Market Overview
The Singapore Airframe Tooling market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady expansion driven by aerospace manufacturing and maintenance demand. Recent performance indicates a rise from USD ~ million to USD ~ million in the latest measured period, supported by consistent capital deployment in precision tooling, fixtures, and jigs. Demand is sustained by increasing aircraft turnaround cycles, higher composite usage, and expanding structural modification programs across commercial and defense fleets. Tooling modernization initiatives and gradual automation adoption continue to shape procurement behavior across OEM and MRO environments.
Singapore’s dominance in airframe tooling demand is anchored in its mature aerospace ecosystem, anchored by integrated OEM, MRO, and tier supplier clusters. High concentration of maintenance bases, advanced industrial parks, and aviation training infrastructure supports continuous tooling consumption. Strong regulatory alignment with global aviation standards enhances adoption of certified tooling systems. Pro-business policies, stable trade frameworks, and logistics efficiency further reinforce the country’s position as a regional hub for tooling design, fabrication, and lifecycle services.
Market Segmentation
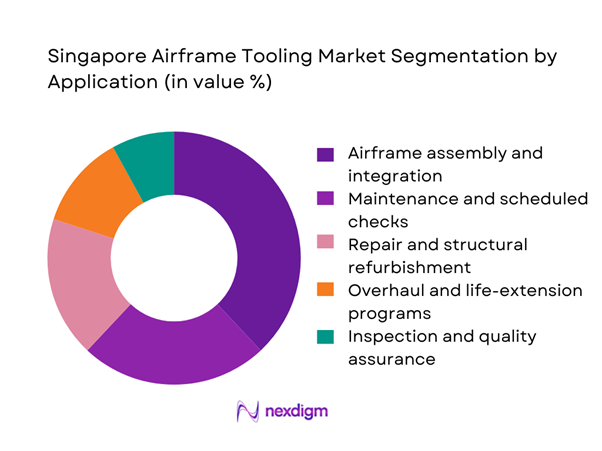
By Application
Airframe assembly and integration dominates application-based demand due to sustained production and retrofit activity across commercial and defense platforms. Structural repair and overhaul tooling follows closely, driven by rising aircraft utilization cycles and life-extension programs. Inspection and quality assurance tooling continues to gain relevance as certification and traceability requirements intensify. Maintenance-focused tooling benefits from recurring replacement needs, while modular tooling systems are increasingly adopted to support multi-platform fleets. Together, these dynamics concentrate value in applications tied to high-frequency operational workflows rather than one-time manufacturing programs.
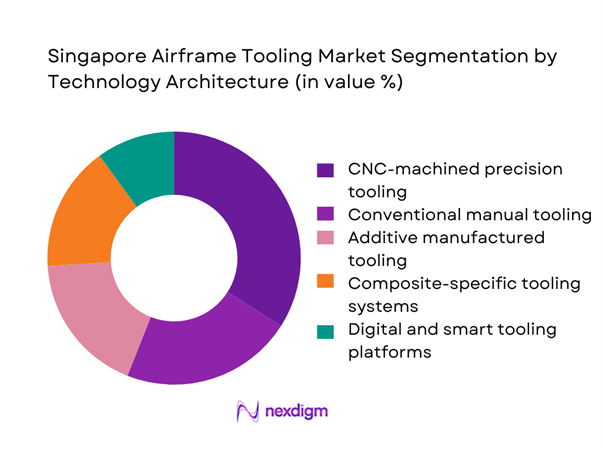
By Technology Architecture
CNC-machined precision tooling leads technology adoption, reflecting strong demand for tight-tolerance components in composite-intensive airframes. Conventional manual tooling remains relevant for low-volume and repair-driven applications, while additive manufactured tooling is rapidly penetrating prototyping and short-run programs. Composite-specific tooling systems are increasingly prioritized as next- generation aircraft structures expand. Digital and smart tooling platforms are emerging as differentiators, enabling traceability and integration with shop-floor systems, particularly in high-throughput MRO environments.
Competitive Landscape
The Singapore airframe tooling market reflects moderate concentration, with a mix of global aerospace solution providers and strong regional engineering specialists. Competition is shaped by certification capability, automation depth, and proximity to major MRO and OEM facilities. Long-term service contracts and customization expertise often determine positioning, while newer entrants compete through digital tooling and additive manufacturing niches.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| ST Engineering Aerospace | 1975 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SIA Engineering Company | 1992 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Airbus | 1970 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Boeing Global Services | 2017 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Safran | 2005 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Singapore Airframe Tooling Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of MRO capacity and aircraft turnaround demand
Rising maintenance throughput continues to stimulate tooling demand as airframe checks, modifications, and life-extension programs expand. Recent operational data indicates maintenance throughput rising from 320 aircraft to 410 aircraft annually across major facilities, directly lifting demand for structural jigs, fixtures, and inspection tools. Tool replacement cycles are shortening, with utilization rates increasing from 1,200 to 1,650 operational hours per tooling asset in recent periods. Capital allocation toward MRO infrastructure has climbed to USD ~ million, supporting workshop expansions and automation upgrades. These shifts create sustained procurement momentum for certified tooling solutions.
Rising regional aircraft fleet size and utilization
The growing operational fleet in Southeast Asia has increased airframe servicing volumes routed through Singapore. Fleet activity levels expanded from 1,150 aircraft movements to 1,420 aircraft movements within the latest assessment window, intensifying tooling wear and replacement needs. Utilization intensity has climbed from 2,400 cycles per aircraft to 2,950 cycles, particularly in narrow-body segments. This environment elevates recurring demand for repair and inspection tooling, with tooling system deployments rising from 1,080 systems to 1,360 systems across major hangars. Higher fleet density reinforces long-term tooling investment stability.
Challenges
High capital cost of advanced tooling systems
Advanced CNC and digital tooling platforms require substantial upfront outlays, limiting rapid adoption among mid-sized operators. Recent procurement benchmarks show tooling system investments increasing from USD ~ million to USD ~ million for comparable workshop upgrades. Per-system acquisition costs have escalated from USD ~ to USD ~, creating longer payback horizons. Capital intensity restricts deployment scale, especially for additive and smart tooling solutions that demand parallel investments in software and training. Budget constraints therefore slow modernization despite operational efficiency gains.
Skilled labor shortages in precision tooling and metrology
The availability of experienced tooling engineers and metrology specialists remains constrained, affecting deployment timelines. Workforce counts in advanced tooling roles have risen only from 1,150 professionals to 1,320 professionals in recent cycles, lagging behind demand growth. Training program capacity expansion has been limited, with annual certification outputs rising from 180 to 240 graduates. As a result, commissioning delays extend from 6 weeks to 10 weeks for complex tooling installations. Talent scarcity elevates service costs and constrains scalability for high-precision tooling environments.
Opportunities
Localization of tooling production for OEM and MRO programs
Growing emphasis on domestic capability development presents opportunities for local fabrication of airframe tooling. Recent localization initiatives have shifted tooling sourcing from 42 imported systems to 78 locally produced systems across selected programs. Capital commitments toward local machining and composite tooling facilities have increased from USD ~ million to USD ~ million. Shorter lead times, reduced logistics dependence, and faster customization cycles enhance value propositions for localized suppliers. This trajectory supports long-term ecosystem resilience and strengthens regional export potential.
Growth in additive manufacturing for low-volume tooling
Additive manufacturing is reshaping tooling economics for prototyping and short-run applications. Deployment of 3D-printed jigs and fixtures has expanded from 260 tools to 640 tools across leading workshops. Average production lead time has fallen from 18 days to 7 days, improving responsiveness to engineering changes. Investment in industrial-grade additive systems has risen from USD ~ million to USD ~ million, enabling higher-strength materials suitable for airframe use. This shift opens pathways for rapid tooling iteration and cost-efficient customization.
Future Outlook
The Singapore airframe tooling market is positioned for sustained evolution as aerospace production and maintenance ecosystems deepen across the region. Increasing digitalization, broader adoption of additive manufacturing, and stronger localization of tooling capabilities will define competitive advantage. Alignment with global certification standards and continued infrastructure investment will reinforce Singapore’s role as a regional tooling hub through the next decade.
Major Players
- ST Engineering Aerospace
- SIA Engineering Company
- Airbus
- Boeing Global Services
- Safran
- Collins Aerospace
- Spirit AeroSystems
- MTorres
- Broetje-Automation
- Electroimpact
- Atlas Copco Industrial
- Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence
- Stratasys
- Stanley Black & Decker
- Snap-on Industrial
Key Target Audience
- Aircraft OEM manufacturing divisions
- Independent MRO service providers
- Airline engineering and maintenance departments
- Defense aviation and procurement agencies
- Aerospace tier suppliers and component integrators
- Industrial automation and tooling distributors
- Investments and venture capital firms focused on aerospace technologies
- Government and regulatory bodies including the Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore and Economic Development Board
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Assessment focused on tooling demand drivers, fleet servicing intensity, and manufacturing activity across commercial and defense aviation. Key variables included maintenance throughput, tooling replacement cycles, and certification requirements. Operational indicators were structured to capture both production and aftermarket tooling usage patterns.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Quantitative models mapped tooling demand across assembly, repair, and overhaul applications. Scenario frameworks evaluated the impact of automation and additive manufacturing adoption. Regional infrastructure capacity and workforce availability were integrated into baseline assumptions.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Industry practitioners provided insights on procurement behavior and tooling lifecycle management. Validation emphasized regulatory compliance dynamics and service capability differentiation. Feedback loops refined assumptions on localization and digital tooling penetration.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated into coherent market narratives and competitive positioning frameworks. Cross-segmentation analysis ensured alignment between technology, application, and end-use trends. Final outputs were structured for strategic decision-making and long-term planning relevance.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, airframe tooling taxonomy across jigs fixtures and assembly aids, market sizing logic by aircraft production and MRO tooling demand, revenue attribution across tooling fabrication leasing and refurbishment services, primary interview program with OEMs MROs and aerospace manufacturers, data triangulation validation assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Care or usage pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Expansion of MRO capacity and aircraft turnaround demand
Rising regional aircraft fleet size and utilization
Shift toward composite-intensive airframes
Government support for aerospace manufacturing localization
Adoption of smart factory and Industry 4.0 practices
Increasing outsourcing of tooling design and fabrication - Challenges
High capital cost of advanced tooling systems
Skilled labor shortages in precision tooling and metrology
Long certification cycles for new tooling solutions
Dependence on imported high-end tooling technologies
Cyclicality of aerospace production demand
Integration complexity with legacy shop-floor systems - Opportunities
Localization of tooling production for OEM and MRO programs
Growth in additive manufacturing for low-volume tooling
Tooling demand from defense modernization programs
Digital retrofit of existing tooling assets
Aftermarket tooling services and lifecycle support
Regional export opportunities within Southeast Asia - Trends
Rising use of 3D-printed jigs and fixtures
Integration of tooling with MES and PLM platforms
Increased focus on lightweight and modular tooling
Growth of collaborative robotics in airframe assembly
Adoption of predictive maintenance for tooling assets
Standardization of tooling across multi-platform fleets - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Commercial aircraft fleets
Military and defense aircraft fleets
Business jets and general aviation fleets
Rotary-wing and special mission fleets
MRO service fleets - By Application (in Value %)
Airframe assembly and integration
Maintenance and scheduled checks
Repair and structural refurbishment
Overhaul and life-extension programs
Inspection and quality assurance - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Conventional manual tooling
CNC-machined precision tooling
Additive manufactured tooling
Composite-specific tooling systems
Digital and smart tooling platforms - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Aircraft OEMs and tier suppliers
Independent MRO providers
Airlines and fleet operators
Defense and government aviation units
Leasing and asset management companies - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone non-connected tooling
Networked shop-floor tooling
IoT-enabled smart tooling
Digital twin integrated tooling
Cloud-connected tooling systems - By Region (in Value %)
Central Singapore aerospace cluster
Seletar aerospace park
Changi aviation ecosystem
Jurong industrial corridor
Other regional aerospace hubs
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (tooling portfolio breadth, aerospace certification compliance, automation integration capability, additive manufacturing expertise, regional service footprint, customization capability, lead time performance, total cost of ownership)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Broetje-Automation
Electroimpact
MTorres
Spirit AeroSystems
Collins Aerospace
Safran Landing Systems
ST Engineering Aerospace
SIA Engineering Company
Airbus
Boeing Global Services
Snap-on Industrial
Stanley Black & Decker
Atlas Copco Industrial
Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence
Stratasys
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


