Market Overview
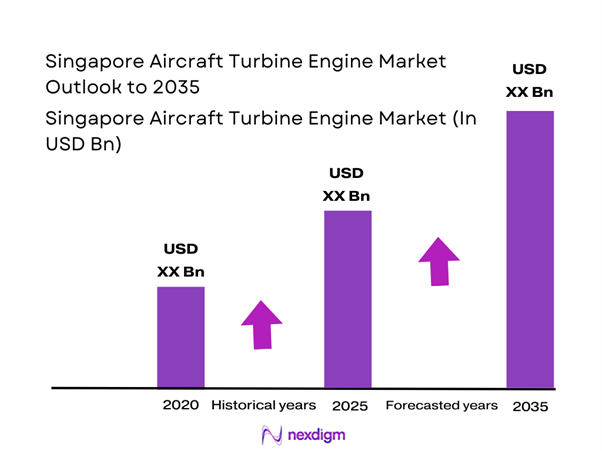
The Singapore aircraft turbine engine market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by steady aftermarket demand and strong regional engine servicing flows. In the most recent two years, the market recorded values of approximately USD ~ million and USD ~ million, reflecting sustained engine overhaul cycles and steady fleet utilization levels. Ongoing investments in advanced maintenance capabilities and digital engine monitoring platforms continue to reinforce Singapore’s role as a critical node in the Asia–Pacific aero-engine ecosystem.
Singapore’s dominance is shaped by the concentration of aerospace engineering infrastructure in Seletar and Changi aerospace zones, supported by a dense network of certified maintenance facilities and component repair specialists. High demand from regional carriers, combined with a mature ecosystem of training institutes and testing laboratories, strengthens operational depth. A stable policy environment, strong intellectual property protection, and streamlined regulatory frameworks further enhance the city-state’s attractiveness for global engine OEM partnerships and regional service headquarters.
Market Segmentation
By Fleet Type
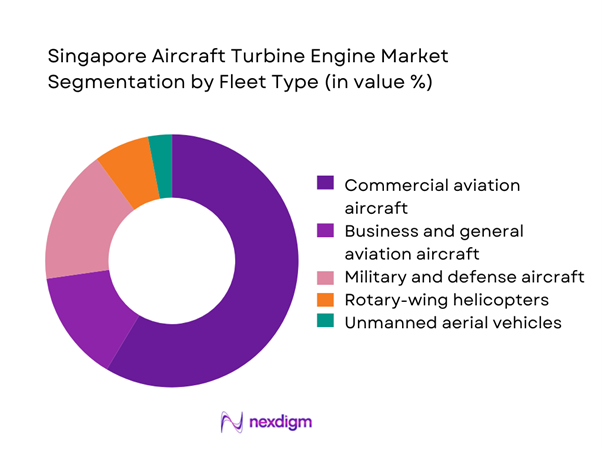
Commercial aviation aircraft dominate the Singapore aircraft turbine engine market due to the city-state’s role as a regional hub for airline operations and heavy maintenance. A large installed base of narrowbody and widebody fleets from Southeast Asian carriers sustains recurring demand for engine overhaul, spare modules, and performance upgrades. Business and general aviation contribute a smaller yet stable share, driven by charter operators and corporate fleets using Singapore as a technical base. Defense aircraft engines account for consistent long-term demand through structured maintenance contracts and modernization programs. Rotary-wing and unmanned platforms are emerging segments, supported by homeland security needs and offshore operations, but remain secondary in overall value contribution.
By Technology Architecture
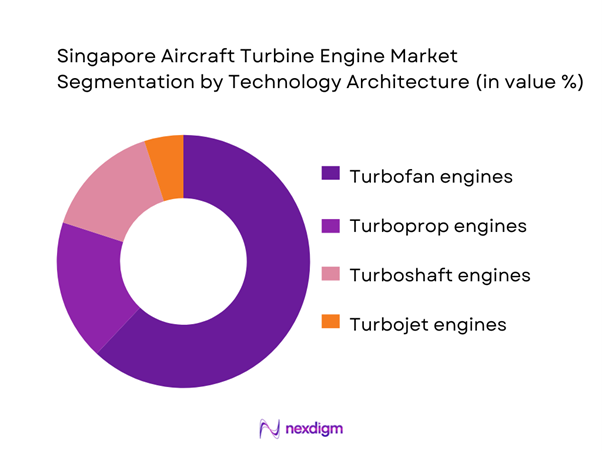
Turbofan engines represent the core of Singapore’s aircraft turbine engine market, reflecting the dominance of commercial airline fleets and the concentration of widebody and narrowbody maintenance programs. Turboprop engines hold a relevant position through regional connectivity aircraft and training fleets, particularly for operators serving secondary routes across Southeast Asia. Turboshaft engines support offshore energy transport, emergency medical services, and defense helicopter operations, generating steady service demand. Turbojet engines form a niche segment linked mainly to legacy military platforms and specialized test applications. The technology mix highlights Singapore’s positioning as a multi-platform engine service hub capable of supporting diverse propulsion architectures.
Competitive Landscape
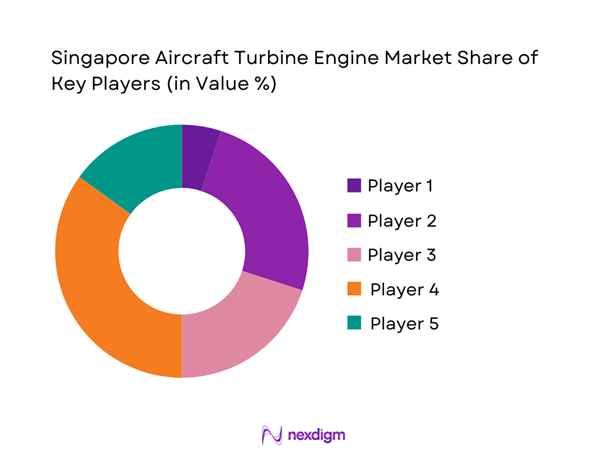
The Singapore aircraft turbine engine market is moderately concentrated, with a small group of global OEMs and leading MRO specialists shaping the competitive environment. Market leadership is defined by long-term airline service agreements, strong defense maintenance contracts, and deep integration into regional fleet support networks, creating high entry barriers for new participants.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Rolls-Royce Holdings | 1906 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GE Aerospace | 1917 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Pratt & Whitney | 1925 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Safran Aircraft Engines | 1945 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ST Engineering Aerospace | 1970 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Singapore Aircraft Turbine Engine Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of Singapore as a regional MRO hub for aero engines
The expansion of Singapore as a regional maintenance hub has driven sustained demand for turbine engine servicing, with annual engine shop visits exceeding ~ units in recent operating cycles. Between 2022 and 2025, the number of certified overhaul programs increased by ~ programs, while capital allocation for engine test facilities reached around USD ~ million. The presence of more than ~ certified technicians and inspectors has strengthened turnaround capacity, enabling operators to reduce average engine downtime by ~ days. This operational depth has translated into higher engine throughput volumes and consistent aftermarket revenue streams for service providers across the ecosystem.
Rising narrowbody fleet activity across Southeast Asia
The surge in narrowbody fleet utilization across Southeast Asia has directly supported turbine engine demand flows through Singapore. From 2022 to 2025, regional narrowbody flight cycles processed through Singapore-based MRO facilities increased by ~ cycles, while inducted engines for scheduled maintenance rose by ~ units. This activity generated service contract values of approximately USD ~ million over the same period. High aircraft utilization rates have accelerated wear patterns, shortening maintenance intervals and boosting demand for spare engines and modular replacements, reinforcing Singapore’s role as the primary engine servicing gateway for regional carriers.
Challenges
High capital cost of new-generation turbine engines
The elevated capital intensity of new-generation turbine engines presents a significant adoption barrier for operators and lessors. Acquisition values for advanced engines introduced between 2022 and 2025 averaged around USD ~ million per unit, with associated tooling and spares packages adding nearly USD ~ million per fleet. For MRO providers, investments in next-generation test cells and digital diagnostics required upfront commitments of roughly USD ~ million. These financial thresholds limit rapid fleet renewal and constrain smaller operators, leading to extended utilization of legacy engines and slowing the pace of technological transition across the market.
Stringent certification and airworthiness requirements
Compliance with evolving certification and airworthiness standards has increased operational complexity for engine operators and service centers. Between 2022 and 2025, regulatory audits and compliance programs expanded by ~ additional inspection cycles annually, while documentation requirements rose by ~ pages per engine program. Certification timelines for new repair capabilities now extend to ~ months, increasing time-to-market for advanced services. These regulatory pressures elevate administrative workloads and raise indirect operating costs by approximately USD ~ million per year for large MRO organizations, creating entry barriers for smaller service providers.
Opportunities
Engine overhaul and life-extension services for aging fleets
The growing population of aging aircraft fleets presents a major opportunity for engine overhaul and life-extension programs in Singapore. From 2022 to 2025, engines exceeding mid-life thresholds entering heavy maintenance increased by ~ units, generating service demand valued at roughly USD ~ million. Life-extension packages involving core refurbishment and module upgrades have added ~ additional flight cycles per engine on average, delaying costly replacements. This trend strengthens recurring service revenues for MRO providers while offering airlines capital efficiency, positioning Singapore as a preferred destination for long-term engine asset management strategies.
Regional demand for engine leasing and pooling solutions
Demand for flexible engine leasing and pooling solutions has accelerated across Southeast Asia, creating new commercial avenues for Singapore-based lessors and service firms. Between 2022 and 2025, pooled spare engine inventories expanded by ~ units, while short-term lease transactions generated approximately USD ~ million in annual contract value. Airlines increasingly rely on these models to mitigate downtime risks and balance cash flow constraints. Singapore’s strong legal framework and asset management expertise support the growth of these services, reinforcing its role as a regional center for engine asset optimization.
Future Outlook
The Singapore aircraft turbine engine market is expected to strengthen its regional leadership role through continued expansion of advanced MRO capabilities and deeper integration into global engine support networks. Ongoing fleet modernization across Asia–Pacific and rising defense aviation requirements will sustain long-term demand. Increased focus on sustainable propulsion technologies and digital maintenance platforms is likely to reshape service offerings. Singapore’s stable regulatory environment and strong aerospace ecosystem position the market for resilient growth through 2035.
Major Players
- Rolls-Royce Holdings
- GE Aerospace
- Pratt & Whitney
- Safran Aircraft Engines
- MTU Aero Engines
- Honeywell Aerospace
- IHI Corporation Aero Engines
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Aero Engines
- Aero Engine Corporation of China
- ST Engineering Aerospace
- SIA Engineering Company
- Lufthansa Technik
- SR Technics
- Safran Aircraft Engine Services Asia
- StandardAero
Key Target Audience
- Commercial airline fleet operators
- Business aviation and charter service providers
- Aircraft and engine leasing companies
- Aerospace maintenance, repair, and overhaul organizations
- Defense ministries and air force logistics commands
- Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore and Ministry of Transport agencies
- Engine component suppliers and system integrators
- Investments and venture capital firms focused on aerospace and mobility
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market boundaries were defined around turbine engine manufacturing, maintenance, and aftermarket services. Core variables included fleet activity levels, engine life cycles, and service interval dynamics. Regulatory, technological, and operational factors influencing demand patterns were mapped to ensure a holistic market framework.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Quantitative modeling was conducted using fleet utilization trends, maintenance cycle benchmarks, and capacity expansion indicators. Demand scenarios were developed across commercial, defense, and business aviation segments. Market structure was validated through operational capacity assessments and ecosystem mapping.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Industry hypotheses were reviewed through structured consultations with aerospace engineers, maintenance managers, and regulatory specialists. Feedback loops were used to refine assumptions on service growth, technology adoption, and policy impact. Validation ensured alignment with real-world operational conditions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated into a coherent analytical framework linking demand drivers, constraints, and opportunity areas. Strategic implications were drawn for stakeholders across the value chain. The final report integrates quantitative insights with qualitative market intelligence for decision-ready outputs.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, aircraft turbine engine taxonomy across commercial business and military aviation, market sizing logic by fleet size and engine delivery cycles, revenue attribution across engine sales spares and MRO services, primary interview program with airlines OEMs MROs and lessors, data triangulation validation assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and scope
- Market evolution
- Engine usage and maintenance pathways
- Aerospace ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and aftermarket channels
- Regulatory and certification environment
- Growth Drivers
Expansion of Singapore as a regional MRO hub for aero engines
Rising narrowbody fleet activity across Southeast Asia
Increased defense spending and fleet modernization programs
Growth in business aviation and charter services
Adoption of fuel-efficient next-generation engines
Strong government support for aerospace manufacturing and services - Challenges
High capital cost of new-generation turbine engines
Stringent certification and airworthiness requirements
Dependence on global OEM supply chains
Skilled labor shortages in advanced engine maintenance
Long replacement cycles of installed engine base
Exposure to cyclical downturns in commercial aviation - Opportunities
Engine overhaul and life-extension services for aging fleets
Regional demand for engine leasing and pooling solutions
Adoption of sustainable aviation fuel compatible engines
Digital twin and predictive maintenance solutions
Participation in global engine component manufacturing programs
Growth in Asia-Pacific military aviation procurement - Trends
Shift toward geared turbofan and ultra-high bypass engines
Increasing role of Singapore in global engine MRO networks
Integration of AI-driven engine health monitoring
Rising localization of engine component repair capabilities
Focus on lower-emission propulsion technologies
Expansion of training academies for aero-engine specialists - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Commercial aviation aircraft
Business and general aviation aircraft
Military and defense aircraft
Rotary-wing helicopters
Unmanned aerial vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Fixed-wing propulsion
Rotary-wing propulsion
Auxiliary power units
Special mission aircraft propulsion
Training and light aircraft propulsion - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Turbofan engines
Turbojet engines
Turboprop engines
Turboshaft engines - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Commercial airline operators
Defense and government aviation units
Business jet and charter operators
MRO and overhaul service providers
Aircraft and engine OEMs - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
FADEC-enabled connected engines
Condition-based monitoring enabled engines
Digitally integrated fleet management engines
Partially connected legacy engines
Non-connected legacy engines - By Region (in Value %)
Central Singapore aerospace cluster
East Singapore aviation zone
North Singapore industrial corridor
West Singapore logistics and engineering belt
Seletar Aerospace Park
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (engine thrust range, fuel efficiency metrics, lifecycle maintenance cost, MRO turnaround time, digital monitoring capability, local support presence, certification coverage, sustainability compliance)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Rolls-Royce Holdings
GE Aerospace
Pratt & Whitney
Safran Aircraft Engines
MTU Aero Engines
Honeywell Aerospace
IHI Corporation Aero Engines
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Aero Engines
Aero Engine Corporation of China
ST Engineering Aerospace
SIA Engineering Company
Lufthansa Technik
SR Technics
Safran Aircraft Engine Services Asia
StandardAero
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


