Market Overview
The Qatar ballistic missile market is aligned with the global ballistic missiles market valued at USD ~ billion, supported by rising geopolitical tensions, defense modernization, and expanding military budgets according to Global Market Insights. Procurement of advanced missile systems and layered air defense technologies continues to stimulate demand, while investments in precision strike capabilities enhance deterrence strategies. Strategic partnerships with international defense contractors further accelerate system acquisitions and technology transfers, reinforcing sustained procurement cycles within the national defense framework.
Doha serves as the central hub for missile procurement, testing coordination, and defense command due to concentrated military infrastructure and government leadership. The United States remains the dominant external supplier, driven by long standing security cooperation and large scale defense agreements such as Patriot and THAAD acquisitions valued at nearly USD 10 billion according to the U.S. Congressional Research Service. Broader Middle Eastern security dynamics and proximity to regional flashpoints further reinforce the country’s prioritization of advanced missile capabilities and integrated deterrence systems.
Market Segmentation
By Product Type:
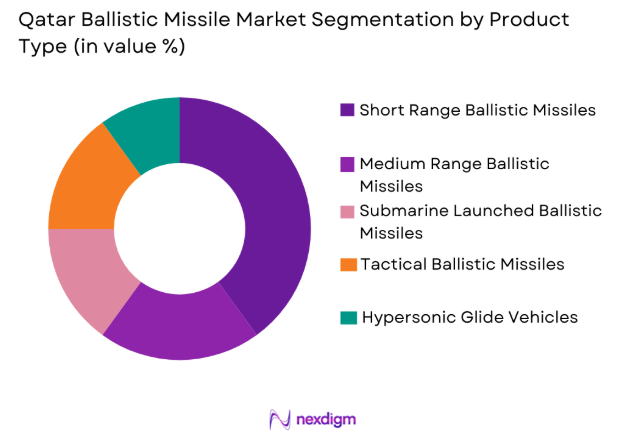
Qatar ballistic missile market is segmented by product type into short range ballistic missiles, medium range ballistic missiles, submarine launched ballistic missiles, tactical ballistic missiles, and hypersonic glide vehicles. Recently, medium range ballistic missiles has a dominant market share due to factors such as strategic deterrence requirements, compatibility with regional defense doctrines, infrastructure readiness, and operational flexibility. These systems provide extended strike capability without the complexity associated with intercontinental platforms, making them suitable for Gulf security dynamics. Defense planners prioritize adaptable payload configurations and rapid deployment potential, while interoperability with allied surveillance and targeting frameworks enhances battlefield effectiveness. Procurement structures favor proven platforms supplied through government agreements, ensuring reliability and lifecycle support. Additionally, expanding investments in missile defense integration indirectly encourage acquisition of complementary offensive systems, consolidating the leadership of medium range variants within national force planning strategies.
By Platform Type:
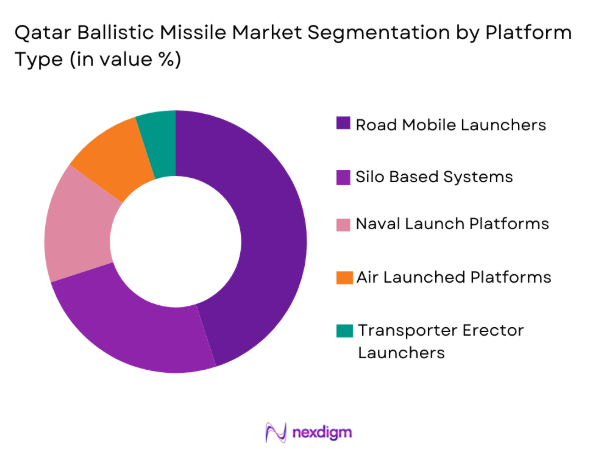
Qatar ballistic missile market is segmented by platform type into road mobile launchers, silo based systems, naval launch platforms, air launched platforms, and transporter erector launchers. Recently, road mobile launchers has a dominant market share due to factors such as survivability advantages, rapid redeployment capability, lower infrastructure dependency, and suitability for dynamic threat environments. Mobile configurations complicate adversary targeting while enabling dispersed operational posture across strategic zones. Defense authorities increasingly value flexibility over fixed installations, particularly in regions exposed to preemptive strike risks. Integration with advanced command networks supports coordinated response frameworks, strengthening operational resilience. Procurement trends indicate preference for launch platforms that balance readiness with logistical efficiency, while modernization initiatives continue to emphasize mobility as a critical component of credible deterrence posture within evolving regional defense architectures.
Competitive Landscape
The market exhibits moderate consolidation characterized by reliance on established international defense manufacturers with proven missile technologies and integrated defense ecosystems. Long term procurement contracts, technology transfer arrangements, and interoperability requirements strengthen the influence of major players, while high entry barriers limit participation from smaller suppliers. Strategic alliances and government mediated acquisitions further concentrate competitive positioning, reinforcing supplier dominance across advanced propulsion, guidance, and launch system segments.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Missile Range Capability |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| RTX Corporation | 1922 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Northrop Grumman | 1939 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MBDA | 2001 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Qatar Ballistic Missile Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Strategic Defense Modernization Programs:
Qatar’s defense establishment is undergoing structured modernization to strengthen deterrence and align with evolving regional security dynamics. Procurement of advanced missile platforms reflects a shift toward integrated warfighting capabilities supported by digital command networks. Military planners emphasize interoperability with allied forces, enabling coordinated response across air and missile defense layers. Continued acquisition programs reinforce readiness while reducing technological gaps against potential adversaries. Investments also prioritize precision guidance and improved propulsion systems to enhance operational effectiveness. Defense cooperation agreements facilitate access to next generation technologies otherwise difficult to develop domestically. Infrastructure upgrades further support deployment flexibility and long term sustainment requirements. The modernization agenda additionally stimulates maintenance, training, and support services ecosystems. Collectively, these factors create sustained procurement momentum that directly accelerates market expansion within the national defense architecture.
Regional Geopolitical Tensions and Deterrence Requirements:
Persistent security uncertainties across the Gulf encourage proactive defense postures centered on credible deterrence. Missile capabilities serve as strategic signaling tools that reinforce national sovereignty and defensive preparedness. Defense leadership increasingly prioritizes layered protection frameworks capable of countering diverse aerial threats. Heightened vigilance drives continuous evaluation of strike range, payload versatility, and response timelines. Strategic geography amplifies the necessity for rapid reaction capabilities supported by advanced surveillance integration. Alliances with technologically advanced partners enhance deterrence credibility while ensuring operational reliability. Security planning now incorporates multi domain coordination linking missile forces with cyber and intelligence assets. The evolving threat environment also encourages redundancy within launch systems to maintain readiness under contested conditions. Such dynamics consistently elevate demand for ballistic missile technologies across procurement cycles.
Market Challenges
High Lifecycle and Acquisition Costs of Missile Systems:
Ballistic missile platforms require substantial capital investment covering procurement, deployment infrastructure, maintenance, and training. Advanced propulsion technologies and precision guidance components significantly elevate system prices. Budget allocations must therefore balance modernization priorities against competing defense requirements. Long term sustainment contracts further increase financial commitments beyond initial acquisition phases. Imported systems often involve expensive support packages that extend operational expenditures. Currency fluctuations and global supply constraints may also affect procurement timelines and affordability. Decision makers consequently conduct rigorous cost benefit assessments before approving purchases. Financial exposure intensifies when integrating multiple defense layers simultaneously. Despite strong fiscal capacity, sustained spending pressures can influence acquisition pacing, creating periodic procurement gaps that moderate short term market growth.
Dependence on Foreign Technology Providers:
Qatar relies heavily on international defense manufacturers for advanced missile technologies due to limited domestic production capability. This reliance introduces vulnerabilities related to export controls and geopolitical policy shifts. Procurement approvals frequently depend on diplomatic alignment with supplier nations. Technology transfer restrictions may limit local operational autonomy and customization potential. Maintenance and upgrade cycles often require continued foreign technical support. Supply chain disruptions can therefore affect readiness levels and delivery schedules. Defense authorities must also navigate complex compliance requirements tied to sensitive military equipment. Negotiations surrounding intellectual property and integration rights may prolong acquisition processes. Such structural dependence creates strategic constraints that shape procurement flexibility and influence long term capability planning.
Opportunities
Expansion of Integrated Missile Defense Architecture:
The development of layered defense networks creates opportunities for complementary ballistic missile acquisitions designed to operate within coordinated detection and interception frameworks. Integrated architectures enhance situational awareness while enabling faster decision cycles across command hierarchies. Defense planners increasingly pursue systems capable of seamless data exchange with radar and surveillance assets. Modernization of command infrastructure further supports multi platform synchronization during complex operations. Vendors offering interoperable technologies stand to benefit from sustained procurement interest. The emphasis on network centric warfare also encourages adoption of advanced communication interfaces. Training ecosystems evolve simultaneously to support operational proficiency. Investments in simulation technologies strengthen readiness without excessive live testing costs. Collectively, integration initiatives generate a favorable environment for advanced missile solutions aligned with future defense doctrines.
Adoption of Next Generation Propulsion and Guidance Technologies:
Emerging advancements in hypersonic propulsion and precision navigation present significant opportunities for capability enhancement. Defense organizations increasingly evaluate systems offering improved maneuverability and reduced interception probability. Technological evolution supports higher mission reliability under contested conditions. Partnerships with innovative defense firms accelerate exposure to cutting edge research outcomes. Modern guidance algorithms enable superior targeting accuracy while minimizing collateral risk. Procurement strategies now emphasize adaptability to accommodate future upgrades. Enhanced propulsion efficiency also contributes to extended operational reach. Research investments worldwide continue to push performance boundaries, influencing buyer expectations. As these technologies mature, adoption potential expands, positioning advanced missile platforms as central components of long term strategic deterrence planning.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to experience steady expansion driven by sustained defense spending, modernization initiatives, and continued geopolitical uncertainty. Technological evolution in propulsion, guidance, and mobility will likely redefine procurement priorities while strengthening deterrence capabilities. Regulatory cooperation with allied nations should facilitate advanced acquisitions and interoperability. Demand is projected to remain supported by integrated defense strategies and infrastructure upgrades, positioning missile capabilities as a central pillar of national security planning over the next five years.
Major Players
- Lockheed Martin
- RTX Corporation
- Northrop Grumman
- Boeing Defense
- MBDA
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Thales Group
- BAE Systems
- L3Harris Technologies
- Kongsberg Defence and Aerospace
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
- Almaz Antey
- Roketsan
- Denel Dynamics
Key Target Audience
- Defense procurement agencies
- Military modernization authorities
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Sovereign wealth funds
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Missile system integrators
- National security councils Strategic defense contractors
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study began by identifying critical variables influencing the ballistic missile ecosystem including procurement budgets, modernization policies, and geopolitical risk indicators. Supply side parameters such as manufacturing capability and technology maturity were mapped. Demand drivers were analyzed through defense planning frameworks and acquisition records. These variables established the analytical boundaries for structured market evaluation.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Data was consolidated from defense publications, government disclosures, and verified industry databases to construct the market baseline. Quantitative insights were triangulated with procurement announcements and technology adoption patterns. Segment structures were developed to reflect operational deployment realities. This approach ensured coherence between macro defense spending trends and missile specific demand.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Preliminary findings were validated through consultation with defense analysts and aerospace subject matter experts. Scenario testing examined procurement continuity under varying geopolitical conditions. Assumptions were refined to eliminate bias and ensure methodological rigor. Feedback loops enhanced reliability across both qualitative and quantitative interpretations.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated data sets were synthesized into a structured narrative aligning with strategic defense developments. Analytical models translated raw information into actionable intelligence for stakeholders. Consistency checks were applied to confirm accuracy across segments. The final output presents a balanced representation of current conditions and forward looking market dynamics.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Rising regional security threats driving strategic deterrence investments
Expansion of integrated missile defense architecture
Modernization of armed forces with advanced strike capabilities
Increasing defense budget allocations toward long-range precision systems
Strategic military alliances supporting technology transfer - Market Challenges
High acquisition and lifecycle costs of missile systems
Dependence on foreign suppliers for critical technologies
Operational restrictions linked to international arms regulations
Complex integration with existing defense infrastructure
Limited domestic manufacturing capabilities - Market Opportunities
Development of indigenous missile support infrastructure
Adoption of hypersonic and next-generation propulsion technologies
Expansion of missile defense interoperability with allied nations - Trends
Shift toward road-mobile missile deployment for survivability
Integration of AI-enabled targeting and guidance
Growing emphasis on multi-layered deterrence strategies
Adoption of canister-based storage for rapid launch readiness
Increasing investment in counter-missile technologies - Government Regulations & Defense Policy
Missile technology controls aligned with international non-proliferation frameworks
Defense procurement policies emphasizing strategic capability enhancement
Bilateral defense cooperation agreements shaping acquisition strategy - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Short-Range Ballistic Missiles
Medium-Range Ballistic Missiles
Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles
Hypersonic Glide Vehicles
Tactical Ballistic Missile Systems - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Road-Mobile Launch Platforms
Silo-Based Platforms
Naval Launch Platforms
Air-Launched Platforms
Transporter Erector Launcher Systems - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
Canisterized Missile Systems
Open Launch Rail Systems
Underground Silo Fitments
Mobile Launch Integration
Containerized Deployment Systems - By EndUser Segment (In Value%)
Qatar Emiri Air Force Strategic Command
Qatar Armed Forces Missile Units
Joint Strategic Defense Command
Integrated Air and Missile Defense Units
Special Strategic Deterrence Forces - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Government-to-Government Agreements
Direct OEM Procurement
Strategic Defense Partnerships
Foreign Military Sales Programs
Classified Defense Contracts - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Solid Propellant Technology
Liquid Fuel Propulsion Systems
Composite Airframe Materials
Advanced Guidance and Navigation Systems
Thermal Protection Materials
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- CrossComparison Parameters (Missile Range Capability, Payload Flexibility, Guidance Accuracy, Mobility, Launch Readiness Time, Technology Transfer Provisions, Lifecycle Support, Interoperability, Survivability Features)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Key Players
Lockheed Martin
Raytheon Technologies
Northrop Grumman
Boeing Defense
BAE Systems
Thales Group
MBDA
Rheinmetall AG
Israel Aerospace Industries
Elbit Systems
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
Almaz-Antey
Denel Dynamics
Roketsan
L3Harris Technologies
- Strategic forces prioritizing long-range deterrence capability
- Air defense units integrating ballistic missile tracking systems
- Joint command structures enhancing rapid response readiness
- Defense leadership focusing on network-centric warfare preparedness
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035