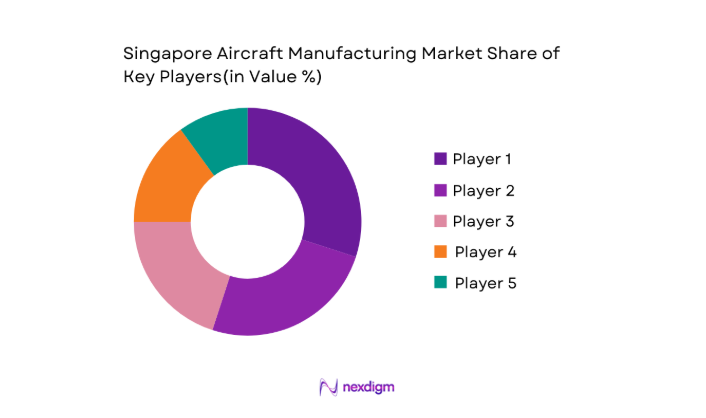
Market Overview
The Singapore aircraft manufacturing market is valued at approximately USD ~ in 2024. This market’s growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for aircraft in the Asia-Pacific region, with airlines, leasing companies, and defense contractors expanding their fleets to meet growing passenger and cargo traffic. Singapore’s strategic location as a key global aviation hub, backed by robust government policies and a growing MRO ecosystem, significantly contributes to its market size. Additionally, the rise of electric and hybrid aircraft and sustainable aviation technologies is expected to further stimulate market growth.
Singapore is one of the key players in the global aircraft manufacturing market due to its well-established aerospace ecosystem. The nation serves as a base for top international OEMs like Rolls-Royce, Pratt & Whitney, and Boeing, which have manufacturing and R&D operations in the region. Singapore’s dominance is attributed to its highly skilled workforce, world-class infrastructure, and government initiatives such as the Singapore Aerospace Industry Strategy and Seletar Aerospace Park. Additionally, regional competition from countries like China and South Korea is rising but Singapore remains ahead due to its advanced MRO capabilities and strategic location in Southeast Asia.
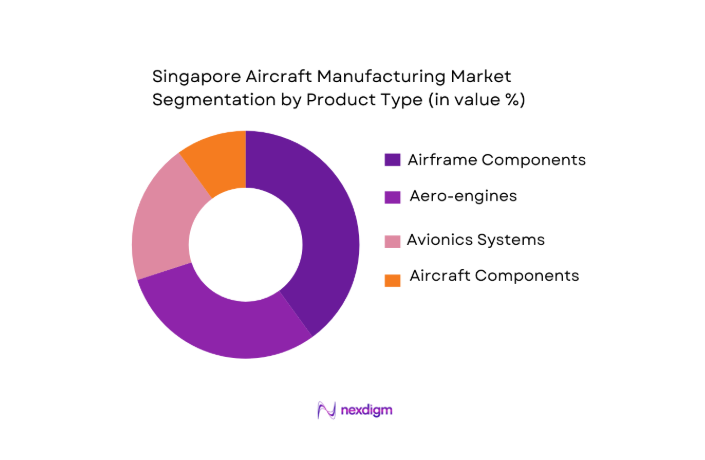
Market Segmentation
By Product Type
The Singapore aircraft manufacturing market is segmented by product type into airframe components, aero-engines, avionics systems, and aircraft components and subsystems. Among these, airframe components dominate the market share in 2024, accounting for nearly ~. This is primarily due to the strong presence of major OEMs and their focus on airframe assembly, particularly in the growing commercial aircraft segment. Companies such as ST Engineering are key players, capitalizing on the demand for both lightweight and composite materials used in airframe production. With the increase in air travel and expansion of fleets across the Asia-Pacific region, airframe production remains a critical part of Singapore’s aerospace manufacturing.
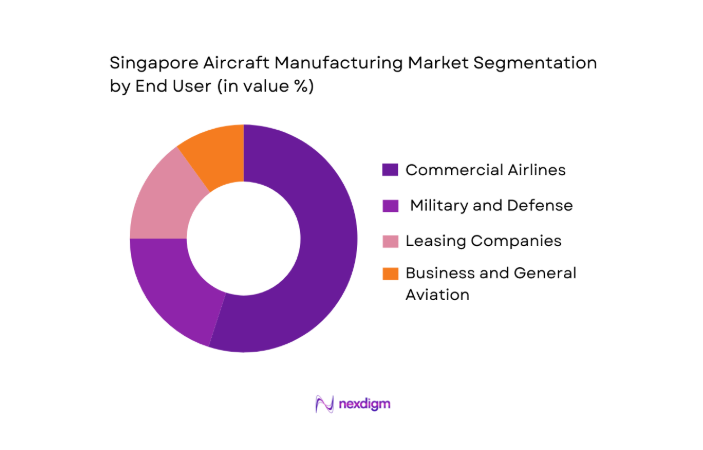
By End User
The market is also segmented by end users, including commercial airlines, military and defense, leasing companies, and business and general aviation. Commercial airlines take the largest share in 2024, at around ~, due to Singapore’s strong air traffic market, led by Singapore Airlines, Scoot, and other regional carriers. The increase in regional travel, supported by Singapore’s aviation infrastructure, has created a robust demand for commercial aircraft. Moreover, Singapore’s commitment to supporting sustainable aviation technologies, such as green aircraft and SAF (sustainable aviation fuel), adds to the attractiveness for airlines seeking to upgrade their fleets.
Competitive Landscape
The Singapore aircraft manufacturing market is highly competitive with both global giants and local players competing for market share. The key market players include multinational manufacturers like Boeing, Airbus, Rolls-Royce, and Pratt & Whitney, alongside strong local contenders such as ST Engineering. These companies benefit from Singapore’s strategic location, world-class manufacturing and repair facilities, and a skilled workforce. Singapore’s aerospace ecosystem is integral to the growth of the Asia-Pacific aviation market, making it an attractive region for aircraft production and servicing.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Core Area of Operation | Market Focus | R&D Investment | Manufacturing Facilities | Strategic Partnerships |
| ST Engineering | 1967 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rolls-Royce Singapore | 1953 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Pratt & Whitney | 1925 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Boeing Singapore | 1950 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Airbus Singapore | 1976 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Singapore Aircraft Manufacturing Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Asia-Pacific Air Travel Rebound & Fleet Modernization Demand
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to see robust growth in air traffic, with the International Air Transport Association (IATA) forecasting that the region will contribute to approximately 40% of global air traffic by 2026. This surge is fueled by an expanding middle class and increasing disposable incomes in key markets such as China and India. According to the World Bank, India’s middle class is projected to grow by over ~ people by 2026, fueling demand for both domestic and international travel. The increased demand for air travel is directly contributing to a rise in fleet modernization. Airlines are investing heavily in modernizing their fleets to meet passenger demands and reduce operating costs, particularly by acquiring fuel-efficient aircraft. For instance, Singapore Airlines has already committed to increasing its fleet of the Airbus A350s to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions in response to growing passenger demand.
Strategic Location as APAC Aerospace Hub
Singapore’s strategic location in the Asia-Pacific region as a global aviation and aerospace hub continues to make it an attractive destination for aircraft manufacturing. The Republic of Singapore is home to some of the world’s busiest airports, with Changi Airport handling over ~ passengers annually, according to the Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore (CAAS). Furthermore, Singapore’s aerospace manufacturing sector benefits from its world-class infrastructure, including the Seletar Aerospace Park, which hosts over 130 companies involved in aviation manufacturing, MRO services, and engineering. This cluster is set to grow even more, with the Singapore Economic Development Board (EDB) aiming to further enhance its aerospace capabilities by 2025 through collaboration with global manufacturers, like Rolls-Royce and Boeing, to drive growth in aircraft assembly and MRO activities. The regional growth in air traffic and Singapore’s strategic location within Southeast Asia further solidify its role as a hub for aerospace operations.
Market Challenges
High Operating Costs
Singapore’s aircraft manufacturing market faces significant challenges due to high operating costs, which are influenced by factors such as labor, real estate, and compliance with stringent environmental regulations. In 2024, the World Bank projected that Singapore’s labor costs would increase by approximately ~ annually, further elevating the financial burden on manufacturers. Real estate costs in key industrial zones like Jurong and Seletar remain high, with industrial space costing around SGD ~ per square foot in prime areas, as reported by the Urban Redevelopment Authority (URA). Additionally, the country’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions requires aircraft manufacturers to invest heavily in compliance with environmental standards, further increasing operational costs. These high operating expenses, particularly in comparison with neighboring countries such as Malaysia and Thailand, could limit the competitiveness of local manufacturers, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Supply chain disruptions remain a key challenge for the Singapore aircraft manufacturing sector, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. The global semiconductor shortage, which affected the production of avionics and flight control systems in 2024, has highlighted vulnerabilities in the supply chain. The Singapore Economic Development Board (EDB) reported that while local aerospace manufacturers have diversified suppliers, ~ of parts and materials still rely on imports from countries like China and the United States. This dependence on external suppliers for critical components exposes manufacturers to potential delays in production and cost inflation. Additionally, the rising cost of raw materials, including titanium and aluminum, further exacerbates the challenges in maintaining supply chain efficiency. The issue is expected to persist in 2025, impacting both the OEM and MRO segments.
Market Opportunities
OEM Assembly Joints with Global Manufacturers
A significant opportunity for Singapore’s aircraft manufacturing market lies in the increasing number of OEM assembly joint ventures with global manufacturers. Leading players like Rolls-Royce and Boeing have set up production facilities in Singapore to take advantage of its strategic location, skilled workforce, and favorable business environment. This trend is supported by the government’s initiatives to attract foreign investment in aerospace manufacturing. In 2024, Boeing expanded its Singapore facility for the assembly of the 787 Dreamliner, while Rolls-Royce continues to increase production capabilities for its Trent engines. Singapore’s Aerospace Industry Transformation Map, launched by the Economic Development Board, aims to drive these collaborations further, with over SGD ~ expected to be invested into the aerospace sector by 2026. These joint ventures will provide a competitive edge in accessing both domestic and global markets while driving technological innovations in aircraft production.
Growth in UAV/UAS & Space-borne Tech Integration
The growing integration of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles and space-borne technologies presents a significant market opportunity for Singapore’s aerospace sector. The Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore (CAAS) forecasts that the use of UAVs will increase by over ~ annually from 2024 to 2026, driven by applications in defense, surveillance, and logistics. Additionally, Singapore is positioning itself as a leader in space tech, with the establishment of the Singapore Space and Technology Association and a focus on satellite manufacturing. The local space industry is expected to see significant growth, fueled by government support and partnerships with international space agencies like NASA and ESA. As these technologies mature, Singapore’s aircraft manufacturers are poised to capitalize on opportunities in UAV/UAS production and space-based technologies, particularly in providing components and systems for satellite communication, data transfer, and remote sensing.
Future Outlook
Over the next decade, the Singapore aircraft manufacturing market is expected to continue its steady growth trajectory. This is driven by the expansion of Asia-Pacific’s aviation sector, particularly as travel demand in the region continues to rise. Additionally, advancements in aerospace technology, such as electric aircraft and sustainable aviation fuel, will likely enhance Singapore’s position as a key player in green aviation. With the government’s continued support for aerospace development and a growing focus on R&D, the market is poised for robust growth, particularly in the manufacturing of new-generation aircraft and related technologies.
Major Players
- ST Engineering
- Rolls-Royce Singapore
- Pratt & Whitney
- Boeing Singapore
- Airbus Singapore
- Singapore Airlines Engineering Company
- Honeywell Aerospace
- GE Aviation
- Safran Aircraft Engines Asia
- Collins Aerospace
- Textron Aviation
- Embraer
- COMAC
- L3 Harris Technologies
- UTC Aerospace Systems
Key Target Audience
- Aircraft Manufacturers
- Airlines
- Aircraft Leasing Companies
- Aerospace Component Suppliers
- Aviation Regulatory Bodies
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Aerospace Technology Developers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
In this phase, we create an ecosystem map of all major stakeholders in the Singapore aircraft manufacturing market, including OEMs, MRO providers, regulators, and end-users. This step is powered by secondary research, utilizing databases such as industry reports, government publications, and trade associations. The goal is to identify and define key market drivers, challenges, and opportunities.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Here, we analyze historical market data, including production volumes, revenue figures, and the growth rate of key product categories. This is followed by a thorough assessment of market penetration rates, the competition landscape, and revenue generation in each segment. Service quality assessments and trends in customer demand are also evaluated.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We develop hypotheses based on market dynamics and test them through interviews with industry experts, including manufacturers, suppliers, and airline executives. These consultations provide real-time operational insights, validating and refining our assumptions to ensure data accuracy and reliability.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
This phase involves synthesizing findings from primary and secondary research into a coherent narrative. We engage with market leaders to gather detailed insights into product innovations, future technology trends, and emerging market opportunities. This research is verified against secondary data, including market forecasts and trend analysis, to finalize the report’s findings.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and scope
- Market dynamics
- Historical overview
- Timeline
- Growth Drivers
Asia‑Pacific air travel rebound & fleet modernisation demand
Strategic location as APAC aerospace hub
MRO ecosystem dominance & transition to high‑value manufacturing - Market Challenges
High operating costs
Supply chain vulnerabilities - Opportunities
OEM assembly joints with global manufacturers
Growth in UAV/UAS & space‑borne tech integration - Trends
Integration of advanced avionics & electrification readiness
Digital manufacturing & predictive maintenance - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2020-2025
- By volume, 2020-2025
- By average price, 2020-2025
- By Platform Type (In Value %)
Narrow‑body aircraft
Wide‑body aircraft
Business jets
Unmanned aerial vehicle - By Product Type (In Value %)
Airframe structures
Aero‑engines & nacelles
Avionics & flight control systems
Aircraft components & subsystems - By Value Chain Activity (In Value %)
Original Equipment Manufacturing
Tier‑1 manufacturing
Maintenance, Repair & Overhaul
Aftermarket services - By End User (In Value %)
Commercial airlines
Leasing companies
Military & defense aviation - By Technology Adoption (In Value %)
Additive manufacturing
Sustainable aircraft technologies
- Market Share of Major Players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Manufacturing footprint density, Aftermarket service network coverage, Certification status, R&D spend intensity, Digital manufacturing capability index, Supply chain integration depth)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing Analysis of Major Players
- Detailed Profile of Major Players
ST Engineering
Singapore Airlines Engineering Company
Rolls‑Royce Singapore
Pratt & Whitney Singapore
Safran Aircraft Engines Asia
GE Aerospace Singapore
Airbus Singapore Pte Ltd
Boeing
BOC Aviation
COMAC
Honeywell Aerospace
Collins Aerospace
L3Harris Technologies
Textron Aviation
Embraer
- Fleet Renewal Economics & Operating Cost Structures
- OEM Selection Criteria
- MRO vs New Build Decision Drivers
- Lease & Financing Considerations
- By Value, 2026-2035
- By Volume, 2026-2035
- By Average Price, 2026-2035