Market Overview
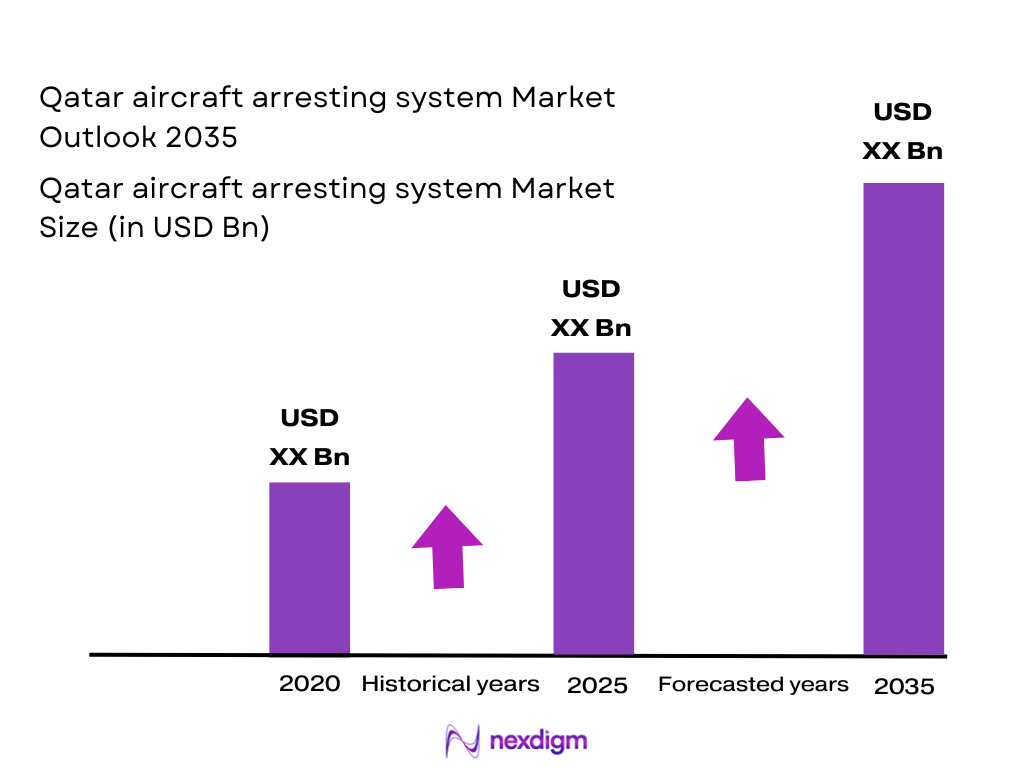
The Qatar Aircraft Arresting System market is valued at approximately USD ~ million in 2025, driven primarily by Qatar’s growing aviation infrastructure and defense modernization. Qatar’s strategic investments in the expansion of Hamad International Airport, alongside military airbases, necessitate the incorporation of advanced arresting systems to ensure safety and operational efficiency. These systems are vital for preventing aircraft overruns during emergency landings, which is critical to safeguarding both aircraft and personnel. The market is driven by increasing air traffic, the need for runway safety improvements, and technological advancements in aircraft arresting mechanisms, such as the adoption of Engineered Materials Arresting Systems (EMAS) and Mobile Aircraft Arresting Systems (MAAS).
Qatar leads the Middle Eastern market for aircraft arresting systems, with Hamad International Airport and key military airbases like Al Udeid Air Base being major hubs for the adoption of such technologies. The nation’s high defense spending, combined with its strategic geographical location and emphasis on modernizing air travel and defense infrastructure, positions it as a key adopter of advanced arresting systems. Qatar’s partnership with global defense and aerospace companies further accelerates its adoption of cutting-edge aircraft arresting solutions, making it a dominant player in the region.
Market Segmentation
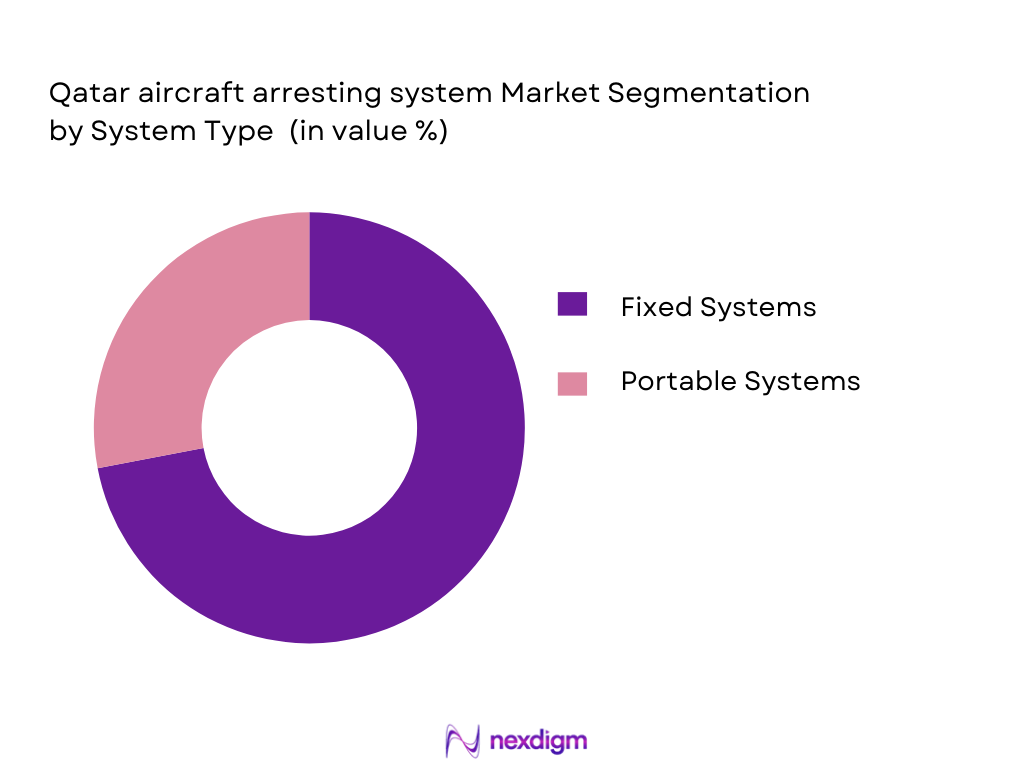
By System Type
The Qatar Aircraft Arresting System market is segmented by system type into Fixed Systems and Portable Systems. Fixed systems, including traditional cable arresting systems, dominate the market due to their permanent installation at airports and military bases. These systems are designed for long-term use and have become a staple in Qatar’s aviation and defense sectors. Fixed arresting systems provide a robust and reliable solution for emergency landings, which is essential in high-traffic airports like Hamad International. Portable systems, although growing in demand for military and temporary airport installations, represent a smaller portion of the market due to the dominance of fixed installations in major infrastructure projects.
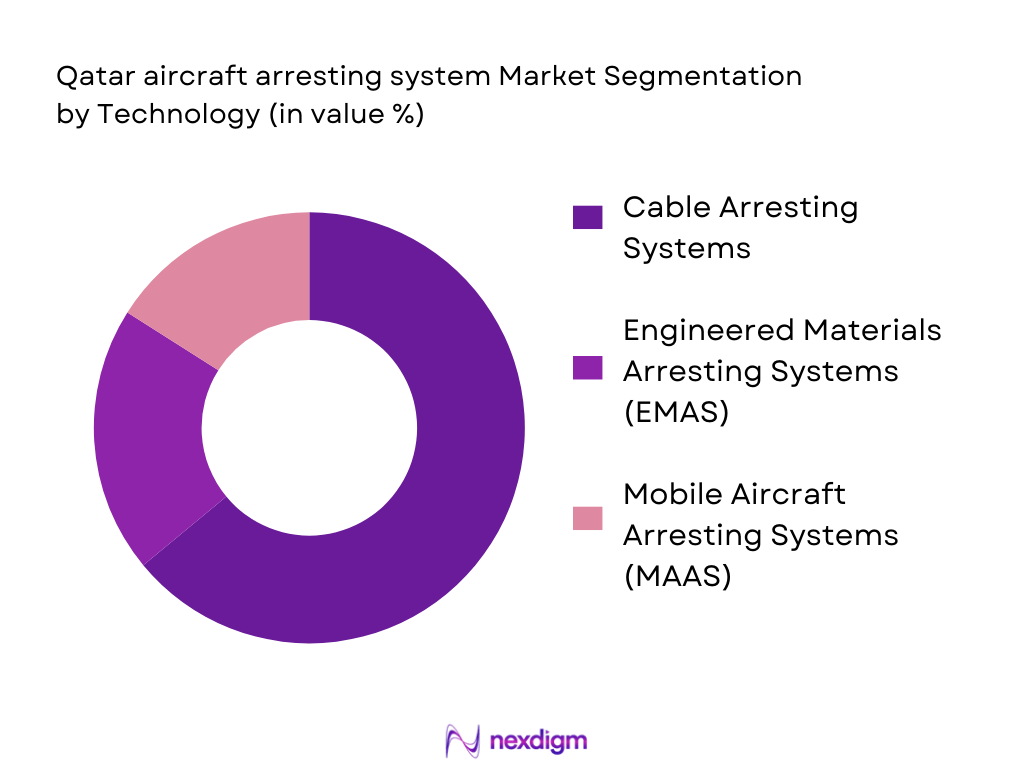
By Technology
The market is segmented by technology into Cable Arresting Systems, Engineered Materials Arresting Systems (EMAS), and Mobile Aircraft Arresting Systems (MAAS). Among these, cable arresting systems continue to dominate the market in Qatar. These systems are widely deployed across military and commercial airports due to their cost-effectiveness and established technology. EMAS is gaining traction in high-risk areas with limited space, offering an alternative to traditional cable systems by using a bed of crushable material to decelerate aircraft. MAAS, while innovative and mobile, is often used for temporary or military deployments and therefore holds a smaller market share.
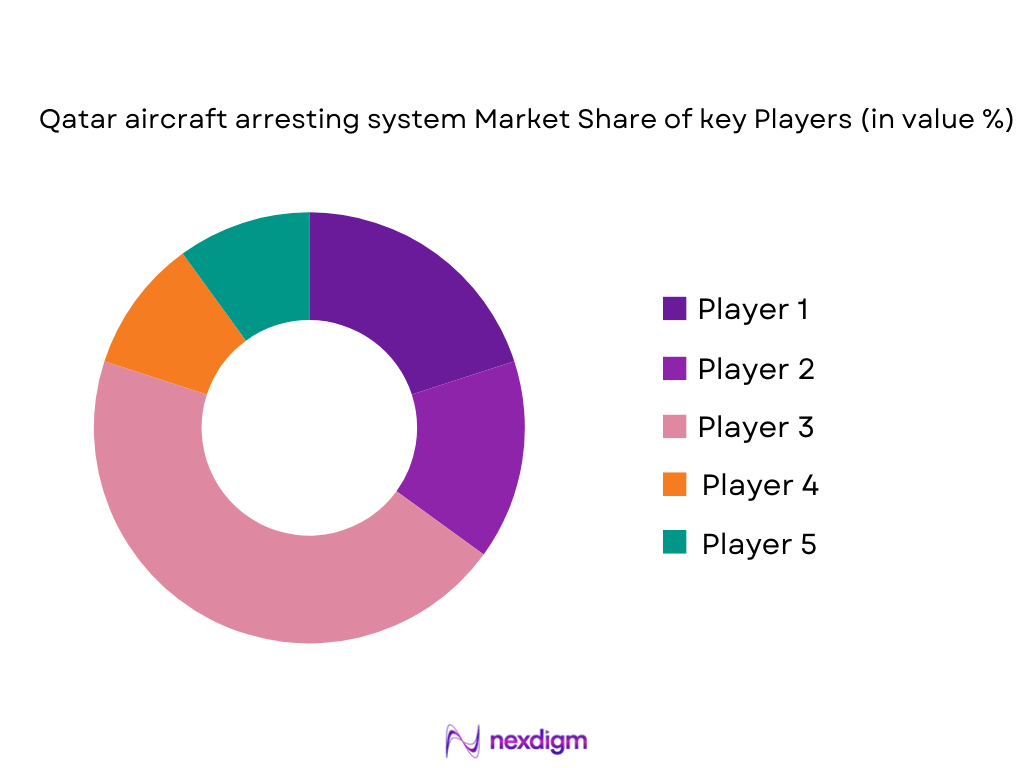
Competitive Landscape
The Qatar Aircraft Arresting System market is highly competitive, with a few key players dominating the landscape. These include both local and international firms that provide comprehensive solutions for aircraft safety. Global players like Zodiac Arresting Systems and Esavian Systems have a significant presence in Qatar, owing to their strong product offerings and established relationships with government agencies and military organizations. Local players also contribute to the market by providing tailored solutions that meet Qatar’s unique operational and environmental needs.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Key Products | Service Capabilities | Market Focus |
| Zodiac Arresting Systems | 1986 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Esavian Systems | 2000 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| General Atomics | 1955 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Foster‑Miller Inc. | 1980 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Scama AB | 1976 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Qatar Aircraft Arresting System Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Urbanization
Qatar’s urbanization is among the highest globally, with an urban population of ~ people in urban areas out of ~ total population, indicating that ~ % of the population resides in urban centers in 2025 according to World Bank data. This intense urban concentration drives the expansion of aviation infrastructure such as Hamad International Airport, which serves densely populated catchment areas, increasing the number of flights and runway operations that require advanced safety systems like aircraft arresting systems to prevent runway overruns. The rise in urban mobility, coupled with nearly ~% annual population growth, places immense pressure on air travel networks and necessitates investments in runway safety infrastructure to support urban residents and business activities.
Industrialization
Industrialization in Qatar, reflected by its strong GDP and diversified non‑hydrocarbon sectors, supports aviation infrastructure growth that directly backs demand for aircraft arresting systems. In 2025, Qatar’s GDP stood at USD ~ billion with GDP per capita at USD ~, highlighting robust economic capacity to invest in advanced aviation safety technologies. Expansion of transport, logistics, and aviation facilities aligned with Qatar National Vision 2030 translates into increased airport throughput and new aviation projects. Because industrialization leads to higher cargo and passenger traffic—seen globally with over ~ million flight departures and ~ billion passengers transported worldwide—airports in Qatar must adopt safety systems to manage intensive runway usage. Advanced arresting systems mitigate risks associated with rapid industrial growth and heavier flight schedules.
Restraints
High Initial Costs
Installation of aircraft arresting systems is capital‑intensive, which can constrain adoption, even in high‑income economies like Qatar. A typical engineered materials arresting system (EMAS) bed installation at large international airports can run into multi‑million dollar projects, with funds committed from national aviation budgets. Qatar’s aviation modernization must weigh these expenditures against other infrastructure priorities. Given that Qatar reported a GDP growth of ~ % in 2025, cost management remains crucial for state projects. While specific system installation costs vary by runway specifications and aircraft categories, the overarching constraint remains substantial upfront capital, leading procurement authorities to phase or extend installation timelines to balance fiscal planning and infrastructure safety improvements.
Technical Challenges
Aircraft arresting systems integrate with complex airport systems and must meet strict safety and engineering standards. As aviation traffic grows—reflected globally with ~ million departures and rising accident rates of ~ accidents per million departures in 2025—the need for precise calibration and interoperability with radar, runway lighting, and emergency response systems becomes more acute. Complex technical specifications require skilled engineering teams for installation and system validation. Qatar must rely on international technical expertise and rigorous testing to ensure systems operate reliably under diverse conditions. Technical certification, compliance with ICAO safety protocols, and adaptation to extreme regional climate factors such as high temperatures strain local technical resources, slowing deployment rates.
Opportunities
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in aircraft arresting system design—such as lighter composite cables, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance tools—present significant opportunities for Qatar’s aviation safety ecosystem. As global aviation recalibrates safety protocols using data analytics and real‑time monitoring, Qatar’s airports can adopt next‑generation arresting solutions that optimize performance and reduce downtime. With international flight departures exceeding ~ million in 2025, there is an increasing focus on embedding smart diagnostics to reduce false activations and maintenance costs, providing better return on infrastructure investments. Embracing technologies like engineered materials arresting systems (EMAS) and AI‑assisted safety analytics improves precision in emergency scenarios and aligns with Qatar’s broader digital transformation goals.
International Collaborations
International collaborations between Qatar’s aviation authorities and global aerospace and defense technology providers support the introduction of advanced aircraft arresting systems. Airports and military airbases benefit from partnerships that bring established best practices and system certification experience. As international flight volumes and safety registry demands rise—supported by ICAO’s recording of increased scheduled flight departures to ~ million in 2025—Qatar is positioned to leverage multinational expertise in arresting system installation, maintenance, and innovation. These collaborations not only enhance runway safety protocols but also enable technology transfer, capacity building, and standardized compliance with international aviation safety norms, fostering a more resilient and interoperable aviation infrastructure
Future Outlook
Over the next 5 years, the Qatar Aircraft Arresting System market is expected to grow significantly, driven by continued investments in aviation safety and military infrastructure. The Qatar government’s push to modernize defense systems and expand its aviation capacity will result in the widespread adoption of advanced arresting systems like EMAS and MAAS. Increased air traffic, combined with stringent safety regulations, will also accelerate the need for these technologies, ensuring steady growth across both the civilian and military sectors.
Major Players in the Market
- Zodiac Arresting Systems
- Esavian Systems
- General Atomics Aeronautical Systems
- Foster-Miller Inc.
- Scama AB
- Curtiss-Wright Corp.
- WireCo WorldGroup
- Atech Inc.
- Thales Arresting Solutions
- Safran Arresting Systems
- Elbit Systems Aviation Technologies
- A-Laskuvarjo Oy
- BAE Systems
- United Technologies Corporation (UTC)
- Airbus Defence and Space
Key Target Audience
- Qatar Civil Aviation Authority (QCAA)
- Qatar Emiri Air Force
- Qatar Airways
- Qatar Ministry of Defence
- Qatar Armed Forces
- Qatar Investment Authority (QIA)
- Global Aerospace Investment Firms
- International Airport Authorities
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves constructing an ecosystem map encompassing all major stakeholders within the Qatar Aircraft Arresting System market. This is underpinned by extensive desk research, using secondary data from credible databases and interviews with key industry players to define the critical market dynamics.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, historical data regarding installations, technology penetration, and system reliability in Qatar’s aviation sector is analyzed to assess the current market size and identify growth patterns. Key insights on adoption rates and technological advancements are compiled from both civil and military domains.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses are validated through consultations with industry experts, manufacturers, and procurement officers. This involves direct interviews with stakeholders across major airports and military airbases to refine assumptions and ensure the accuracy of market projections.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase focuses on synthesizing all gathered data to generate a comprehensive view of the market, including future growth trends, adoption forecasts, and competitive intelligence. In this stage, collaboration with arresting system manufacturers allows for verification of data and insights regarding emerging technologies.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions & Scope, Qatar MAC (Market Adoption Criteria) for Arresting Systems, Data Sources & Primary Interviews (Civil Aviation Authority / Qatar Emiri Air Force), Market Sizing & Forecasting Methods (Revenue / Installation Units / Runway Safety Index), Assumptions & Limitations)
- Aviation Safety Imperatives in Qatar
- Airport Expansion & Modernization Roadmap (Hamad Intl, New Airfields)
- Regulatory & Compliance Framework (QCAR Aerodrome Safety Standards)
- Civil vs. Military Arresting System Requirements
- Value & Supply Chain (Design → Installation → Maintenance → Training)
- Growth Drivers
Rising Air Traffic & Emergency Safety Requirements
Expansion of Qatar Military Aviation Fleet
EMAS Adoption & Runway Safety Mandates - Market Restraints
High Installation & Lifecycle Costs
Complex Regulatory Approvals
Climate Impact on System Reliability - Emerging Opportunities
Technology Upgrades
Defense Modernization & Integration with Next‑Gen Aircraft
Public‑Private Partnerships - Market Trends
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Market Value, 2020-2025
- Volume Consumption Across Subsegments, 2020-2025
- Composite Adoption Intensity, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value %)
Fixed System
Portable System - By Technology (In Value %)
Net Barrier
Cable
Mobile Aircraft Arresting System (MAAS)
EMAS
Carrier Arresting Systems - By End‑User (In Value %)
Commercial Airport
Military Airbase
Aircraft Carrier Deployment - By Platform (In Value %)
Ground‑Based
Ship‑Based
Temporary Field Deployment - By Service Type (In Value %)
Installation
Preventive Maintenance
Emergency Training
- Market Share by Revenue & Installations
- Cross‑Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Market Position in Qatar Aerospace Safety (Military / Civil), Product Portfolio Breadth (Technology Types), System Reliability Scores (Failure & Response Metrics), Regional Service Network in GCC, Contract Wins & Pipeline (Civil / Defense), Price per System Segment (Cable • EMAS • Carrier), After‑Sales Support Footprint )
- Competitor SWOT Analysis
- Pricing Benchmarking
- Detailed Company Profiles of Key Competitors
General Atomics Aeronautical Systems
Runway Safe Group
Zodiac Arresting Systems
Esavian Systems
Curtiss‑Wright Corp.
Atech Inc.
A‑Laskuvarjo Oy
Escribano Mechanical & Engineering
Foster‑Miller Inc.
Scama AB
WireCo WorldGroup
Victor Balata Belting Co.
Safran Arresting Systems
Thales Arresting Solutions
Elbit Systems Aviation Technologies
- Commercial Airports Adoption Patterns
- Military Airbase Requirements & Compliance Needs
- Decision Drivers & Procurement Workflows
- Safety KPI Analysis
- Budget Allocation & Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Considerations
- Forecast by Value & Growth Scenarios, 2026-2035
- Forecast by Volume & Composite Penetration, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Aircraft Segment, 2026-2035


