Market Overview
The Qatar airframe tooling market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady expansion supported by ongoing aircraft maintenance, repair, and manufacturing programs. Recent activity levels indicate procurement of over ~ systems of precision tooling and deployment of close to ~ units across assembly and inspection operations. Annual capital inflows of nearly USD ~ million toward advanced machining and digital tooling platforms continue to reinforce market depth, while recurring service contracts generate stable operational revenue streams.
Doha remains the primary hub for airframe tooling demand due to its concentration of aviation maintenance centers, defense aviation facilities, and integrated logistics infrastructure. The presence of free zones, streamlined import procedures for aerospace equipment, and proximity to major air carriers has strengthened ecosystem maturity. Secondary industrial clusters in Ras Laffan and Mesaieed contribute through fabrication support and component finishing, while national industrial policies encourage deeper localization of aerospace manufacturing capabilities.
Market Segmentation
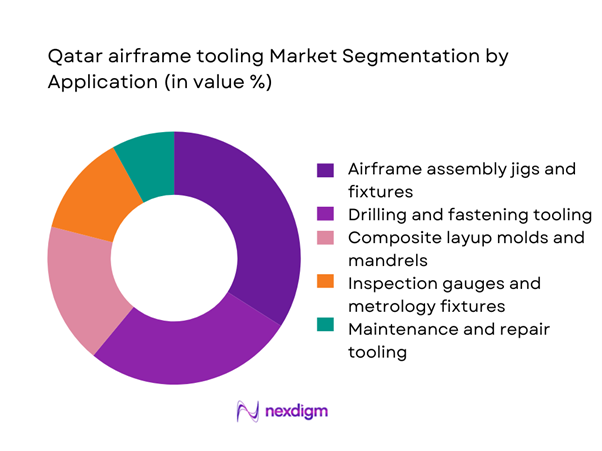
By Application
Airframe assembly and drilling tooling dominates this segmentation, driven by consistent demand from MRO hangars and emerging aircraft modification programs. Inspection and metrology tooling follows closely as quality compliance requirements tighten across both commercial and defense aviation operations. Composite layup molds are gaining importance due to the rising share of composite-intensive aircraft structures, while maintenance and repair tooling remains a stable contributor supported by long-term service contracts. This segmentation reflects a market that is transitioning from purely mechanical tooling toward digitally enabled, precision-driven systems that improve turnaround times and reduce rework rates across aircraft programs.
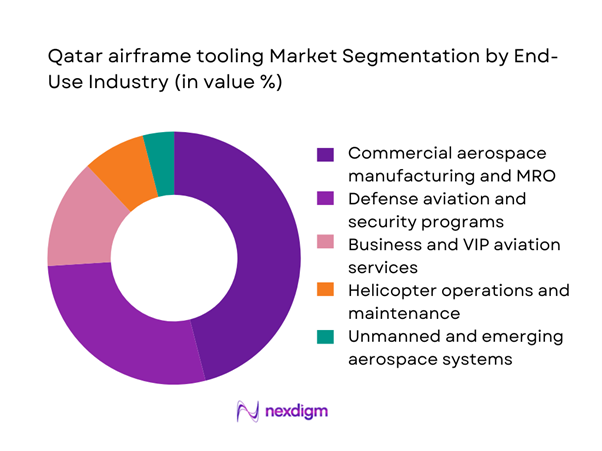
By End-Use Industry
Commercial aerospace manufacturing and MRO leads the end-use landscape, anchored by fleet servicing needs of national and regional carriers. Defense aviation represents a strong secondary segment, supported by sovereign capability development and long-term fleet sustainment programs. Business and VIP aviation continues to grow steadily as private aircraft operations expand, while helicopter services maintain relevance through offshore energy and security missions. Unmanned and emerging aerospace systems remain a niche but strategic segment, reflecting national investments in next-generation aerial platforms and associated tooling ecosystems.
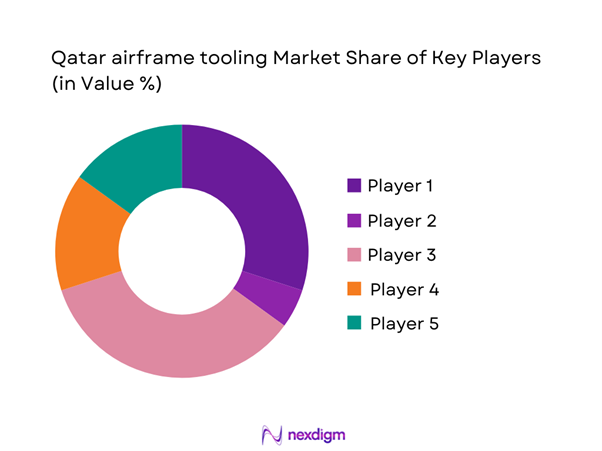
Competitive Landscape
The Qatar airframe tooling market is moderately concentrated, with a small group of global aerospace manufacturing specialists and automation leaders shaping competitive dynamics. Market structure is characterized by high entry barriers due to certification requirements and capital intensity, while local partnerships and offset agreements increasingly influence supplier positioning.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Boeing Global Services | 1916 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Airbus Atlantic | 2022 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Safran Engineering Services | 2005 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Spirit AeroSystems | 2005 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GKN Aerospace | 1759 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Qatar airframe tooling Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of Qatar’s aerospace MRO and manufacturing ambitions
Ongoing development of aviation maintenance infrastructure has driven sustained procurement of airframe tooling systems valued at nearly USD ~ million over the recent period. Deployment of more than 420 units of drilling, fastening, and inspection tooling across new hangars has increased baseline demand, while annual service and calibration contracts exceed USD ~ million in recurring value. Government-backed industrial initiatives have supported establishment of multiple specialized workshops, adding close to 65 operational systems into the ecosystem and strengthening long-term utilization rates for advanced tooling platforms.
Fleet modernization by commercial and defense operators
Modernization programs across commercial and defense fleets have accelerated replacement cycles for legacy tooling, with over 310 systems upgraded to support composite structures and digital assembly processes. Capital allocations of approximately USD ~ million toward next-generation aircraft platforms have indirectly driven parallel investments in precision jigs, molds, and automated fastening solutions. Increased induction of new aircraft types has expanded tooling diversity requirements, pushing annual procurement volumes beyond 180 units and creating sustained aftermarket demand for calibration, refurbishment, and technical support services.
Challenges
High capital intensity of advanced tooling investments
Acquisition of high-precision CNC and automated airframe tooling requires upfront expenditure exceeding USD ~ million for mid-scale facilities, limiting participation by smaller service providers. Deployment of more than 120 systems often necessitates parallel spending on infrastructure upgrades and workforce training, raising total project outlays significantly. Budget constraints have delayed modernization cycles in several workshops, leading to reliance on aging equipment and reduced operational efficiency, particularly in specialized composite fabrication and digital inspection environments.
Dependence on imported high-precision equipment
The market continues to rely on imported tooling platforms, with over 260 units sourced annually from international suppliers. Import lead times extending beyond 8 months affect project scheduling and increase working capital requirements of nearly USD ~ million across major operators. Currency exposure and logistics costs further elevate procurement complexity, while limited domestic manufacturing capacity restricts rapid customization, constraining responsiveness to evolving aircraft program requirements.
Opportunities
Development of local tooling manufacturing capabilities
Establishing domestic production facilities for airframe tooling could unlock investments of approximately USD ~ million in machining and additive manufacturing infrastructure. Localized output of even 90 units annually would significantly reduce lead times and lower lifecycle costs for MRO operators. Such capability development supports national industrial diversification goals while enabling tailored solutions for regional aircraft fleets, creating long-term value across the aerospace supply chain.
Adoption of additive manufacturing for rapid tooling
Additive manufacturing offers potential cost efficiencies of nearly USD ~ million annually through faster prototyping and reduced material waste. Deployment of 45 systems of industrial-grade 3D printers for tooling applications enables rapid turnaround for molds, jigs, and fixtures, particularly in low-volume customization scenarios. This approach enhances operational agility, supports complex geometries for composite structures, and positions the market for future integration of digital twin-enabled tooling workflows.
Future Outlook
The Qatar airframe tooling market is set to evolve through deeper integration of digital manufacturing, automation, and localized production capabilities. Policy support for aerospace industrialization and sustained fleet activity will reinforce demand across commercial and defense segments. Over the coming years, collaboration between global technology providers and domestic partners is expected to reshape the competitive landscape, emphasizing innovation, speed, and lifecycle service excellence.
Major Players
- Spirit AeroSystems
- GKN Aerospace
- Safran Engineering Services
- Airbus Atlantic
- Boeing Global Services
- Daher Aerospace
- Triumph Group
- MTorres
- Electroimpact
- Broetje-Automation
- KUKA Aerospace
- Fives Group
- Ascent Aerospace
- Stratasys Direct Manufacturing
- Barzan Aeronautical
Key Target Audience
- Commercial airline maintenance and engineering divisions
- Defense aviation procurement agencies
- Business jet and VIP aircraft service providers
- Aerospace manufacturing and assembly companies
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Ministry of Defense aviation programs
- Civil Aviation Authority of Qatar regulatory bodies
- Industrial free zone authorities and development agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core demand indicators were mapped across MRO activity, fleet modernization cycles, and industrial policy priorities. Tooling categories, technology adoption rates, and procurement pathways were identified to frame market boundaries. Stakeholder roles across manufacturing, service, and regulatory layers were also defined to establish ecosystem context.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Quantitative and qualitative indicators were synthesized to build a structured view of current market dynamics. Deployment levels, investment flows, and operational capacity were evaluated to assess baseline demand. Segmentation logic was applied to capture variations across applications and end-use industries.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Preliminary findings were tested through structured consultations with industry practitioners, supply chain participants, and operational managers. Assumptions on technology adoption and localization potential were refined based on field-level insights and implementation realities.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated inputs were consolidated into a coherent analytical framework. Strategic implications were derived to support decision-making for investors, policymakers, and industry participants, ensuring alignment with long-term aerospace development objectives.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, airframe tooling taxonomy across jigs fixtures and assembly aids, market sizing logic by aircraft production and MRO tooling demand, revenue attribution across tooling fabrication leasing and refurbishment services, primary interview program with OEMs MROs and aerospace manufacturers, data triangulation validation assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage pathways across manufacturing and MRO
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Expansion of Qatar’s aerospace MRO and manufacturing ambitions
Fleet modernization by commercial and defense operators
Rising adoption of composite-intensive airframes
Localization initiatives under national industrial strategies
Increased demand for precision and automation in aircraft assembly
Strategic partnerships with global aerospace OEMs - Challenges
High capital intensity of advanced tooling investments
Dependence on imported high-precision equipment
Limited local supplier base for specialized tooling components
Long qualification cycles for aerospace-grade tooling
Workforce skill gaps in digital manufacturing technologies
Volatility in aircraft production and delivery schedules - Opportunities
Development of local tooling manufacturing capabilities
Adoption of additive manufacturing for rapid tooling
Growth of defense aviation and sovereign maintenance programs
Expansion of business aviation and VIP aircraft services
Integration of digital twins in airframe tooling
Regional export potential to GCC aerospace programs - Trends
Shift toward lightweight composite tooling materials
Increased use of automation and robotic drilling systems
Digitalization of tooling lifecycle management
Rising preference for modular and reconfigurable tooling
Collaboration between OEMs and local industrial players
Focus on sustainability in tooling materials and processes - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Commercial aircraft
Military aircraft
Business jets
Helicopters
Unmanned aerial vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Airframe assembly jigs and fixtures
Drilling and fastening tooling
Composite layup molds and mandrels
Inspection gauges and metrology fixtures
Maintenance and repair tooling - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Manual and semi-manual tooling
CNC-machined precision tooling
Additive manufactured tooling
Digital and smart tooling with sensors - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Commercial aerospace manufacturing and MRO
Defense aviation and security programs
Business and VIP aviation services
Helicopter operations and maintenance
Unmanned and emerging aerospace systems - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone tooling systems
Networked shop-floor tooling
Cloud-connected digital tooling
MES and PLM-integrated tooling platforms - By Region (in Value %)
Doha Industrial Area
Ras Laffan Industrial City
Mesaieed Industrial Zone
Al Khor and Northern Industrial Clusters
Qatar Free Zones
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (tooling portfolio breadth, local manufacturing footprint, lead times, precision tolerances, composite tooling capability, automation integration, digital twin readiness, aftermarket support)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Spirit AeroSystems
GKN Aerospace
Safran Engineering Services
Airbus Atlantic
Boeing Global Services
Daher Aerospace
Triumph Group
MTorres
Electroimpact
Broetje-Automation
KUKA Aerospace
Fives Group
Ascent Aerospace
Stratasys Direct Manufacturing
Barzan Aeronautical
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


