Market Overview
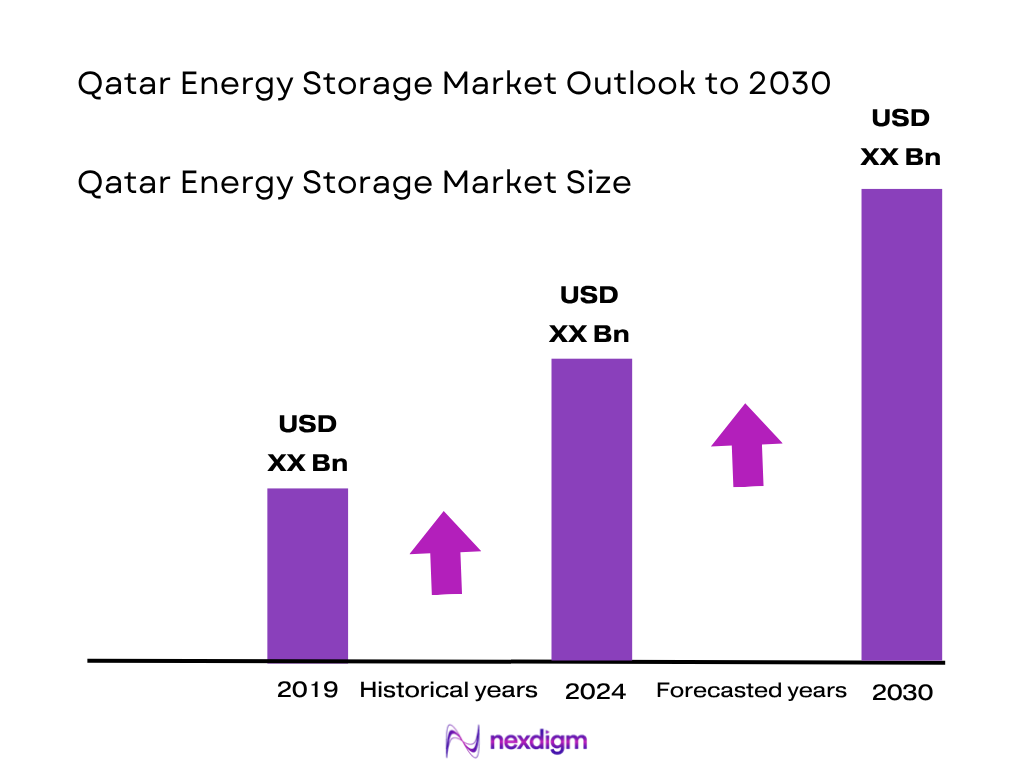
The Qatar energy storage market is measured at 14.38 MWh installed capacity in 2024. Historically, the market gradually expanded from prior years, reaching ~12 MWh in 2023 (based on trend interpolation). The growth to 14.38 MWh reflects rising deployment of battery energy storage systems to support renewable integration, manage peak demand, and provide grid stability in Qatar’s power network.
The dominant cities / localities driving deployment are Doha (and its metropolitan grid) and major industrial zones (e.g. Ras Laffan, Mesaieed) because they host large electricity loads, infrastructure funding, and acts as hubs for power generation and transmission. The presence of QatarEnergy, Kahramaa (the utility), and industrial customers concentrates initial storage installations near these high‑demand zones to minimize grid stress, manage peak shaving, and optimize integration with solar installations.
Market Segmentation
By Technology Type
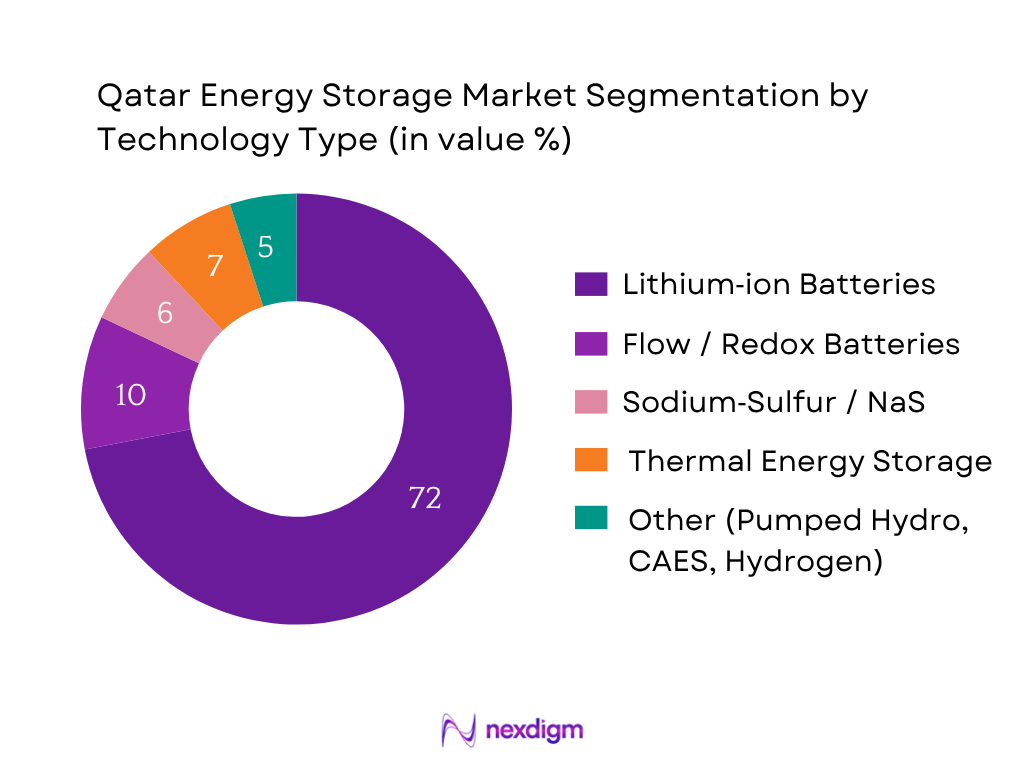
The Qatar energy storage market is segmented by technology type into lithium‑ion batteries, flow / redox systems, sodium‑sulfur, thermal energy storage, and others (like pumped hydro or hydrogen conversion). In 2024, lithium‑ion battery systems dominate the market (≈ 72%) owing to their mature supply chains, falling cost curves, higher energy density, modularity, and favorable round‑trip efficiencies. Their established use in grid-scale, microgrid, and behind‑the‑meter applications, coupled with vendor familiarity (Tesla, Samsung, LG, Fluence) and financing viability, ensures their predominance over newer or less matured alternatives like flow or thermal storage, which are still in pilot phases.
By Application (Use‑Case)
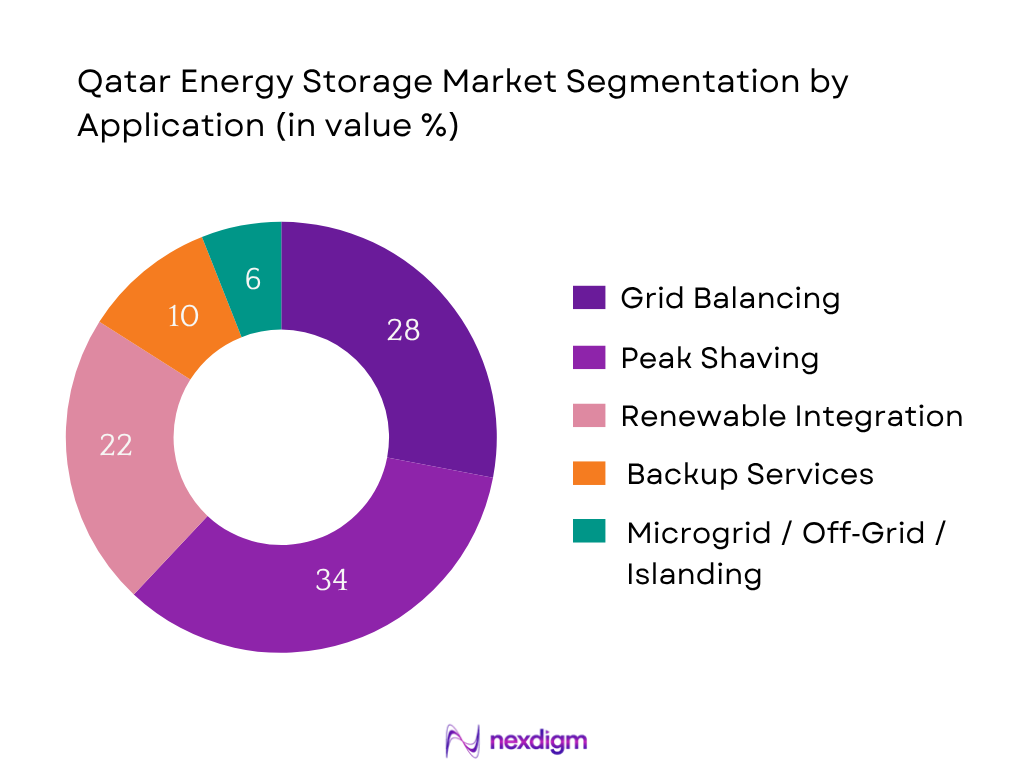
The Qatar energy storage market is segmented into grid balancing/frequency services, peak shaving / load shifting, renewable integration smoothing, backup / black start, and microgrid/off‑grid. In 2024, peak shaving / load shifting holds the largest share (~34%) because of the high daytime load demand and the steep tariff differentials between base and peak periods in Qatar. Operators and utilities prioritize using storage to shift excess generation to peak hours, reduce peak generator dispatch, and flatten demand curves. This use case gives the clearest economic payback in the near term, whereas full grid services or black start functions are ancillary and less frequent.
Competitive Landscape
The Qatar energy storage sector is highly concentrated with a few global and regional players dominating project awards, partnerships with utilities, and system integration contracts. This environment reflects the high technical barriers, capital intensity, and need for trusted track records. Local utilities (e.g. Kahramaa) and major developers tend to partner only with firms offering strong warranties, performance guarantees, and financing support, further reinforcing dominance by established companies.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Portfolio | Presence / Projects in Qatar / GCC | System ASP (USD / kWh) | Finance Model (CAPEX / ESaaS / Leasing) | Local Partnerships / JV | O&M & Degradation Guarantees |
| Tesla | 2003 | USA | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Fluence (Siemens/AES) | 2018 | USA / Germany | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Huawei Digital Power | 1987 | China | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| LG Energy Solution | 1970 | South Korea | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| ABB | 1883 | Switzerland | – | – | – | – | – | – |
Qatar Energy Storage Market Analysis
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Renewable Penetration and Curtailment Risks
Qatar has recently increased its solar generation deployment: by end‑2024, solar capacity reached approximately 1,780 MW out of a total 12 GW generating capacity, representing about 13 % of capacity attributed to solar projects. Meanwhile, renewables currently account for 5 % of the national electricity mix. As more solar is added, the risk of curtailment of surplus generation during midday hours becomes real. Energy storage systems help absorb such excess energy and inject it during demand peaks. Because Qatar is planning to scale its centralized renewables to 4,000 MW by 2030, this increasing penetration directly forces demand for storage to balance oversupply periods and integrate renewables reliably.
Government Mandates and Energy Diversification Targets
Qatar’s National Renewable Energy Strategy sets a goal to elevate renewables’ share from 5 % currently to 18 % of its electricity mix by 2030. The country is also targeting emissions reductions (25 % below business-as-usual baseline) and reduced carbon intensity of power generation by 27 % by 2030. These mandates signal strong governmental commitment, which underpins regulatory frameworks, tenders, subsidies, and preferential procurement for storage systems tied to renewable projects. Project developers seeking to comply must incorporate storage to meet dispatchability and grid integration criteria under the mandates.
Key Market Challenges
High Initial Investment and Long Payback Periods
The upfront cost of deploying storage systems (including battery modules, inverters, wiring, civil works) remains high relative to conventional grid assets. Because per‑kWh battery pack costs are declining but still significant, many project sponsors face multi‑year payback periods. In Qatar, as solar becomes 13 % of capacity and renewables expand, storage must often piggyback on solar tenders, but those tenders may not fully reimburse storage cost. Without time-of-use tariffs or capacity payments, many projects cannot recover investment quickly. Investors must weigh capital risk, particularly for systems that may only operate a few cycles daily.
Technical Barriers (Thermal Runaway, BMS Complexity)
Lithium‑ion batteries carry risks of thermal runaway and require advanced Battery Management Systems (BMS). In hot climates like Qatar, ambient temperatures often exceed 45 °C, requiring robust thermal control and cooling systems, thereby increasing BoS costs. Degradation accelerates in high-heat environments. Integration complexity for grid interconnection, synchronization, protection, and cascading fault modes adds design risk. Such technical challenges raise barriers for newcomers without experience in extreme climates.
Emerging Opportunities
Virtual Power Plants and Aggregated BTM Storage
In Qatar’s industrial and commercial sectors, interest in aggregating behind‑the‑meter (BTM) storage into virtual power plants (VPPs) is rising. With over USD 666.67 million of clean energy investment in 2023, investors are already funding platforms for distributed energy resources. By pooling distributed storage units across facilities, VPPs can bid into grid services markets, provide frequency support, and offer peak load flexibility. This creates scalable revenue streams for storage owners not tied to single-site performance. As grid operators seek distributed flexibility, VPP-enabled storage becomes a compelling growth vector.
Hydrogen Integration and Power‑to‑X Applications
Qatar’s established LNG and petrochemical sectors create synergy for hydrogen-based applications. With vast natural gas infrastructure and electrolysis potential, storage integrated with hydrogen (power-to-gas) projects can store excess renewable energy as hydrogen or ammonia. Though deployment is nascent, companies are evaluating hydrogen storage as a grid-scale long-duration option. The existing gas infrastructure and demand for low-carbon hydrogen in industry offers a pathway for storage firms to diversify beyond batteries, particularly as battery recycling and EoL challenges loom.
Future Outlook
Over the coming years, the Qatar energy storage market is expected to surge, fueled by accelerating solar deployment, utility-scale grid modernization, and supportive national energy strategies. Storage will increasingly serve as the backbone for more flexible, resilient power systems, enabling higher renewable penetrations, improved reliability, and cost arbitrage. The policy and regulatory regime are likely to evolve to support capacity markets, time-of-use tariffs, and incentives for energy storage assets. Looking forward to 2024–2030, the market is anticipated to achieve sustained double- to triple‑digit growth in installed MWh annually. Technologies such as second-life EV batteries, hybrid solar + storage systems, and grid-edge aggregation (virtual power plants) will gain traction. Competitive pressure may compress system costs, while deeper localization (assembly, testing) could enhance project viability. The market will also gradually open to new use cases such as hydrogen storage, longer-duration storage, and cross-border energy exchange across GCC grids.
Major Players
- Tesla
- Fluence (AES / Siemens)
- Huawei Digital Power
- LG Energy Solution
- ABB
- CATL
- Samsung SDI
- BYD
- Panasonic
- Schneider Electric
- Hitachi Energy
- Enerwhere (UAE)
- Siemens Energy
- Enel X
- Wärtsilä
Key Target Audience
- Utilities and Independent Power Produers (IPP)
- National grid operator (Kahramaa / Qatar Electricity & Water Corporation)
- Electric transmission & distribution companies
- Solar & renewable energy project developers
- Energy storage system integrators / EPC firms
- Investments and venture capital firms (investing in energy / cleantech)
- Government & regulatory bodies (Ministry of Energy, Qatar Energy, Qatar National Vision agencies)
- Large industrial, petrochemical, and O&G companies with captive power needs
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
In the initial phase, we develop a stakeholder ecosystem map (utilities, developers, integrators, regulators) and compile critical variables—such as installed capacity, ASP, system costs, degradation rates—from both global and regional databases and desk research.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We collect historical deployment data, cost trends, tender awards, and project pipelines. We model revenue and capacity growth by technology, use case, and geography, validating with published reports and secondary sources.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Key hypotheses (cost declines, adoption curves, business models) are validated via structured interviews (phone / video) with industry experts—utilities, OEM leaders, project financiers—across the Gulf region, especially Qatar.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We merge bottom‑up estimates (project-level build‑ups) with top‑down regional forecasts, reconcile discrepancies, and derive final estimates. Then we produce the narrative, tables, charts, and competitive intelligence for the Qatar storage market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Market Definition and Taxonomy
- Evolution and Transformation of Qatar’s Power Mix
- Timeline of Major Energy Storage Deployments
- Role of Energy Storage in Qatar National Vision and Sustainability Strategy
- Value Chain and Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Key Growth Drivers
Rising Renewable Penetration and Curtailment Risks
Government Mandates and Energy Diversification Targets
Declining Lithium-Ion Battery Prices and Modular Technologies
Grid Stability Needs and Peak Load Management
Industrial and Commercial Energy Cost Optimization - Key Market Challenges
High Initial Investment and Long Payback Periods
Technical Barriers (Thermal Runaway, BMS Complexity)
Regulatory Gaps and Absence of Time-of-Use Tariffs
Limited Local Manufacturing of Components
Energy Storage Waste Management and EoL Recycling - Emerging Opportunities
Virtual Power Plants and Aggregated BTM Storage
Hydrogen Integration and Power-to-X Applications
Local Assembly & System Integrator Ecosystem
Second-Life EV Battery Repurposing
Smart Grid Modernization and AI Integration - Trends
Digital Twin & Predictive Maintenance
Containerized / Plug-and-Play Storage
Hybrid Solar+Storage Deployment by Qatari Utilities
Strategic Alliances and Technology Transfers
Integration with EV Charging Infrastructure - Government Regulation
Net Metering, Storage Incentives, and Project Approvals
Role of KAHRAMAA and QEERI in Storage Policy
National Deployment Targets Under Vision 2030 - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Mapping (Utilities, EPCs, IPPs, OEMs, Storage Aggregators)
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Ecosystem Map (Startups, Integrators, Manufacturers)
- By Installed Capacity (MWh), 2019-2024
- By Energy Output (MW), 2019-2024
- By Revenue (QAR/ USD Million), 2019-2024
- By Average System Cost (USD/kWh), 2019-2024
- By System Utilization Metrics (Round-Trip Efficiency, Depth of Discharge, Cycle Life), 2019-2024
- By Technology Type (In Value %)
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Sodium-Sulfur Batteries
Redox Flow Batteries
Pumped Hydro Storage
Compressed Air and Thermal Storage - By Application (In Value %)
Frequency Regulation
Peak Shaving and Load Shifting
Renewable Energy Integration
Backup & Black Start Services
Microgrid / Off-Grid Systems - By Business Model (In Value %)
Utility-Owned Storage
Third-Party / ESaaS (Energy Storage-as-a-Service)
Hybrid / Co-Ownership Models
Customer-Owned / Behind-the-Meter - By Connection Type (In Value %)
On-Grid (Utility Scale)
Off-Grid (Isolated Systems)
Hybrid (Solar + Storage, Grid + Diesel) - By Storage Capacity Tier (In Value %)
≤1 MWh
1–10 MWh
10–50 MWh
>50 MWh
- Market Share Analysis by Installed Capacity and Revenue
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Installed Projects in Qatar / GCC (MWh/MW), Technology Portfolio (Li-ion, Flow, Others), System ASP (USD/kWh), Depth of Integration (BMS, EMS, Control Stack), Partnerships and Local Collaborations, Revenue by Business Model (CAPEX, ESaaS, Leasing), O&M Cost and System Lifecycle Metrics, Local Manufacturing / Assembly Presence)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Competitors
- Qatar Project Pricing Benchmarks (Tech & Size Wise)
- Detailed Company Profiles
Tesla
Fluence
Huawei Digital Power
Samsung SDI
LG Energy Solution
CATL
Wärtsilä
ABB
Siemens Energy
Sungrow Power Supply Co.
Panasonic
Schneider Electric
Hitachi Energy
BYD Co.
Enerwhere (UAE-based storage EPC active in Qatar)
- Power Utilities and IPPs
- Industrial & Oil & Gas Sector Integration
- Commercial Facilities and Real Estate (Data Centers, Malls)
- Residential Smart Energy Use Cases
- Energy Storage for Defense, Airports, and Special Zones
- By Installed Capacity (MWh), 2025-2030
- By Energy Output (MW), 2025-2030
- By Revenue (QAR/ USD Million), 2025-2030
- By Average System Cost (USD/kWh), 2025-2030
- By System Utilization Metrics (Round-Trip Efficiency, Depth of Discharge, Cycle Life), 2025-2030


