-to-scale transitions and discourages private investment in supporting infrastructure. Clear regulatory direction is essential to unlock confidence among stakeholders and establish consistent operational practices across utilities and service providers.
High upfront infrastructure cost
The capital intensity associated with bidirectional chargers, grid upgrades, and advanced energy management systems presents another major hurdle. Compared to conventional charging stations, V2G-enabled infrastructure requires more sophisticated hardware and software integration, raising installation and maintenance costs. For fleet operators and property developers, the return on investment is not immediately apparent without established revenue models for grid services. This cost barrier limits early adoption to well-funded pilots rather than mass-market deployment. Overcoming this challenge will depend on policy incentives, utility cost-sharing frameworks, and innovative financing models that reduce financial exposure for early adopters.
Opportunities
Commercial fleet electrification
Commercial fleets represent one of the most promising growth avenues for the Philippines V2G market. Delivery vehicles, corporate transport fleets, and public service vehicles operate on predictable schedules and return to centralized depots, making them ideal candidates for aggregated energy services. These fleets can provide utilities with reliable, dispatchable storage capacity during peak demand periods while generating new revenue streams for fleet owners. As fleet electrification accelerates, V2G can be embedded as a standard feature of fleet energy management strategies, positioning the segment as a primary commercial driver of market expansion.
Microgrid and island grid resilience solutions
The Philippines’ geography, characterized by numerous islands and remote communities, creates unique opportunities for V2G in microgrid and off-grid environments. Electric vehicles integrated into local energy systems can enhance resilience by supplying backup power during outages and supporting renewable-heavy microgrids. This application is particularly relevant for disaster-prone areas where grid disruptions are frequent. By enabling localized energy security, V2G becomes not just a grid optimization tool but a resilience strategy that aligns with national priorities on disaster preparedness and energy access, opening new public and private sector investment pathways.
Future Outlook
The Philippines Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market is positioned to evolve from pilot-driven experimentation to structured commercialization as electric mobility, renewable energy, and smart grid initiatives converge. Over the coming years, coordinated efforts between utilities, mobility providers, and technology firms will shape standardized frameworks that enable scalable deployment. As regulatory clarity improves and infrastructure costs decline, V2G is expected to transition into a core component of the country’s distributed energy strategy, supporting grid reliability, energy security, and the broader shift toward a more digital and decentralized power system.
Major Players
- Nissan Motor Corporation
- ABB Ltd.
- Schneider Electric SE
- Nuvve Corporation
- Enel X
- Siemens AG
- BYD Co. Ltd.
- Delta Electronics Inc.
- Hyundai Motor Company
- Mitsubishi Motors Corporation
- Honda Motor Co. Ltd.
- Tesla Inc.
- ChargePoint
- EVBox Group
Key Target Audience
- Electric utilities and distribution companies
- EV manufacturers and automotive OEMs
- Charging infrastructure developers and operators
- Commercial fleet and logistics operators
- Renewable energy project developers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Smart city and urban infrastructure authorities
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research begins with mapping the complete ecosystem of the Philippines Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market, identifying utilities, mobility providers, regulators, and technology vendors. Secondary research across policy documents, industry publications, and proprietary databases establishes the foundational variables that influence market dynamics. These variables form the basis for market sizing and segmentation logic.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical data on electric vehicle adoption, charging infrastructure deployment, and grid modernization initiatives are compiled to construct the market framework. This phase focuses on understanding demand patterns, infrastructure readiness, and revenue generation pathways. Quantitative insights are synthesized with sector-level trends to build a coherent market structure.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Preliminary findings are validated through structured consultations with industry stakeholders including utility planners, fleet managers, and technology providers. These expert discussions refine assumptions related to adoption timelines, commercial models, and regulatory impact. Feedback from practitioners ensures the market narrative reflects operational realities.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase integrates all quantitative and qualitative inputs into a unified analytical framework. Cross-validation of data sources ensures consistency and credibility. The result is a comprehensive, client-ready report that presents a balanced, actionable view of the Philippines Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, terminology and abbreviations, V2G and bidirectional charging taxonomy, market sizing logic by enabled vehicles chargers and dispatched capacity, revenue attribution across hardware software aggregation and services, primary interview program with utilities OEMs charging operators and aggregators, data triangulation and validation approach, assumptions limitations and data gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Readiness of Bidirectional Charging in the Philippines
- Grid Reliability Context and Flexibility Needs in Key Load Centers
- V2G Value Stack Across Vehicle Charger Aggregator and Market Operator
- Interconnection and Export Rules for Distributed Energy Resources
- Utility Program Landscape and Fleet Led Deployment Models
- Growth Drivers
Grid reliability concerns driving interest in flexible capacity
Fleet electrification growth in buses delivery and corporate transport
Rising electricity prices and demand charge exposure for C and I sites
Renewable integration needs and daytime solar variability
Expansion of campus and industrial estate energy management programs - Challenges
Limited bidirectional capable vehicle availability and model constraints
Interconnection approvals and export metering complexity
Battery warranty concerns and cycle life impact perception
Operational complexity for fleet dispatch and charging schedules
Cybersecurity and data governance requirements for grid connected assets - Opportunities
Depot led V2G for e bus fleets and high utilization operators
Bundled charger software and revenue share contracting models
Integration with onsite solar storage and building energy management
Resilience programs for critical facilities and disaster response sites
Standardized interoperability frameworks for chargers vehicles and aggregators - Trends
Shift from pilots to fleet anchored deployments
Growth of virtual power plant models using aggregated EV fleets
Increasing role of microgrids in industrial estates and campuses
Standardization push for communications and metering workflows
Commercialization of bidirectional charging portfolios by charger OEMs - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Enabled Vehicle Base, 2019–2024
- By Bidirectional Charger Installed Base, 2019–2024
- By Dispatchable Capacity and Events Delivered, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Electric bus fleets and public transport operators
Commercial delivery and logistics fleets
Municipal and government fleets
Workplace and campus fleets
Light duty consumer EVs - By Application (in Value %)
Peak shaving and demand response
Backup power and site resilience
Renewable smoothing and curtailment reduction
Microgrid participation and critical facility support
Capacity support for constrained feeders - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
AC bidirectional charging systems
DC bidirectional charging systems
Depot scale bidirectional charging hubs
Onboard inverter enabled bidirectional platforms
Offboard inverter enabled bidirectional platforms - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Utility managed V2G programs
Aggregator managed V2G platforms
Charger operator managed V2G services
OEM managed energy services and app ecosystems
Microgrid controller integrated dispatch platforms - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Electric utilities and distribution operators
Charging infrastructure developers and operators
Fleet operators and depot managers
Commercial and industrial site hosts
Microgrid and energy service companies - By Region (in Value %)
NCR
CALABARZON
Central Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao
- Competitive ecosystem structure across aggregators charger OEMs utilities and fleet operators
- Positioning driven by dispatch performance interoperability and program readiness
- Partnership models across OEMs fleets utilities and energy service providers
- Cross Comparison Parameters (bidirectional charger efficiency, export power rating and duty cycle, interoperability and standards compliance readiness, aggregation platform dispatch latency, metering and settlement capability, cybersecurity posture and device management, program revenue capture and contract flexibility, warranty alignment and battery impact controls)
- SWOT analysis of major players
- Pricing and commercial model benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Nuvve
Fermata Energy
The Mobility House
Autogrid
EnergyHub
ABB
Siemens
Schneider Electric
Eaton
ChargePoint
Wallbox
Enel X
Powerledger
ACEN
MERALCO
- Fleet participation drivers and operational constraints
- Utility program design priorities and performance requirements
- Aggregator contracting models and settlement readiness
- Site host economics for resilience and bill reduction
- Risk factors across warranty liability and uptime expectations
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Enabled Vehicle Base, 2025–2030
- By Bidirectional Charger Installed Base, 2025–2030
- By Dispatchable Capacity and Events Delivered, 2025–2030