Market Overview
Based on a recent historical assessment, the Singapore aviation infrastructure market was valued at USD ~ billion, supported by large-scale capital expenditure programs disclosed by the Ministry of Transport, Changi Airport Group, and the Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore. The market is driven by sustained investments in terminal expansion, airside modernization, air traffic management upgrades, and aviation security systems. Strong passenger recovery, cargo throughput growth, and long-term infrastructure master plans continue to anchor spending across both civil and dual-use aviation facilities.
Based on a recent historical assessment, Singapore dominates the regional aviation infrastructure landscape due to its role as a global air transit and logistics hub. Changi Airport forms the core of this dominance, supported by integrated cargo zones, advanced air navigation facilities, and proximity to major Southeast Asian air corridors. Singapore’s leadership is reinforced by strong government coordination, regulatory clarity, and consistent funding availability. Regional influence is further strengthened by Singapore-based operators managing overseas airport assets and infrastructure projects.
Market Segmentation
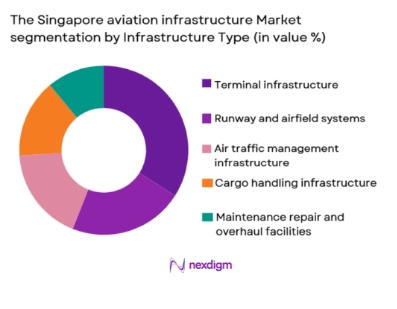
By Infrastructure Type
The Singapore aviation infrastructure market is segmented into terminal infrastructure, runway and airfield systems, air traffic management infrastructure, cargo handling infrastructure, and maintenance repair and overhaul facilities. Recently, terminal infrastructure has held a dominant market share due to sustained investments in passenger processing capacity, terminal automation, and integrated retail and transit facilities. Continuous upgrades at Changi Airport, including smart check-in, baggage handling systems, and inter-terminal connectivity, have driven higher capital allocation toward terminals. The emphasis on passenger experience, operational efficiency, and hub competitiveness has made terminal infrastructure the primary focus of aviation development programs. Strong alignment with tourism, transit traffic, and premium airline operations further reinforces the dominance of this sub-segment.
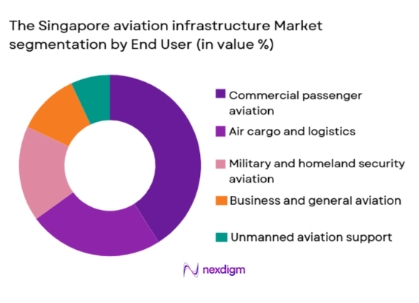
By End-Use Application
The Singapore aviation infrastructure market is segmented into commercial passenger aviation, air cargo and logistics, military and homeland security aviation, business and general aviation, and unmanned aviation support infrastructure. Recently, commercial passenger aviation has accounted for the dominant market share due to Singapore’s position as a major international transit hub and the concentration of long-haul and premium airline operations. Continuous expansion of passenger handling capacity, terminal systems, and airside support infrastructure has prioritized commercial aviation investments. The strong recovery in international travel, coupled with government-backed infrastructure resilience planning, has further elevated spending toward passenger aviation assets, reinforcing its leading position within the market.
Competitive Landscape
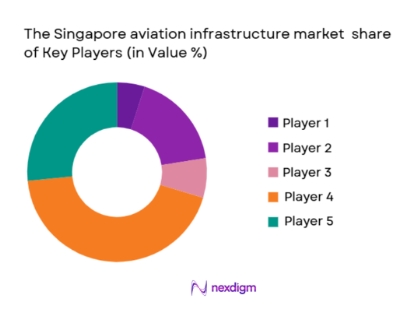
The Singapore aviation infrastructure market is moderately consolidated, with a mix of state-linked enterprises, global aerospace technology providers, and multinational engineering firms. Major players benefit from long-term framework agreements, government partnerships, and high entry barriers created by regulatory compliance and capital intensity. Technology integration capabilities and project execution experience play a decisive role in competitive positioning.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Core Aviation Role |
| Changi Airport Group | 2009 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ST Engineering | 1967 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SATS Ltd | 1972 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales Singapore | 1973 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Siemens Mobility Singapore | 1996 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Singapore Aviation Infrastructure Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Strategic Government-Led Aviation Infrastructure Investment:
Strategic Government-Led Aviation Infrastructure Investment: continues to be a primary force shaping the Singapore aviation infrastructure market as long-term national transport strategies prioritize aviation as a critical economic enabler. Public sector commitments toward airport expansion, air navigation modernization, and security infrastructure provide predictable funding visibility for large projects. These investments are coordinated through multi-agency frameworks that align aviation growth with tourism, trade, and national resilience objectives. High fiscal discipline and centralized planning reduce execution risks and encourage private sector participation. Infrastructure programs are structured to enhance hub competitiveness while meeting future capacity requirements. Continuous reinvestment into existing assets ensures operational reliability and scalability. Government backing also accelerates adoption of advanced technologies across terminals and airside systems. This sustained policy focus underpins stable market expansion and long-term investor confidence.
Regional Hub Position and Passenger Transit Demand:
Regional Hub Position and Passenger Transit Demand: significantly accelerates infrastructure spending as Singapore remains a preferred transfer point for intercontinental travel. High volumes of connecting passengers necessitate advanced terminal layouts, efficient baggage systems, and seamless passenger flow technologies. Airlines operating long-haul and premium services drive demand for high-specification infrastructure and airside support systems. Growth in Southeast Asian travel markets further strengthens transit traffic through Singapore. Infrastructure planning is therefore demand-driven and capacity-focused. Continuous service quality expectations push ongoing upgrades. This reinforces the need for resilient, scalable aviation assets. The hub role sustains continuous infrastructure renewal cycles.
Market Challenges
Land Scarcity and Infrastructure Expansion Constraints:
Land Scarcity and Infrastructure Expansion Constraints: present a structural challenge as aviation infrastructure projects must operate within Singapore’s limited geographic footprint. Airport expansion requires extensive land optimization, reclamation, and vertical development strategies that increase complexity and cost. Balancing aviation needs with urban development priorities intensifies planning constraints. Environmental and sustainability considerations further restrict expansion options. Project timelines are often extended due to multi-layered approvals. High engineering precision is required to avoid operational disruptions. These constraints elevate capital intensity and execution risk. Long-term infrastructure planning must therefore overcome physical limitations while maintaining service continuity.
High Capital Costs and Long Payback Periods:
High Capital Costs and Long Payback Periods: affect investment decision-making as aviation infrastructure assets require substantial upfront expenditure. Returns are typically realized over extended time horizons, increasing exposure to demand volatility and external shocks. Cost escalation risks arise from advanced technology integration and specialized construction requirements. Financing structures must balance public funding with private participation. Budget overruns can strain project viability. Economic uncertainty can delay investment approvals. These financial pressures challenge efficient capital allocation. Market participants must adopt disciplined financial planning.
Opportunities
Smart Airport and Digital Infrastructure Deployment:
Smart Airport and Digital Infrastructure Deployment: offers strong growth potential as Singapore accelerates digital transformation across aviation facilities. Advanced analytics, automation, and integrated data platforms enhance operational efficiency and passenger experience. Digital twins and predictive maintenance systems reduce downtime and lifecycle costs. Biometric processing and AI-driven traffic management improve throughput. These technologies align with national smart city initiatives. Infrastructure digitization creates opportunities for technology vendors and integrators. Continuous innovation strengthens hub competitiveness. The shift toward data-centric infrastructure supports long-term market expansion.
Sustainable and Green Aviation Infrastructure Development:
Sustainable and Green Aviation Infrastructure Development: represents a significant opportunity as regulatory and environmental priorities reshape infrastructure investment. Energy-efficient terminals, sustainable materials, and renewable power integration reduce carbon impact. Green infrastructure enhances regulatory compliance and global reputation. Airlines increasingly prefer airports aligned with sustainability goals. Government incentives support adoption of low-emission technologies. Long-term operational savings justify upfront investment. This transition creates new demand segments. Sustainability becomes a differentiating infrastructure attribute.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Singapore aviation infrastructure market is expected to experience steady expansion supported by continuous government investment, technology adoption, and strong regional air traffic fundamentals. Smart airport systems, sustainability initiatives, and capacity optimization will remain central to infrastructure planning. Regulatory stability and long-term transport strategies are likely to encourage private sector collaboration. Demand from passenger transit, cargo logistics, and security modernization will collectively shape future development priorities.
Major Players
- Changi Airport Group
- ST Engineering
- SATS Ltd
- Thales Singapore
- Siemens Mobility Singapore
- Honeywell Aerospace Singapore
- Collins Aerospace Singapore
- Indra Asia Pacific
- NEC Asia Pacific
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Asia Pacific
- L3Harris Technologies Singapore
- AECOM Singapore
- Jacobs Asia Pacific
- Balfour Beatty Asia
- Boustead Projects
Key Target Audience
- Airlines and airport operators
- Aviation infrastructure developers
- Aerospace and defense companies
- Smart infrastructure technology providers
- Logistics and cargo operators
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Public infrastructure financing agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market variables were identified through analysis of aviation infrastructure investment programs, regulatory documents, and transport development plans. Key demand, supply, and policy indicators were shortlisted for assessment.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Qualitative and quantitative inputs were consolidated to structure market segmentation, competitive dynamics, and infrastructure categories relevant to Singapore’s aviation ecosystem.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through expert opinions, industry publications, and official disclosures to ensure alignment with current market conditions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated insights were synthesized into a structured market report, ensuring consistency, clarity, and relevance for strategic decision-making.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Expansion of regional air passenger and cargo traffic
Strategic positioning as a global aviation hub
Government backed airport modernization initiatives
Integration of smart airport and digital technologies
Rising focus on sustainable aviation infrastructure - Market Challenges
High capital expenditure requirements for infrastructure projects
Land scarcity and spatial constraints
Complex regulatory and compliance frameworks
Skilled workforce availability for advanced systems
Operational disruptions during upgrade activities - Market Opportunities
Development of next generation smart terminal infrastructure
Adoption of sustainable and carbon efficient airport systems
Regional aviation hub services for Southeast Asia - Trends
Automation of passenger processing and terminal operations
Deployment of artificial intelligence in air traffic management
Growth of green and energy efficient airport designs
Integration of biometric and digital identity solutions
Increased resilience planning for climate adaptation - Government Regulations & Defense Policy
Civil aviation authority infrastructure compliance standards
National aviation security and resilience frameworks
Defense airbase modernization and dual use infrastructure policies - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Runway and airside infrastructure systems
Passenger terminal infrastructure systems
Air traffic management and navigation systems
Cargo and logistics handling infrastructure
Maintenance repair and overhaul infrastructure - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Commercial aviation infrastructure
Military aviation infrastructure
General aviation infrastructure
Business jet and VIP aviation facilities
Unmanned aviation support infrastructure - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
Greenfield airport infrastructure development
Brownfield airport expansion projects
Modernization and retrofit installations
Capacity optimization and automation upgrades
Sustainability and energy efficiency retrofits - By EndUser Segment (In Value%)
Airport operators and authorities
Air navigation service providers
Airlines and fleet operators
Defense and homeland security agencies
Cargo and logistics operators - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Government funded infrastructure programs
Public private partnership contracts
Direct procurement by airport operators
Long term concession and lease agreements
International infrastructure development tenders - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Advanced construction materials and composites
Digital airport management platforms
Smart surveillance and security technologies
Next generation navigation and communication systems
Sustainable energy and green building technologies
- Cross Comparison Parameters (infrastructure scope, technological capability, project execution expertise, regulatory compliance strength, financial stability, sustainability integration, regional presence, partnership ecosystem, aftersales support)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Key Players
Changi Airports International
ST Engineering
SATS Ltd
Thales Singapore
Indra Asia Pacific
Siemens Mobility Singapore
Honeywell Aerospace Singapore
Collins Aerospace Singapore
Aviation Partnership Singapore
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Asia Pacific
L3Harris Technologies Singapore
NEC Asia Pacific
Jacobs Asia Pacific Aviation
AECOM Singapore Aviation
Balfour Beatty Asia
- Airport authorities prioritizing capacity optimization and resilience
- Airlines seeking efficient turnaround and passenger handling facilities
- Government agencies focusing on national connectivity and security
- Logistics operators demanding high throughput cargo infrastructure
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035